What Medication Treat Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Tamoxifen may be prescribed for woman of all ages who have been treated for DCIS. In those women past menopause, the doctor may prescribe an aromatase inhibitor. These medications help lower the risk of DCIS or another type of cancer developing in either breast. If either is prescribed, it is suggested that these drugs be taken for five years after surgery.
Treatment For Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
No two patients are the same. Your doctor will tailor your treatment plan based upon your test outcomes and case history. To name a few things, your doctor will consider:.
- Growth location.
- Aggressiveness of the cancer cells.
- Your family history of breast cancer.
- Outcomes of tests for a gene mutation that would increase the danger of breast cancer.
The majority of women with DCIS dont have the breast gotten rid of with a mastectomy. Rather, they have breast-conserving surgery.
Most typical is a lumpectomy followed by radiation. In a lumpectomy, the surgeon gets rid of the cancer and a small area of healthy tissue around it. The tissue is taken to make certain all the cancer cells have actually been eliminated. Lymph nodes under the arm do not need to be gotten rid of as they are with other kinds of breast cancer.
After lumpectomy, radiation substantially decreases the possibility that the cancer will return. If cancer does return, its called recurrence. Radiation can be offered to the entire breast, or it can be taken internally to target certain areas of the breast.
Some women with an incredibly low probability of cancer reoccurrence might have a lumpectomy just. This may be a choice for older women with small growths whose surgery showed huge quantities of healthy tissue on all sides of the cancer. Talk about the dangers of not having radiation with your doctor prior to choosing against it.
If Someone Has Dcis What Should Be The First Step In Deciding On Treatment
A person diagnosed with DCIS usually meets with a breast surgeon first. The doctor will assess the tumors size, grade, and hormone-receptor status, as well as other risk factors that are important for treatment decisions. For example, should a patient get genetic testing for inherited mutations such as BRCA1 or BRCA2, which are known to raise risk for future breast cancer? Do they have a strong family history of the disease?
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
How Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Diagnosed
About 80% of cases are found by mammograms. On the mammogram, it appears as a shadowy area.
If your mammogram suggests that you may have DCIS, your doctor should order a biopsy to analyze the cells and confirm the diagnosis. Biopsies for DCIS are typically done using needles to remove tissue samples from the breast.
If you have DCIS, your doctor may do more tests to gather information about your cancer. These tests may include an ultrasound or MRI. Based on the results of various tests, your doctor will be able to tell the size of your tumor and how much of your breast is affected by the cancer.
More About Invasive Breast Cancer With Central Necrosis
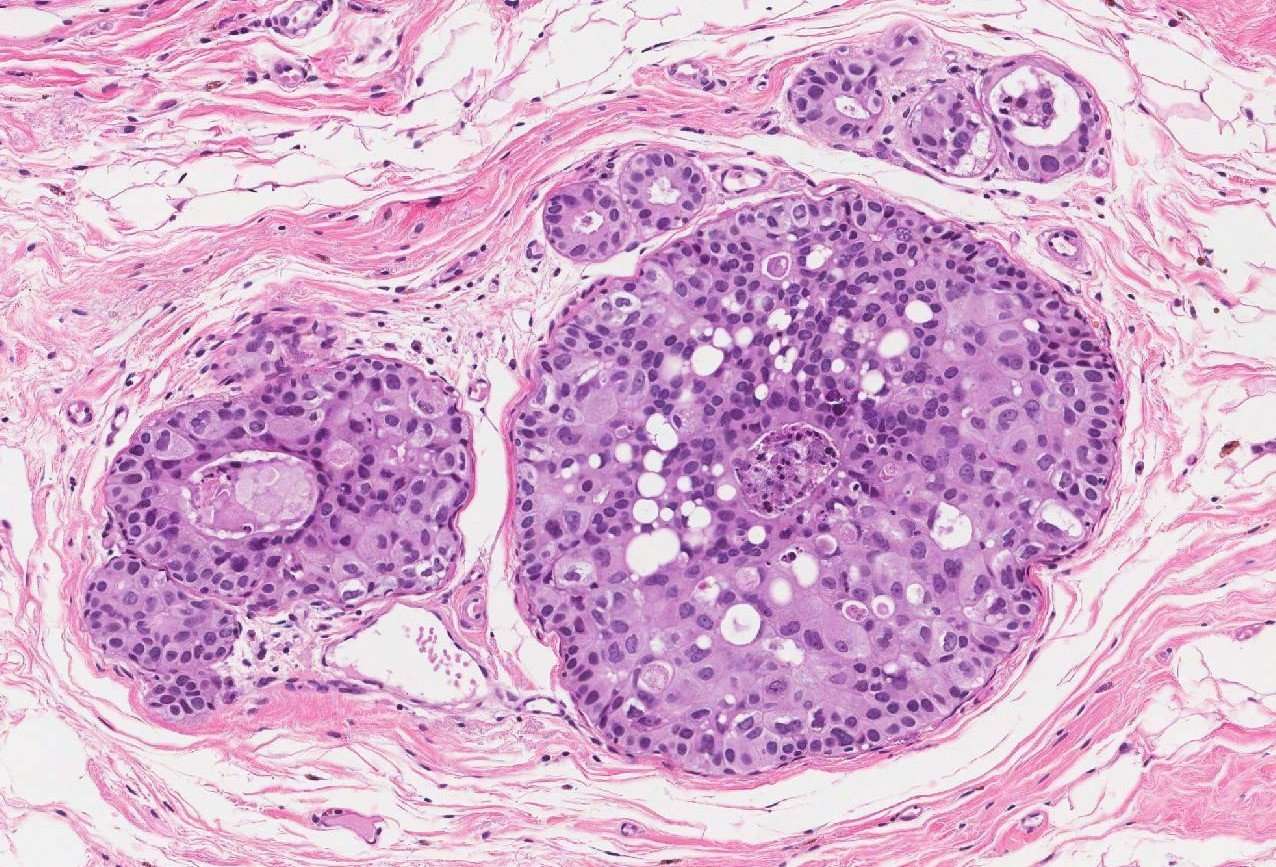
Sometimes medics refer to an infiltrative breast carcinoma with central necrosis as a centrally necrotizing breast carcinoma, . Historically, centrally necrotizing breast carcinomas have an aggressive course.
Histologically, the composition of infiltrating ductal carcinoma with central necrosis is a well-circumscribed nodule with an extensive region of central necrosis. This area of necrosis is usually surrounded by a narrow rim of high-grade tumor cells. But these tumor cells usually show only minimal if any ductal differentiation, ie. they tend not to form into tubules.
The average age of development of an infiltrative ductal carcinoma with central necrosis is hard to estimate, but generally occurs in the mid 50s. Most infiltrative breast carcinomas with central necrosis are estrogen and progesterone receptor negative, making them more resistant to treatment.
Recommended Reading: What Is Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
Health Literacy To Empower Patients
With the right information, patients can make the best decisions about their care. By partnering with patients, healthcare providers, and hospitals, we hope to provide all patients with the tools and knowledge to understand their pathology report.
For more information about this site, contact us at .
Disclaimer: The articles on MyPathologyReport are intended for general informational purposes only and they do not address individual circumstances. The articles on this site are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment and should not be relied on to make decisions about your health. Never ignore professional medical advice in seeking treatment because of something you have read on the MyPathologyReport site. MyPathologyReport is independently owned and operated and is not affiliated with any hospital or patient portal. The articles on MyPathologyReport.ca are intended for use within Canada by residents of Canada only.
Copyright © 2020. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
Our work is generously supported by:
Common Breast Cancer Types
After skin cancer, breast cancer is the most common type of cancer diagnosed in women. About 284,200 cases will be diagnosed in 2021, according to the American Cancer Society . Men also may develop breast cancer, though its much more rare.
Breast cancer is classified into different types based on how the cells look under a microscope. Most breast cancers are carcinomas, a type of cancer that begins in the linings of most organs.
Don’t Miss: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
What Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ , also known as intraductal carcinoma, accounts for one of every five new breast cancer diagnoses. It’s an uncontrolled growth of cells within the breast ducts. Its noninvasive, meaning it hasnt grown into the breast tissue outside of the ducts. The phrase “in situ” means “in its original place.”
DCIS is the earliest stage at which breast cancer can be diagnosed. It’s known as stage 0 breast cancer. The vast majority of women diagnosed with it can be cured.
Even though its noninvasive, it can lead to invasive cancer. It’s important that women with the disease get treatment. Research shows that the risk of getting invasive cancer is low if youve been treated for DCIS. If it isnt treated, 30% to 50% of women with DCIS will get invasive cancer. The invasive cancer usually develops in the same breast and in the same area as where the DCIS happened.
Continued
Whats The Most Effective Treatment For Dcis
Surgery is typically the first treatment for DCIS, and it is very effective. There are two types of surgery used for DCIS. The less-invasive option is a lumpectomy, in which a surgeon removes the area of DCIS as well as a little bit of the normal tissue around it, also referred to as a margin. The other option is a mastectomy, which involves removing the entire breast.
Most people with DCIS undergo a lumpectomy, possibly followed by additional treatments. In some cases, a mastectomy is recommended, especially if the DCIS covers a large area or appears in multiple spots throughout the breast. With either of these surgeries, the survival rate is excellent. Our job is to figure out which type of surgery is best for each patient.
Also Check: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
Removal Of Part Of The Breast
Many women have surgery to remove the area of DCIS and a border of healthy tissue around it. This is called breast conserving surgery, or a wide local excision or sometimes a lumpectomy.
After this surgery, you might have radiotherapy to the rest of the breast tissue if the DCIS cells look very abnormal . The radiotherapy treatment aims to kill off any abnormal cells that might still be in the breast tissue. Your doctor or breast care nurse will discuss with you the possible benefits and risks of radiotherapy.
What Are Some Advantages Of Receiving Treatment For Dcis At Msk
At MSK, we have a very thoughtful approach to personalizing treatment for each person with DCIS. The doctors and patients make treatment decisions as a team. Much of the research determining risk factors for DCIS-related recurrence was done at MSK, and we have a computerized prediction model that can help calculate an individuals risk of recurrence, which helps us decide what treatments are best. Weve tried to figure out who really needs additional treatments, such as radiation or hormone therapy, and who may be able to avoid certain treatments. Our goal is to find the right treatment for each patient, so that they can remain cancer free with an excellent quality of life moving forward.
Recommended Reading: Braf And Melanoma
Breast Cancer Survival Rates Are Affected By Tumor Grade
Breast cancer grade refers to the size and shape of the malignant breast cancer cells. If the breast cancer cells look very different than normal breast tissue cells, and somewhat random in appearance, they are called poorly differentiated and described as high grade.
There are three main breast cancer grades and these are as follows:-
- Grade 1: The cancer cells are well differentiated and look the most like normal cells. These type of cancers tend to be slow-growing.
- Grade 2: These cancer cells are moderately differentiated. This means that the cells look less like normal cells and tend to grow faster.
- Grade 3: Poorly differentiated cells do not appear like normal cells at all and tend to be very fast growing. Hence, the affect on prognosis.
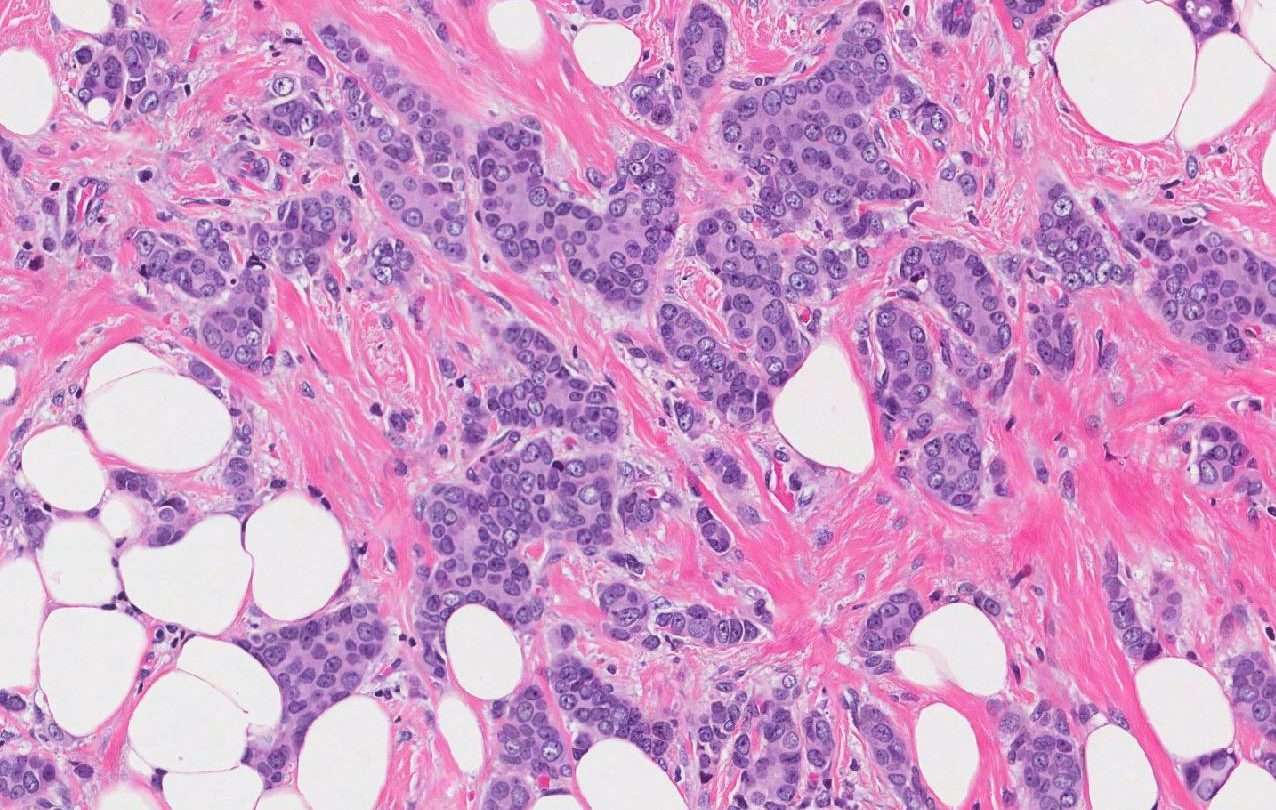
Microscopic Images of Ductal cell carcinoma in Situ Grades 1, 2 and 3
Higher grade breast cancers tend to have a poorer prognosis.
You will be able to find the Grade of your tumor on your pathology report.
Who Is Affected By Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Most women who get DCIS do not have a family history of breast cancer. Only about 5-10% of breast cancer cases are related to a genetic mutation or family history. Red flags for this include having a family history of breast cancer, especially if the cancer was discovered at a younger age, or before 50 years old. Other red flags for breast cancer that may be related to a genetic mutation include a family history of ovarian cancer, male breast cancer, multiple other cancers in the family and Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry. The most common risk factors for breast cancer include being female and getting older, and these are risk factors that cannot be changed.
Because the tissue in mens breasts do not fully develop the way that the tissue in womens breasts do, men do not usually get breast cancer of this type.
Also Check: What Is Braf Melanoma
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: Treatment For Dcis Breast Cancer
Have you started feeling a lump in your breasts? Does your family have a history of breast cancer? If the answer to these questions is positive, then you should read about Invasive Ductal Carcinoma or the Ductal Carcinoma In Situ . It is a type of cancer that grows in the milk glands of a woman and gradually spreads throughout the breasts. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ or DCIS breast cancer symptoms appear at a much later stage. The treatment for invasive breast cancer is through breast removal as well as chemotherapy. However, some Ayurvedic remedies may support in curbing the side effects of the medical treatment.
Putative Genes Involved In Dcis Progression
Eleven comparisons were made two-by-two to obtain the DEGs . Between control and tumor tissues, the greatest differential expression was observed between DCISpure and control , and the lowest, between control and IDCpure .
Additional file Figure S1. shows the comparison of gene expression between control, DCISpure, and IDCpure. Statistically, the invasive tissue exhibited a more similar profile to control than to the in-situ lesions. DCIScomp gene expression retains more similarities with IDCpure , than with DCISpure and has a lower similarity with the control , which suggests progressive molecular alterations from DCISpure to the IDC passing through DCIScomp.
Among the 6 DEGs found between DCISpure and DCIScomp , only IBSP is downregulated in noninvasive lesions .
Table 2 DEGs between DCISpure and DCIScomp and between invasive and noninvasive groups
Don’t Miss: Is Melanoma Cancer Curable
Patient And Tumor Characteristics
We identified a total of 494,801 stage I-III breast cancer patients with either IDC alone or IDC+DCIS who met study inclusion criteria . Patient demographic and clinical-pathologic characteristics are shown in Table . Median follow-up was 4.5 years. Fewer patients were diagnosed with IDC alone than with IDC+DCIS . The median age for the study cohort was 59.7 years. The majority of patients were white , with T1 and N0 tumors, with receptor status ER positive , and PR positive . Among patients with known Her2 status, the majority had Her2 negative disease . Partial mastectomy was performed in 61.6% of patients while 38.4% received mastectomy. The majority of patients received radiation therapy and hormonal therapy . Approximately one half of patients received chemotherapy. The receipt of radiation and systemic therapies in the setting of partial or total mastectomy are presented for node-positive and node-negative patients in Supplementary Table .
Table 1 Demographic and clinical-pathologic characteristics of patient cohort.
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:
Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Recommended Reading: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
About 1 in 5 new breast cancers will be ductal carcinoma in situ . Nearly all women with this early stage of breast cancer can be cured.
DCIS is also called intraductal carcinoma or stage 0 breast cancer. DCIS is a non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer. This means the cells that line the ducts have changed to cancer cells but they have not spread through the walls of the ducts into the nearby breast tissue.
Because DCIS hasnt spread into the breast tissue around it, it cant spread beyond the breast to other parts of the body.
However, DCIS can sometimes become an invasive cancer. At that time, the cancer has spread out of the duct into nearby tissue, and from there, it could metastasize to other parts of the body.
Right now, theres no good way to know for sure which will become invasive cancer and which ones wont, so almost all women with DCIS will be treated.
Students Who Viewed This Also Studied
Ethical and moral dilemma in health and social care environment.docx
University of Maine
Program Design and Implementation Assessment .docx
University of Maine
University of Maine BUSINESS 235
IMG_2489.jpg
University of Maine BUSINESS 235
lux_1018.docx
University of Maine BUSINESS 235
Ethical and moral dilemma in health and social care environment.docx
University of Maine BUSINESS 235
Program Design and Implementation Assessment .docx
University of Maine BUSINESS 235
SIM.docx
You May Like: Stage Iii Melanoma Treatment
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stages
Results from these tests will show the stage of your cancer. Staging is the name for the process doctors use to figure out if and how far breast cancer has spread. Knowing the stage will help guide your treatment.
Doctors can use the results from your diagnostic testing to gather information about the tumor. They group it by a system known as TNM:
- Tumor : How large is the primary tumor? Where is it?
- Node : Has the tumor spread to your lymph nodes? Where? How much?
- Metastasis : Has the cancer spread to other body parts? Which ones? How much?
To stage your cancer, your doctor combines the TNM results with the tumor grade .
Stages include:
- Stage 0: This is noninvasive cancer. Its only in the ducts and hasnt spread .
- Stage IA: The tumor is small and invasive, but it hasnt spread to your lymph nodes .
- Stage IB: Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. Its larger than 0.2 mm but less than 2 mm in size. Theres either no sign of a tumor in the breast or there is, but its 20 mm or smaller .
- Stage IIA: Any one of these:
- Theres no sign of a tumor in the breast. The cancer has spread to between 1 and 3 underarm lymph nodes, but not to any distant body parts .
- The tumor is 20 mm or smaller and has spread to underarm lymph nodes .
- The tumor is between 20 mm and 50 mm but hasnt spread to nearby nodes .
Continued
What Is The Prognosis For Patients Who Have Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
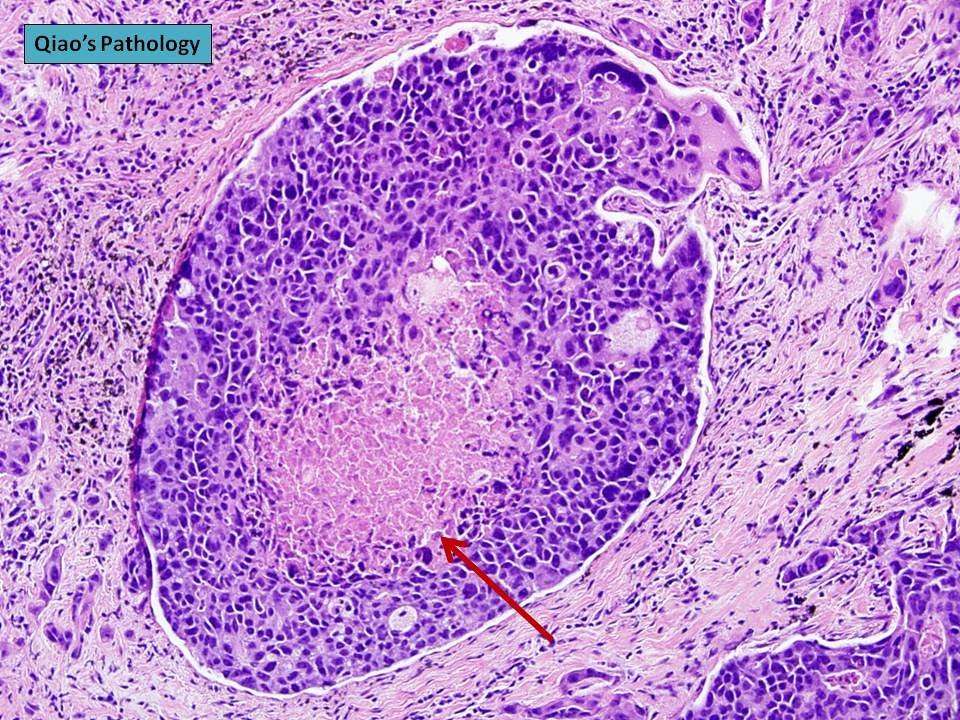
Because DCIS is contained within a specific area of the breast and has not spread, the disease can be controlled and cured with appropriate treatment. After treatment, the outcome for the patient with DCIS is usually excellent.
However, those patients who have had DCIS, even if treated successfully, are at a greater risk than people who have never had breast cancer to have the cancer return or for another type of breast cancer to develop.
Don’t Miss: Squamous Cell Stage 4
Can Dcis Be Left And Not Treated
Because theres no way of knowing when or if DCIS will become invasive, treatment is usually recommended. Its possible this may lead to unnecessary treatment for some people.
The aim of treatment is to remove all the DCIS from within the breast to reduce the chance of it becoming an invasive cancer.
Research is looking at which cases of DCIS are more likely to develop into invasive breast cancer and which could be closely monitored instead of being treated. If you are diagnosed with low-grade DCIS, you may be invited to join a clinical trial.
If you have any questions or concerns about your diagnosis and treatment, talk to your treatment team.