Signs Of Lip And Oral Cavity Cancer Include A Sore Or Lump On The Lips Or In The Mouth
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by lip and oral cavity cancer or by other conditions. Check with your doctor if you have any of the following:
- A sore on the lip or in the mouth that does not heal.
- A lump or thickening on the lips or gums or in the mouth.
- A white or red patch on the gums, tongue, or lining of the mouth.
- Bleeding, pain, or numbness in the lip or mouth.
- Change in voice.
- Loose teeth or dentures that no longer fit well.
- Trouble chewing or swallowing or moving the tongue or jaw.
- Swelling of jaw.
- Sore throat or feeling that something is caught in the throat.
Lip and oral cavity cancer may not have any symptoms and is sometimes found during a regular dental exam.
What Causes Tongue Cancer And What Are The Risk Factors
Some people develop cancer of the tongue with no risk factors. The cancer is more common in older age groups, age 40 and up, although it may be found in young people. It is twice as common in men. Other risk factors are:
- Smoking and drinking alcohol. Smokers are five times more likely to develop tongue cancer than nonsmokers.
- Human papillomavirus , a sexually transmitted disease. HPV 16 and HPV 18 increase the risk of tongue cancer.
- African-American men are at greater risk than Caucasians.
Types Of Mouth Cancer
Mouth cancer is categorised by the type of cell the cancer starts to grow in.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common type of mouth cancer, accounting for 9 out of 10 cases.
Squamous cells are found in many areas of the body, including the inside of the mouth and in the skin.
Less common types of mouth cancer include:
- adenocarcinoma, which is cancers that develop inside the salivary glands
- sarcoma, which grows from abnormalities in bone, cartilage, muscle or other tissue
- oral malignant melanoma, where cancer starts in the cells that produce skin pigment or colour . These appear as very dark, mottled swellings that often bleed
- lymphoma, which grows from cells usually found in lymph glands, but they can also grow in the mouth
Read Also: What Type Of Skin Cancer Spreads The Fastest
What Is The Meaning Of Squamous Cell
DictionaryCancerSquamous cellscellscarcinoma
. Similarly, you may ask, are all squamous cells cancerous?
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is a common form of skin cancer that develops in the squamous cells that make up the middle and outer layers of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is usually not life-threatening, though it can be aggressive.
Additionally, how does squamous cell carcinoma start? Squamous cell carcinoma usually starts out as a small, red, painless lump or patch of skin that slowly grows and may ulcerate. It usually occurs on areas of skin that have been repeatedly exposed to strong sunlight, such as the head, ears, and hands.
People also ask, where are squamous cells found in the body?
Squamous cells are found in a variety of different parts of the body. You can find squamous cells in the mouth, on the lips, and on the cervix. They are also seen in the middle layers of the skin.
What is squamous cell skin cancer?
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer. It’s usually found on areas of the body damaged by UV rays from the sun or tanning beds. Sun-exposed skin includes the head, neck, chest, upper back, ears, lips, arms, legs, and hands. SCC is a fairly slow-growing skin cancer.
What Is The Prognosis Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity
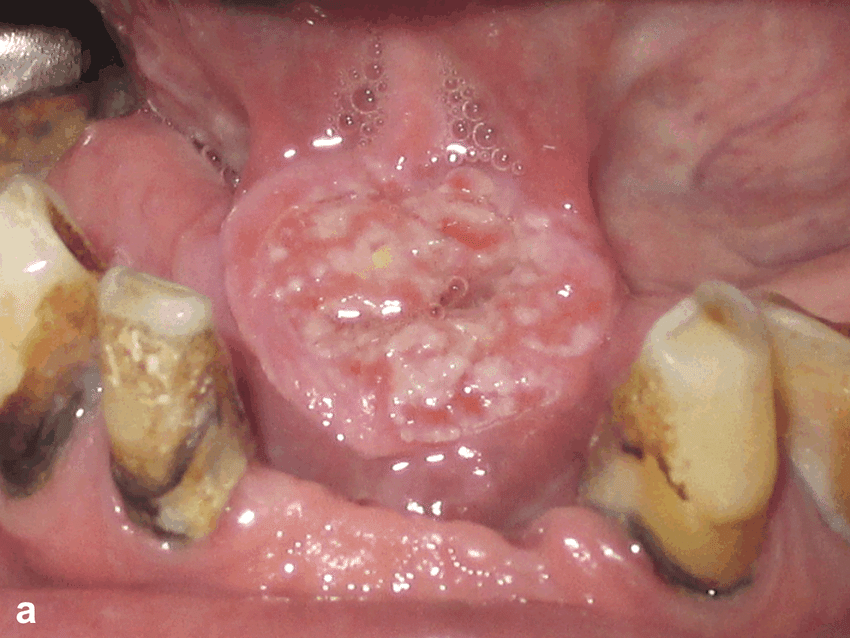
- In general, Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity is an aggressive form of cancer. If metastasis is observed, then the prognosis is guarded or unpredictable
- Tumors in their early stage with complete excisional treatment typically have good prognosis
- In cases of metastasis, its prognosis depends upon a set of several factors that include:
- Stage of tumor: With lower-stage tumors, when the tumor is confined to site of origin, the prognosis is usually excellent with appropriate therapy. In higher-stage tumors, such as tumors with metastasis, the prognosis is poor
- The surgical respectability of the tumor
- Overall health of the individual: Individuals with overall excellent health have better prognosis compared to those with poor health
- Age of the individual: Older individuals generally have poorer prognosis than younger individuals
- Whether the tumor is occurring for the first time, or is a recurrent tumor. Recurring tumors have a poorer prognosis compared to tumors that do not recur
- Response to treatment: Tumors that respond to treatment have better prognosis compared to tumors that do not respond so well to treatment
Recommended Reading: Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Canker Sores: Painful But Not Dangerous
Know how to distinguish a canker sore from something more serious. A canker sore inside your mouth often burns, stings, or tingles before its visible. In the early stages, mouth cancer rarely causes any pain. Abnormal cell growth usually appears as flat patches.
A canker sore looks like an ulcer, usually with a depression in the center. The middle of the canker sore may appear white, gray, or yellow, and the edges are red.
Canker sores are often painful, but they arent malignant. This means that they dont become cancerous. Canker sores usually heal within two weeks, so any sore, lump, or spot in your mouth that lasts longer needs a professional evaluation.
Tobacco And Alcohol Use Can Affect The Risk Of Lip And Oral Cavity Cancer
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk. Risk factors for lip and oral cavity cancer include the following:
- Heavy alcohol use.
- Being exposed to natural sunlight or artificial sunlight over long periods of time.
- Being male.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Causes Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The mutations that occur in the skin cell DNA causes skin cancer. Such changes cause abnormal cells to multiply uncontrollably. When this occurs in squamous cells, it gives rise to squamous cell cancer. DNA mutations are generally caused by UV radiation found in the sun, tanning lamps, and beds.
As we read, exposure to UV radiation increases the risk of cancer. Still, it is pretty shocking to know that less exposure to sunlight or tanning lamps also increases the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Studies also reveal that people with a weak immune system are likely to develop skin cancer. Radiation therapy also increases the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
The Risks The Causes What You Can Do
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is caused by DNA damage that leads to abnormal changes in the squamous cells in the outermost layer of skin.
Understanding what causes this damage and the factors that increase your risk of developing SCC can help you detect the disease early or prevent it from happening in the first place.
These factors increase your SCC risk:
- Unprotected exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
- Weakened immune system due to illness or certain immunosuppressive medications.
- History of skin cancer including basal cell carcinoma .
- Age over 50: Most SCCs appear in people over age 50.
- Fair skin: People with fair skin are at an increased risk for SCC.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop SCC.
- Sun-sensitive conditions including xeroderma pigmentosum.
- Chronic infections and skin inflammation from burns, scars and other conditions.
Read Also: Stage 4 Basal Cell Carcinoma Life Expectancy
Other Types Of Oral Cavity And Oropharynx Cancers
Minor salivary gland cancers: These cancers can start in the glands in the lining of the mouth and throat. There are many types of minor salivary gland cancers, including adenoid cystic carcinoma, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, and polymorphous low-grade adenocarcinoma. To learn more about these cancers, as well as benign salivary gland tumors, see Salivary Gland Cancer.
Lymphomas: The tonsils and base of the tongue contain immune system tissue, where cancers called lymphomas can start. For more information about these cancers, see Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children.
Questions About Oral Cancer Treatment
Designing an oral cancer treatment plan is often determined by where the cancer originated, whether its spread and how severe the side effects may be. Treatment also may be influenced by the stage of the cancer and the patients individual needs and treatment goals.
How is oral cancer typically treated?
Oral cancer may be treated with one therapy or a combination of therapies, depending on where the cancer started and whether the disease has advanced. Surgery is often used to treat oral cancer that hasnt spread. Surgery also is commonly used to treat advanced-stage and recurrent cancers, often in combination with radiation therapy, chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy.
Surgical procedures for oral cancer include:
- Tumor resection, or the removal of the entire tumor and some surrounding tissue
- Mohs micrographic surgery, which removes thin slices of a tumor at a time, recommended to treat some cases of lip cancer
- Mandibulectomy, the removal of all or part of the lower jawbone
- Glossectomy, the removal of all or part of the tongue
- Maxillectomy, the removal of all or part of the hard palate
- Neck dissection, the removal of a few, most or almost all of the lymph nodes on one side of the neck, in cases when cancer has spread to this area
What are the potential side effects of oral cancer treatment?
Aside from side effects that may affect appearance and function, oral cancer treatment may also cause weight loss, fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, taste changes, dry mouth and constipation.
Read Also: Show Me What Skin Cancer Looks Like
What Can You Do To Prevent Oral Cancer
Scientists think that oral cancer starts when the DNA in the cells inside your mouth gets damaged. But some things, including your health habits, can make you more likely to get it. To prevent oral cancer:
- Don’t smoke or use any tobacco products and drink alcohol in moderation .
- Eat a well-balanced diet.
- Limit your exposure to the sun. Repeated exposure increases the risk of cancer on the lip, especially the lower lip. When in the sun, use UV-A/B-blocking sun protective lotions on your skin, as well as your lips.
You can take an active role in detecting oral cancer early, should it occur, by doing the following:
Show Sources
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
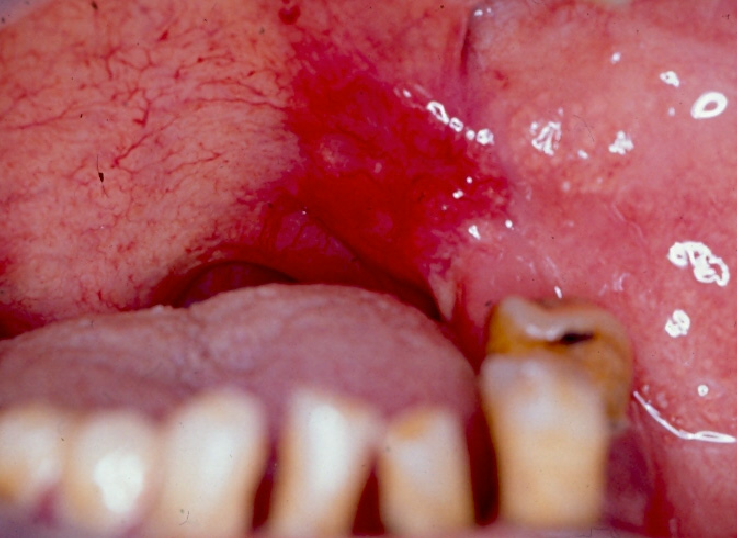
A change in the skin might be the first sign of the presence of basal cancer cells. The changes may include a bump or sore that wont heal. The following can be a few symptoms of the disease:
- A translucent skin-colored bump: The bump can be either white or pink on fair skin, while the bump generally looks brown or shiny black on dark skin. You also might be able to see blood vessels. Sometimes, the bump may bleed.
- Lesions: A brown, black, or blue lesion can appear with a slightly raised translucent border.
- Flat and scaly spots: Such patches can be seen with raised edges. Also, they can grow quite large over a period of time.
- Scar-like lesion: A whitish scar-like lesion without any proper border can also be an essential sign of basal cell carcinoma.
Also Check: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
What Are The Symptoms Of Oral Cancer
The most common symptoms of oral cancer include:
- Swellings/thickenings, lumps or bumps, rough spots/crusts/or eroded areas on the lips, gums, cheek, or other areas inside the mouth
- Velvety white, red, or speckled patches in the mouth
-
- Unexplained bleeding in the mouth
- Unexplained numbness, loss of feeling, or pain/tenderness in any area of the face, mouth, or neck
- Persistent sores on the face, neck, or mouth that bleed easily and do not heal within 2 weeks
- A soreness or feeling that something is caught in the back of the throat
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing, speaking, or moving the jaw or tongue
- Hoarseness, chronic sore throat, or change in voice
If you notice any of these changes, contact your dentist or health care professional immediately.
What Is Transoral Robotic Surgery
Transoral robotic surgery is a minimally invasive treatment method to remove difficult-to-reach oropharyngeal cancers through your mouth. With robotic surgery, your surgeon operates while seated at a console unit, while you are on a nearby operating table. Your surgeon operates using hand and foot controls to position a 3D, high-definition camera and to precisely direct surgical instruments, which are attached to robotic arms. Robotic surgery avoids the larger neck incision and lower jaw splitting required with traditional surgery. Advantages of transoral robotic surgery include a shorter hospital stay, faster recovery, less damage to surrounding tissues and swallowing muscles, avoidance of a tracheostomy breathing tube and less long-term problems with speech and swallowing.
Recommended Reading: Cancer On Arm Pictures
Who Gets Oral Cancer
According to the American Cancer Society, men face twice the risk of developing oral cancer as women. Men who are over age 50 face the greatest risk. It’s estimated that over 50,000 people in the U.S. received a diagnosis of oral cancer in 2019.
Risk factors for the development of oral cancer include:
It is important to note that over 25% of all oral cancers occur in people who do not smoke and who only drink alcohol occasionally.
Initiating And Early Events
HPV-negative HNSCC.
Tobacco consumption is the primary risk factor for development of HPV-negative HNSCC. Tobacco consists of over 5,000 different chemicals, of which dozens have been shown to have carcinogenic activity. The chemicals thought to be most responsible for the cancer-causing effects of tobacco are polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons , including benzopyrene, and nitrosamines, including 4–1–1-butanone and N-nitrosonornicotine ,. In smokeless tobacco, nitrosamines are the dominant carcinogen, whereas the carcinogens in areca nut and betel quid are poorly defined. Tobacco-derived carcinogens, including PAHs and nitrosamines, undergo metabolic activation, with detoxication enzymes and pathways promoting excretion . However, many of the reactive metabolites of these carcinogens can also form covalent DNA adducts, which, if not properly repaired, lead to mutations and other genetic abnormalities. The propensity for tobacco carcinogens to promote genetic changes and neoplastic transformation likely depends on the balance between metabolic activation versus detoxification and DNA repair . The use of tobacco products is also associated with inflammation in the exposed tissues. Coincident with inflammation is the local production of cytokines, chemokines and growth factors that can have an important role in promoting proliferation, angiogenesis and, ultimately, carcinogenesis.
Development of carcinogen-associated, HPV-negative HNSCC.
HPV-positive HNSCC.
You May Like: Precursor To Skin Cancer
What Is The Oropharynx
Your oropharynx is the middle part of your throat just beyond your mouth. Your oropharynx includes the back part of your tongue , your tonsils, your soft palate , and the sides and walls of your throat. Your oropharynx makes saliva, keeps your mouth and throat moist and starts to help digest the food you eat.
After Lip And Oral Cavity Cancer Has Been Diagnosed Tests Are Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Lip And Oral Cavity Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the lip and oral cavity or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment. The results of the tests used to diagnose lip and oral cavity cancer are also used to stage the disease.
Read Also: Mayo Clinic Pictures Of Skin Cancer
Can I Do Anything To Prevent The Development Of Oropharyngeal Cancer
You may not be able to prevent oropharyngeal cancer, but you can take steps to lower your risk. Changes you can make include:
- Dont start smoking. If you smoke or use tobacco products, quit. Continuing to smoke greatly increased the risk of developing a second cancer in the mouth, throat or voice box or lung. Ask your healthcare provider for help. They have many resources and can put you in touch with the information need or other health professionals that can help you quit.
- Dont drink alcohol regularly or heavily. Alcohol increases the cancer-causing effects of tobacco, so its especially important to avoid this combination.
- Avoid human papilloma virus infection. Ask your doctor about the HPV vaccine. Multiple sex partners and oral sex increases your risk of HPV.
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet and exercise regularly.
- See your healthcare provider and dentist on a regular schedule. They can check your mouth and throat and catch any changes early in their development.
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity
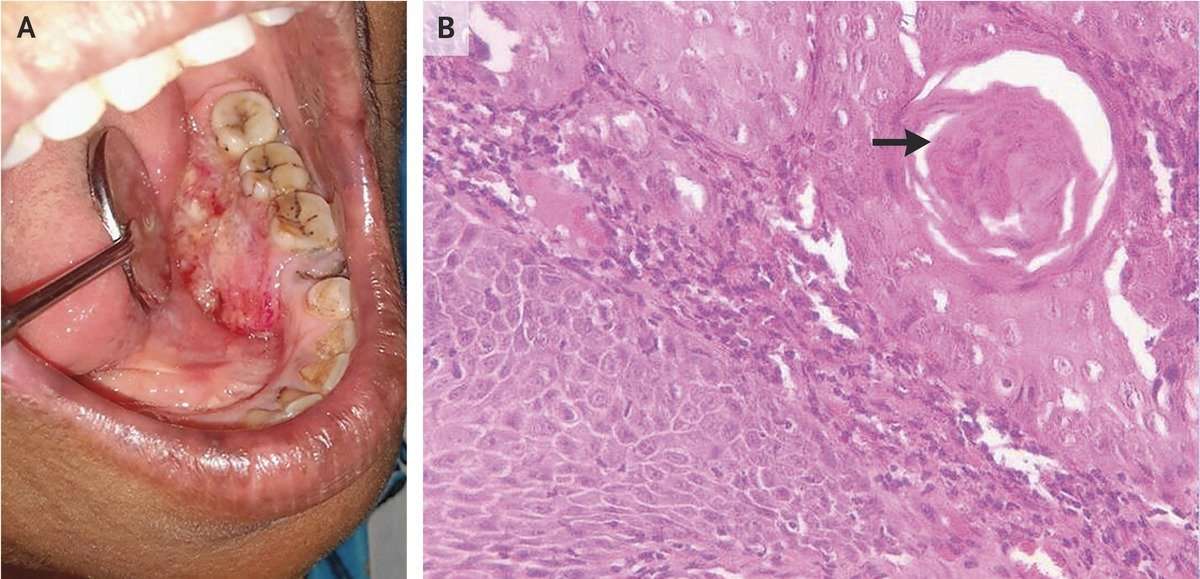
The risk factors for Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity include:
- Smoking and chewing of tobacco are strong risk factors for this type of Oral Cavity Cancer
- Radiation therapy in the face or mouth region
- Arsenic exposure
- Coal tar exposure
- Individuals with weak immune system, which could be due to cancer treatment, AIDS, or those on immunosuppressant drugs after receiving an organ transplant
- Caucasians are more vulnerable compared to other dark-skinned individuals
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
Also Check: Idc Breast Cancer Survival Rate