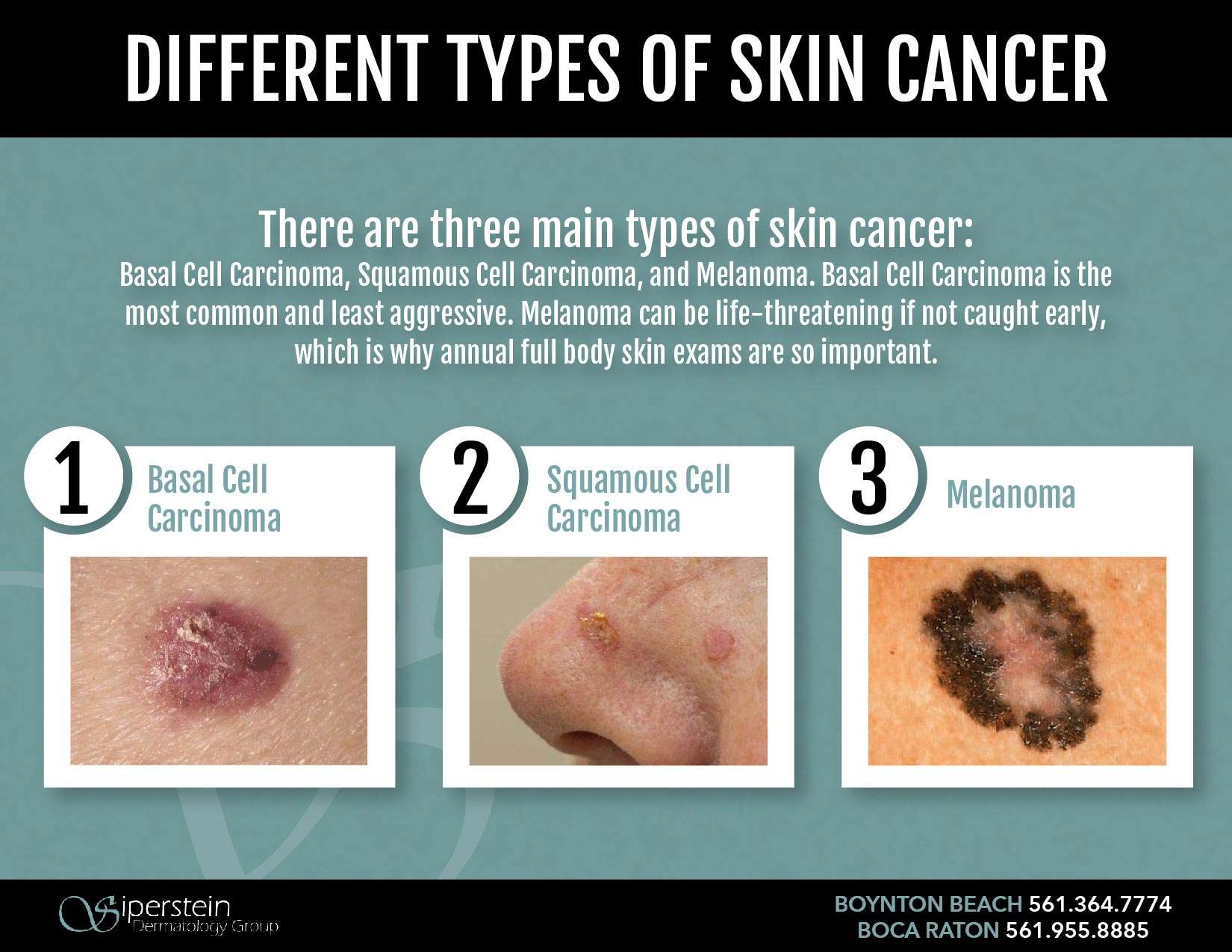
Who Is At Risk
Much like with BCC, the more time you spend in the sun, the more at risk you are for developing SCC. About 90% of nonmelanoma skin cancers are caused by sun exposure, and people who have tanned indoors have a 67% higher risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma.
Your risk for SCC is higher if you:
- Have a history of skin cancer
- Have a history of unprotected exposure to the sun or tanning beds
- Have a weakened immune system due to a chronic condition or medication
- Are over age 50
- Have a history of chronic skin infections, precancerous skin growths or human papillomavirus
What Happens If Basal Cell Carcinoma Is Left Untreated
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer, and it is considered very low risk for metastasizing and spreading to other parts of the body. It is typically very slow-progressing and is usually diagnosed and treated in very early stages. If left untreated, basal cell carcinomas can be locally destructive to the tissues where it grows, and it can invade deeper structures such as nerves, cartilage, and even bone. In most cases, basal cell carcinoma develops on the face, ears, neck, head, shoulders, hands, and other areas that receive frequent sun exposure. The tumors may look like raised bumps on the skin that are usually smooth and pearly/shiny in appearance. Blood vessels can sometimes be seen within the lesions, and in some cases, a wound may form and bleed easily.
Squamous Cell Carcinomas Are More Likely To Spread
Like basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas are curable and can usually be removed completely when caught in time. They are, however, more dangerous than BCC because of their higher likelihood to spread. SCC is more likely to grow into the deeper layers of skin and other tissues in the body than BCC. While basal cell carcinoma usually does not grow into other areas of the body, it can rarely grow into a large tumor on the skin.
Recommended Reading: Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Influence Of Traditional Clinicopathological Melanoma Classification On Prognosis And Management
It has further been suggested that the traditional clinicopathological classification scheme has little if any clinical relevance, particularly in terms of its influence on prognosis and in directing patient management. Indeed it is true that the major histogenetic subtype is not an independent predictor of outcome in patients with clinically localized primary cutaneous melanomas . However, there are some notable exceptions. It is now known, for example, that the desmoplastic melanoma subtype, particularly its pure form, behaves more like a sarcoma than other subtypes of melanoma, with more frequent haematogenous metastasis than lymphatic metastasis . In fact, as a consequence, sentinel node biopsy is not offered to patients with desmoplastic melanomas in some melanoma treatment centres because of the very low frequency of sentinel node positivity . Furthermore, because of its propensity for local recurrence and the frequent difficulty in obtaining adequate excision margins, post operative radiotherapy is often administered in patients with desmoplastic melanoma . This provides another example of how management is impacted by melanoma subtype.
Does Skin Cancer Affect People With Skin Of Color
People of all skin tones can develop skin cancer. If you are a person of color, you may be less likely to get skin cancer because you have more of the brown pigment, melanin, in your skin.
Although less prevalent than in nonwhite people, when skin cancer does develop in people of color, its often found late and has a worse prognosis. If youre Hispanic, the incidence of melanoma has risen by 20% in the past two decades. If youre Black and develop melanoma, your five-year survival rate is 25% lower than it is for white people . Part of the reason may be that it develops in less typical, less sun-exposed areas and its often in late-stage when diagnosed.
Also Check: Skin Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic
What Exactly Is Melanoma
One of three main types of skin cancer , melanoma occurs when cancer strikes your melanocytesthe pigment-producing cells in your skin that give your skin pigment when you freckle or tan. When these cells turn cancerous, you might see a mole thats large, uneven, or somehow doesnt look like your others.
While fair-skinned folk are most prone, people with darker skin get melanomas too, and are often diagnosed later. Melanoma is less prevalent than its sister skin cancers, but spreads faster to other organs. Deep breath thought: When you catch it early enough, its almost always curable.
Unfortunately, about 5% of melanomas are particularly stealth and often diagnosed at a later stage. Thats because they dont resemble the tell-tale brown or black mole that we associate with the cancer. Amelanotic melanomas lack pigment and can be clear, flesh-tone, or pinkish in color. Theyre sneaky!
What Are The Four Main Types Of Melanoma Of The Skin
Superficial spreading melanoma
What you should know: This is the most common form of melanoma.
How and where it grows: It can arise in an existing mole or appear as a new lesion. When it begins in a mole that is already on the skin, it tends to grow on the surface of the skin for some time before penetrating more deeply. While it can be found nearly anywhere on the body, it is most likely to appear on the torso in men, the legs in women and the upper back in both.
What it looks like: It may appear as a flat or slightly raised and discolored, asymmetrical patch with uneven borders. Colors include shades of tan, brown, black, red/pink, blue or white. It can also lack pigment and appear as a pink or skin-tone lesion .
Lentigo maligna
What you should know: This form of melanoma often develops in older people. When this cancer becomes invasive or spreads beyond the original site, the disease is known as lentigo maligna melanoma.
How and where it grows: This form of melanoma is similar to the superficial spreading type, growing close to the skin surface at first. The tumor typically arises on sun-damaged skin on the face, ears, arms or upper torso.
