What Causes Amelanotic Melanoma
Amelanotic melanomas are not common. In fact, according to 2014 research published in JAMA Dermatology, amelanotic melanomas are rare, making up about 2 percent to 20 percent of all melanomas. Though their appearance makes them harder to detect, the causes of amelanotic melanomas are the same as their more recognizable counterparts. Most often, genetic changes to the cells in moles cause them to turn into cancerous cells, or melanoma.
All of your cells contain DNA, a chemical that controls how your genes work. When DNA mutations cause your genes to function abnormally, cells may grow uncontrolled, becoming cancerous. The most common cause of these cellular changes is exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun or a tanning bed, though it may take years after UV exposure for these mutations to occur.
Rare, inherited genetic mutations may also play a role in causing melanoma. Inherited melanomas are caused by changes to tumor suppressor genes, impairing their ability to control cellular growth and ultimately contributing to cancer. People with a condition called xeroderma pigmentosum have an inherited mutation in the genes that repair damaged cellular DNA after UV exposure. These genes dont work properly in those with XP, making them more susceptible to melanoma.
New Hope For Beating Skin Cancers Deadliest Form
It starts as a tiny dark spot on your calf or the crook of your neck or your back. Its probably blotchy, like a Rorschach test, and if a doctor notices it, she is likely to take a second look. Id like to examine this one more closely, she might say about the mark on your skin that youd perhaps never even noticed. And its often good news to hear a doctor say that, because if you catch this little mass of dark, feisty cells before they spread, the inkblot cant seep into your body and stain your liver or bones or brain with cancer.
Related Reading
While relatively rare, with 21 new cases per 100,000 people in the United States each year, melanomas are the most dangerous form of skin cancer that humans develop. They begin when melanocytes, cells that produce and contain the pigment melanin and dictate the tone of a persons skin, mutate and start dividing too quickly, forming these telltale blotches. But once a melanoma has advanced from being an isolated group of cells on the skin and has sent scouts to other parts of the body, its notoriously hard to treat, despite its small size.
Gram for gram, melanoma is the most deadly form of skin cancer, says Stanford dermatologist and melanoma program director Susan Swetter, MD. Differences in survival drop dramatically with only a few millimeters of increased tumor thickness on the skin.
So Can A Melanoma Survivor Live For 30 Years
Yes. Its just that the statistics for 30-year survival rate are not known, because the endpoints are either five years or 10 years.
Its impossible to know how many people in the U.S. are 30+ year survivors of melanoma, let alone a particular stage.
The biggest predictor of whether or not a melanoma survivor will be alive 30 years after diagnosis is likely the stage of the initial disease.
There is no registry for 30+ year survivors of any stage of melanoma.
In this day and age, we can assume that somewhere in cyberspace is a cancer forum in which a 30-year melanoma survivor has posted. Or perhaps they have a blog.
Another way to know theyre out there is by personally knowing one.
If youre a melanoma survivor whos scared you wont be around 30 years from now, you should as all survivors commit to aggressive surveillance of your skin and never let your guard down.
It will also help to do everything possible to prevent heart disease, high blood pressure and stroke.
Theres no way to know how many melanoma survivors died of cardiovascular disease instead people who could have lived to at least that 30-year mark had they not developed unrelated illnesses that shortened their life. Or gotten into a fatal car accident for that matter.
Here are more survival statistics from the SEER Program. The overall five-year survival rate of 92.2 percent includes ALL stages of disease.
