No Skin Cancer Symptoms
Many skin cancers so not display any itchy symptoms and can only be detected by expert examination.
It is recommended that people with no history of Skin Cancer but with a Skin Type I, II and III should have a Skin Check every 12 months.
It is really surprising how often innocent skin changes turn out to be Skin Cancer or precancerous lesions.
Early Detection is the Best Treatment and Could Save Your Life
Common Symptoms Related With Specific Types Of Skin Cancer
Does skin cancer itch? Yes, it does. However, itching alone doesn’s mean anything. Some other symptoms should also be kept in mind so that you can be better prepared.
1. Melanoma
Melanoma refers to a cancerous growth that may appear anywhere on your skin. Most of the time, it occurs on the face or torso in men, while it is mostly on the lower legs in women. Those with darker complexions also run higher risk of developing melanoma on the palms of their hands and the soles of their feet as well.
Melanoma may itch as well as showing other signs and symptoms. Some of the most noticeable symptoms include large brown spots with freckles, moles which are sensitive or bleed, small lesions bordered by red, white, blue, or blue-black coloration, and darker lesions on your hands and feet or in your orifices.
2. Basal Cell Carcinoma
Most commonly, BCC will develop on your neck or face. It is distinguishable by its pearly, waxy bumps or its flat, brown, blue or black lesions.
3. Squamous Cell Carcinoma
SCC develops on the areas of your body which have received higher levels of ultraviolet light exposure. These areas may include your face, lips and back. It is identifiable by the rough, scaly, lumpy lesions or lesions which are flat and bleed easily. SCC will spread more than basal cell carcinoma.
4 Merkel Cell Carcinoma
5. Kaposi Sarcoma
When Should Itchy Skin Raise A Red Flag
Itching per se is not dangerous. As we have mentioned there are numerous reasons for an itchy skin. But when should itchy skin be associated with a cancer symptom?
Basically, patients complain of multiple lesions that are itchy or painful as well as suspicious-looking should raise some confers for non-melanoma skin cancers. According to studies, more than one-third of skin cancer lesions are itchy with fewer than 30 percent being described as painful. Some patients report their lesions are being both painful as well as itchy.
The type of skin cancers mostly associated with itching as skin cancer symptom is basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas, whereas melanoma lesions were least likely to be associated with any kind of painfulness or itchiness. Even though melanomas are less common than basal cell carcinomas or squamous cell skin cancers, they are however far more dangerous.
Although itchy skin alone does not indicate skin cancer, there are a number of other features associated with the lesions that should be noted as being associated with any kind of skin cancer. These include:
- The emergence of new moles
- Moles that increase in size
- Irregular outlines of moles
- Change in color from brown to black
- A spot that becomes raised over time
- Moles with an irregular, rough or ulcerated surface
- Moles that tend to easily bleed
- Spots that look different from others
- Any ulcer or broken down part of the skin which does not heal within 4 weeks
Don’t Miss: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
What You Can Do
If youve already had a BCC, you have an increased chance of developing another, especially in the same sun-damaged area or nearby.
A BCC can recur even when it has been carefully removed the first time, because some cancer cells may remain undetectable after surgery and others can form roots that extend beyond whats visible. BCCs on the nose, ears and lips are more likely to recur, usually within the first two years after surgery.
Heres what you can do to detect a recurrence and safeguard yourself against further skin damage that can lead to cancer:
Reviewed by:
Why Might A Mole Be Itchy But Not Painful
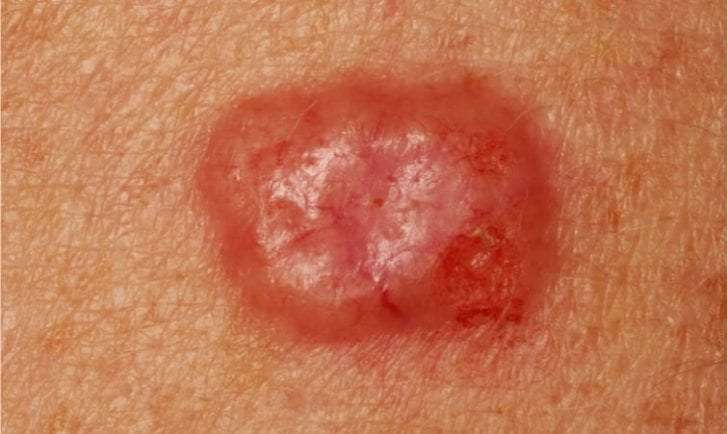
There are many different reasons why a mole could be itchy but not painful, and cancer is possible but not the most probable cause. Itching is caused when your skin’s nerves are irritated. This irritation could be caused by chemicals that are applied to your skin, dry skin, peeling skin caused by a sunburn, and other reasons. However, an itchy mole could also be from changes within the mole itself, and changing moles need your attention.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma Stage 4 Treatments
Study Design And Itch Assessment
After inclusion, detailed information on demographics, clinical history, and physical findings was recorded. All BCCs were divided into the following clinical types: nodular, superficial, morphoeic, and ulcerated .
The main clinical parameter, the presence of itching, was documented, including the affected anatomical locations. A numerical rating scale was utilized to assess maximal values of itch intensity both in the last 3 days and during the course of the tumor. NRS cut-off points were used as follows: 1< 3 points represent mild itch 36 points, moderate itch 78 points, severe itch and 9 points, very severe itch . Additionally, the Four-Item Itch Questionnaire , previously used by our group in many studies on different types of itch , was employed to estimate the extent , intensity , frequency , and sleep disturbances caused by itching. In this scoring, ratings range from 3 to 19 points . Furthermore, various clinical features of itching were assessed, including its exact localization, quality, and description of cutaneous sensations associated with the itch. Moreover, certain factors influencing itch intensity were also examined. The clinical characteristics of itch will be presented in two waysquantitatively, by assessing the intensity of itch in the NRS and 4IIQ scales, as well as descriptively.
What Types Of Skin Cancer Can Cause Itching
When itching is traced to skin cancer, the cancer is usually a non-melanoma type, such as squamous cell carcinoma or, less often, basal cell carcinoma. In general, pain and tenderness are more commonly associated with skin cancer than itchy skin, but cancer can potentially irritate the fine nerve endings in the skin and cause an itching sensation.
An oncologist in the Cutaneous Oncology Program at Moffitt Cancer Center can help you determine if your itchy skin lesion or mole is cancerous. You can request an appointment by calling 1-888-663-3488 or completing our new patient registration form online. Our multispecialty team provides a full range of screening, diagnostic, treatment and supportive care services in one location without the need for referrals.
Recommended Reading: Etiology Of Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome
This rare inherited condition, which is also known as Gorlin syndrome, increases your risk of developing basal cell cancer, as well as other types of tumors. The disease can cause clusters of basal cell carcinoma, especially on areas like your face, chest, and back. You can learn more about basal cell nevus syndrome here.
Can Skin Cancers Cause Itching
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most commonly diagnosed types of skin cancer and are treatable. BCC and SCC can cause itching in about 40% of people. Itching in these cases is typically mild and goes away once the cancer is removed. Melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, rarely causes itching.
If you notice a new mole or changes in an existing mole and want a skin cancer screening, visit our experienced dermatologists at the Skin Center of South Miami. Were experts regarding skin exams and early cancer detection. We deliver personalized dermatology care for every person in every case. Call us at 305-740-6181 orfill out the form on this page to schedule a consultation today.
You May Like: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
How To Examine Your Skin For Signs Of Skin Cancer
- First, you must make sure that you check your entire body and not only the sun-exposed regions for signs of skin cancer. This includes the soles of the feet, in-between the fingers and toes, and also under the nails.
- Ensure that you examine your skin under good lighting
- Check all your skin surfaces, and you may also get assistance from your partner, family member or friend to examine your skin for any abnormal spots or bumps.
Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Squamous cell skin cancers can vary in how they look. They usually occur on areas of skin exposed to the sun like the scalp or ear.
Thanks to Dr Charlotte Proby for her permission and the photography.
You should see your doctor if you have:
- a spot or sore that doesn’t heal within 4 weeks
- a spot or sore that hurts, is itchy, crusty, scabs over, or bleeds for more than 4 weeks
- areas where the skin has broken down and doesn’t heal within 4 weeks, and you can’t think of a reason for this change
Your doctor can decide whether you need any tests.
-
Cancer and its management J Tobias and D HochhauserBlackwell, 2015
-
Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology VT De Vita, TS Lawrence and SA RosenbergWolters Kluwer, 2018
Don’t Miss: Braf Melanoma Treatment
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second-most common type of skin cancer, after basal cell carcinoma. Squamous cells are flat cells near the surface of the skin.
Squamous cell carcinomas most often appear in areas of the body frequently exposed to sunlight, including the lips, face and hands. They can take a variety of forms. For example, a SCC can be:
- A brown spot
- A horn-shaped growth
Some SCCs may itch, bleed or crust over.
SCCs are typically easy to treat. Left untreated, however, they can grow into deeper layers of skin and even metastasize to other parts of the body. While much less deadly than melanoma, SCC kills more than 15,000 Americans each year.
Types Of Skin Malignancies:
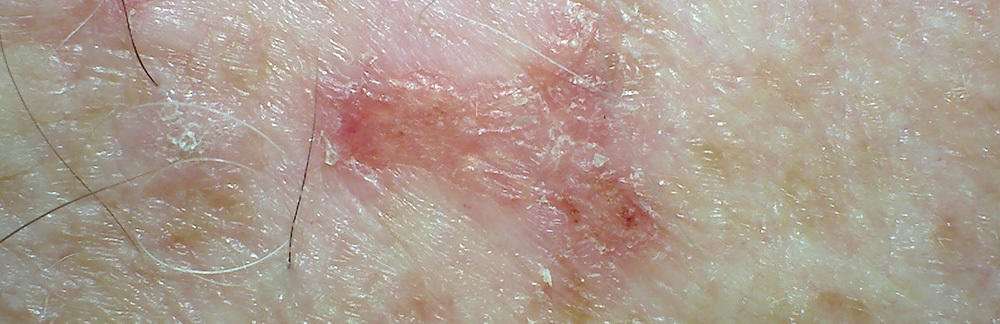
- Melanoma the least common form of skin cancer, but responsible for more deaths per year than squamous cell and basal cell skin cancers combined. Melanoma is also more likely to spread and may be harder to control.
- Nonmelanoma malignancies:
- Squamous cell cancer the second-most common skin cancer. It’s more aggressive and may require extensive surgery, depending on location and nerve involvement.
- Basal cell cancer the most common form of skin cancer. It is rarely fatal but can be locally aggressive.
These skin malignancies are typically caused by ultraviolet radiation from exposure to the sun and tanning beds.
Recommended Reading: Cure For Melanoma Stage 4
How To Spot A Bcc: Five Warning Signs
Check for BCCs where your skin is most exposed to the sun, especially the face, ears, neck, scalp, chest, shoulders and back, but remember that they can occur anywhere on the body. Frequently, two or more of these warning signs are visible in a BCC tumor.
Please note: Since not all BCCs have the same appearance, these images serve as a general reference to what basal cell carcinoma looks like.
An open sore that does not heal
A reddish patch or irritated area
A small pink growth with a slightly raised, rolled edge and a crusted indentation in the center
A shiny bump or nodule
A scar-like area that is flat white, yellow or waxy in color
How Common Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the commonest type of cancer in the United States. The skin is the largest organ in the body with a surface area of around 2 sq ft in an average adult. It acts as a protective barrier against several types of harmful agents, including heat, injuries, light, and infections. Because of the crucial protective functions that the skin performs, it is vulnerable to various conditions, such as allergies, infections, burns, and even cancer.
Depending on the cell from which it originates, skin cancer can be of several types. The most common types of skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. These two types of skin cancers are curable unlike the third most common skin cancer called melanoma. Melanoma is the most dangerous skin cancer, causing many deaths. Even curable skin cancers can cause significant disfigurement to the affected person. Other types of skin cancers include lymphoma of the skin, Kaposi sarcoma, and Merkel cell skin cancer. Knowing the type of skin cancer is crucial for your doctor to decide your treatment.
Also Check: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
Itching Due To Cancer Treatments
There are many cancer treatments that can lead to itching. The most common include some targeted therapies and some immunotherapy drugs, especially interferon and interleukin-2. Many medications can also cause allergic reactions or inflammation of the liver, which in turn, can lead to itching.
Radiation therapy commonly causes itching, especially later on in treatment when the skin begins to heal.
Finding Signs Of Cancer
There is compelling evidence that having a family, partner, or friend help you examine your skin for signs of skin cancer is more accurate than doing it alone. Researchers at Northwestern University found that the benefits of a partner who has been trained to check for changes outweighed the embarrassment of the person being checked. Participants in the study who received skin examination training caught far more irregularities than those in a control group.
As the study of 395 subjects progressed over a period of several months, trust between the partners became stronger, and with trust there was no issue with embarrassment. The results of the study were published in JAMA Dermatology, December 14, 2016
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomasigns And Symptoms
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on the skin, especially a new growth or a sore that doesn’t heal. The cancer may start as a small, smooth, shiny, pale or waxy lump. It also may appear as a firm red lump. Sometimes, the lump bleeds or develops a crust.
Both basal and squamous cell cancers are found mainly on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun the head, face, neck, hands and arms. But skin cancer can occur anywhere.
An early warning sign of skin cancer is the development of an actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin lesion caused by chronic sun exposure. These lesions are typically pink or red in color and rough or scaly to the touch. They occur on sun-exposed areas of the skin such as the face, scalp, ears, backs of hands or forearms.
Actinic keratoses may start as small, red, flat spots but grow larger and become scaly or thick, if untreated. Sometimes they’re easier to feel than to see. There may be multiple lesions next to each other.
Early treatment of actinic keratoses may prevent them from developing into cancer. These precancerous lesions affect more than 10 million Americans. People with one actinic keratosis usually develop more. Up to 1 percent of these lesions can develop into a squamous cell cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most commonly diagnosed skin cancer. In recent years, there has been an upturn in the diagnoses among young women and the rise is blamed on sunbathing and tanning salons.
- Raised, dull-red skin lesion
Taking Care Of Yourself
After you’ve been treated for basal cell carcinoma, you’ll need to take some steps to lower your chance of getting cancer again.
Check your skin. Keep an eye out for new growths. Some signs of cancer include areas of skin that are growing, changing, or bleeding. Check your skin regularly with a hand-held mirror and a full-length mirror so that you can get a good view of all parts of your body.
Avoid too much sun. Stay out of sunlight between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m., when the sun’s UVB burning rays are strongest.
Use sunscreen. The suns UVA rays are present all day long — thats why you need daily sunscreen. Make sure you apply sunscreen with at least a 6% zinc oxide and a sun protection factor of 30 to all parts of the skin that aren’t covered up with clothes every day. You also need to reapply it every 60 to 80 minutes when outside.
Dress right. Wear a broad-brimmed hat and cover up as much as possible, such as long-sleeved shirts and long pants.
Continued
Also Check: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
When Is Itching A Sign Of Skin Cancer
Itchy skin could be a sign of skin cancer if it is accompanied by:
- A new skin growth or lesion
- A change in a mole, such as a spread of pigment beyond the border
- A sore that continually crusts over but doesnt heal
- A rough or scaly skin patch
- A pink, pearly bump that bleeds easily
Because it can be difficult to distinguish between a cancerous and noncancerous skin condition, its important to promptly discuss any new, changing or unusual rashes or moles with a physician.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Signs And Symptoms
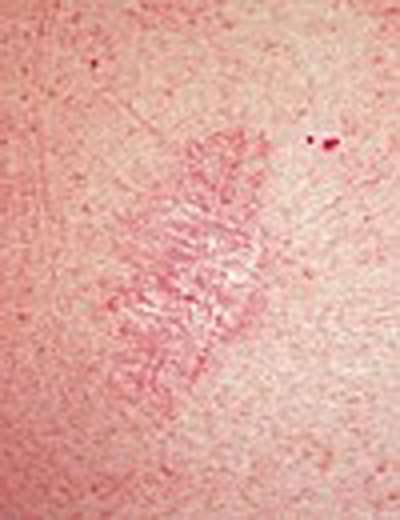
This type of cancer is usually found on sun-exposed areas of the skin like the scalp, forehead, face, nose, neck and back.
Basal cell carcinomas may bleed after a minor injury but then scab and heal. This can happen over and over for months or years with no visible growth, making it easy to mistake them for wounds or sores. They rarely cause pain in their earliest stages.
Appearance
In addition to the bleeding and healing, these are other possible signs of a basal cell cancer:
- A persistent open sore that does not heal and bleeds, crusts or oozes.
- A reddish patch or irritated area that may crust or itch.
- A shiny bump or nodule that is pearly or translucent and often pink, red or white. It can also be tan, black or brown, especially in dark-haired people, and easy to confuse with a mole.
- A pink growth with a slightly elevated, rolled border and a crusted indentation in the center. Tiny blood vessels may appear on the surface as the growth enlarges.
- A scar-like lesion in an area that you have not injured. It may be white, yellow or waxy, often with poorly defined borders. The skin seems shiny and tight sometimes this can be a sign of an aggressive tumor.
Don’t Miss: What Is Melanoma In The Brain