What Are The Treatments For This Type Of Tumor
The course of treatment will depend on how large your cat’s tumor is and how many tumors there are. The most well-described treatment for SCC of the skin is surgery. Surgery appears to provide the best long-term control of the disease, as long as the tumor can be completely removed, meaning no cancer cells are left behind. If the tumor is small and has not spread to other organs, it may be removed by cryosurgery or various other options.
Tumors of the toes require amputation of the affected toe, and tumors of the nose may require a partial removal of the nose. Treatment of SCCs of the nose is often successful with radiation therapy. This therapy involves using a probe to deliver a high dose of radiation to a very small area that only penetrates a few millimeters of skin. This allows for effective tumor control without making your cat sick from radiation.
Multicentric SCCs may be treated with surgery and/or immune-response modifiers.
The role of chemotherapy, including injecting the chemotherapeutic medication directly into the tumor, remains controversial. Your veterinarian will discuss this option with you.
Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Serious Lets Ask Hugh Jackman
Hugh Jackman is no stranger to skin cancer. In August, 2021 the Australian actor posted an after having a second skin biopsy in two years. He urged fans to get their skin checked. A couple of notes please get skin checks often, please dont think it wont happen to you and, above all, please wear sunscreen.
Jackman is committed to raising awareness by using social media to discuss his skin cancer history. In a follow-up post, he explains If by posting about this I remind one person to go see their dermatologist, Im happy.
In 2017, the last time Jackman dealt with basal cell carcinoma , he posted a photo of himself on Instagram showing the aftermath of skin cancer surgery. He assured fans he was okay in his posts caption, thanking frequent skin checks and amazing doctors.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer, with more than 3.6 million cases diagnosed in the U.S. each year. BCC almost never spreads beyond the original tumor site though, and the cure rate after excisional surgery is above 95 percent in most body areas. So, is this form of cancer even something to worry about?
Basal cell carcinoma is not something to be taken lightly, says Deborah S. Sarnoff, MD, president of The Skin Cancer Foundation. Once youve been diagnosed with a BCC, its very likely that you will develop more over the years, leading to continuous treatment and possibly even disfiguration.
S Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma On The Skin
The following pictures show many of the ways that SCC can appear on the skin.
Rough-feeling, reddish patch
This is an early sign of squamous cell carcinoma.
Round growth with raised borders
This squamous cell carcinoma developed from a pre-cancerous growth called an actinic keratosis.
A sore that won’t heal or heals and returns
On the skin or lips, squamous cell carcinoma can look like a sore.
Age spot
This can be a sign of squamous cell carcinoma, which is why you want a board-certified dermatologist to examine your skin before you treat any age spot.
Raised, round growth
This is a common sign of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.
Animal’s horn
When squamous cell carcinoma looks like this, it tends to grow quickly.
Because this common skin cancer can begin on any part of the body that has squamous cells, it can also develop inside the mouth, on the genitals, inside the anus, or in the tissue beneath a fingernail or toenail.
In these areas, this skin cancer may look like a:
-
Sore or rough patch
-
Raised, reddish patch
-
Wart-like sore
-
Brown or black line beneath a nail
Sore inside your mouth
This squamous cell carcinoma started inside the mouth and grew to cover a larger area.
Dark streak beneath a nail
Squamous cell carcinoma can look like a brown or black line beneath a nail, as shown here.
When it develops around the nail, it can look like a wart that just wont go away. If youve had a wart around a fingernail for years, its time for a dermatologist to examine it.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy
What Percentage Of Squamous Cell Skin Cancers Metastasize
Summary. The reported risk for metastasis in squamous cell carcinomas ranges from 0.5% to 16%, a wide spread that can probably be explained by differences in patient populations. Identifying the characteristics associated with a high risk for metastasis would help in determining the need for adjuvant treatment.
