What Is The Survival Rate Of Metastatic Liver Cancer
1. Factors Affecting Survival Rate of Metastatic Liver Cancer
- The type of liver cancer patients suffers from.
- How far cancer has spread in the body and affects other organs.
- The overall health condition of the patient.
- If the patient already gets treatment, what kind of medical treatment is received.
- How well the patients respond to the medical treatment given.
2. Typical Survival Rates of Metastatic Liver Cancer 3. Symptoms of Metastatic Liver Cancer
- Painful feeling on the stomach or area near the right shoulder
- Unexplained loss of appetite
- Feeling full easily even after small portions of meal
- Swelling in the stomach
- The yellow color on skin and eyes
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Sudden bruising or bleeding
Who Gets This Cancer
Liver cancer is more common in men than women, and among Asian/Pacific Islander and American Indian/Alaska Native populations. The rate of new cases of liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer was 9.0 per 100,000 men and women per year based on 20142018 cases, age-adjusted.
Rate of New Cases per 100,000 Persons by Race/Ethnicity & Sex: Liver and Intrahepatic Bile Duct Cancer
Males
Contributors To Mortality Within 2 Years After Diagnosis Of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Univariate analysis revealed that the age increased mortality within the first 2 years after diagnosis .2). Looking at the underlying liver disease, compared to patients with HCV infection, patients with HBV infection were less likely to die within 2 years , whereas the risk of mortality within 2 years of diagnosis was higher in patients with alcoholic liver disease and nonviral/nonalcoholic cryptogenic liver disease . Also, the presence of decompensated cirrhosis significantly increased mortality within the 2 years . Finally, as compared to the LT group, SR only group and patients who did not receive LT or SR had significantly higher mortality within 2 years of diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If Skin Cancer Is Melanoma
Treatment Modality And Survival
This current study attempted to characterize all 10-year survivors as previous studies have described 10-year survival after a particular modality: resection, transplant or RFA. Our study showed long-term survivors mostly occur after resection or transplant, but 10% of our cohort survived long-term with only locoregional therapy. Baseline characteristics in these three groups differed because of requirements for each of the therapies. To avoid confounding factors and bias, we conducted separate analyses for liver transplantation and resection.
Selection of patients for liver transplantation varies depending on the transplant center but generally requires AJCC stage I or II and the absence of macrovascular invasion, tumor rupture, high AFP, morbid obesity and severe medical comorbidities. In our center, we specifically require patients to have BMI 35 or less and AFP < 1000 ng/mL. In this study, only recurrence was a predictor of 10-year survival after transplantation. Surveillance, hypertension were no longer significant after multivariate analysis.
Is Liver Cancer Curable In Kids
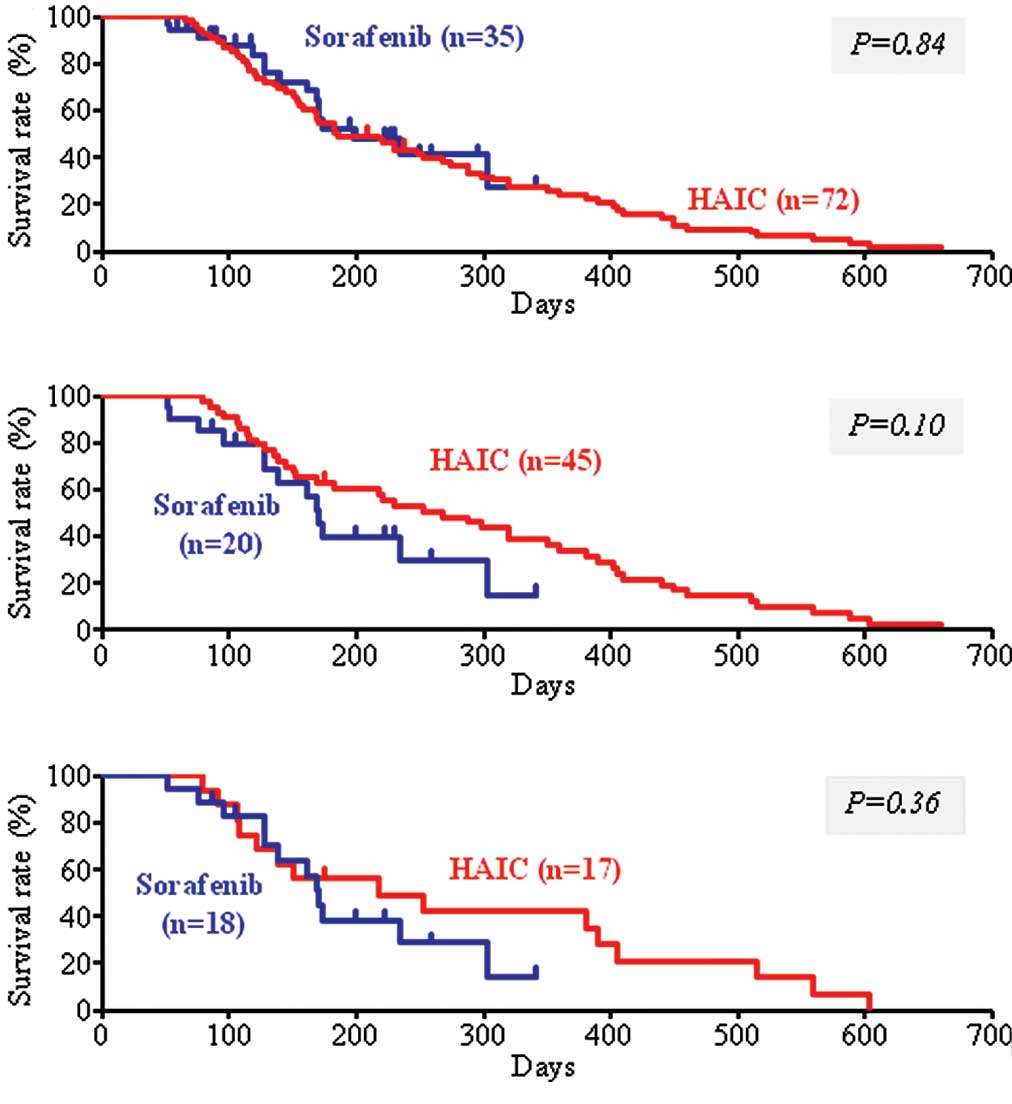
Childhood liver cancer is curable in kids only if it is small and can be removed entirely by surgery. Cure rates of childhood liver cancer are much higher than those of adult liver cancer.
There are two main types of childhood liver cancer, namely, hepatoblastoma and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatoblastoma can be removed completely more often than hepatocellular carcinoma and is curable in more than half of the children.
The treatment of childhood liver cancer depends on:
- The type of cancer
- Stage of cancer
- Your childs overall health
You May Like: What Is The Most Effective Treatment For Melanoma
How Is Fibrolamellar Carcinoma Treated
Surgery: Surgery is used to remove as much of the FLC as possible. This surgery can involve either a resection, where part of the liver is taken out, or a transplant, where the whole liver is taken out and replaced with a donor liver. If the surgeon does a resection, you will be able to live and function well even with part of your liver missing.
Chemotherapy: When surgery is not possible or when the cancer has spread, chemotherapy will be used to treat the FLC.
Embolization Therapy: Depending on where the FLC is, embolization therapy can be used. This type of therapy cuts off the blood supply to the part of the liver where the FLC is located. This causes the FLC to die because it cant get oxygen and nutrients.
What Are The Risk Factors For Liver Cancer Is Liver Cancer Hereditary
Incidence rates of hepatocellular cancer are rising in the United States due to increasing prevalence of cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis C and steatohepatitis .
Cirrhosis of the liver due to any cause is a risk factor for liver cancer. The risk factors for liver cancer in cirrhosis are being male, age 55 years or older, Asian or Hispanic ethnicity, family history in a first-degree relative, obesity, hepatitis B and C, alcohol use, and elevated iron content in the blood due to hemochromatosis.
Chronic hepatitis B infection even without cirrhosis is a risk factor for liver cancer.
Read Also: Is Melanoma The Same As Skin Cancer
Additional File : Figure S1
. Overall survival in patients with BCLC stage 0, A, B, and C disease by Kaplan-Meier analysis. Surgical resection resulted in significantly higher overall survival than radiofrequency ablation and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in BCLC stage 0 . SR resulted in significantly higher overall survival than RFA and TACE in BCLC stage A . SR resulted in significantly higher overall survival than RFA and TACE in BCLC stage A . SR resulted in significantly higher overall survival than RFA, TACE, and other treatment in BCLC stage B . SR resulted in significantly higher overall survival than RFA, TACE, target therapy, radiotherapy , hepatic artery infusion therapy , and best support care in BCLC stage C .
Localized Adult Primary Liver Cancer Treatment
Localized hepatocellular carcinomas that present as a solitary mass in a portion of the liver or as a limited number of tumors without major vascular invasion constitute approximately 30% of the HCC cases.
There are three potentially curative therapies that are acceptable treatment options for small, single-lesion HCC in patients with well-preserved liver function.
Read Also: How To Know If It’s Skin Cancer
Request An Appointment At Moffitt Cancer Center
Please call for support from a Moffitt representative. New Patients and Healthcare Professionals can submit an online form by selecting the appropriate buttonbelow. Existing patients can call . for a current list of insurances accepted at Moffitt.
NEW PATIENTS To request a new patient appointment, please fill out the online form or call 1-888-663-3488.
REFERRING PHYSICIANS Providers and medical staff can refer patients by submitting our online referral form.
Moffit now offers Virtual Visits for patients. If you are eligible for a virtual appointment, our scheduling team will discuss this option further with you.
Moffitt Cancer Center is committed to the health and safety of our patients and their families. For more information on how were protecting our new and existing patients, visit our COVID-19 Info Hub
Ajcc Staging System And Definitions Of Tnm
The TNM classification for staging, proposed by the AJCC, is not widely used for liver cancer. Clinical use of TNM staging is limited because liver function is not considered. It is also difficult to use this system to select treatment options because TNM staging relies on detailed histopathological examination available only after tumor excision. TNM may be useful in prognostic prediction after liver resection.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Tumor = primary tumor N = regional lymph nodes M = distant metastasis. | |
| aReprinted with permission from AJCC: Liver. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp. 28793. | |
| IA | T1a = Solitary tumor 2 cm. |
| N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis. | |
| M0 = No distant metastasis. | |
| T1b = Solitary tumor > 2 cm without vascular invasion. | |
| N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis. | |
| M0 = No distant metastasis. |
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| T = primary tumor N = regional lymph nodes M = distant metastasis. | |
| aReprinted with permission from AJCC: Liver. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp. 28793. | |
| II | T2 = Solitary tumor > 2 cm with vascular invasion, or multiple tumors, none > 5 cm. |
| N0 = No regional lymph node metastasis. | |
| M0 = No distant metastasis. |
References
Read Also: How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed
Inoperable Cancer With Only Local Disease
The cancer is small enough and in the right place to be removed but you arent healthy enough for surgery. Often this is because the non-cancerous part of your liver is not healthy , and if the cancer is removed, there might not be enough healthy liver tissue left for it to function properly. It could also mean that you have serious medical problems that make surgery unsafe.
Definitions Of Liver Diseases
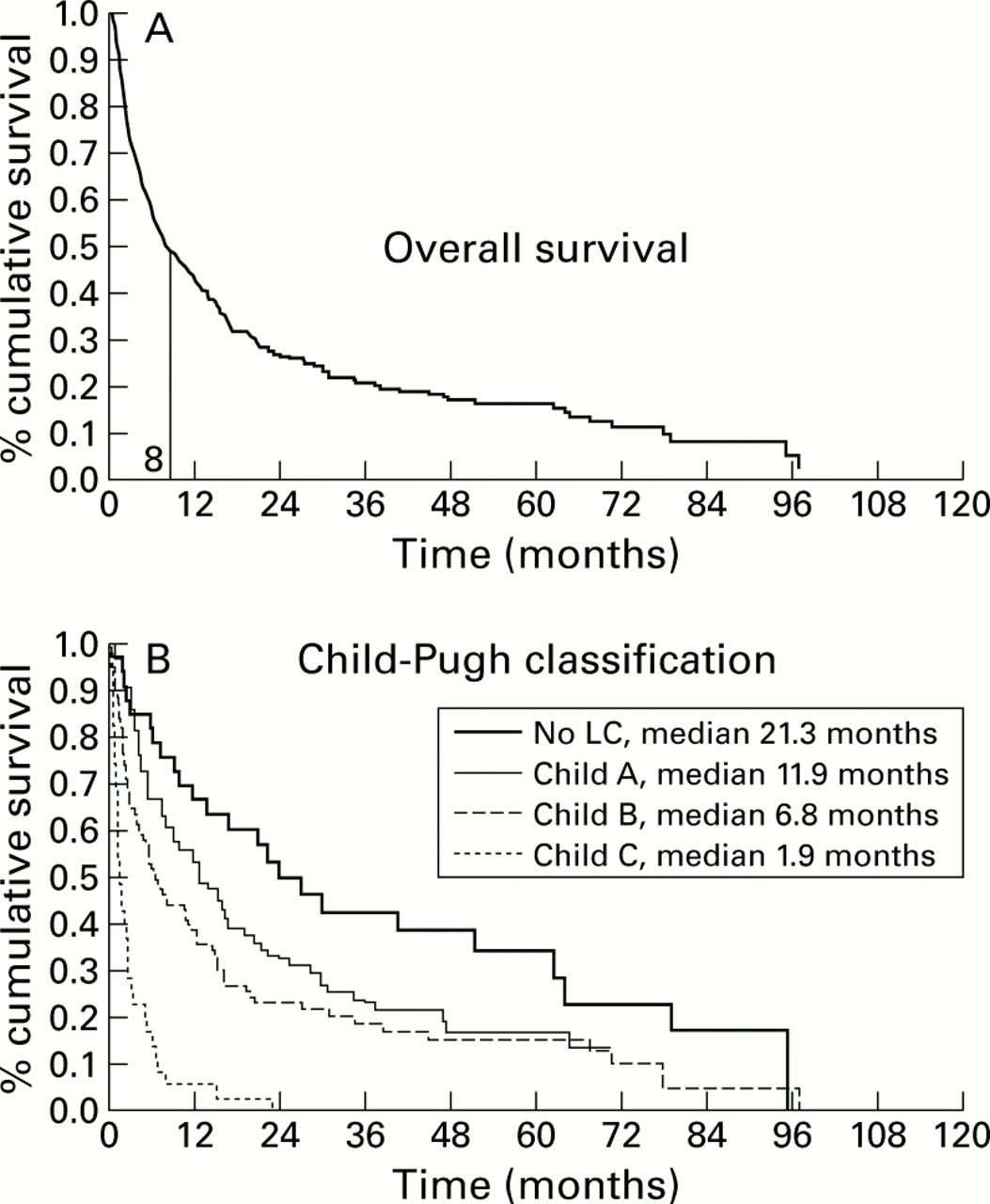
The following 4 categories of chronic liver diseases were identified using the ICD-9 codes: hepatic C virus with codes 070.7, 070.41, 070.44, 070.51, 070.54, V02.62 hepatitis B virus with codes 070.2, 070.3, 070.42, 070.52, V02.61 alcoholic liver disease with codes 303, 291, 571,0, 571.1, 571.2, 571.3, 305.0, V11.3, V79.1 and nonviral and nonalcoholic cryptogenic liver disease with codes 571.8, 571.9, 571.5. Moreover, we identified by codes 789.5 as ascites, 567.23 as spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, 456.0 as esophageal varices with bleeding, 456.2 as esophageal varices in disease classified elsewhere, code underlying cause are cirrhosis of liver and portal hypertension, and 572.2 as hepatic encephalopathy.
Read Also: What Is The Meaning Of Carcinoma
Liver Cancer: Survival Rates And Prognosis
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with liver cancer, you may be worried about the survival rates and what the future may hold. We dont often hear much about liver cancer and when we do, it is usually in the context of how fast it progressed. However, if it is caught early enough, survival rates are comparable to other cancers, with similar prognosis. Learn more about the different stages of liver cancer and the prognosis, or outlook.
Survival In Untreated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A National Cohort Study
-
Contributed equally to this work with: Young Ae Kim, Danbee Kang
Roles Data curation, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Division of Cancer Control & Policy, National Cancer Control Institute, National Cancer Center, Goyang, South Korea
-
Contributed equally to this work with: Young Ae Kim, Danbee Kang
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing original draft
Affiliations Department of Clinical Research Design and Evaluation, SAIHST, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea, Center for Clinical Epidemiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea
-
Roles Conceptualization, Writing review & editing
¶ These author also contributed equally to this work.
Affiliation Department of Clinical Research Design and Evaluation, SAIHST, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, South Korea
-
Roles Conceptualization, Writing original draft
Affiliation Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea
Read Also: How Do You Die From Melanoma
Comparison Of Liver Transplant Recipients To The Patients Who Were Treated With Surgical Resection
Mean age at HCC diagnosis was significantly higher in SR only group than the LT group .1). Mortality within 2 years of diagnosis was significantly higher in the SR group than patients receiving LT . KaplanMeier survival curve for mortality for HCC patients who were treated with different modalities are shown in Fig. . Even after pair-wise matched analysis 2 years mortality was significantly higher in the SR group than the LT group . Also, 73% of HCC patients who received LT had HCV infection and 12% had alcoholic liver disease. In contrast, 57% of HCC patients treated with surgical resection had HCV, whereas 17% had nonviral and nonalcoholic/cryptogenic liver disease. As expected, the rate of decompensated cirrhosis was higher in the LT group than those treated with SR . The prevalence of tumor site stage were similar in the both groups, as 76% of LT group and 74% of SR only group had local disease . Finally, the proportion of patients receiving TACE was significantly higher in the LT group than SR only group .
KaplanMeier survival curves for HCC patients by liver transplant and primary site surgery status in the main cohort. HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma.
Survival Rate By Period
Forty-five year data was divided into nine 5-year calendar periods and three 15-year periods. Great improvement in OS and RS could be observed . For the short-term survival of OS and RS, the recent period of 20022016 has showed markedly improvement of 26.56% in 1-year OS, compared with the middle period of 19872001 and the early period of 19721986 . The 5-year OS has increased from 2.02% in the early period, 4.40% in the middle period to 10.76% in the recent period. Also, significant improvement trend in long-term OS of 10-year could be found: 0.95% in 19721986, 3.00% in 19872001, and 7.02% in 20022016 . Wilcoxon test shows that the 3 period curves had markedly differences, with a Gehan statistic of 1001.30, P value of less than 0.01. Group comparison demonstrates that the recent period had significant high survival than the early and middle periods . For the trends of RSs, Joinpoint Regression shows that the APC of 10-year RS was 5.30% for the whole period the APCs of 5-year RS with 2 segments were 3.42% in 19722006 and 14.64% in 20062016. And for the 1-year RS, 4 segments with APCs of 19.52% in 19721977, 22.34% in 19771981, and 2.54% in 19812005, and 9.93% in 20052016 .
|
Table 3 Observed Survival Rate and Relative Survival Rate of Liver Cancer by Period in Qidong, 19722016 |
Recommended Reading: What Are The 4 Types Of Skin Cancer
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Thoughts On Liver Transplantation
LIVER TRANSPLANT offers the highest rates of long-term survival for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, according to , Assistant Professor of Surgery at Emory University, Atlanta. At the 2017 Debates and Didactics in Hematology and Oncology Conference at Sea Island, Georgia, Dr. Russell described the latest trends in liver transplantation.
The other potentially curative option is surgical resection, and choosing between the two modalities is not always simple. Patients dont always fall into nice slots, she admitted. If both modalities are available to the patient with hepatocellular carcinoma, selection takes into account the degree of cirrhosis, the size and number of lesions, the presence of portal hypertension and comorbidities, and insurance/citizenship status.
Liver transplant offers the best 5-year survival, with studies demonstrating 70% to 80% survival rates, Dr. Russell said.
Determining Eligibility for Transplant
Liver transplant offers the best 5-year survival, with studies demonstrating 70% to 80% survival rates. Maria Russell, MDTweet this quote
The study concluded that liver transplantation is an effective treatment for small, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis, especially those meeting the Milan criteria. Thus, the Milan criteria became the standard for determining eligibility for transplant.
Proposed Changes to Eligibility Criteria
Of Note: The Milan Criteria
- Single tumor 5 cm
- Multiple tumors 3 cm
- No more than 3 tumors
Youll notice that posttransplant survival goes down, suggesting we can take patients with worse disease, but we wont necessarily achieve the same benefit we get under the Milan criteria, Dr. Russell said.
The MELD score is used to determine which patients receive organs. In an attempt to allocate livers to patients who will most benefit from them, the following changes have been proposed4:
- Candidates with small lesions and alpha-fetoprotein < 20 ng/mL should undergo local-regional therapy prior to applying for a standardized MELD exception, which has traditionally been extended to patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Since AFP > 1,000 ng/mL portends for a worse prognosis, these patients are not candidates for the MELD exception criteria.
- Candidates are eligible for inclusion in a downstaging protocol if they have one lesion > 5 cm and 8 cm 2 to 3 lesions each < 5 cm, with a total diameter of all lesions 8 cm or 4 to 5 lesions each < 3 cm, with a total diameter of all lesions 8 cm.
Issues With Downstaging
Whether downstaged patients have survival as good as those meeting the Milan criteria at baseline is not clear, based on a systematic review revealing mixed results.6 This study, however, led to the current University of California San Francisco protocol, which includes the following criteria for transplant after downstaging:
Proposals for Increasing Donor Volume
Don’t Miss: How Often Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Spread
Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Staging System
Currently, the BCLC staging classification is the most accepted staging system for HCC and is useful in the staging of early tumors. Evidence from an American cohort has shown that BCLC staging offers better prognostic stratification power than other staging systems.
The BCLC staging system attempts to overcome the limitations of previous staging systems by including variables related to the following:
- Tumor stage.
- Functional status of the liver.
- Physical status.
- Cancer-related symptoms.
Five stages are identified based on the variables mentioned above. The BCLC staging system links each HCC stage to appropriate treatment modalities as follows:
- Patients with early-stage HCC may benefit from curative therapies .
- Patients with intermediate-stage or advanced-stage disease may benefit from palliative treatments .
- Patients with end-stage disease who have a very poor life expectancy are offered supportive care and palliation.
Treatment Option Overview For Adult Primary Liver Cancer
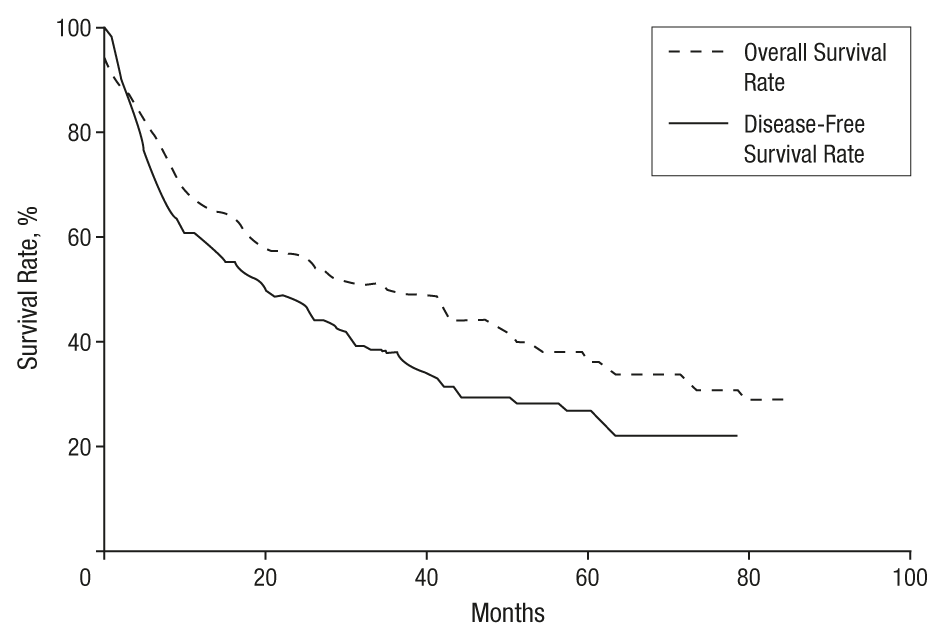
There is no agreement on a single treatment strategy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma . Selection of treatment is complex due to several factors, including:
- Underlying liver function.
- Extent and location of the tumor.
- General condition of the patient.
Several treatments for HCC are associated with long-term survival, including surgical resection, liver transplantation, and ablation. There are no large, robust, randomized studies that compare treatments considered effective for early-stage disease, nor are there studies comparing these treatments with best supportive care. Often, patients with HCC are evaluated by a multidisciplinary team including hepatologists, radiologists, interventional radiologists, radiation oncologists, transplant surgeons, surgical oncologists, pathologists, and medical oncologists.
Best survivals are achieved when the HCC can be removed either by surgical resection or liver transplantation. Surgical resection is usually performed in patients with localized HCC and enough functional hepatic reserve.
For patients with decompensated cirrhosis and a solitary lesion or early multifocal disease , the best option is liver transplantation, but the limited availability of liver donors restricts the use of this approach.
Among noncurative treatments for HCC, transarterial chemoembolization and multikinase inhibitors have been shown to improve survival.
Table 5 shows the standard treatment options for HCC.
References
You May Like: Can Red Spots Be Skin Cancer