Are There Risk Factors For Developing Merkel Cell Carcinoma
- Merkel cell polyomavirus infection This virus was first discovered in 2008, and its still somewhat of a mystery. This virus is found in the cancer cells of 80 percent of people with Merkel cell carcinoma.
- UV light exposure Exposure to the ultraviolet rays is the major risk factor . This exposure can come from the sun, tanning beds, or from UV light treatments for psoriasis.
- Fair skin Nearly 90 of Merkel cell carcinomas occur in white people.
- Old age This form of skin cancer is very rare in people under the age of 50. Over 80 percent of cases form in those over 70. This is probably due to a combination of accumulating UV exposure and a weakening immune system.
- Males Men are twice as likely to get this skin cancer, although again that can simply be a factor that men get more sun exposure.
- Weakened immune system Our immune systems not only fight germs and viruses, they also help the body fight cancer. When these systems are weakened, the patient becomes more likely to develop some types of cancer, including Merkel cell carcinoma.
How Does Mcc Differ In Appearance From Melanoma
Unlike malignantmalignantHaving the ability to grow without normal regulation, to invade local tissues aggressively and/or spread throughout the body.melanomamelanomaA form of skin cancer that begins in melanocytes . Melanoma affects about 42,000 Americans per year and has about a 15% mortality., MCC is essentially never dark brown or black.
What Causes Merkel Cell Cancer
Experts arent exactly sure what causes Merkel cell cancer. But it occurs when Merkel cells in the body change and grow out of control. These abnormal cells may grow to form a lump or mass called a tumor. If the tumor is cancerous, it can grow into nearby areas. It can even spread to other parts of the body .
Don’t Miss: Melanoma On Face Prognosis
Clinical Manifestations Patient Evaluation Staging
MCC often appears as a painless, indurated, erythematous to violaceous nodule with a smooth, shiny surface on sun-damaged skin, and, less commonly, as a plaque with satellite metastases. Surface ulcerations are rare.236238,246,248,287 Heath and colleagues summarized clinical features of MCC in an acronym: AEIOU ,254 suggesting that the clinical appearance of MCC is rather nondescript. MCC occurs predominantly in the head and neck , followed by the extremities and trunk .287 Ten percent of these tumors are in the periocular areas .288 MCC also has been reported in extracutaneous sites, such as the vulva, endocervix, penis, esophagus, bladder, and calvaria.259,289292 The salivary glands, nasal cavity, lip, lymph nodes, vulva, vagina, and esophagus are the most common extracutaneous sites.243 The clinical differential diagnosis includes BCC, SCC, amelanotic melanoma, lymphoma, and metastatic disease. Histologic and immunohistochemical studies are the key to confirmation of the diagnosis.
Diana Bell, in, 2021
You May Like: Are There Stages Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Can Skin Cancer Look Like A Pimple
Did you find a spot on your skin that looks a little suspicious? Are you questioning if it is skin cancer? For starters, let us just say kudos on paying attention! It is so vital to watch yourself for these things because early detection truly saves lives.
As dermatologists we get asked often if skin cancer can look like specific things:
Can skin cancer look like a pimple?Can skin cancer look like a regular mole?
Each type of skin cancer can appear differently.
- Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma can appear as a flesh-colored, pearl-like bump some would say looks like a pimple or a pinkish patch of skin. They are commonly found on the head, neck, and arms, yet can form anywhere on the body, including the chest, abdomen, and legs.
- Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. Squamous cell carcinoma often appears as a red firm bump, scaly patch, or a sore that heals and then re-opens. SCC tends to form on skin that gets frequent sun exposure, such as the rim of the ear, face, neck, arms, chest, and back.
- Melanoma is a deadly form of skin cancer because of its ability to metastasize to local lymph nodes and other organs. It can develop in an existing mole but is actually more likely to suddenly develop as a new dark spot on the skin.
- Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare form of skin cancer that presents with a rapidly growing, painless, firm, shiny nodule typically on the head and neck region.
Also Check: Untreated Cancer Symptoms
How Is Merkel Cell Cancer Diagnosed
The most common way to find Merkel cell cancer is when a lump is found and you see a healthcare provider about it. The healthcare provider will look at and feel the lump. They will ask about your health history, and do a physical exam of your skin.
You may be sent to a dermatologist. This is a doctor with special training to treat skin problems. The doctor may use a special light, magnifying lens, or camera to get a very close look at the lump. You will likely need a biopsy.
A biopsy is the only way to know if a lump or change is cancer. The doctor takes small pieces of tissue from the lump. These samples can be removed with a needle or scalpel, or during surgery. They are checked with a microscope to look for cancer cells.
It can be hard to diagnose MCC. It can look like many other types of cancer. Special lab tests can be used on the biopsy sample to find out whats caused the skin change.
After a diagnosis of MCC, youll likely need more tests. These help your healthcare providers learn more about the cancer. They can help determine the stage of cancer. The stage is how much and how far the cancer has spread in your body. Its one of the most important things to know when deciding how to treat MCC.
Once your cancer is staged, your healthcare provider will talk with you about what the stage means for your treatment. Ask your healthcare provider to explain the stage of your cancer to you in a way you can understand.
More Pictures Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
While the above pictures show you some common ways that BCC can appear on the skin, this skin cancer can show up in other ways, as the following pictures illustrate.
Scaly patch with a spot of normal-looking skin in the center
On the trunk, BCC may look like a scaly patch with a spot of normal-looking skin in the center and a slightly raised border, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can be lighter in some areas and darker in others
While BCC tends to be one color, it can be lighter in some areas and darker in others, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can be brown in color
Most BCCs are red or pink however, this skin cancer can be brown, as shown here.
Basal cell carcinoma can look like a group of shiny bumps
BCC can look like a group of small, shiny bumps that feel smooth to the touch.
Basal cell carcinoma can look like a wart or a sore
The BCC on this patients lower eyelid looks like a wart* in one area and a sore** in another area.
If you see a spot or growth on your skin that looks like any of the above or one that is growing or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist.
Also Check: Stage 1 Cancer Symptoms
What Is The Cure Rate Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
As with melanoma, early diagnosis of Merkel cell carcinoma is imperative to increase the patients odds of successful treatment.
The five-year survival rate for localized Merkel cell carcinoma, meaning it has not spread, is 78%. If the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or other nearby structures, the five-year survival rate is 51%. If it has spread to distant organs or parts of the body, the five-year survival rate is just 17%
What Else Could This Skin Lesion Be
Other skin conditions may look like BCC. Nodular BCC without ulceration may look similar to:3
- Molluscum contagiosum, a viral infection that causes numerous small bumps.
- Sebaceous hyperplasia, a condition characterized by small yellow bumps.
- Intradermal melanocytic nevus, a nest of melanocytes in the dermis layer of skin.
- Fibrous papule, a firm bump that may develop on the nose.
- Other skin cancers
Ulcerated BCC may be confused with squamous cell carcinoma or keratoacantoma.
Conditions that look similar to superficial BCC include:3
Read Also: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Metastasize
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Signs And Symptoms
Generally found on the ears, face and mouth, squamous cell carcinoma can be more aggressive than basal cell. Untreated, it may push through the skin layers to the lymphatic system, bloodstream and nerve routes, where it can cause pain and symptoms of serious illness.
Appearance
Squamous cell cancer often starts as a precancerous lesion known as actinic keratosis . When it becomes cancerous, the lesion appears raised above the normal skin surface and is firmer to the touch. Sometimes the spot shows only a slight change from normal skin.
Other signs include:
- Any change, such as crusting or bleeding, in an existing wart, mole, scar or other skin lesion
- A wart-like growth that crusts and sometimes bleeds
- A scaly, persistent reddish patch with irregular borders, which may crust or bleed
- A persistent open sore that does not heal and bleeds, crusts or oozes
- A raised growth with a depression in the center that occasionally bleeds and may rapidly increase in size
How Can I Help Prevent Merkel Cell Cancer
Early diagnosis and treatment of Merkel cell cancer is important to prevent it from spreading. Be aware of any lumps, growths, moles, or other abnormal areas on your skin. Watch for new spots or areas that are changing. This can include skin marks that grow larger, bleed, crust, or itch. Your healthcare provider may recommend you do a skin self-exam once a month or more. See your healthcare provider if you have any new or changing marks on your skin.
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Appearance Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
MCC usually develops on sun-exposed skin as a painless, firm bump that can be red-purple or skin-colored. Patients frequently point out a new MCC to their doctor because a bump is growing rapidly and/or does not look like anything the patient has ever had before. Most MCCs are diagnosed when a skin biopsybiopsyThe removal of cells or tissue in order to determine the presence, characteristics, or extent of a disease by a pathologist usually using microscopic analysis. is performed to rule out another sun-induced skin cancercancerA term used to describe diseases in which abnormal cells continually divide without normal regulation. Cancerous cells may invade surrounding tissues and may spread to other regions of the body via blood and the lymphatic system. or to remove a presumed cyst. In the vast majority of cases, both the doctor and the patient are surprised by the diagnosis of MCC. For more examples of MCC tumors beyond those presented on this page, visit the Clinical Photos page.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor If I Have Merkel Cell Carcinoma
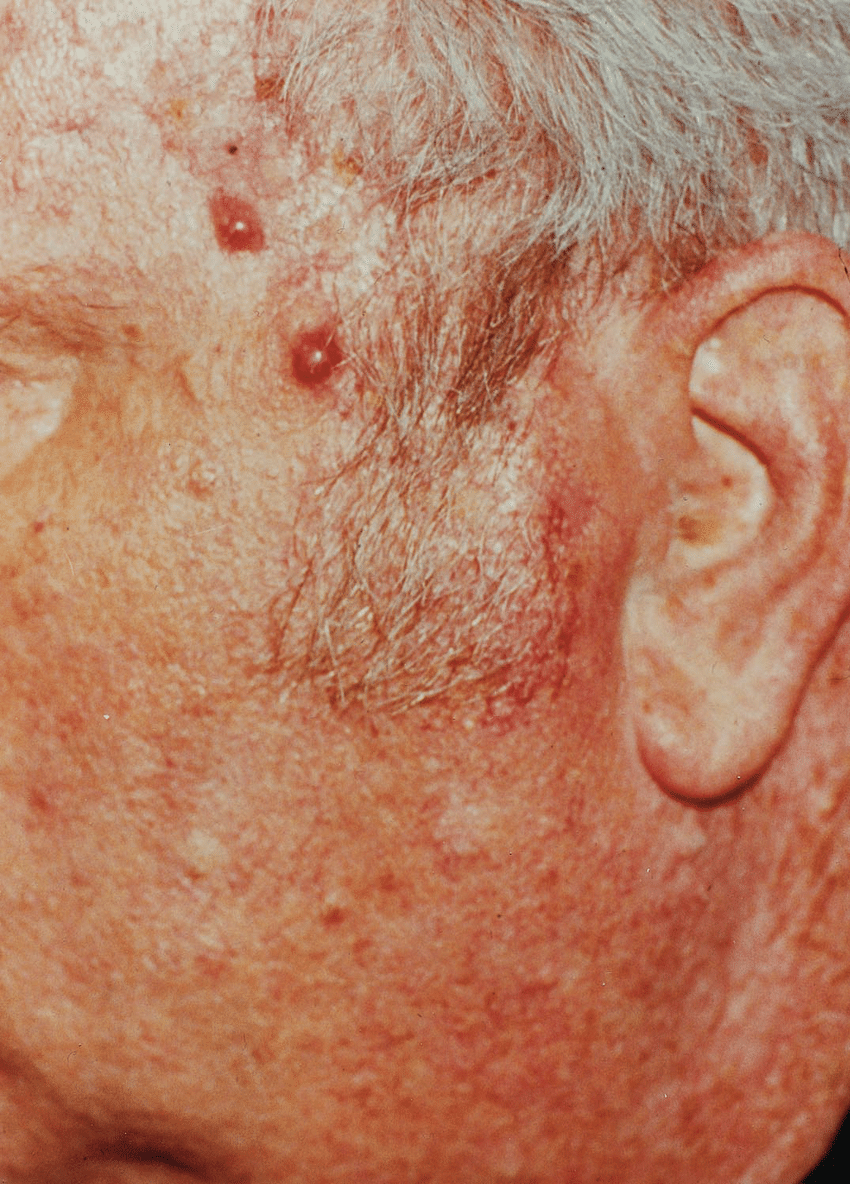
If your doctor diagnoses MCC, you may have many questions about your condition. These may include:
- How can I know whether the cancer has spread?
- Which treatments will be most beneficial for me?
- Is there a chance my cancer could come back after treatment?
- How can I protect my skin to lessen my chances of developing cancer again?
Make sure you contact your doctor if you notice any changes in your skin that worry you.
You May Like: Cell Cancer Symptoms
Where Does Mcc Occur On The Body
MCC primarily occurs on highly sun-exposed skin such as the head/neck and arms , but it can occur anywhere on the body, including sun-protected areas such as the buttock or the scalp under hair.
Solid circles depict MCC tumors that arose on the skin . Open circles indicate MCCs that presented in lymph nodes without an associated primary lesionprimary lesionThe abnormal tissue that appeared first. The majority of Merkel cell carcinoma primary lesions occur in sun-exposed areas. In some cases of MCC the patient has no primary lesion and instead has a nodal presentation . In these cases the primary lesion likely was destroyed by the immune system. . Recent data suggest that patients who present without a primary lesionlesionAn area of abnormal tissue that may be either benign or malignant. originally did have a lesion on the skin, but that their immune system eliminated the tumor. Elimination of the primary lesion is associated with less risk for patients that already have the same stagestagePhysicians determine the stage of cancer by performing physical exams and tests. Stages describe the extent of cancer within the body, especially whether the disease has spread from the primary site to other parts of the body. at presentation .
How Are Mcc Tumors Measured
Merkel cellMerkel cellMerkel cells are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Although the exact function of Merkel cells is unknown, they are thought to be touch receptors. Also known as neuroendocrine cells, they have machinery similar to nerve cells and to hormone-secreting cells. carcinomas are measured by their largest dimension, in centimeters. Among 5722 cases, the average Merkel cell carcinomaMerkel cell carcinomaA skin cancer composed of cells that look microscopically similar to normal Merkel cells present in the skin. MCC was first described in 1972 and only in the 1990s was the CK20 antibody developed to make it easily identifiable by pathologists. Many doctors and patients are not aware of this cancer because of its recent description and relative rarity . About 40% of patients treated for MCC will experience a recurrence, making it far more aggressive than most other types of skin cancer, including melanoma. was 1.7 cm in diameter . Larger MCC tumors are associated with moderately higher risk of recurrence and spread to lymph nodes, but even a very small MCC tumor still has at least a 15% chance of already having spread to nearby lymph nodes.1
Don’t Miss: Well-differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
What You Need To Know
Merkel cell carcinoma is rare and dangerous but treatable, especially when found at an early stage. Be watchful for any new or changing lesions on your skin and look out for these warning signs.
If youve been treated for a previous MCC, pay close attention to the site and the surrounding region. Contact your medical team immediately if you see any suspicious changes.
How to spot a Merkel Cell Carcinoma
APPEARANCE Painless shiny or pearly lesions or nodules
SIZE Dimensions vary, but the average size at detection is 1.7 cm, about the diameter of a dime.
COLOR Skin-colored, red, purple or bluish-red
LOCATION Frequently on sun-exposed areas, often on the head and neck, particularly the eyelids.
While rare, Merkel cell carcinomas are often aggressive and can advance rapidly which is why early detection and removal are especially important. Memorial Sloan Kettering oncologist Sandra DAngelo, MD, shares some important warning signs you should never ignore.
Genuinely Concerned For His Patients
The staff are very friendly and professional. The office has a very nice environment. I purposely traveled from the Fox Chase area of Philadelphia to this office in King Of Prussia to see Dr. Clifford Perlis. He performed MOHS surgery on my face years ago and did a wonderful job in removing the basal cell carcinoma and in leaving a minimal scar. Plus he is genuinely concerned for his patients. I highly recommend this practice.
- Monday
- Tuesday
- Wednesday
- Thursday
- Friday
- Multiple convenient locations
- Blue Cross Blue Shield PPO
- Medicare
Also Check: Basal Cell Carcinoma Etiology
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
Certain things make you more likely to develop SCC:
- Older age
- Blue, green, or gray eyes
- Blonde or red hair
- Spend time outside, exposed to the sun’s UV Rays
- History of sunburns, precancerous spots on your skin, or skin cancer
- Tanning beds and bulbs
- Long-term exposure to chemicals such as arsenic in the water
- Bowens disease, HPV, HIV, or AIDS
Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist who specializes in skin conditions. They will:
- Ask about your medical history
- Ask about your history of severe sunburns or indoor tanning
- Ask if you have any pain or other symptoms
- Ask when the spot first appeared
- Give you a physical exam to check the size, shape, color, and texture of the spot
- Look for other spots on your body
- Feel your lymph nodes to make sure they arent bigger or harder than normal
If your doctor thinks a bump looks questionable, theyll remove a sample of the spot to send to a lab for testing.
Continued
S Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
To help you spot MCC, the following pictures show you diverse ways that it can appear on the skin.
A red or pink spot
Looking much like an insect bite, testing revealed that the reddish spot on this patients shin was actually Merkel cell carcinoma.
Reddish, slightly raised spot that looks like a sore
The reddish, scaly, and slightly raised spot on this patients wrist is Merkel cell carcinoma, which could easily have been mistaken for a sore.
Quickly growing spot on your skin that sometimes bleeds
Any spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way could be a skin cancer.
Quickly growing, firm, dome-shaped growth
This 87-year-old man was concerned about this quickly growing, dome-shaped mass on this lower eyelid, which testing showed was a Merkel cell carcinoma.
A stye or cyst
This aggressive skin cancer can look like a rapidly growing stye or cyst. Unlike a stye or cyst, Merkel cell carcinoma often feels painless.
A growing sore
Sometimes, this aggressive skin cancer looks like a sore, so its important to see a dermatologist if you notice a new spot on your skin that is growing rapidly. Skin cancer can also look like a sore that heals and returns.
Any fast-growing spot or mass
While Merkel cell carcinoma often looks like a dome-shaped growth or slightly raised and scaly patch, it can appear on the skin in diverse ways, as did the Merkel cell carcinoma on this mans head.
Red, pink, or purple spot thats growing
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate