What Does It Mean If In Addition To Cancer My Report Also Mentions Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia Atypical Lobular Hyperplasia Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Intraductal Carcinoma Lobular Carcinoma In Situ Or In
These are terms for certain atypical or pre-cancer changes that can sometimes be seen on biopsy that arent as serious as invasive cancer. If they are found in a needle biopsy that also shows invasive cancer, they are typically not important. They may, however, need to be removed completely as a part of treatment. If they are seen on an excisional biopsy at or near a margin , more tissue may need to be removed .
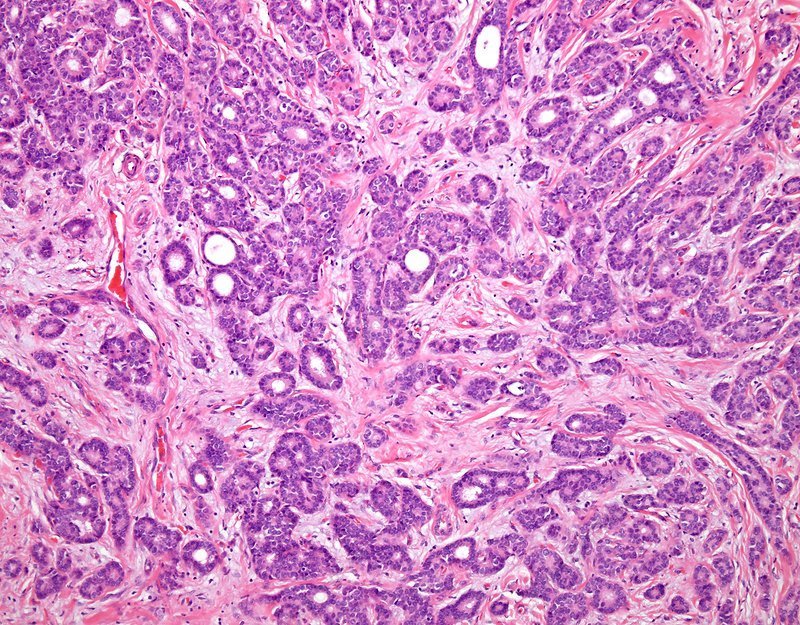
What Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Breast ducts are the passageways where milk from the milk glands flows to the nipple.
Invasive ductal carcinoma is cancer that happens when abnormal cells growing in the lining of the milk ducts change and invade breast tissue beyond the walls of the duct.
Once that happens, the cancer cells can spread. They can break into the lymph nodes or bloodstream, where they can travel to other organs and areas in the body, resulting in metastatic breast cancer.
What If My Report Mentions Margins Or Ink
When an entire tumor is removed, the outside edges of the specimen are coated with ink, sometimes even with different colors of ink on different sides of the specimen. The pathologist looks at slides of the tumor under the microscope to see how close the cancer cells get to the ink . If cancer cells are touching the ink , it can mean that some cancer was left behind, and more surgery or other treatments may be needed. Sometimes, though, the surgeon has already removed more tissue to help make sure that this isnt needed.
Sometimes, all of the invasive cancer is removed, but there may be pre-cancer or another serious condition at or near the margin, such as ductal carcinoma in situ or lobular carcinoma in situ .
If your pathology report shows positive margins, your doctor will talk to you about what treatment is best.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread To Organs
Treatment For Invasive Breast Cancer
As with all types of breast cancer, the treatments youre offered will depend on the features of invasive breast cancer seen under the microscope. This includes the size, grade, hormone receptor status and HER2 status.
Treatment aims to remove the cancer and reduce the risk of it coming back or spreading to other parts of the body.
Side Effects And Complications
All treatments have some side effects that range from mild to severe. Most clear up when treatment ends, but there can be some lasting complications.
Its important to tell your oncologist about all symptoms, even if they seem minor. Your healthcare team will work with you to ease side effects and deal with complications.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Melanoma Survival Rate
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider About Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Fully understanding your situation can empower you and help you take control of your health. Here are some questions you might want to ask your healthcare provider:
- What stage of invasive ductal carcinoma do I have?
- How far has my cancer spread?
- What are my treatment options?
- How long will my treatment take?
- Will I be able to work during my treatment?
- What are my chances of survival?
What Is A Breast Papilloma And Is It Cancer
Also called intraductal papilloma, a breast papilloma is a small, wartlike growth in the breasts milk ducts. This benign condition may cause a clear or bloody discharge from the nipple, or you may feel a small lump behind or next to the nipple. Having one papilloma does not raise your breast cancer risk, though having several of these growths has been linked to higher risk.
Recommended Reading: Stage Iii Melanoma Treatment
What Are Lobular Carcinoma In Situ And Atypical Lobular Hyperplasia
Lobular carcinoma in situ is not considered breast cancer or a precancer because it doesnt turn into invasive cancer if untreated. LCIS and atypical lobular hyperplasia , a similar noncancerous condition, are subtypes of lobular neoplasia, a disorder marked by abnormal cells in the breasts lobules . Since LCIS and ALH raise your risk for breast cancer in the future, if youve been diagnosed with either of them, talk to your doctor about how often you should be screened for breast cancer and whether you should have any additional screening tests.
How Can I Reduce My Risk For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Like most cancers, knowing your family history can help you take preventative steps, such as early screenings and mammograms. Even though invasive ductal carcinoma cant be prevented altogether, there are steps you can take to lower your risk:
- Maintain a healthy body weight.
- Dont smoke.
- Eat a healthy, well-balanced diet.
- Undergo genetic testing for gene mutations if recommended based on family history.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Spreading To Lymph Nodes
Part 3histologic Types Of Invasive Breast Carcinoma
Invasive carcinomas are divided into two large categories based on the histology: invasive ductal and invasive lobular. Many of the histologic subtypes, such as tubular carcinoma, mucinous carcinoma, medullary carcinoma, invasive papillary carcinoma, invasive micropapillary carcinoma, and invasive apocrine carcinoma, are considered special variants of invasive ductal carcinoma. As with in situ lesions, the designations invasive ductal and invasive lobular refer to a growth pattern and do not necessarily imply a site of origin. A morphologic study by Wellings and colleagues19 demonstrated that most breast carcinomasboth ductal and lobularoriginate in the terminal duct lobular unit.
Frederick C. Koerner MD, in, 2009
How Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer Diagnosed
Inflammatory breast cancer can be difficult to diagnose. Often, there is no lump that can be felt during a physical exam or seen in a screening mammogram. In addition, most women diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer have dense breast tissue, which makes cancer detection in a screening mammogram more difficult. Also, because inflammatory breast cancer is so aggressive, it can arise between scheduled screening mammograms and progress quickly. The symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer may be mistaken for those of mastitis, which is an infection of the breast, or another form of locally advanced breast cancer.
To help prevent delays in diagnosis and in choosing the best course of treatment, an international panel of experts published guidelines on how doctors can diagnose and stage inflammatory breast cancer correctly. Their recommendations are summarized below.
Minimum criteria for a diagnosis of inflammatory breast cancer include the following:
- A rapid onset of erythema , edema , and a peau dâorange appearance and/or abnormal breast warmth, with or without a lump that can be felt.
- The above-mentioned symptoms have been present for less than 6 months.
- The erythema covers at least a third of the breast.
- Initial biopsy samples from the affected breast show invasive carcinoma.
Imaging and staging tests include the following:
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Recommended Reading: Well-differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
How Grade Affects Treatment Options
Your treatment team will consider the grade of your cancer when deciding which treatment to offer you.
If you have grade 3 breast cancer, youre more likely to be offered chemotherapy. This is to help destroy any cancer cells that may have spread as a result of the cancer being faster growing.
Chemotherapy is less likely for grade 1 and grade 2 cancers.
The grade of your cancer alone will not determine what treatment youre offered. Your treatment team will consider the grade alongside all other information about your cancer when deciding on the best treatment options for you.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Skin Cancer Naturally
Additional And Relevant Useful Information For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast :
- Japan is an exception of a developed nation with lowered incidences of breast cancer, unlike European nations and America.
- Current studies have shown that aromatase inhibitors, medications that block estrogen hormonal effects in the body, reduce the risk of recurrence of breast cancer. Recent studies have shown that treatment using aromatase inhibitors can be given up to 10 years without affecting the quality of life of women
- Tumors that are negative for estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2/neu have worse prognosis. Such tumors are called âtriple-negativeâ tumors
The following DoveMed website links are useful resources for additional information:
Recommended Reading: 2nd Stage Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Dcis
DCIS usually has no symptoms. Most cases of DCIS are found during routine breast screening or if a mammogram is done for some other reason.
Occasionally DCIS is found when someone has a breast change such as a lump or discharge from the nipple. However, if someone with DCIS has a breast change its more likely they will also have an invasive breast cancer.
Some people with DCIS also have a type of rash involving the nipple known as Pagets disease of the nipple, although this is rare.
Symptoms Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Make an appointment to see your doctor if you notice anything different or unusual about the look and feel of your breasts.
The symptoms of breast cancer include:
- a new lump or thickening in your breast or armpit
- a change in size, shape or feel of your breast
- skin changes in the breast such as puckering, dimpling, a rash or redness of the skin
- fluid leaking from the nipple in a woman who isnt pregnant or breast feeding
- changes in the position of nipple
Don’t Miss: Stage 4 Basal Cell Carcinoma Life Expectancy
How Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast Diagnosed
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast may be diagnosed in the following manner:
- Complete physical examination with comprehensive medical and family history evaluation
- The following information may be sought by the healthcare provider:
- Family history of breast cancer and ovarian cancer
- Family history of BRCA 1 or BRCA 2 mutation
- History of pregnancy
How Fast Does Dcis Progress
Grade 1 DCIS is almost always ER and PR positive and is a very slow growing form of cancer. It can take years, even decades, to see progression of the disease. In some cases, it may take such a long time to spread beyond the breast duct that it is not an event that will happen during a persons lifetime.
Also Check: Well Differentiated Meaning
You May Like: Prognosis Of Skin Cancer
What Do Cancer Stages And Grades Mean
The stage of a cancer describes the size of a tumour and how far it has spread from where it originated. The grade describes the appearance of the cancerous cells.
If youre diagnosed with cancer, you may have more tests to help determine how far it has progressed. Staging and grading the cancer will allow the doctors to determine its size, whether it has spread and the best treatment options.
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:
Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Prognosis
What Can You Tell Me About Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stages
Staging describes how advanced your cancer is, based on the location, size and how far it has spread. There are five stages of ductal carcinoma:
- Stage 0: The cancer is localized to your milk ducts. This stage is also known as non-invasive ductal carcinoma in situ.
- Stage 1: The cancer has spread outside of your milk ducts to the breast tissue, but it hasnt spread to your lymph nodes. In some cases, the cancer may have spread to your lymph nodes, but not to your surrounding breast tissue.
- Stage 2: The tumor is small and has spread to one to three of your lymph nodes. Or, the tumor is larger, but hasnt spread to any of your lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: The cancer has often spread to more than three of your lymph nodes or is causing inflammation of most of your breast skin, but hasnt spread to other areas of your body.
- Stage 4: The cancer has spread to your other organs, which may include your bones, liver, lungs, brain, chest wall or distant lymph nodes.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
You may want to ask your provider:
- What type of breast cancer recurrence do I have?
- Has the cancer spread outside the breast?
- What stage is the breast cancer?
- What is the best treatment for this type of breast cancer?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Most breast cancer recurrences respond well to treatments. You may be able to try new drugs or combination therapies in development in clinical trials. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option based on your unique situation.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 03/24/2021.
References
Read Also: Is Stage 2 Breast Cancer Bad
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Survival Rate
How Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast Treated
Treatment options available for individuals with Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast are dependent upon the following:
- Type of cancer
- The staging of the cancer
- Whether the cancer cells are sensitive to certain particular hormones, and
- Personal preferences
In general, breast cancer stages range from 0 to IV. 0 may indicate a small and non-invasive cancer, while IV indicates that the cancer has spread to other areas of the body. Briefly, as per US National Cancer Institute , breast cancer is staged as follows:
- Stage 0 : The abnormal cancer cells are confined to their site of origin
- Stage I: The tumor is 2 centimeters in diameter or less, and has not spread outside the breast
- Stage II: The tumor may be up to 5 centimeters in diameter and may have spread to lymph nodes. Another criteria is that the tumor may be larger than 5 centimeters in diameter, but has not spread to surrounding lymph nodes
- Stage III: The tumor may be more than 5 centimeters in diameter and may have spread to several axillary lymph nodes, or to the lymph nodes near the breastbone. The cancer may also have spread to the breast skin/chest wall, causing ulcer-like sores, or a swelling
- Stage IV: The tumor has spread outside the breast and to other organs, such as the bones, liver, lungs, or brain, regardless of its size
If breast cancer is diagnosed, staging helps determine whether it has spread and which treatment options are best for the patient.
Hormone therapy:
Dont Miss: What Does Stage 3 Melanoma Mean
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment
What is invasive ductal carcinoma?
About 80 percent of all breast cancer diagnoses.
Carcinoma refers to a type of cancer that begins in the skin cells or the tissues lining your internal organs. Adenocarcinomas are more specific types of carcinomas that originate in the glandular tissue of the body.
Invasive ductal carcinoma, also known as infiltrating ductal carcinoma, gets its name because it begins in the milk-carrying ducts of the breast, and spreads to surrounding breast tissues. The two most common forms of invasive breast cancer are:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. Accounts for
- . This type begins in the milk-producing lobules.
While IDC can affect women at any age, its most frequently diagnosed in
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with IDC, rest assured that there are many different forms of treatment available.
The treatments for IDC fall into two main types:
- Local treatments for IDC target the cancerous tissue of the breast and the surrounding areas, such as the chest and lymph nodes.
- Systemic treatments for IDC are applied throughout the body, targeting any cells that may have traveled and spread from the original tumor. Systemic treatments are effective at reducing the likelihood that the cancer will return once it has been treated.
Don’t Miss: Does Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What Does It Mean If My Doctor Asks For A Special Molecular Test To Be Performed On My Specimen
Molecular tests such as Oncotype DX® and MammaPrint® may help predict the prognosis of certain breast cancers, but not all cases need these tests. If one of these tests is done, the results should be discussed with your treating doctor. The results will not affect your diagnosis, but they might affect your treatment.
Types Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Most invasive ductal carcinomas are the general type. However, there are four additional sub-types that are much less common:
- Medullary ductal carcinoma – these tumors look aggressive, but are often slow-growing. They are named because they look similar to a part of the brain called the medulla. They are often found in women whose ages are the late 40s to early 50s. The BRCA1 gene raises the risk for this kind of tumor.
- Mucinous ductal carcinoma – this is a less aggressive tumor where cancer cells are surrounded by a puddle of mucin . This cancer most often develops in women in their 60s and beyond.
- Papillary carcinoma – these are very rare kinds of IDC that have a tumor with fingers that grow out and reach toward nearby healthy cells. They most often occur in women after menopause. Sometimes the cells are abnormal and grow very quickly.
- Tubular ductal carcinoma – a less aggressive, slow-growing tumor that grows in very small tube shapes. It is most often found in women in their early 50s.
You May Like: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread