What Should I Do If I Suspect I Have Basal Cell Carcinoma
If you have a spot thats not healing or otherwise looks suspicious, get it checked out by a dermatologist. Most dermatologists can identify basal cell carcinoma very quickly due to their specialized training in skin cancers. Over 90% of basal cell carcinomas can be identified on physical exams alone.
If we visually identify a basal cell spot, we perform a skin biopsy. Skin biopsies are relatively simple procedures that only require local anesthesia. We take a sample of the bump and submit it for review to a pathologist. Under the microscope, basal cell carcinoma is very clear. With this process, dermatologists are able to diagnose basal cell carcinoma with a high sense of confidence theyre not often mistaken.
Read Also: What Is Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Cbd Stops Tumor Growth
CBD might restrict cancerous cell development in skin cancer due to its anti-inflammatory features and its capacity to curb the growth of the blood vessels required to grow a tumor. There might also be a further direct impact of cannabinoids on tumor growth and on causing unwanted cell death .
The anti-proliferative properties of CBD help to curb tumor cell growth in lung, breast, prostate, lymphomas, skin, and pancreatic cancer cells.
A study published in 2015 in The Journal of Investigative Dermatology discovered that a CBD mixture supported autophagy of cancerous cells. Autophagy is a normal cellular mechanism that disassembles unwanted or dysfunctional components. It assists cells to eliminate degraded cellular components and encourage their recycling.
Studies have displayed that CBD can aid endocannabinoid receptors to revert to normal function and stop the progress of skin cells that are becoming cancerous. Early evidence suggests that cannabinoids function to regulate cell-survival and cell-death pathways differently in tumor and non-tumor cells, indicating that phytocannabinoids like CBD can probably be applied to target cancerous growths without harming healthy cells.
While no set serving size of CBD for adults is present, experts advise 10 to 20mg daily, or a ratio of 1 to 6mg every 10 pounds of body weight, as a safe beginning point. You can also refer to the packaging of most commercially existing CBD products for suggested serving sizes.
How Can Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin Be Prevented
Currently, Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is a malignant skin cancer that has no preventive measures. However, the following factors may help reduce the risk for the condition:
- Avoid or minimize sun exposure
- Limit the use of tanning beds, tanning parlors
- Smoking cessation
- If it is caused by certain underlying disorders, then treating the underlying condition may help in the treatment and early cure of Nodular BCC of Skin
- Regular medical screening at periodic intervals with blood tests, scans, and physical examinations, are mandatory, due to its metastasizing potential and high possibility of recurrence. Often several years of active vigilance is necessary
Read Also: How Likely Is Skin Cancer
Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
In addition to basal cell carcinoma, this autosomal dominant disorder can result in the early formation of multiple odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies. Various tumors such as medulloblastomas, meningioma, fetal rhabdomyoma, and ameloblastoma also can occur.
Odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies may be seen. Mutations in the hedgehog signaling pathway, particularly the patched gene, are causative.
Go to Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome to see more complete information on this topic.
What Are The Clinical Features Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
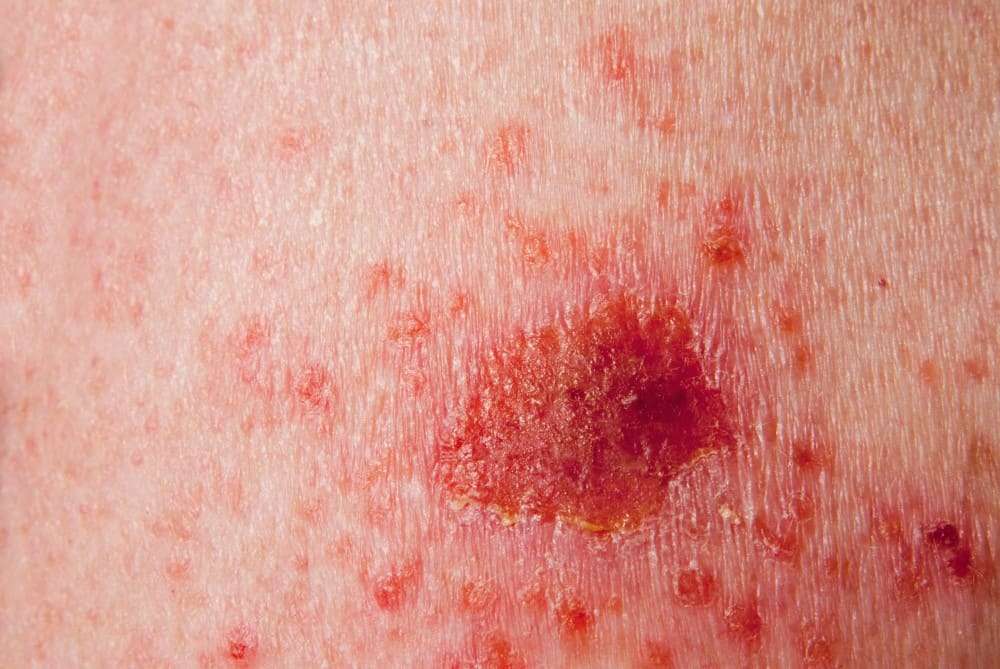
BCC is a locally invasive skin tumour. The main characteristics are:
- Slowly growing plaque or nodule
- Skin coloured, pink or pigmented
- Varies in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter
- Spontaneous bleeding or ulceration
BCC is very rarely a threat to life. A tiny proportion of BCCs grow rapidly, invade deeply, and/or metastasise to local lymph nodes.
Don’t Miss: How Deadly Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cbd Manages Body Inflammation Efficiently
Cannabinoids, such as CBD, have been found to suppress inflammatory reactions, which subsides symptoms of ailments that involve inflammation.
This is possible because of the cannabinoids that contain properties that can be modulated through pathways that are related to cytokine suppression in inflammatory spots and triggering unwanted cell death within immune cells. Therefore, CBD may be an advantageous preventative therapy for cancers that impact chronic inflammation in the body by restricting tumor growth.
Mohs Microscopically Controlled Surgery
|
Because skin cancer cells often have spread beyond the edges of the visible patch on the skin, doctors sometimes use a special surgical technique to make sure they remove all of the cancer. In this technique, called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery or Mohs micrographic surgery, doctors first remove the visible tumor and then begin cutting away the edges of the wound bit by bit. During surgery, doctors examine pieces of tissue to look for cancer cells. Tissue removal from the area continues until the samples no longer contain cancer cells. This procedure enables doctors to limit the amount of tissue removed and thus is especially useful for cancers near such important sites as the eye. After removing all of the cancer, doctors decide how best to replace the skin that has been cut away. They may bring the edges of the remaining skin together with sutures or use a skin graft or skin flap. Or they may place dressings on top of the wound and let the skin heal on its own. Mohs surgery reduces recurrence rates for skin cancers. This surgery is useful for basal cell and squamous cell cancers but is less often used for melanoma. |
Don’t Miss: Where Does Skin Cancer Start
How Dangerous Is Bcc
While BCCs rarely spread beyond the original tumor site, if allowed to grow, these lesions can be disfiguring and dangerous. Untreated BCCs can become locally invasive, grow wide and deep into the skin and destroy skin, tissue and bone. The longer you wait to have a BCC treated, the more likely it is to recur, sometimes repeatedly.
There are some highly unusual, aggressive cases when BCC spreads to other parts of the body. In even rarer instances, this type of BCC can become life-threatening.
Whats That On Your Face Ali
Born and raised in Los Angeles, Sweeney and her two older siblings enjoyed a quintessential Southern California lifestyle. She recalls spending countless days swimming and horseback riding, running marathons and triathlons. She is also an avid gardener and hiker. All of that amounts to a lot of time in the sun. You cant stay out of the sun in Los Angeles, she said. Its just not possible.
Because she is fair-skinned and freckles easily, Sweeney always followed her mothers lead, vigilantly applying sunscreen and wearing hats to shield her face from the rays. As an adult, she saw her dermatologist for regular skin checks, even before her father was diagnosed with advanced BCC in the early 2000s. Sweeney thought she was doing everything right and then, during a routine skin check, her dermatologist asked the dreaded question, Whats that on your nose, Ali?
I think its just a pimple I keep picking at, Sweeney said.
Her dermatologist replied, I dont think thats a pimple. Sweeney felt her breath quicken as the doctor took a sample of the lesion to send to the lab for a biopsy.
What Sweeney had thought was a harmless blemish on the flare of her right nostril was, in fact, a BCC. Her initial reaction? Well, its just skin cancer, she thought. Im not dying. You try to tell yourself its no big deal.
Also Check: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
The Risks The Causes What You Can Do
Basal cell carcinoma is caused by damage and subsequent DNA changes to the basal cells in the outermost layer of skin. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun and indoor tanning is the major cause of BCCs and most skin cancers.
Understanding what causes BCC and the factors that increase your risk of getting it can help you prevent the disease or detect it in its earliest stages, when its easiest to treat.
These factors increase your BCC risk:
Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
This is a type of excision that uses a microscope to remove the lesion layer by layer until no signs of cancer are present. The microscope allows the doctor to pinpoint the cancerous areas of skin to better target removal and save healthy skin. This is a very effective form of removal with a success rate of 99 percent or higher.
Don’t Miss: Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Malignant
What You Can Do
If youve already had a BCC, you have an increased chance of developing another, especially in the same sun-damaged area or nearby.
A BCC can recur even when it has been carefully removed the first time, because some cancer cells may remain undetectable after surgery and others can form roots that extend beyond whats visible. BCCs on the nose, ears and lips are more likely to recur, usually within the first two years after surgery.
Heres what you can do to detect a recurrence and safeguard yourself against further skin damage that can lead to cancer:
Reviewed by:
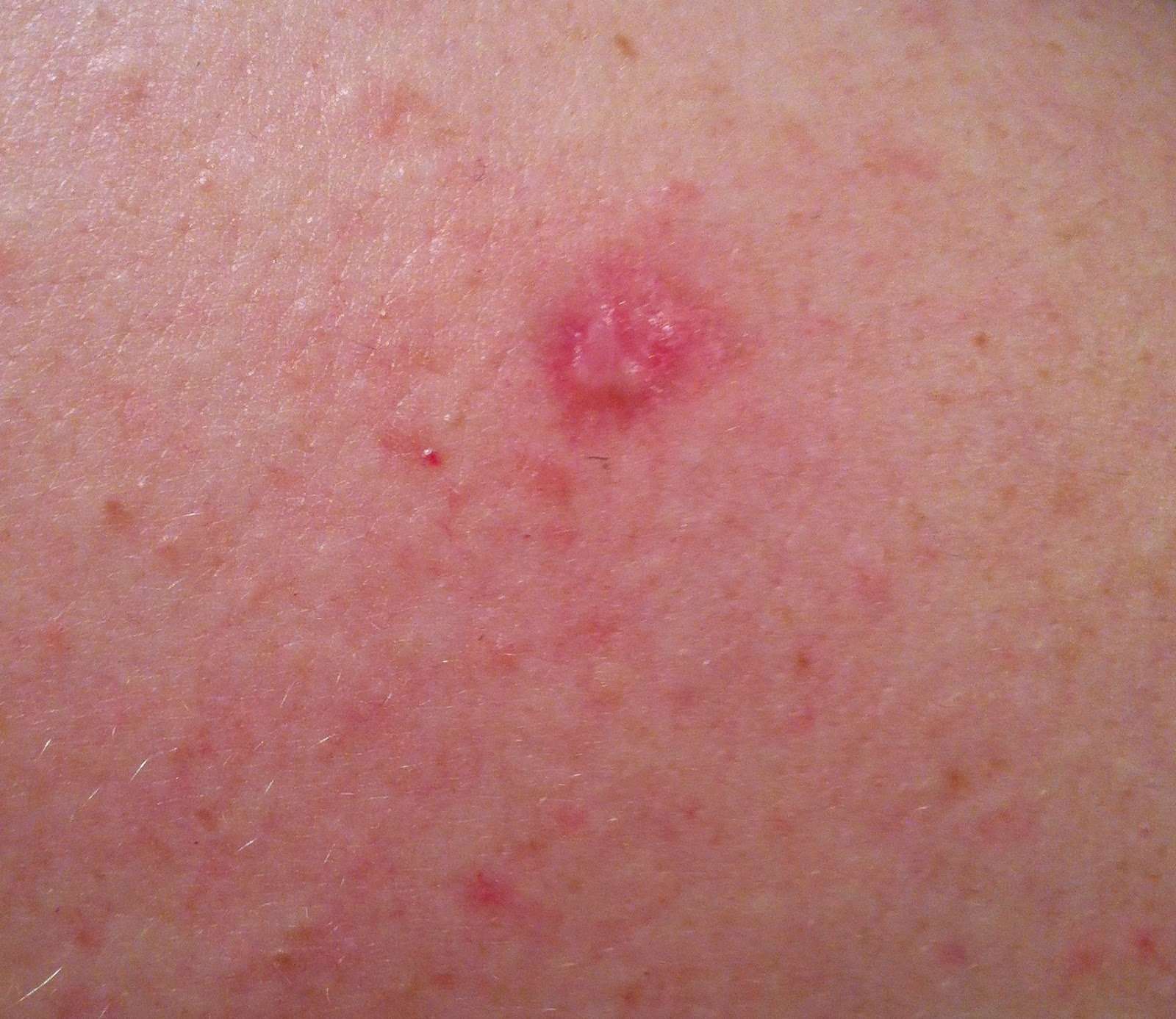
What Do Basal Cell Carcinomas Look Like
BCCs often appear as a change in your skin, such as a lump or a sore that does not heal.;
The main features are:
- slow growing ;months to years
- a pearly white, skin-coloured or pink bump;that is translucent
- waxy, small, raised lesions that may have a dent in the centre
- brown or blue-black areas, in some cases
- a scaly red flat mark on the skin, in some cases
- a tendency to bleed or turn into an ulcer
- scaly, oozing or crusted areas
- varying in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter.
You May Like: What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
Dna Mismatch Repair Proteins
DNA mismatch repair proteins are a group of proteins that physiologically stimulate G2 cell cycle checkpoint arrest and apoptosis. Failure of MMR proteins to detect induced DNA damage results in the survival of mutating cells. MMR protein levels have been found to be higher in nonmelanoma skin cancers than in normal skin, and there is also some evidence of MMR dysregulation.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment
After a doctor examines the carcinoma, a biopsy is needed to confirm the cancer. If tumor cells are visible, treatment is required. Treatment will vary based on the type, size, depth, and location of the carcinoma as well as individual patient concerns. The cancer is most commonly treated through surgery on an outpatient basis in a physicians clinic or office.
A doctor will usually choose from the following main forms of treatment:
You May Like: How Long Does Melanoma Take To Spread
What Are The Possible Complications Of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
The complications of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin could include:
- If the tumor becomes big, develops into a firm mass and ulcerates, it can get secondarily infected with bacteria or fungus
- Metastasis to regional lymph nodes can occur. The tumor can also infiltrate into surrounding structures
- Nodular BCC of Skin can cause cosmetic issues, since these skin tumors can cause large ulceration
- Recurrence of the tumor after a period of time; recurrence is frequently common with large tumors
- Side effects of chemotherapy and radiation
Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Common
If youve been diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma or BCC, you have plenty of company. As the most common type of cancer in the world, doctors diagnose millions of people with BCC every year. In the United States alone, its estimated that about 2 million Americans hear, You have basal cell carcinoma, each year.1
Most people who develop this skin cancer have fair skin that they seldom protected with sunscreen or sun-protective clothing. Before they developed skin cancer, they often noticed signs of sun damage on their skin, such as age spots, patches of discolored skin, and deep wrinkles.
Dermatologist examining patient for signs of skin cancer
You have a greater risk of developing this skin cancer if youve seldom protected your skin from the sun throughout your life or used tanning beds.
Although BCC is most common in people who have fair skin, people of all colors get this skin cancer.
For most people, BCC is not life-threatening. It tends to grow slowly. It seldom spreads to another part of the body. Even so, treatment is important.
When found early, this skin cancer is highly treatable. An early BCC can often be removed during an appointment with your dermatologist.
Given time to grow, this skin cancer can grow deep, injuring nerves, blood vessels, and anything else in its path. As the cancer cells pile up and form a large tumor, the cancer can reach into the bone beneath. This can change the way you look, and for some people the change may be disfiguring.
Recommended Reading: What Is Soft Tissue Carcinoma
What Are The Risk Factors For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma are all skin cancers caused by exposure to damaging ultraviolet raysfrom natural and artificial sunlight. There’s also a genetic condition called basal cell nevus or Gorlin syndrome, which can cause people to develop hundreds of basal cell skin cancers, but it’s extremely rare, says Dr. Christensen.
People at the highest risk for basal cell carcinoma tend to have fair or light-colored skin, a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Fair-skinned people have a 50 percent risk of developing basal skin cancer at some point in their lives, Dr. Christensen says. The cancer is the result of cumulative damage of years spent in the sun, and may take 20 years to manifest.
Although it’s often more common in older people, it can occur in younger adults, too.
Basal cell carcinoma spreads very slowly and very rarely will metastasize, Dr. Christensen says. But if it’s not treated, basal cell carcinoma can continue to grow deeper under the skin and cause significant destruction to surrounding tissues. It can even become fatal. For example, an untreated basal cell carcinoma on the face can grow into the bones and, over time, directly into the brain, Dr. Christensen says.
What Will Happen After Treatment
Youll be glad when treatment is over. Your doctor will want you to check your skin at least once a month. It will be very important to protect yourself from getting too much sun.
For years after treatment ends, you will see your skin cancer doctor. At first, your visits may be every few months. Then, the longer youre cancer-free, the less often the visits are needed. Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. Your doctor will ask about symptoms and check you for signs of the cancer coming back or a new skin cancer. Other exams and tests may also be done.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as good as you can.
You May Like: How Can Skin Cancer Kill You
Basal Cell Carcinoma Staging
Staging;is the process of determining whether cancer has spread and, if so, how far. The stage of the disease may affect the treatment plan.
The stage is based on the size of the tumor, how deeply into the skin it has grown, and whether cancer has spread beyond the tumor to the lymph nodes. Your doctor will look at the results of the biopsy to determine the stage.;In rare cases, your doctor may recommend imaging such as CT or PET-CT scan to see if the cancer has spread beyond the skin
Stages are numbered in Roman numerals between 0 and IV.
Most non-melanoma skin cancers are Stage 0 or Stage 1. Stage 3 and 4 are relatively rare. Based on the type of cancer, the stage of cancer, your overall health, and other factors, your doctor works with you to develop a treatment plan.
High risk features for primary tumor staging
- Depth/invasion: >2 mm thickness , Clark level IV, Perineural invasion
- Anatomic: Primary site ear
- Location: Primary site hair-bearing lip
- Differentiation: Poorly differentiated or undifferentiated
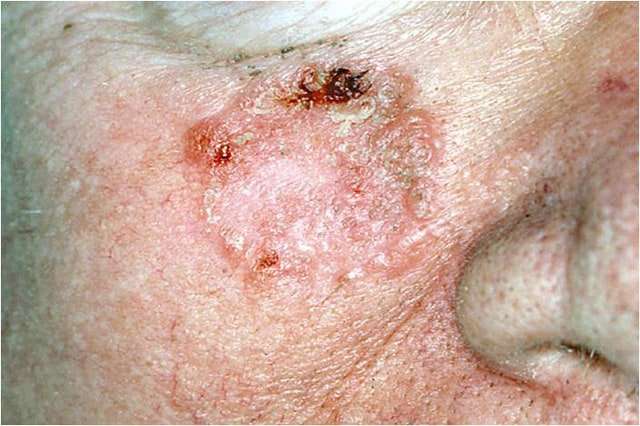
Pigment Basal Cell Carcinoma
The pigmentation can be found in different clinical versions of basal cell carcinoma including nodular, micronodular, multifocal and superficial BCC, and the color varies from dark brown to black . Histology showed nests of basaloid cells, abundance of melanin and melanophages, and moderate inflammatory infiltrate. The melanocytes are located among tumor nests, while the melanophages are present in the stroma. The differential diagnosis has to be made with malignant melanoma.
An irregular, periphery spreading erosive pigmented plaque on head of a 78 years old woman
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Basal Cell Carcinoma
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma is an aggressive type of skin cancer that requires surgical treatment. Subtypes of infiltrative basal cell lesions include micronodular carcinoma and morpheaform carcinoma.
Causes: Infiltrative forms of basal cell cancer, like those of the nodular and superficial types, are linked to both genetic factors and environmental factors such as prolonged sun exposure in youth.
Symptoms: The symptoms of infiltrative basal cell lesions vary according to subtype. Micronodular lesions are typically firm, yellowish-white in color, and have a distinct border. Morpheaform lesions resemble plaque or scar tissue, have vague and far-reaching borders, and are prone to crusting and bleeding.
Diagnosis and Treatment: A thorough skin biopsy is necessary for this type of basal cell cancer, as infiltrative lesions are visually easy to mistake for other non-cancerous forms of scar tissue. Surgical excision with margin examination, radiation therapy, and Mohs micrographic surgery are the most effective treatment options.
Once a patient has been diagnosed with one of the types of basal cell cancer, he or she can discuss treatment options with medical professionals and can proceed with having the cancer removed. Because several effective basal cell surgical procedures and medication options are available, patients who are diagnosed while the disease is in early stages often have a very good prognosis.