What Medications Treat Small
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses medications to kill cancer cells. Patients may take these medications by mouth , but doctors usually inject them into a vein .
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment because the medications enter the bloodstream, travel throughout the body, and kill cancer cells wherever they are. However, some normal cells are also killed .
Doctors usually give chemotherapy at intervals to ensure that the bone marrow has recovered before the next dose of chemotherapy is given.
Extensive research and clinical trials have identified different chemotherapy medications in the last three decades for the treatment of lung cancer. Response rates with these medications are more than 80% in patients with small-cell lung cancer who were previously untreated.
While doctors use some medications alone, they use some in combination with others for greater effectiveness. An oncologist recommends chemotherapy specific to the patient’s condition.
Chemotherapy medications used for the treatment of small-cell lung cancer include the following:
Rather than using a single agent therapy, combinations of drugs are most commonly used. Commonly used chemotherapy regimens in small-cell lung cancer include the following:
Treatment of Limited-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Treatment of Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Treatment of Relapse of Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Radiation Therapy
Immunotherapy
How Will The Doctor Know If I Have Lung Cancer
Symptoms of lung cancer are cough, chest pain, and trouble breathing. The doctor will ask you questions about your health and do a physical exam.
If signs point to lung cancer, more tests will be done. Here are some of the tests you may need:
Chest x-ray: This is often the first test used to look for spots on your lungs. If a change is seen, you will need more tests.
CT scan: This is also called a CAT scan. A CT scan is a special kind of x-ray that takes detailed pictures of your insides. CT scans can also be used to do a biopsy .
PET scan: A type of sugar is put in one of your veins for this test. Then, pictures of your insides are taken with a special camera. If there is cancer, the sugar shows up as hot spots where the cancer is found. This test is helpful when your doctor thinks the cancer has spread, but doesnt know where.
Biopsy: For a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of the lung tumor. Its sent to the lab to see if there are cancer cells in it. This is the best way to know for sure if you have cancer.
Bronchoscopy: A thin, lighted, flexible tube is passed through your mouth into the bronchi. The doctor can look through the tube to find tumors. The tube also can be used to take out a piece of the tumor or fluid to see if there are cancer cells.
Blood tests: Blood tests are not used to find lung cancer, but they are done to tell the doctor more about your health.
How Do I Know Which Type Of Lung Cancer I Have
When your physician first suspects you have lung cancer, you will likely need a medical imaging scan, such as an MRI or X-ray, to identify any abnormal growths. If a tumor is present, an oncologist will obtain a small sample of the lesion through a biopsy, which will then be examined through a microscope to determine the kind of lung cancer you have. Each type of lung cancer has different characteristics that helps with identification. For example, as its name suggests, the cells of small cell lung cancer are typically smaller than the cells of non-small cell lung cancer. The most effective course of treatment for you will depend on the type and subtype of your malignancy, in addition to many other factors.
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Alberto Chiappori.
If you have been recently diagnosed with lung cancer, Moffitt Cancer Center can provide you with the comprehensive treatment you need to achieve the best possible outcome and an improved quality of life. The specialists in our Thoracic Oncology Program create individualized treatment plans for our patients to address the challenges of each unique cancer. Schedule a consultation at Moffitt by calling or by submitting a new patient registration form form online. Referrals are not required.
- BROWSE
Also Check: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
What Will Happen After Treatment
Youll be glad when treatment is over. But its hard not to worry about cancer coming back. Even when cancer never comes back, people still worry about this.
For years after treatment ends, you will see your cancer doctor. Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. You will have exams, blood tests, and maybe other tests to tell if the cancer has come back.
For the first year after treatment, your visits may be every 2 to 3 months. You may have CT scans and blood tests. After the first year or so, your visits might be every 6 months, and then at least once a year after 5 years.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as well as you can.
Citation Doi And Article Data
Citation:DOI:Dr Luke DanaherRevisions:see full revision historySystems:
- Small cell carcinoma of the lung
- Oat cell carcinoma
- Oat cell carcinoma of the lung
- Small cell bronchogenic carcinoma
Small cell lung cancer , also known as oat cell lung cancer, is a subtype of bronchogenic carcinoma separated from non-small-cell lung cancer as it has a unique presentation, imaging appearances, treatment, and prognosis. SCLCs are neuroendocrine tumors of the lung that rapidly grow, are highly malignant, widely metastasize, and, despite showing an initial response to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, have a poor prognosis and are usually unresectable.
You May Like: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
What Are The Risks For Developing Sclc
The leading risk for developing SCLC is smoking tobacco. The more you smoke and the earlier in life you began smoking, the greater your risk for SCLC. Other risk factors include exposure to secondhand smoke, workplace carcinogens, radiation and/or environmental pollution, as well as family history of lung cancer and previous HIV infection.
Causes Of Small Cell Lung Cancer
Smoking cigarettes is the main cause of lung cancer. People who do not smoke can still develop lung cancer, but their risk is much lower. If someone stops smoking, their risk of developing lung cancer falls over time. After about 15 years it is almost the same as a non-smoker. Lung cancer is also more common in older people.
If these tests show anything abnormal, your GP will refer you to a chest specialist within 2 weeks. Sometimes they will do this before getting the result of the chest x-ray.
At the hospital, the specialist will explain any other tests you need.
Other tests you may have at the hospital include:
PET-CT scan
A PET-CT scan is a combination of a CT scan, which takes a series of x-rays to build up a three-dimensional picture and a positron emission tomography scan.
Biopsy
The doctor or nurse collects samples of cells or tissue from the lung or nearby lymph nodes. The samples are checked under a microscope for cancer cells. This test can help diagnose lung cancer and show whether it is small cell lung cancer or non-small cell lung cancer . There are different ways of collecting biopsies, including:
Waiting for tests results can be a difficult time, we have more information that can help.
Don’t Miss: Osteomyoma
Exams And Tests For Lung Cancer
Staging
- Staging of the cancer provides important information about the outlook of the patient’s condition and helps the doctor plan the best treatment. Although other cancers are categorized from stage I to stage IV, small-cell lung cancer is classified in two stages.
- Limited stage: In this stage, the tumor is confined to one side of the chest, the tissues between the lungs, and nearby lymph nodes only.
- Extensive stage: In this stage, cancer has spread from the lung to other parts of the body.
What About Other Treatments I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat your cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to be helpful. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything you are thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Read Also: Does Insurance Cover Skin Cancer Screening
Small And Large Cell Cervical Cancer
Small cell cervical cancer and large cell cervical cancer make up a rare subtype of cervical cancer. They are aggressive forms of a larger group of tumors called neuroendocrine cancers. These cancers occur in the hormone-producing cells of the body’s neuroendocrine system, which is composed of cells that are a cross between endocrine cells and nerve cells.
Of the 11,000 new cases of cervical cancer diagnosed in the United States each year, approximately 100 cases will be small cell or large cell cervical cancer. Unlike other types of cervical cancer, SCCC and LCCC have no definitive link to the human papilloma virus . Because these tumors are so rare, the cause is not yet fully understood.
Small cell and large cell cervical cancers are the most common type of neuroendocrine tumor in the cervix, but still accounts for less than 1% of all cervical cancers.
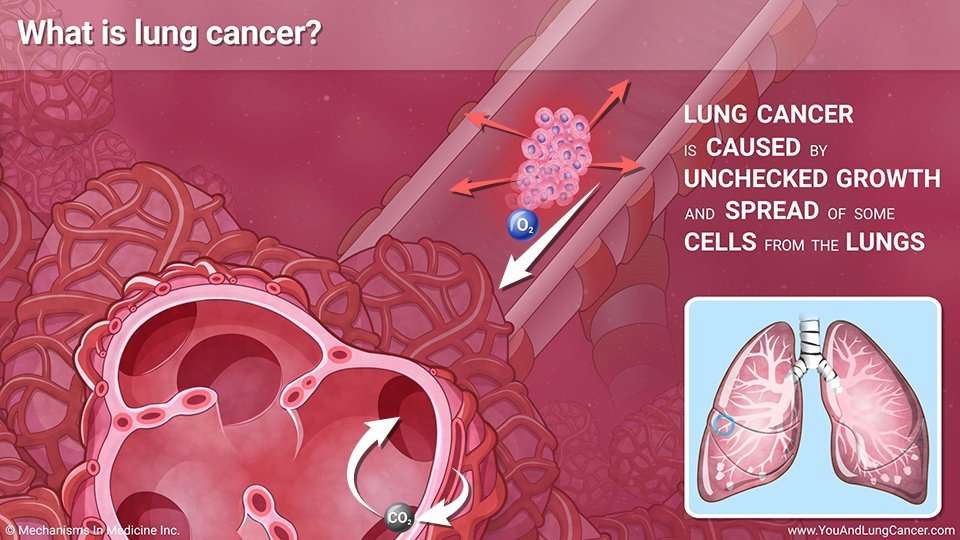
What Is Lung Cancer
Cancer is not just one disease. There are many types of cancer. But all cancers start when a group of cells in the body grows out of control. Cancer cells keep on growing and can crowd out normal cells. This makes it hard for the body to work the way it should.
Cancer can start any place in the body. It can start in the breast, the lungs, the colon, or even in the blood. Cancer that starts in the lung is called lung cancer.
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. For instance, cancer cells in the lung can travel to the bone and grow there. When cancer cells spread, its called metastasis.
Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when lung cancer spreads to the brain , its still called lung cancer. Its not called brain cancer unless it starts in the brain.
The lungsAsk your doctor to show you on this picture where your cancer is found.
Read Also: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
What Are The Complications Of Small Cell Lung Cancer
Metastasis, or cancer spread, is a top concern for people who have small cell lung cancer. Small cell lung cancer can grow quickly and affect the brain, bones and liver and adrenal glands . Small cell lung cancer that spreads is treatable but generally isnt curable. Other complications include:
- Pleural effusion .
- Cancer recurrence after treatment, often in the central nervous system or chest.
- Pain.
- Shortness of breath.
Small Cell Lung Cancer Survival Rates

Even with advanced treatment options, the small cell lung cancer survival rate is not as good as it is with other types of lung cancer. SCLC can grow and spread quickly. And according to statistics, the likelihood of living for five years after you’ve been diagnosed with SCLC is between 3% and 27%, depending on how advanced the cancer is when it’s found.
Hearing this and the fact that SCLC is not usually not curable is difficult. But the disease is always treatable, and newer approaches have improved patients’ ability to manage the disease and live longer than before.
Read Also: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
How Can I Prevent Small Cell Lung Cancer
Because tobacco use is the top cause of small cell lung cancer, not smoking is the best way to protect your health. When you quit smoking regardless of your age or years of tobacco use your lungs start to heal, and cancer risk diminishes. These steps may also help:
- Eat a nutritious diet.
- Test your home for radon, a natural, odorless, radioactive gas.
- Install a mitigation system to remove radon from your home, if needed.
- Protect yourself from cancer-causing chemicals at work.
Rare Forms Of Lung Cancer
Several types and subtypes of lung cancer are very rare. They include:
- Adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung, a hybrid of adenocarcinoma and squamous cell lung cancer
- Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, an aggressive subtype of non-small cell lung cancer
- Salivary gland-type lung carcinoma, which is most often found in the central airways of the lungs
- Lung carcinoids, a rare type of cancer often found in younger than average lung cancer patients
- Mesothelioma, a rare type of cancer that develops in thin tissue called mesothelium, which lines the lungs and abdomen
Mediastinal tumors are also rare and develop in the mediastinum, which separates the lungs in the center of the chest.
The trachea , esophagus, heart, connective tissues and other organs are part of the mediastinum. In adults, most mediastinal tumors form in the front of the mediastinum and typically fall into one of the following categories:
- Germ cell tumors
Recommended Reading: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Surgery For Small Cell Lung Cancer
In most cases, you will not have surgery if you have small cell lung cancer. In a few cases, if the cancer is very small and has not spread, surgery might be done to take out all or part of your lung.
Sometimes, fluid collects in the chest and causes breathing problems. This fluid can be taken out by putting a small tube in the chest. After the fluid is drained out, a drug is put into the tube. This helps seal the space and keep fluid from building up again.
Side effects of surgery
Any type of surgery can have some risks and side effects. Be sure to ask the doctor what you can expect. If you are having problems, let your doctors know. Doctors who treat people with lung cancer should be able to help you with any problems that come up.
Other Types Of Lung Tumors
Along with the main types of lung cancer, other tumors can occur in the lungs.
Lung carcinoid tumors: Carcinoid tumors of the lung account for fewer than 5% of lung tumors. Most of these grow slowly. For more information about these tumors, see Lung Carcinoid Tumor.
Other lung tumors: Other types of lung cancer such as adenoid cystic carcinomas, lymphomas, and sarcomas, as well as benign lung tumors such as hamartomas are rare. These are treated differently from the more common lung cancers and are not discussed here.
Cancers that spread to the lungs: Cancers that start in other organs can sometimes spread to the lungs, but these are not lung cancers. For example, cancer that starts in the breast and spreads to the lungs is still breast cancer, not lung cancer. Treatment for metastatic cancer to the lungs is based on where it started .
You May Like: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What Is Small Cell Lung Cancer
Small cell lung cancer is fast-growing lung cancer that develops in the tissues of the lungs. By the time a person gets a diagnosis, small cell lung cancer has typically spread outside of the lungs. This cancer is also more likely than other types of lung cancer to come back after treatment. Small cell lung cancer is sometimes, but not often, called oat cell cancer because the small, oval-shaped cells look like oat grains under a microscope.
Effective Options For Early And Advanced Bcc
When detected early, most basal cell carcinomas can be treated and cured. Prompt treatment is vital, because as the tumor grows, it becomes more dangerous and potentially disfiguring, requiring more extensive treatment. Certain rare, aggressive forms can be fatal if not treated promptly.
If youve been diagnosed with a small or early BCC, a number of effective treatments can usually be performed on an outpatient basis, using a local anesthetic with minimal pain. Afterwards, most wounds can heal naturally, leaving minimal scarring.
Options include:
Don’t Miss: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Patients May Want To Think About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today’s standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
Small Cell Lung Cancer Stages

After someone is diagnosed with small cell lung cancer , doctors will try to figure out if it has spread, and if so, how far. This process is called staging. The stage of a cancer describes how much cancer is in the body. It helps determine how serious the cancer is and how best to treat it. Doctors also use a cancer’s stage when talking about survival statistics.
The stage of SCLC is based on the results of physical exams, biopsies, imaging tests, and any other tests that have been done .
Don’t Miss: Basal Skin Cancer Survival Rates