Pick A Part: The Skin
Pick A Part is an interactive game for you to test your knowledge. To play:
- Drag the appropriate choices from the column on the bottom and place them in order in the boxes on the left. Note that you will only use five of the six choices to complete the game.
- When done, click on ‘Check’ to see how many you got correct.
- For incorrect answers, click on ‘Description’ to review information about the processes.
- To try again, choose ‘Reset’ and start over.
For help please refer to the Anatomy of the Skin page.
What Is Black Salve
Black salve is a paste, poultice, or ointment made of various herbs. Its applied directly to areas of the body with the hope of burning away or drawing out cancer.
Black salve is commonly made with zinc chloride or the flowering North American plant, bloodroot . Bloodroot contains a powerfully corrosive alkaloid called sanguinarine.
Black salves are classified as escharotics because they destroy skin tissue and leave behind a thick scar called an eschar.
Black salve was commonly used during the 18th and 19th centuries to chemically burn off tumors that were isolated to the top layers of skin. Today, its been promoted and used by naturopaths as an alternative cancer treatment, with dubious results.
dont support the claims that black salve is an effective treatment for melanoma and other types of skin cancer. Some alternative medical practitioners believe black salve:
- reduces excess fluid
- enhances oxygen flow to the brain
- strengthens enzyme structure
Mohs Micrographic Surgery: For Trickier Cancers
During a Mohs procedure, a specially trained dermatologist or surgeon removes a very thin layer of skin containing the tumor.
While the patient waits, the sample is examined under a microscope to see if there are any cancer cells.
The procedure is repeated, with the doctor removing one thin layer at a time, until a tissue sample is cancer-free. The process can take several hours.
The Mohs technique is considered the gold standard for treating many squamous cell cancers, basal cell cancers, and some melanomas, says the SCF.
It has the highest cure rate and spares as much healthy skin surrounding the tumor as possible, leaving the smallest possible scar.
As with other skin cancer surgeries, it is typically done on an outpatient basis in a doctors office with local anesthesia.
But because it is so complex and time-consuming, skin cancer experts have devised guidelines for when it is the best option.
Its often used when theres a high risk of recurrence, the extent of the cancer is hard to determine, or the cancer is in a part of the body where appearance or function are high priorities, such as near the eye, the middle of the face, the ears, or the fingers, notes the American Cancer Society .
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Cancer Kill
Why A Mole May Need To Be Removed
Moles are common skin growths. You probably have more than one on your face and body. Most people have 10 to 40 moles somewhere on their skin, according to the American Academy of Dermatology.
Most moles are harmless and nothing to worry about. Unless a mole is cancerous, you dont need to have it removed unless it bothers you. But if you dont like the way it affects your appearance, or if its getting irritated from rubbing against your clothes, removing the mole is still an option.
The best way to know if a mole is cancerous is to see a dermatologist for an annual skin cancer screening. If you have a history of skin cancer, your dermatologist may recommend screening more often.
Meanwhile, you should schedule a checkup with your dermatologist if you notice any moles that:
- are asymmetrical
- are not uniform in color
- have a diameter thats larger than a pencil eraser
- are evolving or changing in size, shape, or color
These are known as the ABCDEs of mole checks.
These types of moles should be evaluated by a dermatologist, who can then decide if they should be tested for skin cancer.
A dermatologist can typically remove a mole during a routine office visit. Sometimes a follow-up visit is necessary to complete a mole removal.
Two main types of surgical procedures are used for mole removal:
If necessary, your dermatologist can evaluate the mole thats been removed for skin cancer.
When Should I See My Doctor
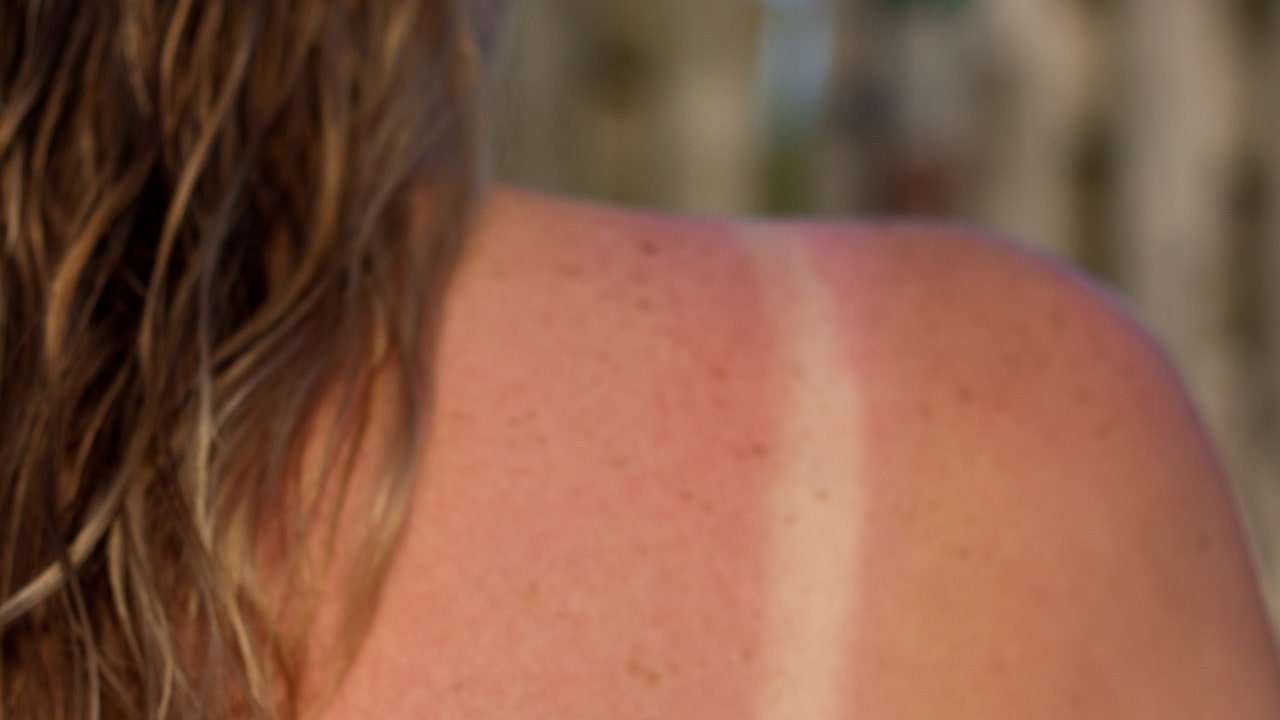

Its important to check your own skin regularly to find any new or changing spots.
See your doctor or dermatologist straight away if you notice any changes to your skin, such as:
- an ‘ugly duckling’ a spot that looks or feels different to any others
- a spot that changes size, shape, colour or texture over time
- a sore that doesnt go away after a few weeks
- a sore that itches or bleeds
See the ‘ABCDE’ of skin cancer, above.
Read Also: Cell Cancer Symptoms
Other Dermatological Ways To Remove Sun Spots
If you have multiple sun spots or aging spots that you would like to have removed, there are a variety of other procedures that you can have done at your dermatologist’s office.
- Chemical Peel: A chemical is applied to your skin to cause a massive exfoliation. Over the next two weeks, the skin on your face will peel off and new skin cells will regenerate. There are three types of peels: superficial, medium, and deep. The type is determined by the depth and severity of the burn.
- Intense Pulsed Light: Mostly used for capillary damage and hair removal, IPL is administered using broad spectrum light therapy.
- Laser Therapy: A laser is used to target pigmentation but not normal healthy skin cells. The laser pulse feels like being flicked with a rubber band.
- Microdermabrasion: The peeling of the skin using crystals.
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomatreatments
Numerous treatment options are available for basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. Your therapy will depend upon the type of skin cancer you have and its stage.
- Surgery Many skin cancers can be cut from the skin quickly and easily. In fact, the cancer is sometimes completely removed at the time of the biopsy, and no further treatment is needed.
- Curettage and Electrodesiccation Doctors commonly use a type of surgery called curettage. After a local anesthetic numbs the area, the cancer is scooped out with a curette, an instrument with a sharp, spoon-shaped end. The area is also treated by electrodesiccation. An electric current from a special machine is used to control bleeding and kill any cancer cells remaining around the edge of the wound. Most patients develop a flat, white scar.
Also Check: Lobular Breast Cancer Stage 1
Are There Effective Ways To Remove Moles At Home
A number of websites offer do-it-yourself tips for removing a mole at home. These methods are not proven to work, and some may be dangerous. You should talk with your doctor about your options before you try any home remedies for mole removal.
Some of these unproven methods include:
- burning the mole off with apple cider vinegar
- taping garlic to the mole to break it down from the inside
- applying iodine to the mole to kill the cells inside
- cutting off the mole with scissors or a razor blade
Other home remedies that claim to remove moles include applying:
- a mixture of baking soda and castor oil
- banana peel
- aloe vera
- flaxseed oil
Pharmacies and online stores also sell mole removal creams. To use these creams, you first scrape off the top part of the mole. Then you rub the cream into the mole. The products claim that within a day after applying the cream, a scab will form. When the scab falls off, the mole will go with it.
That said, you should never remove a mole at home. Mole removal should be done by a medical professional like a dermatologist, who can send it to a lab to be evaluated for cancer.
Curettage And Electrodesiccation For Low Risk Cancers
A technique combining curettage and desiccation is often used for small, superficial, uncomplicated basal cell skin cancer or squamous cell skin cancer.
It is typically performed on an outpatient basis in a doctors office with local anesthesia.
After numbing the tumor and the surrounding area skin, the doctor scrapes off the problematic area with a curette, an instrument with a sharp, ring-shaped tip, according to the Skin Cancer Foundation .
Next, the physician cauterizes the site of the tumor with a small device called an electrocautery needle, which stops the bleeding and destroys any stray cancer cells. No stitches are required.
The scrape-and-burn procedure may be repeated once or twice during the same office visit and can be used on multiple locations.
This method generally leaves a small scar.
Also Check: Untreated Cancer Symptoms
When To Call Your Surgeon
If you develop excessive pain, bleeding that will not stop, spreading redness, drainage of pus, fevers, chills or other concerning symptoms, call your surgeon as you may need to be evaluated in person. Luckily, rates of infection and bleeding after the electrodesiccation and curettage are lower than after a skin cancer excision.
After your wound heals and a scar forms, let your physician know if you start developing skin changes around the area. Skin cancers can return even after this procedure. Regardless, you should continue regular skin exams with your physician as surveillance for skin cancer.
Are There Complications Of Skin Cancer Treatment
Most skin cancer treatments involve some localised damage to surrounding healthy skin such as swelling, reddening or blistering of the skin where the cancer is removed. Your doctor will explain any specific risks, which may include:
- pain or itching where the skin has been treated, or if lymph nodes have been removed
- scarring or changes to skin colour, after a skin cancer has been removed
- bleeding during or after surgery for more complicated skin cancers
- reactions sometimes your body may react to medicines used in treatment or surgery
- lymphoedema if your lymph nodes have been removed your neck, arm or leg may swell with fluid.
Its best to manage complications as early as possible, so ask your doctor for advice.
Also Check: Stage 2 Cancer Symptoms
Oral Medications For Advanced Bcc
It is rare for skin cancer to reach advanced stages, but when it does, oral medications may help. In addition to chemotherapy, targeted drugs may be used to treat advanced skin cancer. Targeted therapy means that the medication is able to directly target the cancer cells without destroying healthy cells. This can help to reduce side effects from treatment.
Vismodegib and sonidegib are hedgehog pathway inhibitors that work to prevent cancer cells from growing and spreading. The capsules are taken once per day and may be considered after surgery and other treatments. These medications come with several possible side effects and should never be taken during pregnancy since they can affect fetal growth.
Cetuximab is an EGFR inhibitor that can help to stop the spread of cancerous squamous cells. Its possible side effects include skin infections, diarrhea, mouth sores, and loss of appetite.
Risk Factors For Melanoma
Risk factors specific to melanoma:
- Sun Burn
Watch the video below to learn about some great skin cancer prevention tips. Watch the full interview with Dr. Suephy Chen.
Sun exposure:Sun exposure increases one’s risk of skin cancer. Individuals are inevitably exposed to sunlight, or ultraviolet radiation, during their daily activities. However, certain outdoor behaviors elevate an individual’s likelihood of developing cancer. Infrequent, but intense exposure to sunlight during childhood increases one’s risk of developing melanoma. 1 Melanoma is often observed in areas of the body that receive infrequent but intense sun exposure such as the neck and the back of the legs. 19
Also, it is important to note that cutaneous melanoma may occur in regions of the body typically shielded from sunlight such as the groin and bottom of the feet.
Family HistoryIndividuals who have first degree relatives, including parents, siblings or children, diagnosed with melanoma have an 8 to 12 fold increased chance of developing melanoma. 10 This increased risk is likely due to a biological predisposition to cancer development.
Melanocytic NeviThe medical term for a marking on the skin, such as a mole or birthmark, is “nevus” . Most melanocytic nevi develop during childhood and adolescence as a result of sunburn and sun exposure. The presence of melanocytic nevi is associated with an increased risk of developing melanoma.10
Don’t Miss: Ductal Invasive Carcinoma Survival Rate
Do I Need To Take Any Precautions While Using Imiquimod
When using this medicine, you should:
Keep all appointments with your dermatologist. These follow-up visits allow your dermatologist to determine if the medicine is working for you. You should never use your own judgment to determine this. Your dermatologist considers many factors, not only whether your skin is clearing. If the medicine does not work, you may need to use a different treatment to prevent the disease from progressing.
Protect your skin from the sun. This helps reduce your risk of developing new AKs and skin cancers. To do this, you should seek shade when outdoors wear long sleeves, pants, a wide-brimmed hat, and sunglasses and use a sunscreen. Be sure to use sunscreen that is broad-spectrum, SPF30+, and water-resistant.
Avoid sexual activity while the medicine is on your skin. Even if you use a condom or other type of protection, this may not prevent the imiquimod from spreading to your partner.
Targeted Therapy: Targeting Cancer Mutations
Targeted therapy, another revolutionary new category of treatment, focuses on characteristics of skin-cancer cells that make them different from normal cells, such as gene changes.
For instance, about one-half of all melanomas have mutations in the BRAF gene that cause out-of-control cellular growth.
Oral drugs that target this mutation are called BRAF inhibitors. These include Zelboraf and Taflinar . BRAF inhibitors are often combined with medication that targets a protein called MEK. Two such drugs are Mekinist and Cotellic .
Read Also: Basal Cell Carcinoma Late Stages
How Long Will I Have To Use Imiquimod
This varies from patient to patient. Your dermatologist will tell you how long you will need to use the cream and how often to apply it. The following table shows the typical treatment plan for each of the skin diseases that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved imiquimod to treat.
How to use imiquimod
| Maximum of 16 weeks |
What Does The Research Say About Apple Cider Vinegar And Skin Cancer
Studies that examine a link between an acidic environment in the body and cancer have shown mixed results.
In one 1996 paper published in Clinical & Experimental Metastasis, scientists found that human melanoma cells may grow and spread more quickly in an acidic environment. But this study was performed on cultured cell samples in a lab.
Other experiments have shown no link between an acidic environment and cancer activity.
Some organizations, such as the American Institute for Cancer Research , say foods like apple cider vinegar have little effect on the bodys pH level. In fact, many experts believe it would be nearly impossible to alter the cell environment to create less acidity in the body.
According to the American Dietetic Association, Large, well-designed clinical trials on the effectiveness of the many claims made for the alkaline diet are lacking.
The inconsistent and insignificant amount of research on the topic has led most health experts to conclude theres not enough research to show apple cider vinegar can treat skin cancer.
RELATED: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Help Multiple Sclerosis?
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Melanoma Survival Rate
What Are The Claims About Skin Cancer And Apple Cider Vinegar
Various internet sites and blogs claim that apple cider vinegar can help treat skin cancers, including basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, melanomas, and precancerous lesions . Other sources offer tutorials for removing moles or skin tags.
Most of these sites provide personal, anecdotal accounts from people who say the vinegar cured their skin cancer.
Some of the sources encourage patients to drink apple cider vinegar, while others suggest applying it directly to the skin cancer. Many recommend doing both.
RELATED: Can Apple Cider Vinegar Help Treat Crohns?
How Do You Treat Skin Cancer On The Nose
The nose is a relatively common spot for skin cancer to develop. Skin cancer often starts on the face because it’s usually the body part that’s exposed to the sun. The two most common types of skin cancer that develop on the nose are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma . While both types of skin cancer should be addressed right away, BCC is usually slow-growing and SCC grows more quickly. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer ,with about 80% of cases occurring on the face and 25 to 30% on the nose.
The third type of skin cancer, melanoma, is rare and much more serious. It almost always requires excisional surgery to remove it. Fortunately, most forms of skin cancer are very treatable, especially when caught early. Treatment may include surgery, radiation, topical treatments, and more.
Also Check: Stage 1 Cancer Symptoms
How The Electrodesiccation And Curettage Procedure Is Performed
First, your surgeon will use a sharp curette to scrape the tumor. There is a textural difference between cancer and the normal skin which helps guide your surgeon in terms of the extent of scraping. Next, a device with a needle-like metal tip is used to dry out the tissue using an electric current, in a procedure called electrodesiccation.