Read Also: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
What Are The Survival Rates For Scc
The vast majority of SCC is cured. Only about 2 percent to 5 percent of SCC cases grow back or spread. Unfortunately, because cases of SCC are not reported to the U.S. cancer registry it is hard to estimate survival rates. It is clear that metastatic SCC is very difficult to treat. . In large groups of people studied who have distant metastatic SCC, about 70 percent died from their disease.14,15
Signs Of Melanoma In Situ
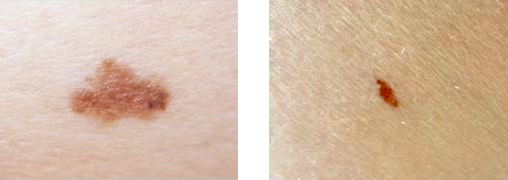
According to the American Cancer Society, the most important warning sign of melanoma is an existing mole or spot on the skin that is changing in shape, color, or size. This spot may look vastly different from the other spots on your skin. A new lesion on the skin can also indicate melanoma. If you notice any of these warning signs, see your physician at once.
The ABCDE rule is an easy-to-remember guide to help you identify melanoma. When performing your monthly at home skin check, look for:
- Asymmetry: A birthmark or mole that is not symmetrical. That means that one-half does not match the other.
- Border: Look for edges that are blurred, notched, ragged or otherwise irregular.
- Color: The color may include different shades of black or brown. It will usually not have the same color all over. It may sometimes appear with patches of blue, white or pink.
- Diameter: Any spot or mole larger than about ¼ inch should be checked by a physician.
- Evolving: A spot or mole that is changing in color, shape or size.
If you notice any of the above symptoms, contact a dermatologist right away. Additionally, keep in mind that a dermatologist’s eye is going to be much more advanced at detecting cancers. Keep up with your annual or biannual skin checks for maximum protection.
Don’t Miss: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Treatments For Stage I Melanoma
Your doctor will most likely treat stage 1 melanoma with surgery called wide excision, which cuts out the melanoma along with a margin of healthy surrounding skin. The amount of healthy skin removed is determined by the location and the thickness of the melanoma being treated.
While wide excision surgery is often the only treatment necessary, in some cases a doctor may also choose to check for cancer in nearby lymph nodes by performing a sentinel lymph node biopsy. If cancer cells are found in the lymph nodes, further treatment will become necessary, such as a lymph node dissection , chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapies.
Stop Tumors In Their Tracks
Every melanoma has the potential to become deadly, but the difference between an in situ melanoma and one that has begun to metastasize cannot be overstated. There is a drastic change in the survival rate for the various stages of tumors, highlighting the importance of detecting and treating melanomas before they have a chance to progress. Its impossible to predict exactly how fast a melanoma will move from stage to stage, so you should be taking action as soon as possible.
To be sure youre spotting any potential skin cancers early, The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends monthly skin checks, and scheduling an annual total body skin exam with a dermatologist. These skin exams can help you take note of any new or changing lesions that have the potential to be cancerous, and have them biopsied and taken care of before they can escalate.
Trust your instincts and dont take no for an answer, Leland says. Insist that a doctor biopsy anything you believe is suspicious.
Also Check: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
How Do You Treat Stage 4 Melanoma
The good news is that even stage 4 melanoma can be treated. The sooner the cancer is found, the sooner it can be removed and the higher your chances are for recovery. Stage 4 melanoma also has the most treatment options, but these options depend on:
- where the cancer is
- how advanced the cancer has become
- your age and overall health
How you respond to treatment also affects your treatment options. The five standard treatments for melanoma are:
- surgery: to remove the primary tumor and affected lymph nodes
- chemotherapy: a drug treatment to stop growth of cancer cells
- radiation therapy: the application of high-energy X-rays to inhibit growth and cancer cells
- immunotherapy: treatment to boost your immune system
- targeted therapy: the use of drugs or other substances to attack cancer drugs
Other treatments may also depend on where the cancer has spread to. Your doctor will discuss your options with you to help map out a treatment plan.
Skin Checks In Future
- detect any evidence of the melanoma returning or spreading to other organs, and
- identify new melanomas.
If the original melanoma returns, it is likely to be in the first 1-2 years after diagnosis . People who have had a melanoma have an increased risk â as much as 5 to 10 fold â of developing a new melanoma in future. This increased risk persists lifelong .
The usual follow-up for a patient with melanoma in situ is:
- full body skin cancer check for melanoma and other skin cancers, plus examination of lymph nodes and abdomen for signs of spread: 6-monthly for two years, then 12-monthly for the next three years and then
- a full body skin cancer check for melanoma and other skin cancers every year for life .
Read Also: Does Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Survival For All Stages Of Melanoma
Generally for people with melanoma in England:
- almost all people will survive their melanoma for 1 year or more after they are diagnosed
- around 90 out of every 100 people will survive their melanoma for 5 years or more after diagnosis
- more than 85 out of every 100 people will survive their melanoma for 10 years or more after they are diagnosed
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These figures are for people diagnosed in England between 2013 and 2017.
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account that some people would have died from other causes if they had not had cancer.
If Youve Been Diagnosed With Stage Iv Or Even Stage Iii Melanoma Youll Likely Be Wondering If Youll Be Alive 30 Years From Now If Youre Middle Age Or Younger
In general, survival rate statistics for melanoma are generally calculated at five years and 10 years after initial diagnosis, says Kara Shah, MD, an adult and pediatric dermatologist and founder of Kenwood Dermatology in Cincinnati, OH.
The five-year survival rate for metastatic melanoma is only four percent, according to the National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program.
Stage IV melanoma involves distant metastasis to other body organs or to distant areas of skin, says Dr. Shah.
For local disease the five-year survival is 84 percent.
While melanoma is unlikely to recur after more than 10 years since diagnosis, it does recur in a small minority of patients , says Dr. Shah.
Recommended Reading: Well-differentiated Meaning
How Is Amelanotic Melanoma Diagnosed
To diagnose all forms of melanoma, a biopsy must be taken in order to determine whether cancerous cells are present. The area of concern may be treated first with a local anesthetic, and the unusual mole or growth is carefully removed to be evaluated by a dermatopathologist, a specialist in diagnosing skin cancer. The specialist completes a pathology report that includes the following details:
Thickness. The pathology report will include details on the thickness of the melanoma, which may be thin , intermediate or thick . Thin melanomas have the lowest risk of metastasizing .
Ulceration. Also included is whether there is ulceration, or loss of surface skin, on the melanoma. The presence of ulceration is linked with increased risk of metastasis and a greater chance that the cancer will occur again.
Mitotic rate. The rate at which cells are dividing is also noted, as its helpful in determining the odds of recovering from the melanoma.
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Whether these immune cells are found in the biopsy will also be determined.
Melanoma is diagnosed as one of these four types:
Survival Rates By Stage
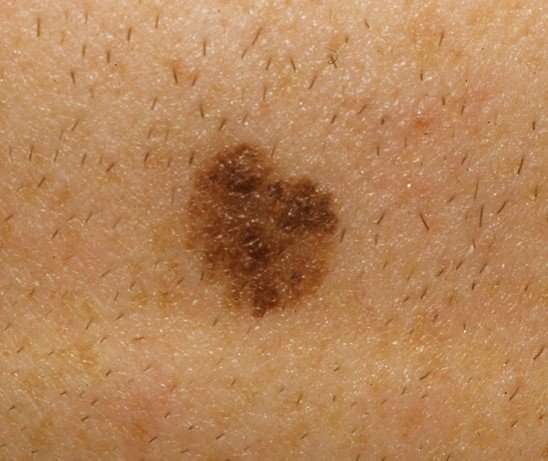
Stage 0
When melanoma is found and treated early, the chances for long-term, disease-free survival are excellent. With treatment , patients with Stage 0 melanoma have a five- and ten-year overall survival rate of 99%-100%.
Stage I
With the right surgery, patients with Stage I melanoma are considered at low risk for local recurrence or for regional and distant metastases. Despite the low risk, skin self-examinations and physical examinations for early detection of new or recurrent melanoma are important for Stage I survivors.
Large-scale studies have shown the following probabilities of melanoma-free survival. It is important to remember that statistics on the survival rates for people with melanoma are based on annual data from past cases and over multi-year timeframes. Survival rates do not predict your survival.
Stage II
With treatment, Stage II melanoma is considered intermediate- to high-risk for local recurrence or distant metastasis. Skin self-examinations and physical examinations for early detection of new or recurrent melanoma are critical for Stage II survivors.
Large-scale studies have shown the following probabilities of melanoma-free survival. It is important to remember that statistics on the survival rates for people with melanoma are based on annual data from past cases and over multi-year timeframes. Survival rates do not predict your survival.
Stage III
Stage IV
The following factors may provide a relatively more favorable prognosis:
References:
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize
Surgical Treatment Of Stage I Melanoma
The standard treatment of stage I melanoma is surgical removal with pathologically confirmed negative margins. Efforts been made to reduce the amount of normal skin removed without compromising the cure rate achieved with surgery. A melanoma greater than 1 millimeter appears to require a greater surgical margin to reduce the rate of recurrence at the site of origin. Most surgeons recommend a surgical margin of 2 centimeters surrounding the entire cancer for melanomas greater than 1 mm. The need for skin grafting occurs in approximately 10% of patients. Surgical margins greater than 2 cm are no more effective and require skin grafting in a higher fraction of patients .
Evaluation of the regional lymph nodes by performing a sentinel lymph node biopsy as a staging procedure for patients with a primary melanoma greater than 1 mm is recommended. SLNB should also be considered in patients with thin melanomas and adverse prognostic factors, such as vertical growth phase, Clark Level IV, regression, and ulceration.
The surgical treatment of stage I melanoma typically involves a single procedure in which a local excision of the cancer is performed as well as a SLNB. Approximately 15% of patients undergoing SLNB have a positive SLN . Ninety-five percent of patients with a confirmed negative sentinel node are free of cancer and require no additional treatment.
Strategies To Improve Treatment
Cure rates are so high with melanoma in situ that there are essentially no outstanding treatment issues. However, there are outstanding issues for the prevention of the development of additional melanomas. The diagnosis of melanoma in situ, which is believed to be a precursor for invasive melanoma, may be an indication that genetic and environmental influences may be present in an individual that place them at increased risk for developing other in situ or melanomas in the future. Individuals with melanoma in situ should have routine skin evaluations performed by dermatologists bi-annually.
Avoiding the major cause of cutaneous melanoma, sun exposure, is of crucial importance in preventing new melanomas. The guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology include:
- Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a SPF of at least 15 on all exposed skin, including the lips, even on cloudy days.
- If exposed to water, either through swimming or sweating, a water-resistant sunscreen should be used.
- Reapply sunscreen frequently.
- Wear a broad-brimmed hat and sunglasses.
- Sit in the shade whenever possible.
- Wear protective, tightly-woven clothing.
- Plan outdoor activities early or late in the day to avoid peak sunlight hours between 10 am and 4 pm.
Also Check: Cell Cancer Symptoms
Can Melanoma Be Cured
Most melanomas can be treated and removed with surgery if they are caught early.2 Melanomas are removed with a procedure called wide excision. Excision means cut out. The surgeon removes the entire tumor, along with some of the healthy skin surrounding it, called the margin. The purpose of the margin is to remove any cancer cells that might have spread. This reduces the risk that the tumor comes back.2
Melanoma may come back in its original location or on a new part of the body. The risk of recurrence depends on many factors, including:3
- What type of melanoma it is
- Where it is located
Your doctor is the best person to advise you about the risk of recurrence based on your melanoma.
Even if one melanoma is removed, you have a higher risk of another melanoma. Follow-up examinations are very important to check for recurrence of the initial melanoma or development of a new melanoma. Ask your doctor how often and for how many years you should have follow-up exams.
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for melanoma skin cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread beyond the skin where it started.
- Regional: The cancer has spread beyond the skin where it started to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the lungs, liver, or skin on other parts of the body.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Survival Rate