What it looks like: It may look like a flat or slightly raised, blotchy patch with uneven borders. Color is usually blue-black, but can vary from tan to brown or dark brown.
Acral lentiginous melanoma
What you should know: This is the most common form of melanoma found in people of color, including individuals of African ancestry.
Also Check: Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Skin Cancer Types And Treatment Options
While there are many different types of skin cancer, there are four common types that will be discussed. Here are the signs, symptoms, and treatments for each type of common skin cancer.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is among the most common and least worrisome type of skin cancer. It often develops on areas of the skin that are the most exposed to sunlight, including the scalp, face, and neck area.
It shows itself as a mildly transparent bump on the skin, though it can take other forms as well.
Some signs of this type of cancer can include:
- Pearly white bumps on the skin, or a bump of skin with a translucent outside these often have visible blood vessels underneath and has a tendency to rupture or bleed
- Brown, black, or blue lesions with a raised, translucent border
- Scaly reddish patches on the back or chest
- Waxy white lesions without a visible border
- While basal cell carcinoma is usually not dangerous, you should contact a doctor if you notice any sudden changes to an existing bump, or if a bump that was previously removed has resurfaced.
If you should discover a bump on your skin, dont worrybasal cell carcinoma can usually be removed with a simple skin biopsy, or removing the small piece of cancerous skin. Cases of basal cell carcinoma spreading or developing into other types of cancer are rare, but you should still talk with your doctor about it to be safe.
Melanoma
There are steps you can take to find out if your mole is normal and healthy.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
Questions to ask your dermatologist may include:
- What type of skin cancer do I have?
- What stage is my skin cancer?
- What tests will I need?
- Whats the best treatment for my skin cancer?
- What are the side effects of that treatment?
- What are the potential complications of this cancer and the treatment for it?
- What outcome can I expect?
- Do I have an increased risk of additional skin cancers?
- How often should I be seen for follow-up checkups?
Recommended Reading: Well Differentiated
Risk Factors Of Skin Cancer
Anyone can get skin cancer, however, certain factors may increase your chances of getting it. These factors include:
- Fair skin. Less melanin in your skin means you have less protection from UV radiation. Natural blonds or redheads, those with light-colored eyes, and freckles make you a bigger candidate for skin cancer. Those who have a history of sunburns also have an increased skin cancer risk .
- Considerable sun exposure. If you like to work on your tan, you might not be doing yourself any favors, especially if youre not protected by sunscreen, clothing, or a hat. The extra UV rays make you more prone to skin cancer.
- Moles. Moles, especially irregular or large moles, are more likely to become cancerous down the road. If you have abnormal moles, be sure to check them regularly to make sure they havent changed.
- Sunny climates. You may live in a sunny paradise, but it means youre exposing yourself to more sunlight than folks who live in cooler climates. Make sure you cover up to avoid putting yourself at additional risk.
- Weakened immune systems. People with weakened immune systems, including those with HIV/AIDS or those with organ transplants, should be aware of their increased risk of skin cancer.
- History of skin cancer. If your parents or siblings have had skin cancer, it should serve as a warning that you should be extra cautious. Additionally, if you have a personal history with skin cancer, you may be at risk to get it again.
A Dangerous Skin Cancer
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that begins in cells known as melanocytes. While it is less common than basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma , melanoma is more dangerous because of its ability to spread to other organs more rapidly if it is not treated at an early stage.
Learn more about melanoma types, risk factors, causes, warning signs and treatment.
Melanoma Fact
Only 20-30% of melanomas are found in existing moles.
While 70-80% arise on normal-looking skin.
Don’t Miss: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
What Is Skin Cancer
Within our bodies, our cells are constantly replicating and growing. The death and subsequent regeneration of cells cause rapid and constant turnover, and its how we heal and repair our bodies. Cancer will occur when cells divide and grow in an uncontrolled manner. This abnormal pattern of growth causes dysregulation and results in a spread to neighboring tissues.
Cancer keeps growing as the cells multiply over and over. When cancer cells grow through normal body tissue, this can create a tumor. This can then spread to other areas of the body, resulting in metastasis or a secondary tumor. While most cancers are due to gene changes that occur over a patients lifetime, some cancers can be genetic and due to the inheritance of faulty genes down family lines.
Skin cancer is classified as the uncontrollable growth of abnormal cells in the outermost skin layer, called the epidermis. When DNA damage goes unrepaired, this triggers the development of mutations, which cause skin cells to multiply rapidly and form tumors.
There are four main types of skin cancer: squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and Merkel cell cancer. While there are a few other skin cancer types, like sarcomas, they are all classified as non-melanoma skin cancers and are rare.
You might also be wondering what skin cancer is most common. Heres a rundown of the different types of skin cancer.
Melanoma Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In Melanocytes
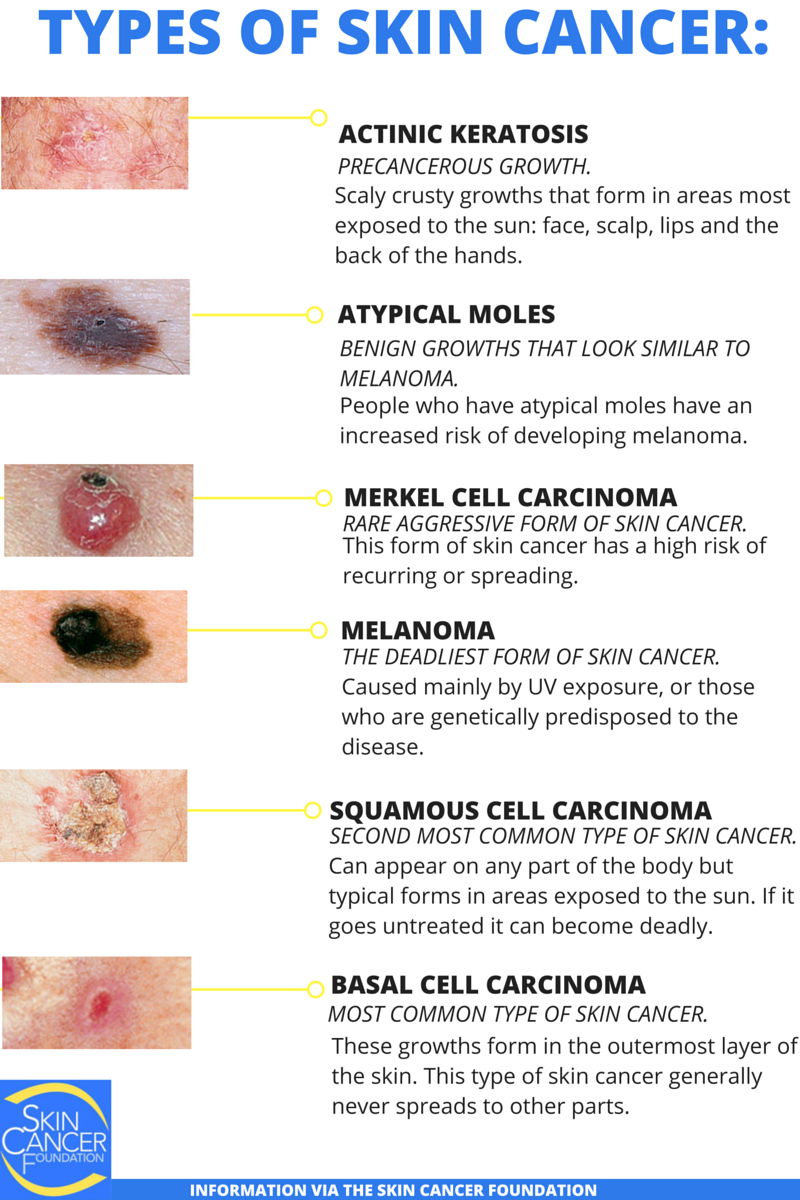
The skin is the bodys largest organ. It protects against heat, sunlight, injury, and infection. Skin also helps control body temperature and stores water, fat, and vitamin D. The skin has several layers, but the two main layers are the epidermis and the dermis . Skin cancer begins in the epidermis, which is made up of three kinds of cells:
- Squamous cells: Thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis.
- Basal cells: Round cells under the squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: Cells that make melanin and are found in the lower part of the epidermis. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun or artificial light, melanocytes make more pigment and cause the skin to darken.
Don’t Miss: Clear Cell Carcinoma Symptoms
The Four Main Types Of Cutaneous Melanoma
Cutaneous melanoma is the most common of these categories, and the four main types of cutaneous melanoma include:
All types of melanoma require immediate attention, as they are more successfully treated when caught in their early stages. If you suspect you may have a form of skin cancer, call or complete our new patient registration form online. No referral is necessary to meet with the multispecialty team of oncologists who specialize in skin cancer.
- BROWSE
How Is Melanoma Diagnosed
Melanoma may be suspected because of a lesions clinical features or because of a history of change. The dermatoscopic appearance is helpful in the diagnosis of featureless early melanoma. Some melanomas are extremely difficult to recognise clinically.
The suspicious lesion is surgically removed with a 2 to 3-mm clinical margin for pathological examination . A partial biopsy is best avoided but may be considered in large lesions.
The pathological diagnosis of melanoma can be very difficult. Histological features of superficial spreading melanoma in situ include the presence of buckshot scatter of atypical melanocytes within the epidermis. These cells may be enlarged with unusual nuclei. Dermal invasion results in melanoma cells within the dermis or deeper into subcutaneous fat.
Immunohistochemical stains may be necessary to confirm melanoma.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Keeping Cancer In Check
Chronic exposure to the sun or intermittent sunburns can lead to skin cancer. Skin cancer risk doubles with five or more sunburns in a lifetime, but just one bad sunburn can double the risk of melanoma. While skin cancer is uncommon in African Americans, Latinos and Asians, it can also be more deadly because they are often diagnosed later in the course of the disease.
Its important to examine your skin regularly. You should report any changes in an existing mole or any new moles to your physician. People with fair complexions have the highest risk of developing skin cancer, but everyone should avoid the sun and practice safety measures to protect their skin.
The American Cancer Society recommends the Slip, Slop, Slap and Wrap policy. When you go out in the sun, slip on a shirt, slop on sunscreen, slap on a hat and wrap on sunglasses to protect your eyes and the sensitive skin around them.
Exposure to the UV rays of tanning lamps is not safe. Tanning lamps give out UV rays, which can cause long-term skin damage and can contribute to skin cancer. Tanning bed use has been linked with an increased risk of melanoma, especially for people under 30. Most doctors and health organizations recommend not using tanning beds and sun lamps.
Also Check: What Is The Best Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Who Is Most At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can develop skin cancer, youre at increased risk if you:
- Spend a considerable amount of time working or playing in the sun.
- Get easily sunburned have a history of sunburns.
- Live in a sunny or high-altitude climate.
- Tan or use tanning beds.
- Have light-colored eyes, blond or red hair and fair or freckled skin.
- Have many moles or irregular-shaped moles.
- Have actinic keratosis .
- Have a family history of skin cancer.
- Have had an organ transplant.
- Take medications that suppress or weaken your immune system.
- Have been exposed to ultraviolet light therapy for treating skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
Also Check: Well-differentiated
How Do You Know If A Spot Is Skin Cancer
To learn more you can read this article on the signs of skin cancer or this article on melanoma symptoms, but dont forget to get any skin concern you may have checked out by your doctor.
You can also read our guide on how to check your skin regularly, if you want to learn more about how to form a skin checking routine for yourself.
Benign Tumors That Start In Melanocytes
A mole is a benign skin tumor that develops from melanocytes. Almost everyone has some moles. Nearly all moles are harmless, but having some types can raise your risk of melanoma. See Risk Factors for Melanoma Skin Cancer for more information about moles.
A Spitz nevus is a kind of mole that sometimes looks like melanoma. Its more common in children and teens, but it can also be seen in adults. These tumors are typically benign and dont spread. But sometimes doctors have trouble telling Spitz nevi from true melanomas, even when looking at them under a microscope. Therefore, they are often removed, just to be safe.
You May Like: Ductal Invasive Carcinoma Survival Rate
Lentigo Maligna And Lentigo Maligna Melanoma
What it is: While lentigo maligna is a very early stage of melanoma that sits on the surface of skin, lentigo maligna melanoma is slow moving yet invasive, spreading into deeper layers. Elderly people are more vulnerable. Its unlikely that a lentigo maligna will morph into a lentigo maligna melanoma over time, but also not impossible. The estimated risk of progression was just three and half percent per year, and based on the patients studied, it took 28.3 years for lentigo maligna to progress into lentigo maligna melanoma, according to a 2019 study in Melanoma Research.
Where youll find it: Highly sun-damaged areas, most commonly your face.
What it looks like: It starts off looking like a patch of brown, a flat freckle, or a sun spot, but then grows in size and changes in pigment.