What Causes Subungual Melanoma
Most cases of skin melanoma are caused by sun exposure. This is why dermatologists warn against tanning and unprotected sun exposure. However, subungual melanoma isnt usually caused by the sun. Most cases seem to be caused by injury or trauma. It also tends to affect middle-aged and older adults with darker skin.
Additionally, subungual melanoma is more prevalent in the nails of your thumbs and big toes.
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
A sentinel lymph node biopsy is a procedure to test for the spread of cancer.
It may be offered to people with stage 1B to 2C melanoma. It’s done at the same time as surgical excision.
You’ll decide with your doctor whether to have a sentinel lymph node biopsy.
If you decide to have the procedure and the results show no spread to nearby lymph nodes, it’s unlikely you’ll have further problems with this melanoma.
If the results confirm melanoma has spread to nearby nodes, your specialist will discuss with you whether further surgery is required.
Additional surgery involves removing the remaining nodes, which is known as a lymph node dissection or completion lymphadenectomy.
Melanoma Recurrence Beyond The Original Site
Melanoma recurrences can also result when there is melanoma growth beyond the area originally removed by surgery, sometimes in nearby lymph nodes or other areas of tissue. Melanomas also can be spread by the bloodstream, resulting in new areas of re-growth. If a melanoma is going to recur, it will usually recur within the first two to five years after the original diagnosis and treatment. Patients having a local recurrence are strongly at risk of recurrence elsewhere in the body.
Factors that increase the risk of a recurrence are:
- Thicker original melanomas, especially if located on the head, neck, hands and feet.
- Presence of ulceration in the original melanoma
- Lymph nodes positive for melanoma
Because of the high prevalence of metastasis, patients with local or regional recurrences of melanoma should have a physical examination and and imaging scans of the chest, abdomen and pelvis. The scan will take detailed, cross-sectional images of tissue. The scanning can be with a high-quality CT scan or with a combined PET-CT scan. Johns Hopkins nuclear medicine specialists have studied the application of combined positron emission tomography scanning with CT scanning to detect recurrent melanoma.
Surgery remains the first-line treatment for local and regional recurrences. Lymph node metastasis detected by physical examination or scanning may be treated by complete surgical removal of regional lymph nodes .
Other treatments occasionally appropriate include:
Request an Appointment
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
How Do You Treat Skin Cancer On The Nose
The nose is a relatively common spot for skin cancer to develop. Skin cancer often starts on the face because it’s usually the body part that’s exposed to the sun. The two most common types of skin cancer that develop on the nose are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma . While both types of skin cancer should be addressed right away, BCC is usually slow-growing and SCC grows more quickly. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer ,with about 80% of cases occurring on the face and 25 to 30% on the nose.
The third type of skin cancer, melanoma, is rare and much more serious. It almost always requires excisional surgery to remove it. Fortunately, most forms of skin cancer are very treatable, especially when caught early. Treatment may include surgery, radiation, topical treatments, and more.
When Melanoma Can’t Be Cured
If your cancer has spread and it is not possible to cure it by surgery, your doctor may still recommend treatment. In this case, treatment may help to relieve symptoms, might make you feel better and may allow you to live longer.Whether or not you choose to have anti-cancer treatment, symptoms can still be controlled. For example, if you have pain, there are effective treatments for this. General practitioners, specialists and palliative care teams in hospitals all play important roles in helping people with cancer.
Don’t Miss: How Quickly Does Renal Cell Carcinoma Grow
Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 /pd
The PD-1 receptor binds to PD-L1 and PD-L2, acts as a T-cell co-inhibitory molecule, and suppresses T-cell activation. Further than being expressed on the antigen-presenting cells, ligands are also expressed in many human tumors and in cells within the TME, in response to inflammatory stimuli. Yet, the utility of PD-L1 immunostaining as a predictive biomarker for anti-PD-1 treatment remains unclear.
Nivolumab is a high-affinity anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody that inhibits the binding between the PD-1 receptor and its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. Nivolumab was approved by the FDA for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma. The blockade of the interaction between PD-1 and its ligands mediates immune responses and induces antitumor activity that reduces tumor progression. Nivolumab, with a PFS of 6.9 months, seems to be more efficient than monotherapies with ipilimumab, which display a median PFS of 2.9 months, or chemotherapy, with a median PFS of 2.2 months. The combination of nivolumab and ipilimumab achieved a median PFS of 11.5 months, superior than monotherapies, especially in patients with PD-L1 negative tumors.,
Other anti-PD-L1 molecules are used in Phase I/II trials, such as durvalumab in combination with other immunotherapies and targeted therapies , CK-301 , avelumab in combination with other immunotherapies , and atezolizumab in combination with other immunotherapies and targeted therapies .
Recurrence In Nearby Lymph Nodes
If nearby lymph nodes werenât all removed during the initial treatment, the melanoma might come back in these lymph nodes. Lymph node recurrence is treated by lymph node dissection if it can be done, sometimes followed by adjuvant treatments such as radiation therapy and/or immunotherapy or targeted therapy . If surgery is not an option, radiation therapy or systemic treatment can be used.
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Surgical Management Of Melanoma
The first-line or standard treatment for most melanomas is surgical excision. Thin tumors generally can be removed during an outpatient surgery, with a centimeter of normal appearing skin surrounding the melanoma. Surgery cures the majority of people with early stages of melanoma when they have early, thin tumors that have not spread from the original site.
Surgery for melanomas that are not very thin may require a wider excision of two centimeters of skin around the melanoma. This is usually performed as an outpatient procedure. Simple surgical procedures can still allow for a primary closure of most wounds, but occasionally, a skin graft or more complex reconstruction is required to close the wound. In cases where the melanoma is known to have spread to the lymph nodes, the lymph nodes may also need to be surgically removed.
During surgery, your doctor will remove the tumor along with an area of surrounding skin in order to lower the risk of a recurrence. How much skin is removed along with the tumor depends on the tumors thickness, which helps determine the stage of melanoma. Johns Hopkins surgical oncology faculty have led studies and chair international committees that have determined the following criteria for the margin of tissue removed during surgery and the classification of melanomas, depending on their size, into specific stages.
Reconstruction Of Your Wound Site
After the melanoma is removed, you may need to have reconstruction on your wound site. Your surgeon will speak with you about what type of reconstruction is right for you, before your surgery. You may have both a head and neck surgeon and a plastic surgeon as part of your surgical team.
Types of reconstruction
Recommended Reading: How Long For Melanoma To Metastasize
What Does Scalp Melanoma Look Like
Melanoma is one of the most serious forms of cancer, and because its appearance can closely mimic natural moles, freckles, and age spots, it can be easy to overlook. Its important to know what to look for and perform regular skin cancer screenings to ensure you receive treatment for this condition in the earliest stages. According to Dr. Gregory Walker of U.S. Dermatology Partners in Waco, Texas, Melanoma can be easily overlooked in obvious places on the body, but many people dont know that the scalp, fingernails and toenails, and other harder to see areas often hide this condition until it has progressed to more advanced stages. Patients who know what to look for and regularly screen their skin for cancers, are much more likely to receive a diagnosis in early, more treatable stages. Keep reading to hear more from Dr. Walker about what scalp melanoma looks like and how to check for this condition and prevent serious health concerns.
What Are The Types Of Melanoma
Depending on the site of occurrence, there are 3 types of melanoma:
Ocular melanoma Melanoma that occurs in the melanocytes of the eyes is called ocular melanoma. It can be further subdivided into conjunctival melanoma and uveal melanoma.
Cutaneous melanoma Melanoma that occurs in the skin is subdivided into 4 types:
- Nodular melanoma This is an aggressive melanoma and accounts for ~ 15% to 30% of the melanoma cases. It is commonly observed in middle-aged people.
- Superficial spreading melanoma This type of melanoma accounts for 70% of the melanoma cases and develops from an existing mole.
- Acral lentiginous melanoma Unlike most other melanomas, this type of melanoma is more common in dark-skinned individuals. This type of melanoma is found below the nails, and on the palms and the soles of feet.
- Lentigo maligna melanoma Such tumors are large and flat and observed in light-skinned women, people who have spent a lot of time outdoors, and in elderly people. These tumors occur on the face and do not spread much. They account for only approximately 10% of the cutaneous cases.
Mucosal melanoma This type of tumor is difficult to detect and is found in the mucosal areas of the neck and head, the lower digestive and urinary tracts, and the vagina in females. They account for only 1% of all the cases of melanoma and patients with this type of cancer do not have a good survival rate.
Recommended Reading: What Do Skin Cancer Sores Look Like
The Stage Of Melanoma Depends On The Thickness Of The Tumor Whether Cancer Has Spread To Lymph Nodes Or Other Parts Of The Body And Other Factors
To find out the stage of melanoma, the tumor is completely removed and nearby lymph nodes are checked for signs of cancer. The stage of the cancer is used to determine which treatment is best. Check with your doctor to find out which stage of cancer you have.
The stage of melanoma depends on the following:
- The thickness of the tumor. The thickness of the tumor is measured from the surface of the skin to the deepest part of the tumor.
- Whether there are:
- Satellite tumors: Small groups of tumor cells that have spread within 2 centimeters of the primary tumor.
- Microsatellite tumors: Small groups of tumor cells that have spread to an area right beside or below the primary tumor.
- In-transit metastases: Tumors that have spread to lymph vessels in the skin more than 2 centimeters away from the primary tumor, but not to the lymph nodes.
Metastatic Or Advanced Skin Cancer
It is uncommon, but non-melanoma skin cancer can spread to another part in the body from where it started. In these situations, doctors call it metastatic cancer. If this happens, it is a good idea to talk with doctors who have experience in treating it. Doctors can have different opinions about the best standard treatment plan. Clinical trials might also be an option. Learn more about getting a second opinion before starting treatment, so you are comfortable with your chosen treatment plan.
Surgery alone cannot always eliminate skin cancer that has metastasized. If cancer cannot be removed with surgery, it is called unresectable. To control distant spread, a persons treatment plan may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and/or targeted therapy. Palliative care will also be important to help relieve symptoms and side effects.
Squamous cell carcinoma. Metastatic or unresectable squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is rare, so treatment plans often use the same treatments that have worked in people with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck that may not have started on the skin. Chemotherapy usually includes taxanes, such as docetaxel or paclitaxel , and platinums, such as carboplatin or cisplatin . The main side effects of these medicines include fatigue, low blood cell counts, rashes, diarrhea, and changes in sensation in the tips of the fingers or toes. Learn more about the basics of chemotherapy.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Are The Symptoms Of Subungual Melanoma
When you hear the word melanoma, your first thought might be irregular-shaped moles on the skin caused by sun damage. But since subungual melanoma affects the nail matrix, the signs and symptoms dont look like a typical mole on the skin.
Symptoms of this condition include:
- a light- to dark-brown colored band on the nail thats usually vertical
- a dark band on the nail that slowly expands and covers more of the nail
- dark nail pigmentation that expands to the surrounding skin
- a nodule underneath the nail with or without a pigmentation band
- nail brittleness and cracking
- bleeding at the site of pigmentation
Its important to note that not all cases of this condition cause pigmentation changes in the nail. While this can make the melanoma more challenging to detect, a telltale sign of the condition is that it usually affects one nail at a time.
When Should I Call My Doctor
You should have a skin examination by a doctor if you have any of the following:
- A personal history of skin cancer or atypical moles .
- A family history of skin cancer.
- A history of intense sun exposure as a young person and painful or blistering sunburns.
- New or numerous large moles.
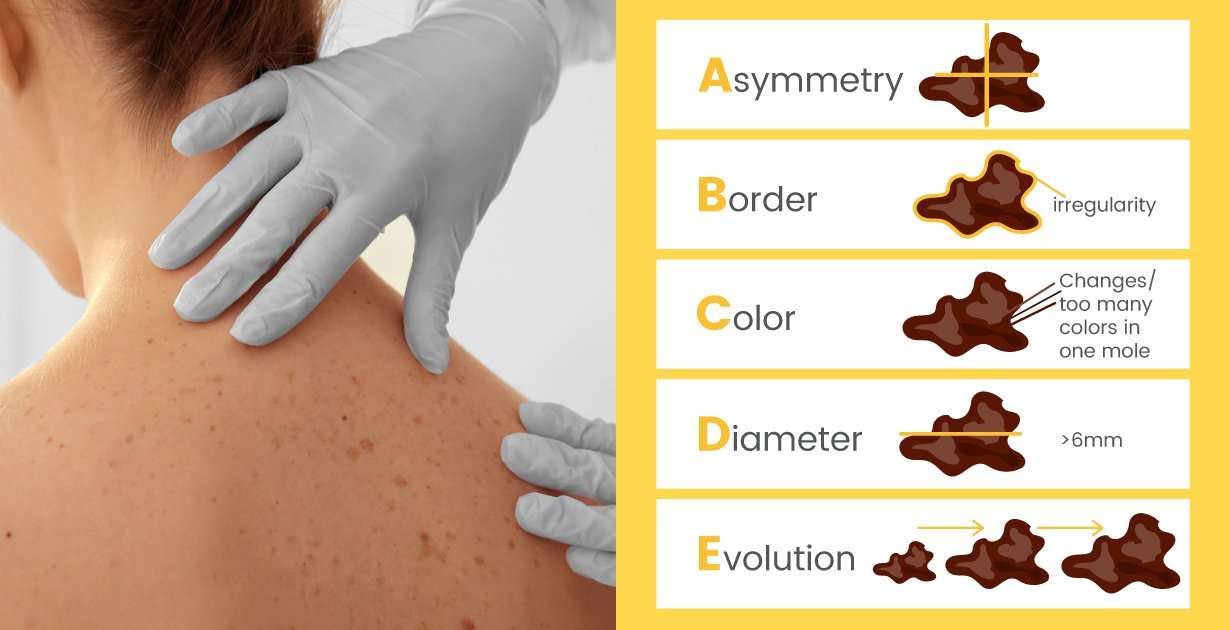
- A mole that changes in size, color or shape.
- Any mole that itches, bleeds or is tender.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Receiving a diagnosis of melanoma can be scary. Watch your skin and moles for any changes and seeing your doctor regularly for skin examinations, especially if youre fair-skinned, will give you the best chances for catching melanoma early when its most treatable.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 06/21/2021.
References
You May Like: What Is Multiple Melanoma Cancer
Thinking About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
Clinical trials are carefully controlled research studies that are done to get a closer look at promising new treatments or procedures. Clinical trials are one way to get state-of-the art cancer treatment. In some cases they may be the only way to get access to newer treatments. They are also the best way for doctors to learn better methods to treat cancer. Still, they’re not right for everyone.
If you would like to learn more about clinical trials that might be right for you, start by asking your doctor if your clinic or hospital conducts clinical trials.
What Is Malignant Melanoma
Malignant melanoma skin cancer is an aggressive, potentially fatal type of cancer that can rapidly spread to other parts of the body.
It often starts with a change in a mole or a new growth on normal skin.
Certain skin types are more at risk than others.
- The main cause is sun exposure due to ultra violet radiation from exposure to the sun, sunbeds, or a history of sunburn, especially in childhood.
- Signs and symptoms include a new growth or sore on the skin that does not heal in 3-4 weeks, a sore that continues to itch, scab or bleed or unexplained continued ulceration.
- Fair, easily burned skin has a higher risk of developing a melanoma.
Read Also: How Long Does It Take To Get Melanoma Biopsy Results
Recurrence In Other Parts Of The Body
Melanoma can also come back in distant parts of the body. Almost any organ can be affected. Most often, the melanoma will come back in the lungs, bones, liver, or brain. Treatment for these recurrences is generally the same as for stage IV melanoma . Melanomas that recur on an arm or leg may be treated with isolated limb perfusion/infusion chemotherapy.
Melanoma that comes back in the brain can be hard to treat. Single tumors can sometimes be removed by surgery. Radiation therapy to the brain may help as well. Systemic treatments might also be tried.
As with other stages of melanoma, people with recurrent melanoma may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial.
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor. Your doctor may have reasons for suggesting a treatment plan different from these general treatment options. Don’t hesitate to ask him or her questions about your treatment options.
Who Are They For
Not every patient has mutations in their melanoma that are affected by the drugs that are currently available or in trial. Part of treatment at Melanoma Institute Australia includes being tested for these mutations and pairing you with the best option for your situation.
Some of the drugs are still under investigation in clinical trial testing. That means that even though you might have the mutation that correlates to a drug, the trials inclusion criteria could still prevent you from qualifying. Take a look at the Clinical Trials section of this site to learn more about how trials work.
Recommended Reading: How Is Metastatic Melanoma Diagnosed
Recommended Reading: What Is The Deadliest Type Of Skin Cancer