Taking Care Of Yourself
Hearing that your cancer has spread is scary, but a lot of research is underway to find new treatments. And there are treatments available to try to stop the disease from spreading, so you can live longer.
It’s important to have support and to talk about your fears and feelings, too. Your doctor can help you find a cancer support group.
These tips may help you feel better during melanoma treatment:
- If you lose your appetite, eat small amounts of food every 2 to 3 hours instead of bigger meals. A dietitian can give you other tips on nutrition and eating during your cancer treatment. Ask your doctor for a referral.
- Exercise can help you feel better overall and fight fatigue. But listen to your body, and balance rest and activity.
- Get the kind of emotional support that’s right for you. It could be from family, friends, your cancer support group, or a religious group.
Melanoma Skin Cancer Growth Rate
Melanoma skin cancer is the most dangerous and aggressive type of skin cancer, but it is significantly less common than other, non-melanoma types of skin cancer like Squamous cell carcinoma and Basal cell carcinoma. Melanoma skin cancer has a rapid growth rate, which is what makes it so dangerous it can turn life-threatening in just six weeks and poses a high risk of spreading to other parts of the body if left untreated. The early form of squamous cell carcinoma is known as Bowens disease.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
Certain things make you more likely to develop SCC:
- Older age
- Blue, green, or gray eyes
- Blonde or red hair
- Spend time outside, exposed to the sun’s UV Rays
- History of sunburns, precancerous spots on your skin, or skin cancer
- Tanning beds and bulbs
- Long-term exposure to chemicals such as arsenic in the water
- Bowens disease, HPV, HIV, or AIDS
Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist who specializes in skin conditions. They will:
- Ask about your medical history
- Ask about your history of severe sunburns or indoor tanning
- Ask if you have any pain or other symptoms
- Ask when the spot first appeared
- Give you a physical exam to check the size, shape, color, and texture of the spot
- Look for other spots on your body
- Feel your lymph nodes to make sure they arent bigger or harder than normal
If your doctor thinks a bump looks questionable, theyll remove a sample of the spot to send to a lab for testing.
Continued
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
Predictions Based On Doubling Times
Looking at doubling times of tumors is helpful only if the estimated doubling times can be used to predict the growth of a persons tumor. One study looked at predicted survival times of people who had inoperable lung cancers and found that there was a close correlation between survival predicted from doubling time and actual survival.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Causes
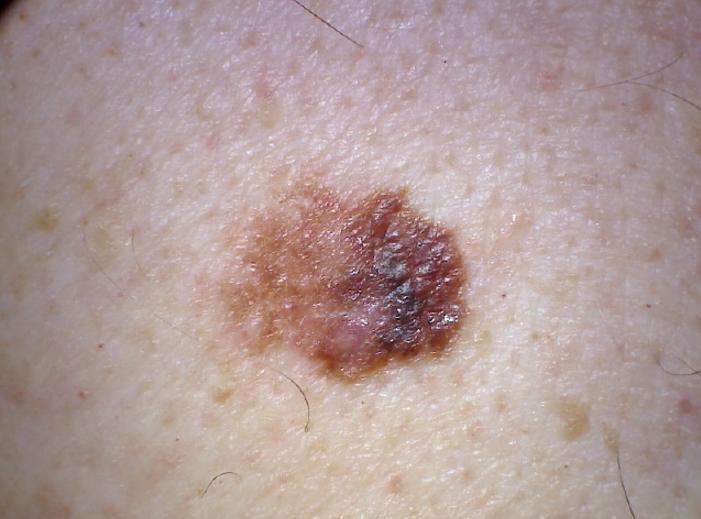
Exposure to ultraviolet rays, like the ones from the sun or a tanning bed, affects the cells in the middle and outer layers of your skin and can cause them to make too many cells and not die off as they should. This can lead to out-of-control growth of these cells, which can lead to squamous cell carcinoma.
Other things can contribute to this kind of overgrowth, too, like conditions that affect your immune system.
Recommended Reading: Does Sunburn Cause Skin Cancer
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Squamous cell skin cancer is mainly caused by cumulative ultraviolet exposure from the sun, according to Dr. Leffell.
