Treatment By Stage Of Melanoma
Different treatments may be recommended for each stage of melanoma. General descriptions by stage are below. Your doctor will recommend a specific treatment plan for you based on the stage and other factors. Detailed descriptions of each type of treatment are provided earlier on this page. Clinical trials may also be a treatment option for each stage.
Stage 0 melanoma
Stage 0 melanoma is almost always treated with surgery alone, usually a wide excision.
Stage I melanoma
Stage I melanoma is usually treated with surgical removal of the tumor and some of the healthy tissue around it. The doctor may recommend lymph node mapping, and some lymph nodes may be removed.
Stage II melanoma
The standard treatment for stage II melanoma is surgery to remove the tumor and some of the healthy tissue around it. While this surgery is being done, lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy may also be done. In some people with stage II melanoma, treatment with interferon may be recommended after surgery to lower the chances of the cancer coming back. Treatment in a clinical trial for stage II melanoma may also be an option. Ask your doctor about what clinical trials may be available for you.
Stage III melanoma that can be removed with surgery
Advanced melanoma
-
The persons age and overall health
-
The locations and number of metastases
-
How fast the disease is spreading
-
The presence of specific genetic mutations in the tumor
-
The patients preferences
Treating brain metastases
Radiation Therapy After Melanoma Surgery
Sometimes we recommend radiation therapy in the area where surgery was performed to remove melanoma. For some people, this approach may reduce the chance that the melanoma will come back in that specific area.
One method we use is called intensity-modulated radiation therapy . It was developed by MSK experts. IMRT allows us to deliver more-precise doses of radiation to the affected area while reducing the risk that healthy tissue is injured.
In addition, MSK is currently the leading center in North America participating in an international research study to determine if radiation after surgery helps prevent melanoma in the head and neck area from coming back.
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Melanoma Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
You May Like: What Is Pre Melanoma Called
Risk Of Further Melanomas
Most people treated for early melanoma do not have further trouble with the disease. However, when there is a chance that the melanoma may have spread to other parts of your body, you will need regular check-ups. Your doctor will decide how often you will need check-ups everyone is different. They will become less frequent if you have no further problems. After treatment for melanoma it is important to limit exposure to the suns UV radiation. As biological family members usually share similar traits, your family members may also have an increased risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. They can reduce their risk by spending less time in the sun and using a combination of sun protection measures during sun protection times. It is important to monitor your skin regularly and if you notice any changes in your skin, or enlarged lymph glands near to where you had the cancer, see your specialist as soon as possible.
Who Are They For
Not every patient has mutations in their melanoma that are affected by the drugs that are currently available or in trial. Part of treatment at Melanoma Institute Australia includes being tested for these mutations and pairing you with the best option for your situation.
Some of the drugs are still under investigation in clinical trial testing. That means that even though you might have the mutation that correlates to a drug, the trials inclusion criteria could still prevent you from qualifying. Take a look at the Clinical Trials section of this site to learn more about how trials work.
Recommended Reading: How Is Metastatic Melanoma Diagnosed
Read Also: What Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Treatments For Melanoma Skin Cancer
If you have melanoma skin cancer, your healthcare team will create a treatment plan just for you. It will be based on your health and specific information about the cancer. When deciding which treatments to offer for melanoma skin cancer, your healthcare team will consider:
- the of the cancer whether it is early stage, locoregional or metastatic
- the risk that the cancer will come back
- where the cancer is located
- how treatments will affect how you look
- your personal preferences
When Should I See My Doctor
Its important to check your own skin regularly to find any new or changing spots.
See your doctor or dermatologist straight away if you notice any changes to your skin, such as:
- an ‘ugly duckling’ a spot that looks or feels different to any others
- a spot that changes size, shape, colour or texture over time
- a sore that doesnt go away after a few weeks
- a sore that itches or bleeds
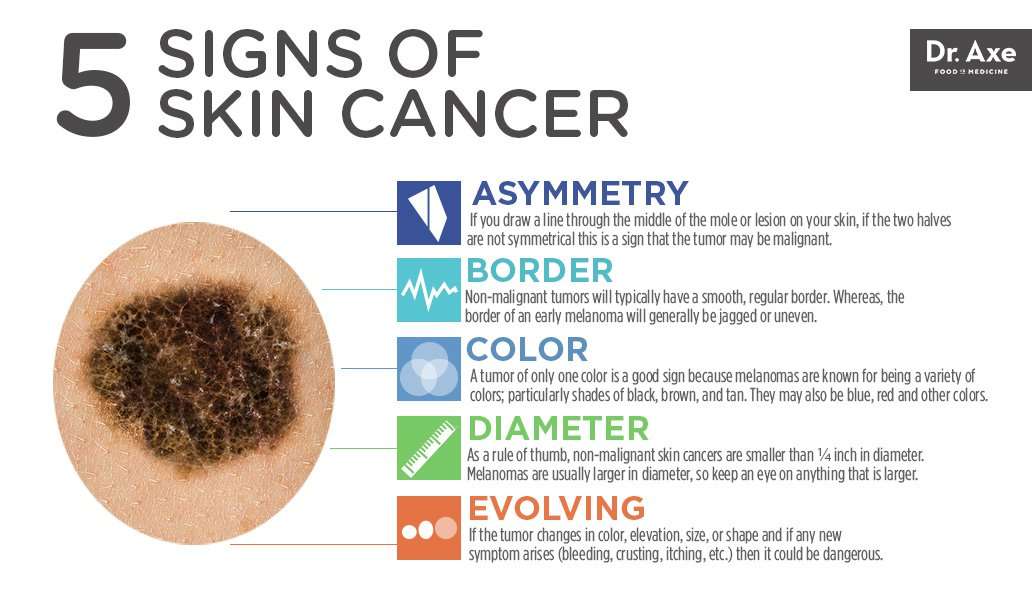
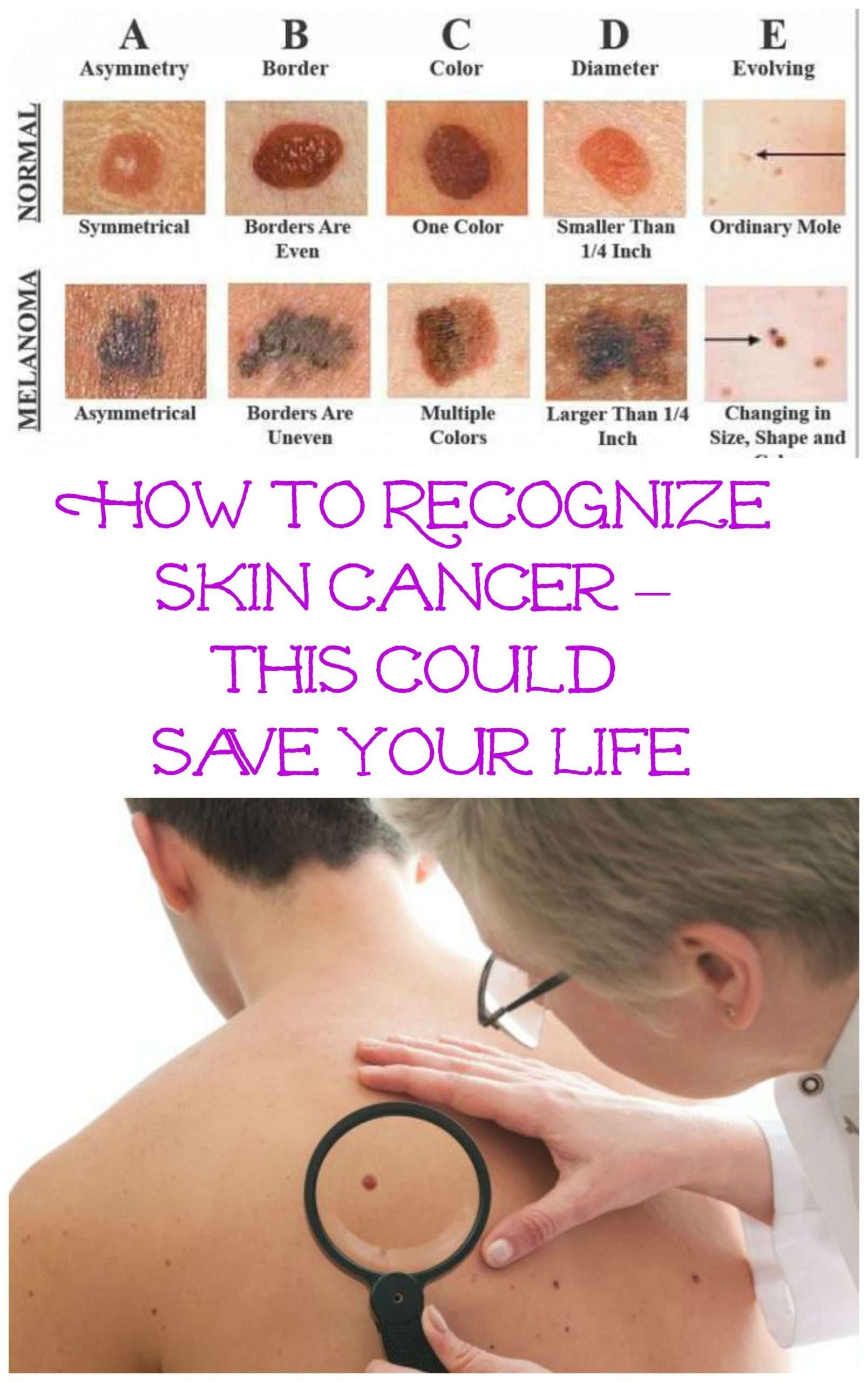
See the ‘ABCDE’ of skin cancer, above.
You May Like: How To Catch Skin Cancer Early
What You Can Do
Check yourself: No matter your risk, examine your skin head-to-toe once a month to identify potential skin cancers early. Take note of existing moles or lesions that grow or change. Learn how to check your skin here.
When in doubt, check it out. Because melanoma can be so dangerous once it advances, follow your instincts and visit your doctor if you see a spot that just doesnt seem right.
Keep in mind that while important, monthly self-exams are not enough. See your dermatologist at least once a year for a professional skin exam.
If youve had a melanoma, follow up regularly with your doctor once treatment is complete. Stick to the schedule your doctor recommends so that you will find any recurrence as early as possible.
Reviewed by:
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Whether you are thinking about treatment, getting treatment, or not being treated at all, you can still get supportive care to help with pain or other symptoms. Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life.
Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help.
The American Cancer Society also has programs and services including rides to treatment, lodging, and more to help you get through treatment. Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
After Melanoma Has Been Diagnosed Tests May Be Done To Find Out If Cancer Cells Have Spread Within The Skin Or To Other Parts Of The Body
The process used to find out whether cancer has spread within the skin or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. It is important to know the stage in order to plan treatment.
For melanoma that is not likely to spread to other parts of the body or recur, more tests may not be needed. For melanoma that is likely to spread to other parts of the body or recur, the following tests and procedures may be done after surgery to remove the melanoma:
The results of these tests are viewed together with the results of the tumor biopsy to find out the stage of the melanoma.
Recurrence In Other Parts Of The Body
Melanoma can also come back in distant parts of the body. Almost any organ can be affected. Most often, the melanoma will come back in the lungs, bones, liver, or brain. Treatment for these recurrences is generally the same as for stage IV melanoma . Melanomas that recur on an arm or leg may be treated with isolated limb perfusion/infusion chemotherapy.
Melanoma that comes back in the brain can be hard to treat. Single tumors can sometimes be removed by surgery. Radiation therapy to the brain may help as well. Systemic treatments might also be tried.
As with other stages of melanoma, people with recurrent melanoma may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial.
The treatment information given here is not official policy of the American Cancer Society and is not intended as medical advice to replace the expertise and judgment of your cancer care team. It is intended to help you and your family make informed decisions, together with your doctor. Your doctor may have reasons for suggesting a treatment plan different from these general treatment options. Don’t hesitate to ask him or her questions about your treatment options.
Also Check: Can Squamous Cell Turn Into Melanoma
What Home Remedies For Skin Cancer Can I Try
Here are a few ideas for taking charge of your skin health:
- Prevention is better than a cure. Ultraviolet light exposure is the most important risk factor for skin cancer. There are many things that you can do for yourself and your family to reduce UV exposure, including:
- Use a broad spectrum sunscreen with sun protection factor 15 or higher.
- Seek shade between 10 am and 2 pm.
- Wear long sleeves, long pants, a wide-brimmed hat, and sunglasses.
- Avoid indoor tanning beds.
- Talk to your doctor.If you see a suspicious lesion, it is critically important to get an accurate diagnosis from your doctor. It may turn out not to be skin cancer at all. If it is skin cancer, discuss the treatment options with your doctor. Explain your concerns about scars or side effects. There may be several ways to treat the cancer. You may be able to find a treatment that meets your financial needs and cosmetic preferences with acceptable side effects.
Recurrence In Nearby Lymph Nodes
If nearby lymph nodes werenât all removed during the initial treatment, the melanoma might come back in these lymph nodes. Lymph node recurrence is treated by lymph node dissection if it can be done, sometimes followed by adjuvant treatments such as radiation therapy and/or immunotherapy or targeted therapy . If surgery is not an option, radiation therapy or systemic treatment can be used.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Renal Cell Carcinoma
How Serious Is My Cancer
If you have melanoma, the doctor will want to find out how far it has spread. This is called staging. Your doctor will want to find out the stage of your cancer to help decide what type of treatment is best for you.
The stage describes the growth or spread of the melanoma through the skin. It also tells if it has spread to other parts of your body.
Your cancer can be stage 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4. The lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, like stage 4, means a more serious cancer that has spread beyond the skin. Be sure to ask the doctor about the cancer stage and what it means for you.
Treating Stage I Melanoma
Stage I melanoma is typically treated by wide excision . The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma. Most often, no other treatment is needed.
Some doctors may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to look for cancer in nearby lymph nodes, especially if the melanoma is stage IB or has other characteristics that make it more likely to have spread. You and your doctor should discuss this option.
If the SLNB does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If cancer cells are found on the SLNB, a lymph node dissection might be recommended. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
You May Like: Can Skin Cancer Look Like Psoriasis
How Do Dermatologists Diagnose Melanoma
When you see a board-certified dermatologist, your dermatologist will:
-
Examine your skin carefully
-
Ask questions about your health, medications, and symptoms
-
Want to know if melanoma runs in your family
If any spot on your skin looks like skin cancer, your dermatologist will first numb the area and then remove all of it. This can be done during an office visit and is called a skin biopsy. This is a simple procedure, which a dermatologist can quickly, safely, and easily perform.
Having a skin biopsy is the only way to know for sure whether you have skin cancer.
The tissue that your dermatologist removes will be sent to a lab, where a doctor, such as a dermatopathologist, will examine it under a high-powered microscope. The doctor is looking for cancer cells.
What this doctor sees while looking at your tissue will be explained in the pathology report, including whether cancer cells were seen. If melanoma cells are seen, the report will include many important details, including:
-
The type of melanoma
-
How deeply the melanoma tumor has grown into the skin
-
How quickly the melanoma cells are growing and dividing
If its possible to tell the stage of the melanoma, the report will include this information.
Stages of melanoma
Heres an explanation of what each stage of melanoma means:
Stages of melanoma
Stage 0
The melanoma has spread to either: One or more nearby lymph node Nearby skin
Once the stage is known, the next step is treatment.
Treating Stage 4 Melanoma
If melanoma comes back or spreads to other organs it’s called stage 4 melanoma.
In the past, cure from stage 4 melanoma was very rare but new treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted treatments, show encouraging results.
Treatment for stage 4 melanoma is given in the hope that it can slow the cancer’s growth, reduce symptoms, and extend life expectancy.
You may be offered surgery to remove other melanomas that have grown away from the original site. You may also be able to have other treatments to help with your symptoms, such as radiotherapy and medicine.
If you have advanced melanoma, you may decide not to have treatment if it’s unlikely to significantly extend your life expectancy, or if you do not have symptoms that cause pain or discomfort.
It’s entirely your decision and your treatment team will respect it. If you decide not to receive treatment, pain relief and nursing care will be made available when you need it. This is called palliative care.
You May Like: What Does Negative For High Grade Urothelial Carcinoma Mean
The Stage Of Melanoma Depends On The Thickness Of The Tumor Whether Cancer Has Spread To Lymph Nodes Or Other Parts Of The Body And Other Factors
To find out the stage of melanoma, the tumor is completely removed and nearby lymph nodes are checked for signs of cancer. The stage of the cancer is used to determine which treatment is best. Check with your doctor to find out which stage of cancer you have.
The stage of melanoma depends on the following:
- The thickness of the tumor. The thickness of the tumor is measured from the surface of the skin to the deepest part of the tumor.
- Whether there are:
- Satellite tumors: Small groups of tumor cells that have spread within 2 centimeters of the primary tumor.
- Microsatellite tumors: Small groups of tumor cells that have spread to an area right beside or below the primary tumor.
- In-transit metastases: Tumors that have spread to lymph vessels in the skin more than 2 centimeters away from the primary tumor, but not to the lymph nodes.
Oral Medications For Advanced Bcc
It is rare for skin cancer to reach advanced stages, but when it does, oral medications may help. In addition to chemotherapy, targeted drugs may be used to treat advanced skin cancer. Targeted therapy means that the medication is able to directly target the cancer cells without destroying healthy cells. This can help to reduce side effects from treatment.
Vismodegib and sonidegib are hedgehog pathway inhibitors that work to prevent cancer cells from growing and spreading. The capsules are taken once per day and may be considered after surgery and other treatments. These medications come with several possible side effects and should never be taken during pregnancy since they can affect fetal growth.
Cetuximab is an EGFR inhibitor that can help to stop the spread of cancerous squamous cells. Its possible side effects include skin infections, diarrhea, mouth sores, and loss of appetite.
Read Also: May Is Melanoma Awareness Month