What Do Cutaneous Melanoma Metastases Look Like
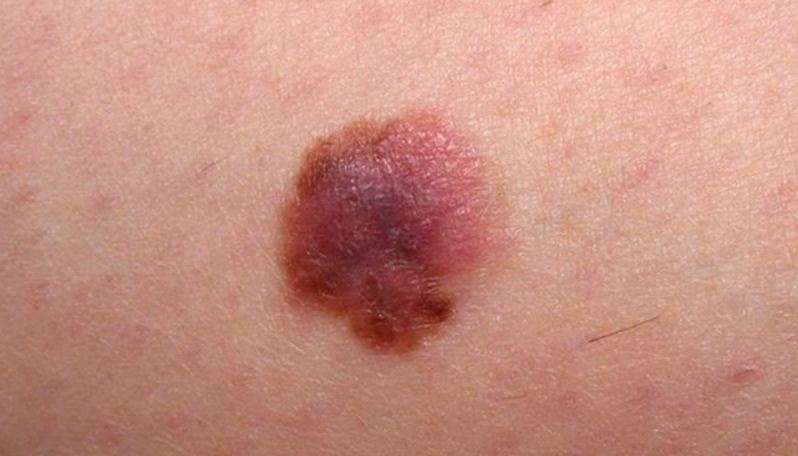
Cutaneous melanoma metastases usually grow rapidly within the skin or under the skin surface dermal metastases are more common than subcutaneous. They are usually firm or hard in consistency. Cutaneous metastases may be any colour but are often black or red. They may also ulcerate and bleed.
Cutaneous metastatic melanoma
Epidermotropic metastatic melanoma is rare. In this case, the metastases develop more superficially than usual, within the epidermis. Epidermotropic metastatic melanoma is often initially misdiagnosed as the primary melanoma. The diagnosis of epidermotropic metastatic melanoma should be considered if multiple lesions arise with similar pathology.
Subcutaneous metastases are skin coloured or bluish lumps. They are usually painless.
Subcutaneous metastatic melanoma
Obstruction of lymphatic vessels due to melanoma in the lymph nodes or surgical removal of the lymph glands can result in swelling of the associated limb .
Metastatic melanoma
What Causes Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma occurs when one of the skins basal cells develops a mutation in its DNA. Basal cells are responsible for producing new skin cells. As they do so, older skin cells are pushed toward the skin surface, where they die and are sloughed off. DNA in the basal cell controls this function.
Read Also: Can Skin Cancer Be Cured With Cream
What Is Skin Cancer
Cancer can start any place in the body. Skin cancer starts when cells in the skin grow out of control.
Skin cancer cells can sometimes spread to other parts of the body, but this is not common. When cancer cells do this, its called metastasis. To doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the skin.
Cancer is always named based on the place where it starts. So if skin cancer spreads to another part of the body, its still called skin cancer.
The skin
Ask your doctor to use this picture to show you where your cancer is
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Skin Cancer On Your Ear
Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
This is the second most common form of skin cancer, it occurs most commonly on the head and neck, and exposed arms. However, these are frequently seen on the front of the legs as well, or the shin area. This form of skin cancer grows more quickly, and though it can be confined to the top layer of skin, it frequently grows roots. Squamous cell carcinoma can be more aggressive and does have a potential to spread internally. This is more likely in cases where an individual is immunosuppressed, or the tumor is invading deeply in the second layer of skin, or tracking along nerves. These tumors need to be treated early as they are not only locally destructive, but can spread along nerves, into lymph nodes, and internally.
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Oral Cavity
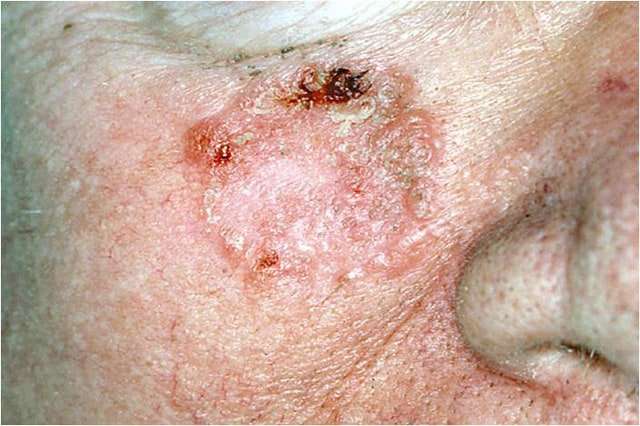
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity is a common malignant tumor of the mouth that typically affects elderly men and women. It is more aggressive than conventional squamous cell carcinoma affecting other body regions
- The cause of the condition is unknown, but genetic mutations may be involved. Factors that may influence its development include smoking and chewing of tobacco, radiation treatment for other reasons, and exposure to coal tar and arsenic
- The squamous cell carcinoma may appear as slow-growing skin lesions. The lesions may ulcerate and cause scarring of the oral cavity. It may be difficult to eat, swallow food, or even to speak
- The treatment of choice is a surgical excision with clear margins followed by radiation therapy or chemotherapy, as decided by the healthcare provider. In majority of the cases, the prognosis is good with appropriate treatment
- Nevertheless, the prognosis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Oral Cavity depends upon many factors including the stage of the tumor and health status of the affected individual. There is a possibility of local or regional metastasis, which can involve the lymph nodes. This may dictate the course of the condition
Read Also: How Fast Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Spreading To The Lymph Nodes
When a tumor gets too big, it requires more oxygen and nutrients to survive.
This is when the tumor sends out signals that cause new blood vessels to grow into the tumor , bringing the nutrients and oxygen it needs. After angiogenesis occurs, cancer cells are now able to break off and enter the bloodstream.
They can also break off and spread through the lymphatic system . When this happens, the cancer cells can now settle and take root in a new area of the body. Once the cancer cells have spread to the lymph nodes its considered stage three melanoma.
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
There are several types of basal cell carcinomas.
The nodular type of basal cell carcinoma usually begins as small, shiny, firm, almost clear to pink in color, raised growth. After a few months or years, visible dilated blood vessels may appear on the surface, and the center may break open and form a scab. The border of the cancer is sometimes thickened and pearly white. The cancer may alternately bleed and form a scab and heal, leading a person to falsely think that it is a sore rather than a cancer.
Other types of basal cell carcinomas vary greatly in appearance. For example, the superficial type appears as flat thin red or pink patches, and the morpheaform type appears as thicker flesh-colored or light red patches that look somewhat like scars.
You May Like: How Rare Is Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Treating Stage 4 Melanoma
If melanoma comes back or spreads to other organs it’s called stage 4 melanoma.
In the past, cure from stage 4 melanoma was very rare but new treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted treatments, show encouraging results.
Treatment for stage 4 melanoma is given in the hope that it can slow the cancer’s growth, reduce symptoms, and extend life expectancy.
You may be offered surgery to remove other melanomas that have grown away from the original site. You may also be able to have other treatments to help with your symptoms, such as radiotherapy and medicine.
If you have advanced melanoma, you may decide not to have treatment if it’s unlikely to significantly extend your life expectancy, or if you do not have symptoms that cause pain or discomfort.
It’s entirely your decision and your treatment team will respect it. If you decide not to receive treatment, pain relief and nursing care will be made available when you need it. This is called palliative care.
What Is Metastatic Skin Cancer
Metastatic skin cancer is any kind of skin cancer that has spread from the skin to other organs and tissues. Melanoma is the rarest type of skin cancer, but its also the most likely to metastasize. It can also appear on parts of the body that are not normally exposed to skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are more common forms of skin cancer, but these cancers are not very likely to spread. However, its worth noting that squamous cell carcinoma is somewhat more likely to spread than basal cell carcinoma.
All three types of skin cancer are most likely to spread by coming into contact with the lymph nodes, and spreading to other parts of the body from there.
Read Also: How Long Can You Live With Melanoma Untreated
Treating Stage 3 Melanoma
If the melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes , further surgery may be needed to remove them.
Stage 3 melanoma may be diagnosed by a sentinel node biopsy, or you or a member of your treatment team may have felt a lump in your lymph nodes.
The diagnosis of melanoma is usually confirmed using a needle biopsy .
Removing the affected lymph nodes is done under general anaesthetic.
The procedure, called a lymph node dissection, can disrupt the lymphatic system, leading to a build-up of fluids in your limbs. This is known as lymphoedema.
Cancer Research UK has more information about surgery to remove lymph nodes.
So How Much Of A Melanoma Can You Deliberately Pick Off
Well, if you go deep enough, says Dr. Schultz, you may in fact remove the entire thing, and if it was only a suspicious or abnormal, meaning precancerous mole, then that mole no longer has the ability to cause a melanoma, and the person has succeeded in permanently removing the threat of it becoming a melanoma.
However, this never validates picking at what you suspect is melanoma.
Advanced melanoma. Cancer.gov
The problem is that there is no way of knowing without examining the specimen with a microscope, whether its been removed completely.
And if it hasnt, then its even worse because the surface can heal , and the remaining abnormal mole continues to grow under the skin, explains Dr. Schultz.
And can turn into melanoma and remain undetected until it has invaded deep into the skin, which when it reaches blood or lymph vessels is how it spreads , which is what kills people.
The first sites that this cancer tends to spread to are the lungs and brain.
Five-year survival rate for this disease at stage IV is 15-20 percent
10-year survival rate is 10-15 percent.
Dr. Schultz continues, As a dermatologist who specializes in the early detection, prevention and treatment of skin cancer and especially abnormal moles and melanoma, when I examine patients and think a mole is suspicious, and I put in anesthesia and use my surgical skills to remove it, about 10 percent of the time even I dont remove the entire abnormal mole.
Cancer cell.Shutterstock/Lightspring
You May Like: How Fast Does Melanoma Metastasis
Melanomas That Could Be Mistaken For A Common Skin Problem
Melanoma that looks like a bruise
Melanoma can develop anywhere on the skin, including the bottom of the foot, where it can look like a bruise as shown here.
Melanoma that looks like a cyst
This reddish nodule looks a lot like a cyst, but testing proved that it was a melanoma.
Dark spot
In people of African descent, melanoma tends to develop on the palm, bottom of the foot, or under or around a nail.
Did you spot the asymmetry, uneven border, varied color, and diameter larger than that of a pencil eraser?
Dark line beneath a nail
Melanoma can develop under a fingernail or toenail, looking like a brown line as shown here.
While this line is thin, some are much thicker. The lines can also be much darker.
Staging For Merkel Cell Cancer
Doctors use the TNM system to describe the stage of Merkel cell cancer. Doctors use the results from diagnostic tests and scans to answer these questions:
-
Tumor : How large is the primary tumor? Where is it located?
-
Node : Has the tumor spread to the lymph nodes? If so, where and how many?
-
Metastasis : Has the cancer spread to other parts of the body? If so, where and how much?
The results are combined to determine the stage of Merkel cell cancer for each person.
There are 5 stages: stage 0 and stages I through IV . The stage provides a common way of describing the cancer, so doctors can work together to plan the best treatments.
Stage 0: This is called carcinoma in situ. Cancer cells are found only in the top layers of the skin. The cancer does not involve the lymph nodes, and it has not spread.
Stage I: The primary tumor is 2 centimeters or smaller at its widest part. The cancer has not spread to the lymph nodes or to other parts of the body.
Stage IIA: The tumor is larger than 2 cm and has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
Stage IIB: The tumor has grown into nearby tissues, such as muscles, cartilage, or bone. It has not spread to the lymph nodes or elsewhere in the body.
Stage III: The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes. The tumor can be any size and may have spread to nearby bone, muscle, connective tissue, or cartilage.
Stage IV: The tumor has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the liver, lung, bone, or brain.
You May Like: How Dangerous Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Whats The Outlook For Stage 4 Melanoma
Once the cancer spreads, locating and treating the cancerous cells becomes more and more difficult. You and your doctor can develop a plan that balances your needs. The treatment should make you comfortable, but it should also seek to remove or slow cancer growth. The expected rate for deaths related to melanoma is 10,130 people per year. The outlook for stage 4 melanoma depends on how the cancer has spread. Its usually better if the cancer has only spread to distant parts of the skin and lymph nodes instead of other organs.
What Stages Have To Do With Cancer Spread
Cancers are staged according to tumor size and how far it has spread at the time of diagnosis. Stages help doctors decide which treatments are most likely to work and give a general outlook.
There are different types of staging systems and some are specific to certain types of cancer. The following are the basic stages of cancer:
- In situ. Precancerous cells have been found, but they havent spread to surrounding tissue.
- Localized. Cancerous cells havent spread beyond where they started.
- Regional. Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, tissues, or organs.
- Distant. Cancer has reached distant organs or tissues.
- Unknown. Theres not enough information to determine the stage.
- Stage 0 or CIS. Abnormal cells have been found but have not spread into surrounding tissue. This is also called precancer.
- Stages 1, 2, and 3. The diagnosis of cancer is confirmed. The numbers represent how large the primary tumor has grown and how far the cancer has spread.
- Stage 4. Cancer has metastasized to distant parts of the body.
Your pathology report may use the TNM staging system, which provides more detailed information as follows:
T: Size of primary tumor
- TX: primary tumor cant be measured
- T0: primary tumor cant be located
- T1, T2, T3, T4: describes the size of the primary tumor and how far it may have grown into surrounding tissue
N: Number of regional lymph nodes affected by cancer
M: Whether cancer has metastasized or not
Recommended Reading: How Long Before Melanoma Spreads
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of cancer, but also the least likely to spread. In particular, BCCs rarely spread beyond the initial tumor site. However, left untreated, BCCs can grow deeper into the skin and damage surrounding skin, tissue, and bone. Occasionally, a BCC can become aggressive, spreading to other parts of the body and even becoming life threatening. Also, the longer you wait to have your BCC treated, the more likely it is to return after treatment. Like BCCs, SCCs are highly curable when caught and treated early. However, if left to develop without treatment, an SCC can become invasive to skin and tissue beyond the original skin cancer site, causing disfigurement and even death. Over 15,000 Americans die each year from SCCs. And even if untreated carcinomas dont result in death, they can lead to large, open lesions on the skin that can cause discomfort, embarrassment, and infection.
How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Squamous cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes , and when spreading does occur, it typically happens slowly. Indeed, most squamous cell carcinoma cases are diagnosed before the cancer has progressed beyond the upper layer of skin. There are various types of squamous cell carcinoma and some tend to spread more quickly than others.
Read Also: How Fast Does Melanoma Develop
How Is The Stage Determined
The system most often used to stage basal and squamous cell skin cancers is the American Joint Commission on Cancer TNM system. The most recent version, effective as of 2018, applies only to squamous and basal cell skin cancers of the head and neck area . The stage is based on 3 key pieces of information:
- The size of the tumor and if it has grown deeper into nearby structures or tissues, such as a bone
- If the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- If the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body
Numbers or letters after T, N, and M provide more details about each of these factors. Higher numbers mean the cancer is more advanced.
Once a persons T, N, and M categories have been determined, this information is combined in a process called stage grouping to assign an overall stage. The earliest stage of skin cancer is stage 0 . The other stages range from I through IV . As a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, such as stage IV, means cancer has spread more.
If your skin cancer is in the head and neck area, talk to your doctor about your specific stage. Cancer staging can be complex, so ask your doctor to explain it to you in a way you understand. For more information, seeCancer Staging.
What Does A Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like
BCCs can vary greatly in their appearance, but people often first become aware of them as a scab that bleeds and does not heal completely or a new lump on the skin. Some BCCs are superficial and look like a scaly red flat mark on the skin. Others form a lump and have a pearl-like rim surrounding a central crater and there may be small red blood vessels present across the surface. If left untreated, BCCs can eventually cause an ulcer hence the name rodent ulcer. Most BCCs are painless, although sometimes they can be itchy or bleed if caught.
Don’t Miss: How Serious Is Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Because basal cell carcinoma is often caused by sun exposure, people can help prevent this cancer by doing the following:
-
Avoiding the sun: For example, seeking shade, minimizing outdoor activities between 10 AM and 4 PM , and avoiding sunbathing and the use of tanning beds
-
Wearing protective clothing: For example, long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats
-
Using sunscreen: At least sun protection factor 30 with UVA and UVB protection used as directed and reapplied every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating but not used to prolong sun exposure
In addition, any skin change that lasts for more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a doctor.