Stage Iia & Iib Treatment Options
Stage II is divided into subcategories known as IIA and IIB.
In general, stage IIA describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- no tumor can be found in the breast, but cancer is found in 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes or in the lymph nodes near the breast bone or
- the tumor measures 2 centimeters or smaller and has spread to the axillary lymph nodes or
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but not larger than 5 cm and has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes
Still, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- has not spread to the lymph nodes or parts of the body away from the breast
it will likely be classified as stage IB.
Similarly, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- has not spread to the lymph nodes
- has an Oncotype DX Recurrence Score of 9
it will likely be classified as stage IA.
In general, stage IIB describes invasive breast cancer in which:
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but no larger than 5 cm small groups of breast cancer cells larger than 0.2 mm but not larger than 2 mm are found in the lymph nodes or
- the tumor is larger than 2 cm but no larger than 5 cm cancer has spread to 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes or to lymph nodes near the breastbone or
- the tumor is larger than 5 cm but has not spread to the axillary lymph nodes
Still, if the cancer tumor measures between 2 and 5 cm and:
- cancer is found in 1 to 3 axillary lymph nodes
What Is Stage Iii Breast Cancer
In stage III breast cancer, the cancer has spread further into the breast or the tumor is a larger size than earlier stages. It is divided into three subcategories.
Stage IIIA is based on one of the following:
- With or without a tumor in the breast, cancer is found in four to nine nearby lymph nodes.
- A breast tumor is larger than 50 millimeters, and the cancer has spread to between one and three nearby lymph nodes.
In stage IIIB, a tumor has spread to the chest wall behind the breast. In addition, these factors contribute to assigning this stage:
- Cancer may also have spread to the skin, causing swelling or inflammation.
- It may have broken through the skin, causing an ulcerated area or wound.
- It may have spread to as many as nine underarm lymph nodes or to nodes near the breastbone.
In stage IIIC, there may be a tumor of any size in the breast, or no tumor present at all. But either way, the cancer has spread to one of the following places:
- ten or more underarm lymph nodes
- lymph nodes near the collarbone
- some underarm lymph nodes and lymph nodes near the breastbone
- the skin
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:
Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis and treatment options depend on the following:
- The stage of the cancer .
- The type of breast cancer.
- Estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor levels in the tumor tissue.
- Human epidermal growth factor type 2 receptor levels in the tumor tissue.
- Whether the tumor tissue is triple negative .
- How fast the tumor is growing.
- How likely the tumor is to recur .
- A womans age, general health, and menopausal status .
- Whether the cancer has just been diagnosed or has recurred .
Breast Cancer Survival Rates For All Types Of Breast Cancers
Breast cancer survival rates and prognosis are determined by so many different factors that it is always difficult to make generalizations.
NOTE: this page has been recently updated with the most up-to-date statistics. Prognosis has improved so much because breast cancer treatments have become more effective since this page was first created. Remember that survival is better than listed here. Most importantly, ask your oncologist and specialist team, who keep current with the latest statistics and best treatments.
Read Also: Does Insurance Cover Skin Cancer Screening
The Tnm System The Grading System And Biomarker Status Are Combined To Find Out The Breast Cancer Stage
Here are 3 examples that combine the TNM system, the grading system, and the biomarker status to find out the Pathological Prognostic breast cancer stage for a woman whose first treatment was surgery:
If the tumor size is 30 millimeters , has not spread to nearby lymph nodes , has not spread to distant parts of the body , and is:
- Grade 1
- PR-
The cancer is stage IV .
Breast Cancer Survival Rates According To The Stage Of The Cancer
Breast cancer stage of course refers to the spread and size of cancer at diagnosis. Stage zero means the breast cancer is still in situ or contained. Whereas, stage IV means that the cancer has metastasised to other body regions. The stage of cancer at diagnosis affects prognosis.
The statistics below are taken from the from the SEER database of the National Cancer Institute between the years 1975 to 2010.
The 5 year survival rate means that within 5 years around 93 people out of 100, diagnosed with Stage II breast cancer, will still be alive.
Also Check: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
How Treatment Can Impact Survival Of Early Stage Breast Cancer
In most cases, the earlier breast cancer is first diagnosed and treated, the better the chance of survival. Cancer cells often become more difficult to treat and may develop drug resistance once they spread. The aim of treatment for Stage 1 and 2 breast cancer is to remove the breast cancer, and any other cancer cells that remain in the breast, armpit or other parts of the body but cannot be detected. Having treatment at this stage can also reduce the risk of the cancer coming back.
Read more:
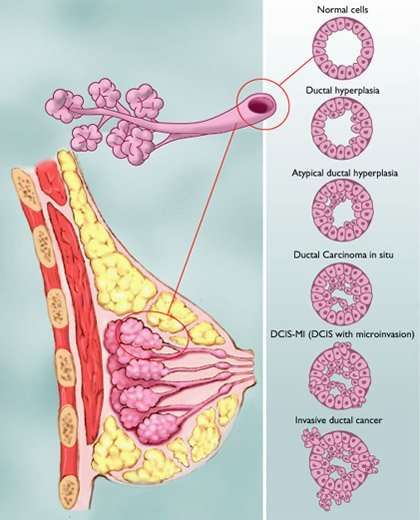
Invasive Carcinoma Of No Special Type
| Invasive carcinoma of no special type | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Invasive ductal carcinoma |
| Histopathologic types of breast cancer, with relative incidences and prognoses, with “invasive ductal carcinoma” at bottom left | |
| Oncology, Dermatology, Breast surgery |
Invasive carcinoma of no special type also known as invasive ductal carcinoma or ductal NOS and previously known as invasive ductal carcinoma, not otherwise specified is a group of breast cancers that do not have the “specific differentiating features”. Those that have these features belong to other types.
In this group are: pleomorphic carcinoma, carcinoma with osteoclast-like stromal giant cells, carcinoma with choriocarcinomatous features, and carcinoma with melanotic features. It is a diagnosis of exclusion, which means that for the diagnosis to be made all the other specific types must be ruled out.
Read Also: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Stage 1 breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. The breast cancer has spread from its original location to the surrounding tissue but it is still contained in a relatively small area.
If you are diagnosed with Stage 1 breast cancer, this means that the tumour is less than 2 centimetres in size. No cancer cells have been found in the lymph nodes or other parts of the body at this stage.
Symptoms Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Make an appointment to see your doctor if you notice anything different or unusual about the look and feel of your breasts.
The symptoms of breast cancer include:
- a new lump or thickening in your breast or armpit
- a change in size, shape or feel of your breast
- skin changes in the breast such as puckering, dimpling, a rash or redness of the skin
- fluid leaking from the nipple in a woman who isnt pregnant or breast feeding
- changes in the position of nipple
You May Like: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Talk To Your Doctor To Find Out What Your Breast Cancer Stage Is And How It Is Used To Plan The Best Treatment For You
After surgery, your doctor will receive a pathology report that describes the size and location of the primary tumor, the spread of cancer to nearby lymph nodes, tumor grade, and whether certain biomarkers are present. The pathology report and other test results are used to determine your breast cancer stage.
You are likely to have many questions. Ask your doctor to explain how staging is used to decide the best options to treat your cancer and whether there are clinical trials that might be right for you.
The treatment of breast cancer depends partly on the stage of the disease.
For treatment options for stage IIIB, inoperable stage IIIC, and inflammatory breast cancer, see Treatment of Locally Advanced Inflammatory Breast Cancer.
For treatment options for cancer that has recurred near the area where it first formed , see Treatment of Locoregional Recurrent Breast Cancer.
For treatment options for stage IV breast cancer or breast cancer that has recurred in distant parts of the body, see Treatment of Metastatic Breast Cancer.
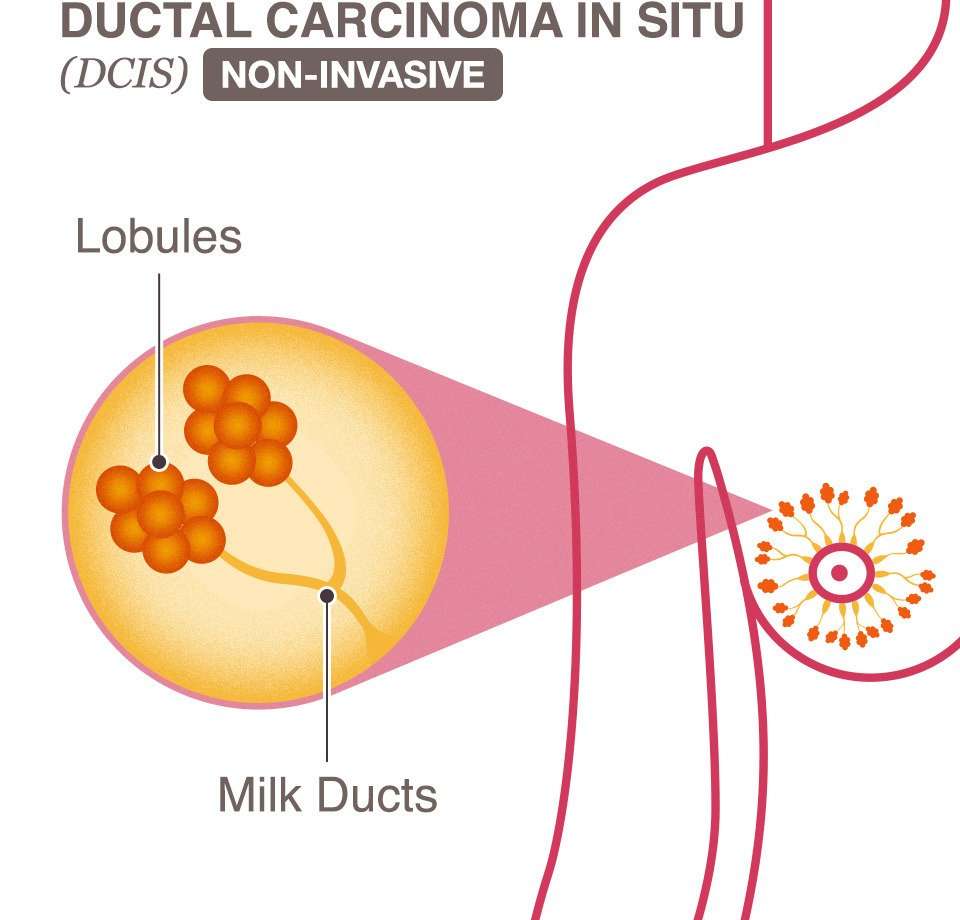
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Also Check: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
Causes Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Unfortunately, doctors have yet to figure out the exact cause of invasive ductal carcinoma. When you get this type of cancer, it means something damaged your cells’ DNA and caused it to change. The result is that the cells grow abnormally and uncontrollably in your breast tissue.
Doctors are still looking for genetic and environmental factors that damage the DNA. They have determined that caffeine, deodorant, microwaves and cell phone use do not lead to this type of cancer.
Types Of Stage 1 And 2 Breast Cancer
The most common types of invasive breast cancers are named after the area of the breast where they begin. Types of early breast cancers include:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma IDC means that the cancer originated in the milk ducts of the breast, and has spread into the surrounding breast tissue. IDC is the most common type of breast cancer, accounting for 80% of all breast cancers.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma ILC means that the cancer originated in the milk-producing lobules of the breast, and has spread into the surrounding breast tissue. ILC is the second most common type of breast cancer, and accounts for 10% of breast cancers.
- There are also other less common forms of invasive breast cancer, such as inflammatory breast cancer and Pagets disease of the nipple. For more information on the various types of invasive breast cancer, including the less common forms, please visit Types of Breast Cancer page.
Don’t Miss: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
The general invasive ductal carcinoma survival rate is a helpful benchmark that provides physicians with a uniform way to describe and discuss patient outcomes. Of course, a survival rate is merely an average of the experiences of a large group of people that occurred several years ago. No patient can ever be considered average, and many patients experience much better outcomes than the general survival rate would suggest. As new and better treatments are being developed and put into use, the survival rate is continually improving, and individuals who are diagnosed with breast cancer today are living longer and higher-quality lives than those who were diagnosed even only a few years ago. As such, the overall survival rate is not a reliable indicator of any specific patients prognosis.
Many individual factors can influence the invasive ductal carcinoma survival rate, including:
- Whether the cancer is newly diagnosed or a recurrence
- The stage of the cancer at the time of diagnosis, and whether it is confined to a breast or has spread to lymph nodes and other tissues and organs
- The hormone-receptor status of the cancer
- The HER2 status of the cancer
- The growth rate of the cancer cells
- The cancers response to treatment
- A patients age, overall health and menopausal status
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Cell Staging
Cancer has stages 1 to 4. In obtaining the right stages of the cancer cells, there are several factors to consider. These are:
- If the cancer cells has spread deep down the tissues
- If the cancer cells invades any parts of the body and adjacent lymph nodes
- The size and shape of the carcinoma
The grading of IDC:
- Grade 1- well differentiated or low grade
- Grade 2- moderately differentiated or intermediate stage
- Grade 3- poorly differentiated or high grade
Recommended Reading: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
More Information About The Tnm Staging System
The T category describes the original tumor:
- TX means the tumor can’t be assessed.
- T0 means there isn’t any evidence of the primary tumor.
- Tis means the cancer is “in situ” .
- T1, T2, T3, T4: These numbers are based on the size of the tumor and the extent to which it has grown into neighboring breast tissue. The higher the T number, the larger the tumor and/or the more it may have grown into the breast tissue.
The N category describes whether or not the cancer has reached nearby lymph nodes:
- NX means the nearby lymph nodes can’t be assessed, for example, if they were previously removed.
- N0 means nearby lymph nodes do not contain cancer.
- N1, N2, N3: These numbers are based on the number of lymph nodes involved and how much cancer is found in them. The higher the N number, the greater the extent of the lymph node involvement.
The M category tells whether or not there is evidence that the cancer has traveled to other parts of the body:
- MX means metastasis can’t be assessed.
- M0 means there is no distant metastasis.
- M1 means that distant metastasis is present.
How To Improve Your Breast Cancer Survival Rates
While some things that influence breast cancer survival rates cannot be changed , there are several ways a patient can potentially improve his or her outcomes. For instance:
- Studies suggest that outcomes tend to be better for patients who undergo radiation therapy after surgery. Even though surgery by itself can be effective, radiation therapy can destroy residual cells that were not visible or accessible during an operation.
- Hormone therapies can help prevent recurrences in patients whose tumors are found to be hormone-receptive. Some of these therapies are only available through clinical trials patients can discuss the potential risks and benefits of participation with their treatment teams.
- The outcomes for stage 0 breast cancer are generally more favorable than the outcomes for more advanced stages of breast cancer. Although ductal carcinoma in situ does not always progress into a more invasive malignancy, treating it early before it progresses to a more advanced stage of cancer can improve a patients outcome.
Not only are there several ways to improve survival outcomes, but also quality of life outcomes as well. For instance, reconstructive surgery can be performed to improve aesthetic results after a lumpectomy or mastectomy. Women who hope to breastfeed can discuss possible breast-tissue-sparing techniques with a surgeon. Additionally, supportive care services are available to help patients better manage the side effects of breast cancer treatment.
Recommended Reading: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Metastasis
Less Common Invasive Breast Cancers
- Inflammatory breast cancer is an aggressive form of locally advanced breast cancer. Its called inflammatory breast cancer because the main warning signs are swelling and redness in the breast.
With inflammatory breast cancer, warning signs tend to arise within weeks or months. With other breast cancers, warning signs may not occur for years.
- Paget disease of the breast is a cancer in the skin of the nipple or in the skin closely surrounding the nipple. Its usually found with an underlying breast cancer.
- Metaplastic breast cancers tend to be larger and have a higher tumor grade than more common breast cancers. Metaplastic breast cancers can be hard to diagnose because the tumor cells can look very different from the tumor cells of more common breast cancers.
What Is Stage 4 Breast Cancer
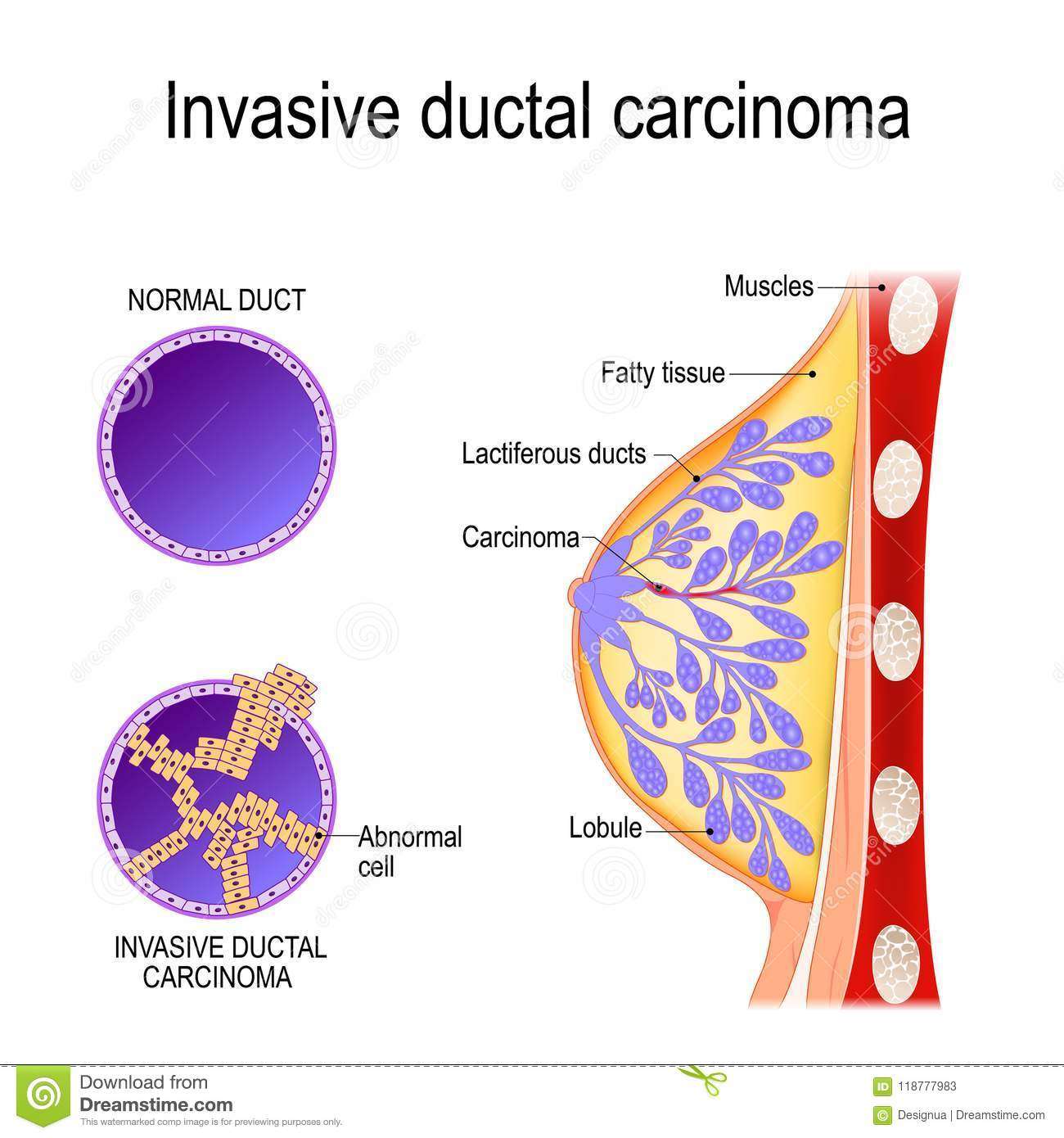
Also known as metastatic breast cancer, the cancer in this stage has spread beyond the breast, underarm and internal mammary lymph nodes to other parts of the body near to or distant from the breast. The cancer has spread elsewhere in the body. The affected areas may include the bones, brain, lungs or liver and more than one part of the body may be involved.
At stage 4, TNM designations help describe the extent of the disease. Higher numbers indicate more extensive disease. Most commonly, stage 4 breast cancer is described as:,
- T: T1, T2, T3 or T4 depends on the size and/or extent of the primary tumor.
- N1: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes.
- M1: The disease has spread to other sites in the body.
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn