What Are Some Of The Lesser
Some of the less common skin cancers include the following:
Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer most commonly seen in people who have weakened immune systems, those who have human immunodeficiency virus /AIDS and people who are taking immunosuppressant medications who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplant.
Signs and symptoms of Kaposi sarcoma are:
- Blue, black, pink, red or purple flat or bumpy blotches or patches on your arms, legs and face. Lesions might also appear in your mouth, nose and throat.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare cancer that begins at the base of the epidermis, the top layer of your skin. This cancer starts in Merkel cells, which share of the features of nerve cells and hormone-making cells and are very close to the nerve ending in your skin. Merkel cell cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body than squamous or basal cell skin cancer.
Signs and symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma are:
- A small reddish or purplish bump or lump on sun-exposed areas of skin.
- Lumps are fast-growing and sometimes open up as ulcers or sores.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually appears on your eyelid. This cancer tends to develop around your eyes because theres a large number of sebaceous glands in that area.
Signs and symptoms of sebaceous gland carcinoma are:
- A painless, round, firm, bump or lump on or slightly inside your upper or lower eyelid.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans
Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal cell cancer can occur anywhere on the body, but it typically develops on areas regularly exposed to the sun. This type of cancer may appear on your face, neck, or other body parts in the form of:
-
Flat patches of spots, or lesions, which may be red, purple, or brown in color
-
Slightly raised, brown or reddish lesions
-
Fully raised, bumpy lesions with a red or brown color
If you think you may be experiencing any of the symptoms of different skin cancers described above, you should call a doctor to discuss your symptoms. You may find that you simply have a large, non-cancerous mole, and can have your concerns put to rest by a professional. On the other hand, your doctor may be able to diagnose your condition and recommend treatment sooner rather than later. Either way, it is best to be on the side of caution and speak with your doctor about what youve noticed.
How The Government Of Canada Protects You
The Public Health Agency of Canada monitors cancer in Canada. PHAC identifies trends and risk factors for cancer, develops programs to reduce cancer risks, and researches to evaluate risks from the environment and human behaviours. Health Canada also promotes public awareness about sun safety and the harmful effects of UV rays.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Cancer Prognosis
Skin Cancer On The Face: Types And Prevention
Casey Gallagher, MD, is board-certified in dermatology. He is a clinical professor at the University of Colorado in Denver, and co-founder and practicing dermatologist at the Boulder Valley Center for Dermatology in Colorado.
Because it is exposed to the sun more than other parts of the body, the skin on your face is especially vulnerable to skin cancer. And skin cancer on the face can be mistaken for other conditionssuch as age spots, pimples, scarring, acne, styes, and cysts.
Skin cancers that tend to occur more often on the face include actinic keratosis, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. The face is also a common site of melanoma and there are several other lesser-common skin cancers that can affect the face. The risk of getting skin cancers on the face increases with high amounts of sun exposure and other ultraviolet light exposure.
About 75% of non-melanoma skin cancers occur on the head or neck.
Skin cancer occurs when cells in the skin’s layers become damaged in ways that cause them to look and act differently than the normal healthy cells around them and start to grow out of control. UV rays play a major role in damaging cells by causing gene mutations.
You can watch for signs of skin cancer on your face by paying attention to new or odd-looking spots or feeling growths, splotches, or moles.
Types Of Dog Skin Cancer
There are several different types of dog skin cancer. Three of the most common are:
- Melanoma
My goal with this post is to help you
- Get more familiar with what these growths look like.
- Know how they act in the body.
- Know when you need to be aggressive with care at home.
So heres what you need to know about the 6 skin cancers dogs can get.
Read Also: Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Wound Infection After Surgery
There is a risk of infection after skin cancer surgery, says Lucas. While in the office or the hospital we do everything as clean and infection-free as possible, but youre leaving the office with a fresh wound. It needs to be kept clean and protected and you need to be careful, she says.
Most surgical wound infections happen within 30 days of after surgery. There may be pus draining from the wound which can be red, painful, and hot to the touch.
A staph infection is probably the most common infection. Staph is found on all our skin some people carry this in their noses and in other areas, says Lucas.
There are risk factors that increase a persons chance of developing a surgical wound infection, including poorly controlled diabetes, an immune disorder, being overweight or obese, smoking, steroid use, or if the surgery lasted more than two hours.
There are ways to reduce the risk of infection after surgery, according to Lucas:
- Wash hands thoroughly before performing twice-a-day wound care.
- Avoid performing wound care in the bathroom if possible lots of bacteria can live in there.
- After cleaning the wound, keep it lubricated with something like Vaseline to keep the stich line moist.
- Be cautious when out and about and dont engage in strenuous activity.
Why Not To Leave Skin Cancer Untreated
Skin cancer has two sides. On the one hand, it is fairly easy to detect and treat when done so at an early stage. On the other hand, when left untreated, skin cancer can cause disfigurement and even death. This is the dark side of skin cancer. Find out the sobering consequences of allowing skin cancer to develop into later stages.
Recommended Reading: What Does Melanoma In Situ Look Like
Are All Moles Cancerous
Most moles are not cancerous. Some moles are present at birth, others develop up to about age 40. Most adults have between 10 and 40 moles.
In rare cases, a mole can turn into melanoma. If you have more than 50 moles, you have an increased chance of developing melanoma.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Your skin is the largest organ in your body. It needs as much attention as any other health concern. What may seem like an innocent cosmetic imperfection, may not be. Performing regular skin self-checks is important for everyone and is especially important if you are a person at increased risk of skin cancer. Skin cancer is also color-blind. If you are a person of color, skin cancer can happen to you. Check your skin every month for any changes in skin spots or any new skin growths. Consider taking skin selfies so you can easily see if spots change over time. If youre a person of color, be sure to check areas more prone to cancer development, such as the palms of your hands, soles of your feet, between your toes, your genital area and under your nails. Takes steps to protect your skin. Always wear sunscreen with SPF of at least 30 every day of the year. Wear UV-A/UV-B protective sunglasses, wide-brimmed hats and long-sleeve shirts and pants. See your dermatologist at least once a year for a professional skin check.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 11/19/2021.
References
The Spread Of Melanoma Metastasis
If you or a family member or friend have recently been diagnosed with melanoma, you may be wondering, just where and why can melanoma spread?
With surgery, melanoma confined to the skin has a 5-year survival rate in 98% of cases. Unfortunately, if the lesion recurs , gets thicker, or spreads from the skin to the lymph nodes or distant organs, it becomes much more dangerous. This occurs in stage III and IV melanoma and is called melanoma metastasis.
Don’t Miss: Is An Itchy Neck A Sign Of Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage 3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
How Do You Know If A Spot Is Skin Cancer
See a board-certified dermatologist if you spot anything changing, itching, or bleeding on your skin. New, rapidly growing moles, or moles that itch, bleed, or change color are often early warning signs of melanoma and should be examined by a dermatologist.
Recommended Reading: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
What Will Happen After Treatment
Youll be glad when treatment is over. Your doctor will want you to check your skin at least once a month. It will be very important to protect yourself from getting too much sun.
For years after treatment ends, you will see your skin cancer doctor. At first, your visits may be every few months. Then, the longer youre cancer-free, the less often the visits are needed. Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. Your doctor will ask about symptoms and check you for signs of the cancer coming back or a new skin cancer. Other exams and tests may also be done.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as good as you can.
What Is The Outlook For People With Skin Cancer
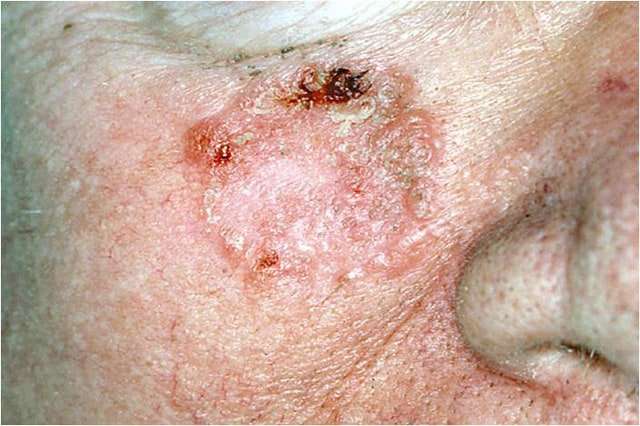
Nearly all skin cancers can be cured if they are treated before they have a chance to spread. The earlier skin cancer is found and removed, the better your chance for a full recovery. Ninety percent of those with basal cell skin cancer are cured. It is important to continue following up with a dermatologist to make sure cancer does not return. If something seems wrong, call your doctor right away.
Most skin cancer deaths are from melanoma. If you are diagnosed with melanoma:
- The five-year survival rate if its detected before it spreads to the lymph nodes is 99%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 66%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to distant lymph nodes and other organs is 27%.
Recommended Reading: Stage 1 Cancer Symptoms
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Skin Cancer
Basal and squamous skin cancer may look like:
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas that look a lot like a scar
- Raised reddish patches that might itch
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Small, pink or red, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas
- Pink growths or lumps with raised edges and a lower center
- Open sores that dont heal, or that heal and then come back
- Wart-like growths
What Causes Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin occurs when the flat, thin squamous cell in the middle and outer layers of the skin develop mutations in their DNA. The mutations trigger the squamous cell to grow out of control. Ultraviolet radiations found in sunlight may prompt the cells to mutate.
Other factors that can increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma include
- Fair skin: Having less pigment in the skin provides less protection from the damaging UV rays.
- Excessive sun exposure: Exposure to UV rays from sunlight may increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- History of sunburns: History of blistering sunburns as a child or teenager increases the risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma.
- Rare genetic disorder: People with a genetic disorder that causes extreme sensitivity to sunlight are more prone to squamous cell carcinoma.
- Weakened immune system: People with conditions that lead to a weak immune system are highly prone to squamous cell carcinoma.
- A previous history of squamous cell carcinoma will most probably be the causative factor.
- A previous history of precancerous skin lesions, such as actinic keratosis or Bowen disease, can increase the chance of squamous cell carcinoma.
Read Also: Is Melanoma Cancer Curable
Other Cancers On The Face
A few other rare skin cancers that might happen on the face:
- Lymphoma of the skin is an uncommon type of white blood cell cancer.
- Kaposi’s sarcoma is cancer caused by a herpes virus in immunosuppressed patients that causes skin lesions on the face. They look like painless purplish spots.
- Skin adnexal tumors is a rare cancer type that starts in hair follicles or skin glands.
- Sarcomas are tumors of the connective tissuesspecifically the fat, nerves, bone, skin, and muscles 80% of which occur in the face, head, or neck.
- Cutaneous leiomyosarcoma is an uncommon soft-tissue sarcoma that can happen on the face.
What Happens During A Skin Cancer Screening
Skin cancer screenings may be done by yourself, your primary care provider, or a dermatologist. A dermatologist is a doctor who specializes in disorders of the skin.
If you are screening yourself, you will need to do a head-to-toe exam of your skin. The exam should be done in a well-lit room in front of a full-length mirror. You’ll also need a hand mirror to check areas that are hard to see. The exam should include the following steps:
- Stand in front of the mirror and look at your face, neck, and stomach.
- Women should look under their breasts.
- Raise your arms and look at your left and right sides.
- Look at the front and back of your forearms.
- Look at your hands, including between your fingers and under your fingernails.
- Look at the front, back, and sides of your legs.
- Sit down and examine your feet, checking the soles and the spaces between the toes. Also check the nail beds of each toe.
- Check your back, buttocks, and genitals with the hand mirror.
- Part your hair and examine your scalp. Use a comb along with a hand mirror to help you see better. It may also help to use a blow dryer to move your hair as you look.
If you are getting screened by a dermatologist or other health care provider, it may include the follow steps:
The exam should take 10-15 minutes.
Recommended Reading: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 1
You Can Find Skin Cancer On Your Body
The best way to find skin cancer is to examine yourself. When checking, you want to look at the spots on your skin. And you want to check everywhere from your scalp to the spaces between your toes and the bottoms of your feet.
If possible, having a partner can be helpful. Your partner can examine hard-to-see areas like your scalp and back.
Getting in the habit of checking your skin will help you notice changes. Checking monthly can be beneficial. If you have had skin cancer, your dermatologist can tell you how often you should check your skin.
People of all ages get skin cancer
Checking your skin can help you find skin cancer early when its highly treatable.
How Do People Get Hpv
HPV can be passed from one person to another by skin-to-skin contact, such as occurs with sexual activity. The main way HPV is spread is through sexual activity, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. HPV can be spread even when an infected person has no visible signs or symptoms.
The virus can also be spread by genital contact without sex, although this is not common.
HPV infection is very common. Most men and women who have ever had sex get at least one type of genital HPV at some time in their lives. Anyone who has had sex can get HPV, even if it was only with only one person, but infections are more likely in people who have had many sex partners. Even if a person delays sexual activity until marriage, or only has one partner, they are still at risk of HPV infection if their partner has been exposed.
You cannot get HPV from:
- Toilet seats
- Even if it has been years since you were sexually active
- Even if you do not have any signs or symptoms
You May Like: What Is Braf Melanoma