Pitfalls In The Diagnosis Of Sclc
There are a number of pitfalls in the diagnosis of SCLC. These include lack of cytologyhistology correlation, crush artifact, Merkel cell carcinoma, primitive neuroectodermal tumor , keratin-negative SCLC, diminished proliferation rate in SCLC after chemotherapy and combined SCLC and large cell carcinoma.
SCLC is readily diagnosed by cytology hence, it is important to correlate the findings in any biopsy that may be paired with a cytology sample. Often in very challenging biopsies, the diagnosis may be more readily established based on the cytology sample. If this correlation is not made between biopsy and cytology, it is possible to have a diagnosis of SCLC in one specimen and non-small cell carcinoma in the other specimen.
A keratin-negative tumor that looks like SCLC should raise the consideration of malignant lymphoma, malignant melanoma, a crushed carcinoid tumor and PNET. Other stains such as lymphoid markers , melanoma markers a Ki-67 stain and CD99 may be helpful in this differential diagnosis, respectively. It is extremely unusual to encounter a keratin-negative SCLC. When this occurs and other differential diagnostic considerations seem excluded, several keratin antibodies other than CK7/CK20 may be helpful. When all keratins are negative, if the morphology is characteristic and other tumors have been excluded, the finding of TTF-1 and NE marker expression can help support a SCLC diagnosis.
Figure 8
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have small cell lung cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get small cell lung cancer?
- What stage is the lung cancer? What does this mean for my prognosis?’
- What is the best treatment for the small cell lung cancer I have?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- How can I stop smoking?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Early cancer screenings and treatment advancements are helping people with small cell lung cancer live longer. If youre at high risk for small cell lung cancer due to a history of smoking, talk to your healthcare provider about getting annual lung cancer screenings. These screenings can catch cancer early, when its most treatable. Its never too late to gain health benefits when you stop smoking even if you already have lung cancer. Your provider can help you quit.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 10/12/2020.
References
Causes Of Small Cell Lung Cancer
Smoking cigarettes is the main cause of lung cancer. People who do not smoke can still develop lung cancer, but their risk is much lower. If someone stops smoking, their risk of developing lung cancer falls over time. After about 15 years it is almost the same as a non-smoker. Lung cancer is also more common in older people.
If these tests show anything abnormal, your GP will refer you to a chest specialist within 2 weeks. Sometimes they will do this before getting the result of the chest x-ray.
At the hospital, the specialist will explain any other tests you need.
Other tests you may have at the hospital include:
PET-CT scan
A PET-CT scan is a combination of a CT scan, which takes a series of x-rays to build up a three-dimensional picture and a positron emission tomography scan.
Biopsy
The doctor or nurse collects samples of cells or tissue from the lung or nearby lymph nodes. The samples are checked under a microscope for cancer cells. This test can help diagnose lung cancer and show whether it is small cell lung cancer or non-small cell lung cancer . There are different ways of collecting biopsies, including:
Waiting for tests results can be a difficult time, we have more information that can help.
You May Like: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Whether you are thinking about treatment, getting treatment, or not being treated at all, you can still get supportive care to help with pain or other symptoms. Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life.
Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help.
The American Cancer Society also has programs and services including rides to treatment, lodging, and more to help you get through treatment. Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists.
For Most Patients With Small Cell Lung Cancer Current Treatments Do Not Cure The Cancer
If lung cancer is found, patients should think about taking part in one of the manyclinical trials being done to improve treatment. Clinical trials are taking place in most parts of the country for patients with all stages of small cell lung cancer. Information about ongoing clinical trials is available from the NCI website.
Also Check: What Is The Leading Cause Of Skin Cancer
How Is Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosed
Chest X-rays are typically the first step to screen for any type of lung cancer. If images show suspicious spots on a lung, your healthcare provider may order one or more of these diagnostic tests:
- Imaging scans:Computed tomography and positron emission tomography scans detect lung tumors. These tests also can help gauge cancer spread. CT scans are the primary way to diagnose lung cancer.
- Sputum cytology: This test checks for cancer cells in sputum, mucus coughed up from the lungs.
- Biopsy: A needle biopsy removes tissue samples from the lungs. Lab pathologists check the biopsy for cancer cells.
- Bronchoscopy: Using a bronchoscope, your provider looks inside the lungs airways for tumors. At the same time, providers can remove tissue samples to biopsy.
How Can I Prevent Small Cell Lung Cancer
Because tobacco use is the top cause of small cell lung cancer, not smoking is the best way to protect your health. When you quit smoking regardless of your age or years of tobacco use your lungs start to heal, and cancer risk diminishes. These steps may also help:
- Eat a nutritious diet.
- Test your home for radon, a natural, odorless, radioactive gas.
- Install a mitigation system to remove radon from your home, if needed.
- Protect yourself from cancer-causing chemicals at work.
You May Like: Basal Cell Carcinoma Etiology
What Is Small Cell Carcinoma
Small cell carcinoma is one of the most aggressive forms of cancer. While it represents 13% of all lung cancers, it is otherwise rare, accounting for less than 1% of colorectal and breast cancer diagnoses. Among patients with small cell prostate cancer, roughly 50% initially show signs of small cell carcinoma but only 1% are formally diagnosed.
At Regional Cancer Care Associates, our oncologists offer treatment for all types of small cell carcinoma to help patients relieve symptoms and restore their quality of life.
Citation Doi And Article Data
Citation:DOI:Dr Luke DanaherRevisions:see full revision historySystems:
- Small cell carcinoma of the lung
- Oat cell carcinoma
- Oat cell carcinoma of the lung
- Small cell bronchogenic carcinoma
Small cell lung cancer , also known as oat cell lung cancer, is a subtype of bronchogenic carcinoma separated from non-small-cell lung cancer as it has a unique presentation, imaging appearances, treatment, and prognosis. SCLCs are neuroendocrine tumors of the lung that rapidly grow, are highly malignant, widely metastasize, and, despite showing an initial response to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, have a poor prognosis and are usually unresectable.
You May Like: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What About Other Treatments I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat your cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to be helpful. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything you are thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
LCNEC is a high-grade non-small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma that meets the following criteria: neuroendocrine morphology: organoid, palisading, trabecular or rosette-like growth patterns non-small cell cytological features: large size, polygonal shape, low N/C ratio, coarse or vesicular nuclear chromatin and frequent nucleoli high mitotic rate with a mean of 60 mitoses per 2mm2 frequent necrosis and at least one positive neuroendocrine immunohistochemical marker or neuroendocrine granules by electron microscopy ., It is very difficult to diagnose LCNEC based on small biopsy specimens such as needle or bronchoscopic biopsy specimens as it is usually very difficult to be certain of the neuroendocrine morphology without a substantial sampling of the tumor. However, criteria have been proposed to diagnose LCNEC based on cytology. The term large cell carcinoma, with neuroendocrine morphology can be used for tumors resembling LCNEC by light microscopy but lacking proof of neuroendocrine differentiation by electron microscopy or immunohistochemistry. The term combined LCNEC is appropriate for those tumors containing components of other histological types of NSCLC, such as adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. The main criteria for distinguishing SCLC from LCNEC are discussed above and summarized in .
Figure 9
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
The Following Stages Are Used For Small Cell Lung Cancer:
Limited-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
In limited-stage,cancer is in the lung where it started and may have spread to the area between the lungs or to the lymph nodes above the collarbone.
Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
In extensive-stage,cancer has spread beyond the lung or the area between the lungs or the lymph nodes above the collarbone to other places in the body.
Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
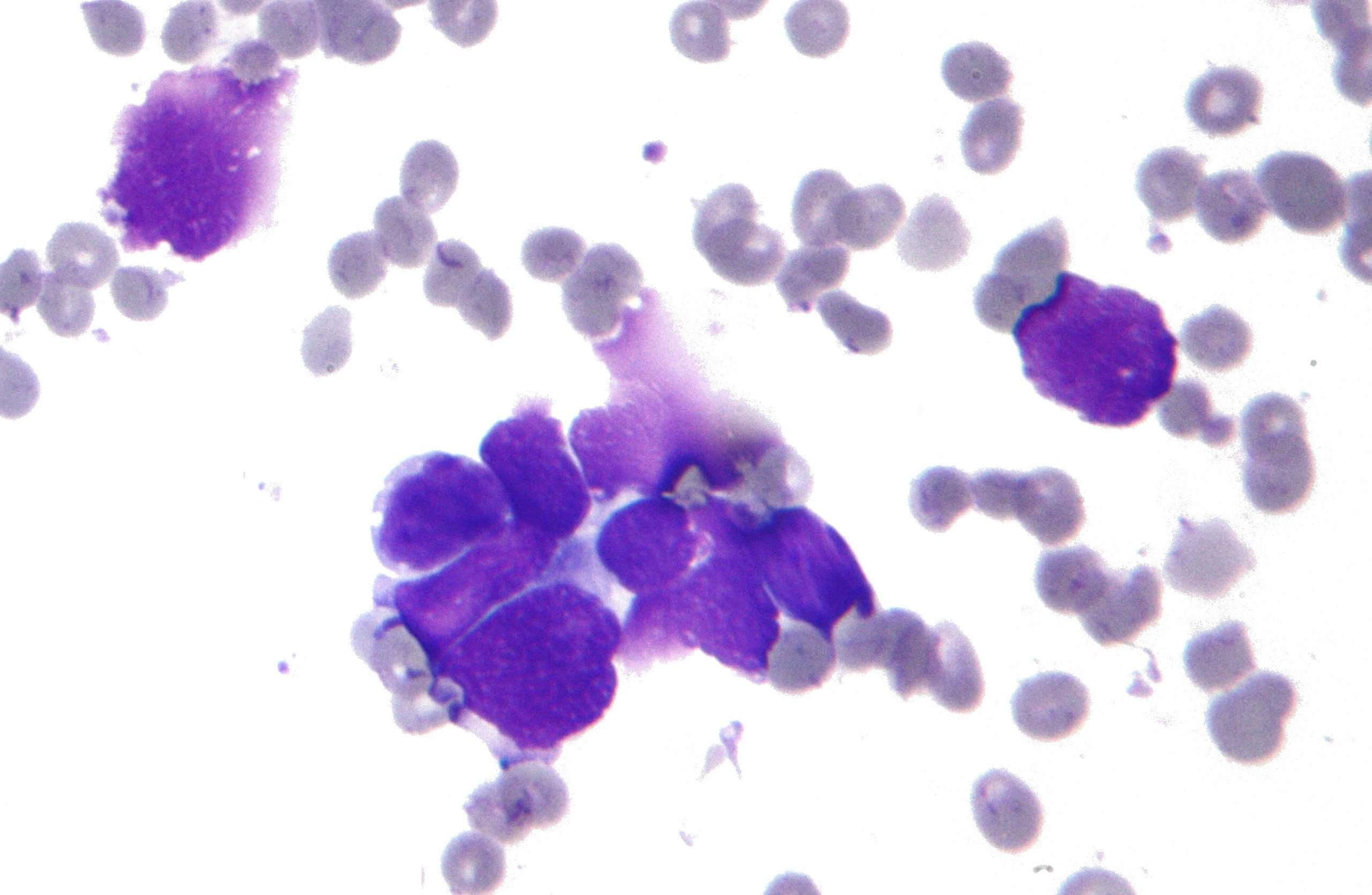
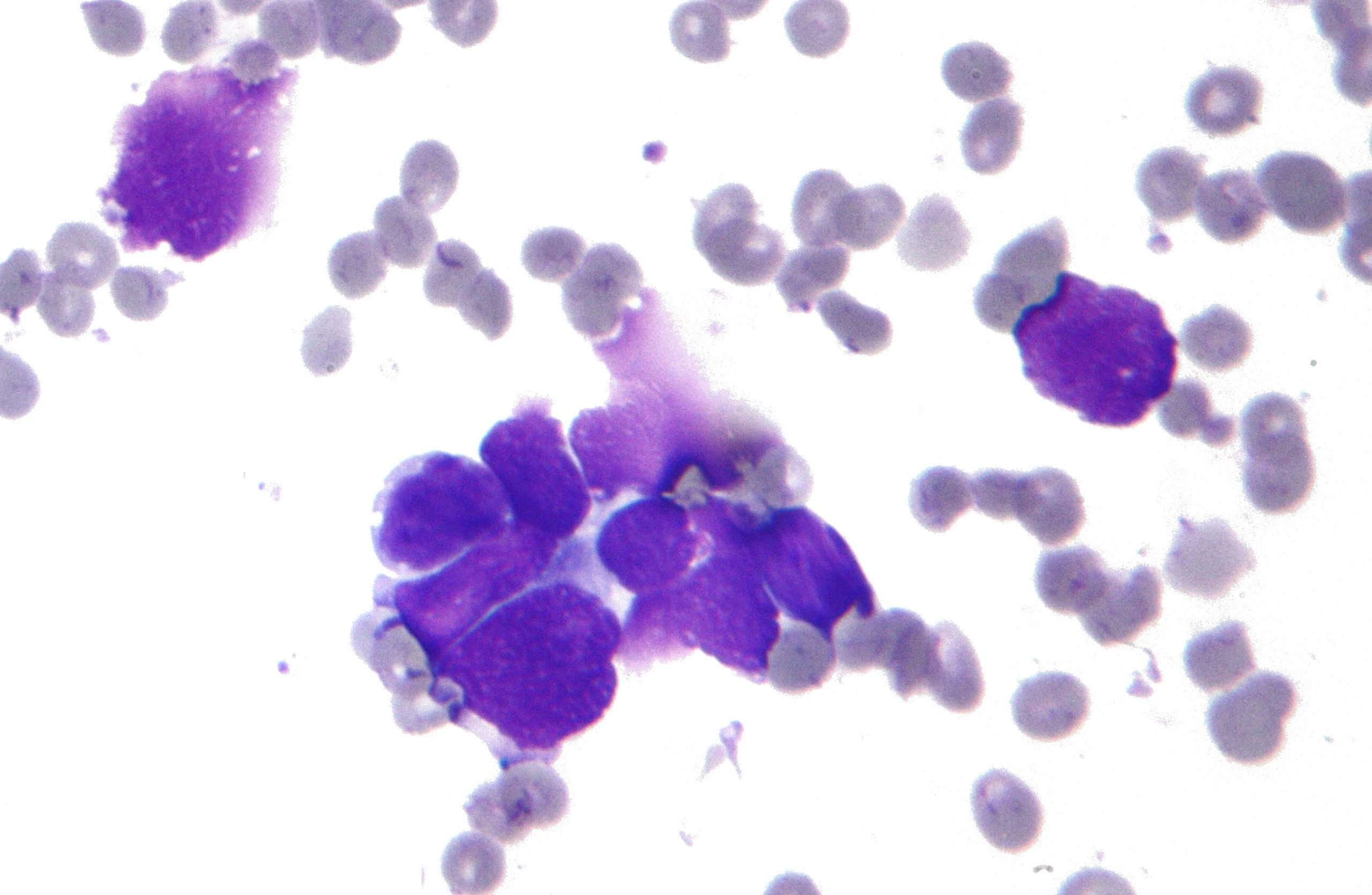
Small cell lung carcinoma accounts for 25% of all lung cancers in the United States as well as in Europe. Two-thirds of SCLC are proximal and present as a perihilar tumor. The 1999 WHO/IASLC classification presents only two types of SCLC: SCLC and combined SCLC .
SCLC has a distinctive histological appearance. Tumor cells have a small size, not exceeding that of three lymphocytes. They have a round or fusiform shape, scant cytoplasm with a nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio of 9 to 10, a finely granular nuclear chromatin , and absent or inconspicuous nucleoli . Owing to the scarcity of cytoplasm, nuclear molding and smearing of nuclear chromatin is frequent, caused by crush artifact. There is usually an extensive necrosis and mitotic rate exceeding 20 and reaching 100 mitoses per 2 mm2 area. Most often, the growth pattern consists of diffuse sheets, although endocrine differentiations with rosettes, palisading, ribbons, and organoid nesting might be seen.
The immunohistochemical features of SCLC are not required for the diagnosis of SCLC. However, crush artifact is common in small biopsy specimens for immunohistochemistry for neuroendocrine differentiations and keratins, and common leucocytes antigens become more useful in marking SCLC versus lymphoid cells, respectively. Moreover, the most important differential diagnosis resides in the distinction between SCLC and nonsmall cell lung carcinoma because of different therapeutic implications.
Combined Small Cell Lung Cancer
Also Check: What Is Braf Melanoma
What You Need To Know
- The most common types of lung cancer include lung nodules, non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer and mesothelioma.
- Rare lung cancers often don’t originate in the lung.
- Rare lung cancers vary according to size, recommended treatment options and rate of metastasis.
The most common types of lung cancer are those found right in the lungs. Other rarer types of cancer may also occur in the lungs and chest wall.
What Is Lung Cancer
Cancer is not just one disease. There are many types of cancer. But all cancers start when a group of cells in the body grows out of control. Cancer cells keep on growing and can crowd out normal cells. This makes it hard for the body to work the way it should.
Cancer can start any place in the body. It can start in the breast, the lungs, the colon, or even in the blood. Cancer that starts in the lung is called lung cancer.
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. For instance, cancer cells in the lung can travel to the bone and grow there. When cancer cells spread, its called metastasis.
Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when lung cancer spreads to the brain , its still called lung cancer. Its not called brain cancer unless it starts in the brain.
The lungsAsk your doctor to show you on this picture where your cancer is found.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate
Small Cell Lung Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Lung
The lungs are a pair of cone-shaped breathing organs that are found in the chest. The lungs bring oxygen into the body when you breathe in and take out carbon dioxide when you breathe out. Each lung has sections called lobes. The left lung has two lobes. The right lung, which is slightly larger, has three. A thin membrane called thepleura surrounds the lungs. Two tubes called bronchi lead from thetrachea to the right and left lungs. The bronchi are sometimes also affected by lung cancer. Small tubes called bronchioles and tiny air sacs calledalveoli make up the inside of the lungs.
There are two types of lung cancer:small cell lung cancer andnon-small cell lung cancer.
This summary is about small cell lung cancer and its treatment. See the following PDQ summaries for more information about lung cancer:
Other Types Of Lung Tumors
Along with the main types of lung cancer, other tumors can occur in the lungs.
Lung carcinoid tumors: Carcinoid tumors of the lung account for fewer than 5% of lung tumors. Most of these grow slowly. For more information about these tumors, see Lung Carcinoid Tumor.
Other lung tumors: Other types of lung cancer such as adenoid cystic carcinomas, lymphomas, and sarcomas, as well as benign lung tumors such as hamartomas are rare. These are treated differently from the more common lung cancers and are not discussed here.
Cancers that spread to the lungs: Cancers that start in other organs can sometimes spread to the lungs, but these are not lung cancers. For example, cancer that starts in the breast and spreads to the lungs is still breast cancer, not lung cancer. Treatment for metastatic cancer to the lungs is based on where it started .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What Are The Stages Of Small Cell Lung Cancer
Healthcare providers use a two-stage system to diagnose the spread of small cell lung cancer. This information also helps guide treatment. The two stages of small cell lung cancer are:
- Limited: Cancer is confined to one lung and nearby lymph nodes.
- Extensive: Cancer has spread to the other lung and lymph nodes. It also may have spread to bones, the brain and other organs.
How Does Treatment Differ
Like most cancers, the treatment options are dependent on the stage the disease. The pace of treatment for SCLC is generally faster than NSCLC due to the tumors ability to quickly spread. NSCLC is less aggressive however, it is typically identified at a later stage. In fact, only an approximate 25% of NSCLC patients are diagnosed at stage 1 or 2. For the minority who are diagnosed at stage 1 or 2, surgery to remove the tumor is often an option. Patients in the later stages are typically treated with chemotherapy and radiation.
The treatment for SCLC is typically done at a much faster pace, seeing as the tumor is able to quickly spread. Chemotherapy and radiation put approximately a quarter of patients into remission, however this type of cancer is likely to spread to other parts of the body. Some healthcare professionals may preventatively treat the brain with radiation, as these cancer cells are likely to end up in the brain.
Also Check: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Do I Know Which Type Of Lung Cancer I Have
When your physician first suspects you have lung cancer, you will likely need a medical imaging scan, such as an MRI or X-ray, to identify any abnormal growths. If a tumor is present, an oncologist will obtain a small sample of the lesion through a biopsy, which will then be examined through a microscope to determine the kind of lung cancer you have. Each type of lung cancer has different characteristics that helps with identification. For example, as its name suggests, the cells of small cell lung cancer are typically smaller than the cells of non-small cell lung cancer. The most effective course of treatment for you will depend on the type and subtype of your malignancy, in addition to many other factors.
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Alberto Chiappori.
If you have been recently diagnosed with lung cancer, Moffitt Cancer Center can provide you with the comprehensive treatment you need to achieve the best possible outcome and an improved quality of life. The specialists in our Thoracic Oncology Program create individualized treatment plans for our patients to address the challenges of each unique cancer. Schedule a consultation at Moffitt by calling or by submitting a new patient registration form form online. Referrals are not required.
- BROWSE