Daily year-round exposure to the suns UV light and intense exposure in the summer months add to the damage that causes this type of cancer, he says. People at the highest risk for squamous cell skin cancer tend to have light or fair-colored skin blue, green or gray eyes a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Squamous cell cancers occur four times more frequently in men than in women.
Although squamous cell cancer can be more aggressive than basal cell cancer, the risk of this type of cancer spreading is lowas long as the cancer is treated early, Dr. Leffell says. He notes that the lesions must be treated with respect because they may grow rapidly and invade deeply. While it is more difficult to treat squamous cell cancer that has metastasized, up to half of cases can be cured.
In a small percentage of cases, squamous cell skin cancer can grow along the tiny nerves in the skin. In this very serious condition, the squamous cell cancer of the face or scalp can travel along the nerves and spread to the brain.
Also Check: What Can Happen If Skin Cancer Is Left Untreated
How Will Your Doctor Diagnose Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Your doctor will first examine the area in question, looking for things such as: the size, whether or not the borders are clearly or poorly defined, and location, including whether or not the spot is situated on top of a previous injury. The next step is a biopsy, which is the removal of tissue for examination under a microscope. If a tumor is considered to be high-risk, your doctor might order imaging scans to determine if nearby lymph nodes are involved or if the tumor has invaded other tissue in the area.
Don’t Miss: Carcinoma Cancer Symptoms
Chemotherapy For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Superficial Squamous Cell Carcinoma may be able to be treated with topical chemotherapy that is applied to the skin as an ointment or cream. This type of treatment is only for skin cancers that biopsy-proven to affect only the top layer of skin.
5-fluorouracil is approved for the treatment of Superficial Squamous Cell Carcinoma, however, invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma should not be treated topically due to the risk of spread.
Not All Cells Divide At The Same Time
Growth rates and doubling time matter, but in real life there are exceptions to every rule. Growth rate estimates are based on an exponential model. For example, one cell becomes two, two become four, four then become eight, and so on. In real life, however, not all cells are dividing at the same rate and at the same time.
Different types of cancer have different “growth fractions,” a measure of the proportion of cells that are in an active cell cycle. Some cancers, such as childhood leukemias, have a very high growth fraction, meaning a large number of cells is dividing at a specific time. Other cancers, such as breast cancer, have a low growth fraction.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Life Expectancy
When To Seek Medical Care
If you develop a new bump on sun-exposed skin, or if you have a spot that bleeds easily or does not seem to be healing, then you should make an appointment with your primary care physician or with a dermatologist. You should also make an appointment if an existing spot changes size, shape, color, or texture, or if it starts to itch, bleed, or become sore to the touch.Try to remember to tell your doctor when you first noticed the lesion and what symptoms, if any, it has. Also, young adults should ask adult family members whether or not they have ever had a skin cancer and relay this information to their physician.
Dont Miss: What Is The Difference Between Age Spots And Skin Cancer
What Is The Treatment For Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cutaneous SCC is nearly always treated surgically. Most cases are excised with a 310 mm margin of normal tissue around a visible tumour. A flap or skin graft may be needed to repair the defect.
Other methods of removal include:
- Shave, curettage, and electrocautery for low-risk tumours on trunk and limbs
- Aggressive cryotherapy for very small, thin, low-risk tumours
- Mohs micrographic surgery for large facial lesions with indistinct margins or recurrent tumours
- Radiotherapy for an inoperable tumour, patients unsuitable for surgery, or as adjuvant
You May Like: What Does Cancer Look Like Outside The Body
How Quickly Does Skin Cancer Appear On The Body
Have you noticed the appearance of a sudden, unusual growth on your skin? Certain types of skin cancer, like melanoma, can show up very quickly and without warning. So, how can you know if its truly a cause for concern? The only way to determine if a skin growth is cancerous is by getting a skin cancer screening from a qualified provider. The expert dermatology team at Advanced Dermatology offers skin cancer screenings to detect many types of skin cancer and can offer a variety of appropriate treatment solutions at our practice locations in Katy, League City, Pearland, and Sugar Land, TX. So, reach out to us for a screening as soon as you notice an irregular spot.
How long does it take skin cancer to appear?
There’s no set timeline for skin cancer growth and appearance. While some skin cancer lesions appear suddenly, others grow slowly over time. For example, the crusty, pre-cancerous spots associated with actinic keratoses can take years to develop. Other forms of skin cancer, like melanoma, can appear very suddenly, while at other times, the lesions can vanish and reappear.
Where is skin cancer commonly found on the body?
Signs of skin cancer
The specific symptoms can vary based on each individual type of skin cancer. During a skin cancer screening performed in one of our Houston, TX area offices, our dermatologists look for the following types of cancer:
Get a skin cancer diagnosis in Houston, TX
When Does Lung Cancer Begin
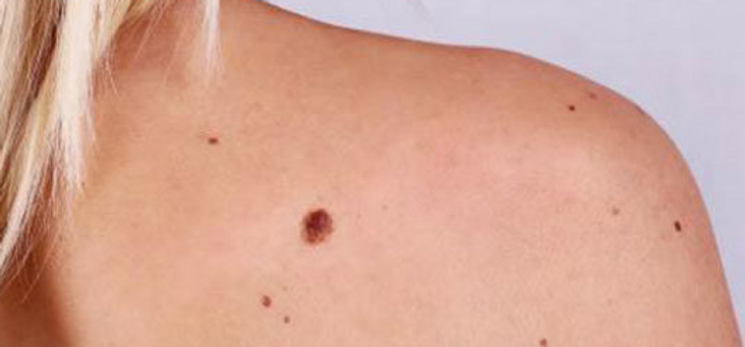
A different question looks at when the lung cancer first began. People may think of a stressful time in their life, or a specific chemical exposure, and wonder if it could have been the cause of their cancer. There isnt a precise answer, but there are some theories.
One idea is to look at the patterns of mutation. A 2017 study published in the New England Journal of Medicine suggested that it takes along time for a lung cancer to develop, perhaps decades, especially for lung adenocarcinomas.
Also Check: Skin Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic
What Your Doctor Is Reading
If you are interested in more advanced reading on this topic, weâve made content from our health professional site, Medscape, available to you on WebMD.
Show Sources
American Cancer Society: “Melanoma Skin Cancer Overview,” “Treatment of melanoma sin cancer by stage,â “Targeted therapy for melanoma skin cancer.”
Cancer Research UK: “Living with Advanced Melanoma.”
FDA: “FDA approves Yervoy to reduce the risk of melanoma returning after surgery,” “FDA approves Cotellic as part of combination treatment for advanced melanoma.”
Macmillan Cancer Support: “Symptoms of advanced melanoma.”
National Cancer Institute: “What You Need to Know About Melanoma and Other Skin Cancers.”
Skin Cancer Foundation: “Melanoma.”
Are You At Risk
The skin is the largest organ of the body. It is also our bodys first line of defense. There are numerous factors which may increase your risk of skin cancer:
- Genetics: Individuals with fair complexions are at the greatest risk. Your risk is also increased if your parents, children, or siblings have had skin cancer.
- Sun Exposure: Over the course of a lifetime, exposure to the sun can lead to a higher risk of skin cancer. Tanning beds and other false sunlight are no exception.
- Immunosuppression: Immunosuppression therapy following organ transplants, chemotherapy, AIDS, and other treatments can put you at a significant risk for skin cancer.
- Lifespan: Human life expectancy has increased from forty-two years in 1904 to close to eighty years today. As a result, the number of skin cancers being seen around the world is increasing.
You May Like: Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Turn Into Melanoma
Also Check: Melanoma Stage 3 Symptoms
How To Improve Your Odds
Even if youve exhausted all of your treatment options, you dont have to give up. Researchers are always testing new SCC treatments in clinical trials. Getting into one of these studies could give you access to a drug or therapy that might slow or stop your cancer.
To avoid the worsening of your skin cancer or a new cancer in a different area, protect yourself from the suns damaging UV rays. Wear sun-protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat whenever you go outdoors. Apply a layer of broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
Also check your own skin for any new growths on a regular basis. Report any skin changes to your doctor right away.
Recommended Reading: What Does Melanoma Look Like On Your Face
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Most basal cell and squamous cell cancers can be cured with surgery or other types of treatments that affect only the spot on the skin.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age and overall health
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 3 Melanoma Look Like
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Squamous cell cancers are usually raised growths, ranging from the size of a pea to the size of a chestnut. They may appear as scaly red patches, open sores or protruding growths with a dented center, or they may look like a wart. Most are found in areas of the body that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the ears, lips, face, balding scalp, neck, hands, arms, and legs. Less commonly, they may appear on mucous membranes and genitals. Regardless of what form the bumps take, they do not heal or go away on their own.
What Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Skin malignancies are the most common cancer in the United States, responsible for more than half of all new cancer cases. These can be broken down into melanoma and non-melanoma malignancies, which are squamous cell cancer and basal cell cancer. These skin malignancies are caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Squamous cell cancer is the second most common form of skin cancer. It is more aggressive and may require extensive surgery depending on location and nerve involvement. Radiation, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are used in advanced cases.
You May Like: Clear Cell Carcinoma Symptoms
How Do You Know If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has Spread
After identifying that you have squamous cell carcinoma, your doctor will need to know the stage in which the disease is. Even if the spread of squamous cell carcinoma is slow, the doctor will need to know to develop the right treatment plan.
The TNM system is the system that is used to stage many types of cancer. TNM has its meaning. T is for tumor it helps explain how deep the primary tumor grows across the layers of the skin or the tissues near the skin. N is for nodes, which helps understand whether the cancer cells have spread to the lymph nodes close to the tumor. M stands for metastasis this tries to determine whether cancer has spread to other vital organs in the body like the liver, lungs, or brain.
Patients with squamous cell carcinoma need to have a skin cancer doctor discussion guide and have constant communication with their doctor to avoid inconvenience in their medications. Communication, in this case, can be in the form of emails, phone calls, or visits to hospitals to see the progress and treatment process required for squamous cell carcinoma. This will help understand the rate of squamous cell carcinoma spread in the body.
Do You Need Chemotherapy For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
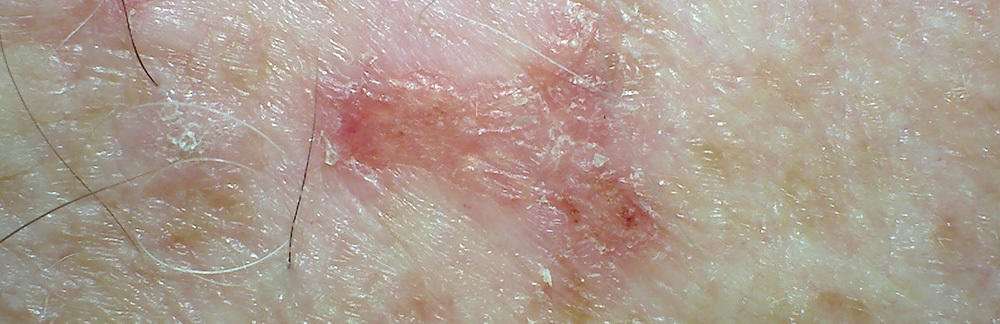
Because just about all squamous cell carcinoma is usually localized it is typically not treated with chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is used for widespread cancer cell eradication, not localized growths. Chemotherapy could be used for a very small percentage of these cases, typically if the cancer has spread.
About 95 percent of squamous cell carcinomas are detected early, and this makes them easy to treat. All treatment options are highly successful, but Mohs micrographic surgery is the most successful while taking the least amount of healthy skin.
Also Check: What Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Look Like On The Face
Recommended Reading: Large Cell Carcinoma Definition
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treatment
Squamous cell carcinoma can usually be treated with minor surgery that can be done in a doctors office or hospital clinic. Depending on the size and location of the SCC, your doctor may choose different techniques to remove it.
For small skin cancers:
- Curettage and electrodessication : removing the top layer of the skin cancer then using an electronic needle to kill cancer cells
- Laser therapy: an intense light destroys the growth
- : a photosensitizing solution applied to your skin then activated with a light or daylight, or sometimes with intense pulsed light
- Cryosurgery: freezing of the spot using liquid nitrogen
For larger skin cancers:
- Excision: cutting out the cancer spot and some healthy skin around it, then stitching up the wound
- Mohs surgery: excision and then inspecting the excised skin using a microscope this requires stitching up the wound
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage squamous cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is assigned to one of the five squamous cell carcinoma stages, which are labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of squamous cell cancer are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high risk features.
Stage 3 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Also Check: Melanoma Stage 4 Treatments