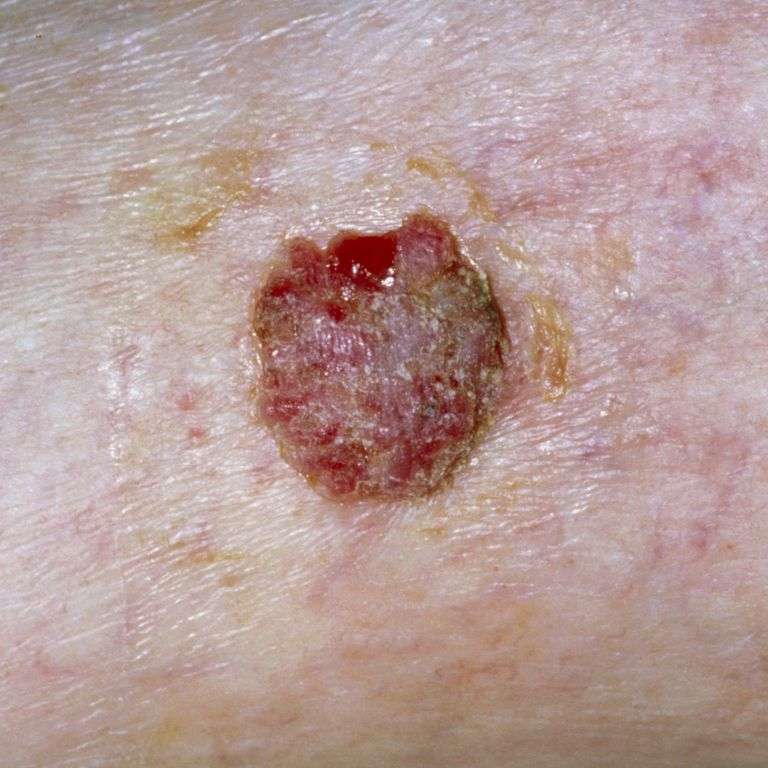
Basal Cell Carcinoma Signs And Symptoms
This type of cancer is usually found on sun-exposed areas of the skin like the scalp, forehead, face, nose, neck and back.
Basal cell carcinomas may bleed after a minor injury but then scab and heal. This can happen over and over for months or years with no visible growth, making it easy to mistake them for wounds or sores. They rarely cause pain in their earliest stages.
Appearance
In addition to the bleeding and healing, these are other possible signs of a basal cell cancer:
- A persistent open sore that does not heal and bleeds, crusts or oozes.
- A reddish patch or irritated area that may crust or itch.
- A shiny bump or nodule that is pearly or translucent and often pink, red or white. It can also be tan, black or brown, especially in dark-haired people, and easy to confuse with a mole.
- A pink growth with a slightly elevated, rolled border and a crusted indentation in the center. Tiny blood vessels may appear on the surface as the growth enlarges.
- A scar-like lesion in an area that you have not injured. It may be white, yellow or waxy, often with poorly defined borders. The skin seems shiny and tight sometimes this can be a sign of an aggressive tumor.
You May Like: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Early Detection Best Practices
When caught promptly, almost all squamous cell carcinomas of the skin can be successfully treated. But when they become more advanced, these skin cancers can become dangerous.
Thats why its important to be on the lookout for any SCC warning signs, including new,changing or unusual skin growths.
Diagnosing Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The main way to diagnose squamous cell carcinoma is with a biopsy. This involves having a small piece of tissue removed from the suspicious area and examined in a laboratory.
In the laboratory, a pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope to determine if it is a skin cancer. He or she will also stage the cancer by the number of abnormal cells, their thickness, and the depth of penetration into the skin. The higher the stage of the tumor, the greater the chance it could spread to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma on sun-exposed areas of skin usually does not spread. However, squamous cell carcinoma of the lip, vulva, and penis are more likely to spread. Contact your doctor about any sore in these areas that does not go away after several weeks.
Don’t Miss: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
How Is Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated
An exact diagnosis will dictate what method of invasive squamous cell carcinoma treatment will be most effective. Options include:
- Mohs surgery: using a scalpel, this procedure surgically removes cancerous cells while leaving behind unaffected areas.
- Chemotherapy: using intravenous drugs, this treatment floods the body with medicine designed to break down and destroy infected cells.
- IG-SRT: using radiotherapy technology, this method uses low-level doses of radiation to target cancer from the surface down, achieving results without cutting or drugs.
Talk with your dermatologist to determine whats best for you.
Waited For My Scheduled Skin Check
I already had a regular skin check scheduled with my dermatologist in a few weeks, so I decided to wait until that appointment to have it looked at. And honestly, within a week I was ready to call her to have her look at it sooner because it was that painful. Every time it rubbed against my clothing, it hurt. When I turned over at night while I was sleeping, it hurt and the pain woke me up.
During the appointment, when I told my doctor it appeared out of nowhere and it hurt, she told me she thought it was squamous cell skin cancer because they tend to appear suddenly. She biopsied it, and when the results came back as squamous cell, we scheduled surgery. During the surgery, I asked her why it had hurt so much, and she said that was typical of squamous cell areasâ they grow rather suddenly and become a placeholder of space in a place they dont belong.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Skin Cancer
You May Like: Does Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Cbd Oil For Cats With Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
All cats respond to situations in their unique ways But when it comes to feline SCC, there’s one underlying commonality that all affected cats can relate to, which is the fact that oral SCC is very uncomfortable. Even though cats frequently hide away and cover up signs of pain as best as they can, cats with SCC are still experiencing serious levels of discomfort.
If your cat has oral SCC, we highly suggest introducing CBD oil as a botanical supplementary part of their lifestyle. Known for its pain-relieving abilities and its calming effects, cannabidiol oil is an all-natural way of minimizing discomfort levels for the sake of helping your cat maneuver through the process of oral SCC treatment as comfortably as possible.
From capsules that are easy to swallow and chewy snacks for cats to pet-friendly CBD oils and externally-applied hemp-derived creams, Innovet has a wide array of cannabidiol products that are safe for cats. Help your cat survive the intensity of feline SCC treatments by adding CBD into the mix.
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Cats
Also known as oral squamous cell carcinoma , squamous cell carcinoma in cats is a type of cancer that takes place in the mouths of felines. The two most common areas for this type of cancer to arise include the tongue as well as the upper or lower jaw.
As cancer, most tumors that SCC causes has the potential to spread throughout the body, even though it begins as a contained cancerous tumor only in the mouth. So, a malignant oral tumor is one that can soon spread to other parts of your cat’s body, which leads to something known as metastasis.
As a metastatic form of cancer, it has the potential to spread to the surrounding lymph nodes, which poses a dangerous threat to the overall well being of your cat. If the cancer cells move from the mouth to the lymph nodes, it can travel throughout the body and create cancer in other organs, complicating the treatment process and making it hard to get your cat into a state of remission successfully.
Knowing that SCC can evolve from a contained tumor to a metastatic case of cancer is a very daunting fact to digest. So, let’s step back for a moment and focus on what you can do to help identify a possible case of SCC in your cat.
The sooner the tumor location is detected, the more effective the treatment will be because the cancer is tackled at an earlier stage. How about we explore the symptoms of oral SCC in cats!
Recommended Reading: Immunotherapy For Malignant Melanoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
Certain things make you more likely to develop SCC:
Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist who specializes in skin conditions. They will:
- Ask about your medical history
- Ask about your history of severe sunburns or indoor tanning
- Ask if you have any pain or other symptoms
- Ask when the spot first appeared
- Give you a physical exam to check the size, shape, color, and texture of the spot
- Look for other spots on your body
- Feel your lymph nodes to make sure they arent bigger or harder than normal
If your doctor thinks a bump looks questionable, theyll remove a sample of the spot to send to a lab for testing.
Continued
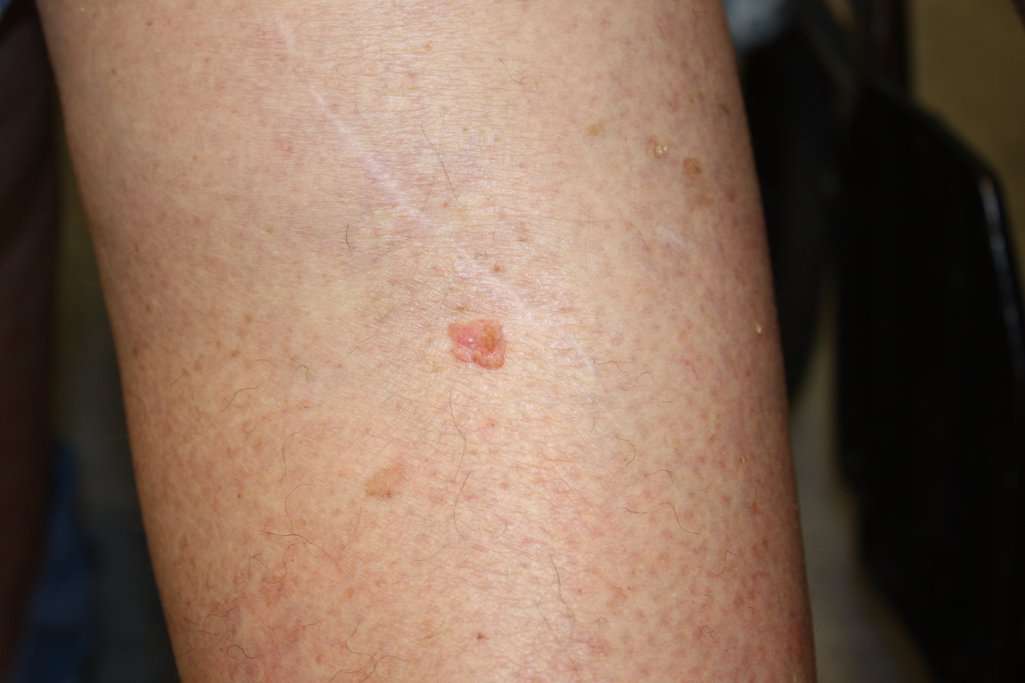
Do Not Wait To Have Painful New Areas Checked
Squamous cell skin cancer can be unpredictable. My first squamous cell area did not hurt, but it bled. My second squamous cell area did not bleed, but it hurt. If you have an area appear suddenly and it doesnt go away within a relatively short period of time, please make an appointment to have it looked at.
Squamous cell carcinoma can spread to your tissue, bones, and lymph nodes, making it harder to treat. Squamous cell is more dangerous than basal cell, and early diagnosis and treatment are best.
Also Check: Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Does Skin Cancer Hurt To The Touch
In the case of melanoma, a painless mole may start getting tender, itchy, or painful.
Other skin cancers generally do not hurt to touch until they have advanced to become large. The peculiar absence of pain in a skin sore or a rash often directs the diagnosis toward skin cancer.
When skin cancer has grown considerably, it may ulcerate and cause symptoms, such as pain and discomfort. Skin cancer generally presents as:
- New growth on the skin
- A changing mole or a mole that looks different from others
- A rough or scaly patch on the skin
- A non-healing ulcer or sore or one that keeps coming back
- A mole or spot that has an irregular shape or appearance
- A skin patch or mole with an uneven color
- A brown or black streak under a nail
- A skin patch that itches or bleeds
- A skin patch or growth that is increasing in size
Skin cancer can be detected quite easily since you can see the changes occurring on your skin. Sometimes skin cancer may arise at relatively concealed places, such as inside your mouth, around your genitals, or under a nail. Thus, you must examine yourself thoroughly, preferably in front of a mirror or with the help of your partner, friend, or family member, to look for any signs that may indicate skin cancer.
Causes Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cells are a normal skin cell near the epidermis . With SCCs, your body grows too many of the cells. Usually its because the cells DNA has been damaged. That damage comes mainly from sunlight but other things can damage it including:
- Other UV light exposure .
- Ionizing radiation .
- Viral infections .
- Chemicals .
Also, certain genetic conditions, illnesses that cause skin inflammation or scarring , and medical treatments that suppress the immune system , can increase your risk of SCCs. These illnesses and treatments cause chronic damage to the skin and/or the inability of DNA to repair itself.
Dr. Rx
The virus that causes warts can cause some SCCs. Sometimes patients with numerous SCCs who are immunosuppressed may be able to decrease their risk of getting an SCC by getting the HPV vaccination. Dr. Levy
Don’t Miss: Chances Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreading
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Squamous cells are small, flat skin cells in the outer layer of skin. When these cells become cancerous, they typically develop into flat or raised, rounded skin tumors. Sometimes the skin around the tumors gets red and swollen.
Most cases of squamous cell carcinoma occur in people who have spent lots of time in the sunespecially those with fair skin and blue eyes. Some cases develop on skin that has been injured or exposed to cancer-causing agents. This type of squamous cell cancer can develop on:
-
Scars, burns, and long-lasting ulcers
-
The legs and body of workers exposed to poisons, harsh chemicals, and agents like tar and soot
-
Skin affected by genital warts
-
Red patches of skin covered with white scales, a condition called psoriasis, treated with certain therapies.
People with a weakened immune system are at especially high risk of developing squamous cell cancer. This includes people who:
-
are HIV positive
-
have received an organ transplant
-
Taking immune-suppressing medications.
When it is found early and removed, squamous cell carcinoma causes little skin damage. But if the cancer is not removed when itâs small, it can leave a scar. In a small number of cases, the cancer spreads to the lymph nodes and other parts of the body. Squamous cell carcinoma is most likely to spread when it is on the lips, ears, or genitals.
What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinomas are usually raised growths, ranging from the size of a pea to the size of a chestnut. They may appear as scaly red patches, open sores or protruding growths with a dented center, or they may look like a wart. Most are found in areas of the body that are frequently exposed to the sun, such as the ears, lips, face, balding scalp, neck, hands, arms, and legs. Less commonly, they may appear on mucous membranes and genitals. Regardless of what form the bumps take, they do not heal or go away on their own.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Is Mohs Surgery Better Than Excision
As mentioned earlier, Mohs is more reliable and boasts a higher cure rate than standard surgical excisions. Plus, Mohs is often the cheaper of the two surgeries. For these reasons, more and more patients are directed toward Mohs micrographic surgery to eliminate their basal or squamous cell carcinoma.
What Causes Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Repeated exposure to ultraviolet light, either from the sun or from tanning beds, is the main cause of SCC. Indoor tanning is linked to about 168,000 cases of SCC in the US each year.
People with light skin, light hair , and light eyes have a higher risk of skin cancer in general, as well as SCCs. However, most of the skin cancers that develop in African Americans are SCCs.
Other risk factors include:
- Having an impaired immune system, including:
- Cancers of the blood or bone marrow.
- Chronic infections like HIV.
- Taking immunosuppressive medications, including chemotherapy or some biologic medications.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival