Who Gets Melanoma In Situ
There were 2423 melanoma registrations in New Zealand in 2015. The New Zealand Cancer Registry does not publish the figures for melanoma in situ, but unpublished data suggest that about the same number of people are diagnosed with in-situ melanoma as those diagnosed with invasive melanoma .
The mean age of diagnosis is 61 years, but melanoma in situ can also be diagnosed in young people . Mostly it is diagnosed in people who have many melanocyticnaevi or in older people with fair skin.
Patients with melanoma in situ may have also been diagnosed with other keratinocytic forms of skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma, actinickeratosis, intraepidermalsquamous cell carcinoma, and cutaneoussquamous cell carcinoma.
What Is The Outlook For Patients With Nodular Melanoma
The risk of spread and ultimate death from invasive melanoma depends on several factors, but the main one is the measured thickness of the melanoma at the time it was surgically removed.
The Melanoma Guidelines report that metastases are rare for melanomas < 0.75mm and the risk for tumours 0.751 mm thick is about 5%. The risk steadily increases with thickness so that melanomas > 4 mm have a chance of metastasis of about 40%.
New Zealand statistics gathered by the Cancer Registry between 1994 and 2004 revealed 15,839 invasive melanomas. Of these, 52% were under 0.75 mm in thickness, 22% were between 0.76 and 1.49 mm, 15% were between 1.5 and 3 mm in thickness and 11% were more than 3 mm in thickness. Thicker tumours were slightly more likely to be diagnosed in males and more likely in older people than younger ones.
What Is A Melanoma In Situ
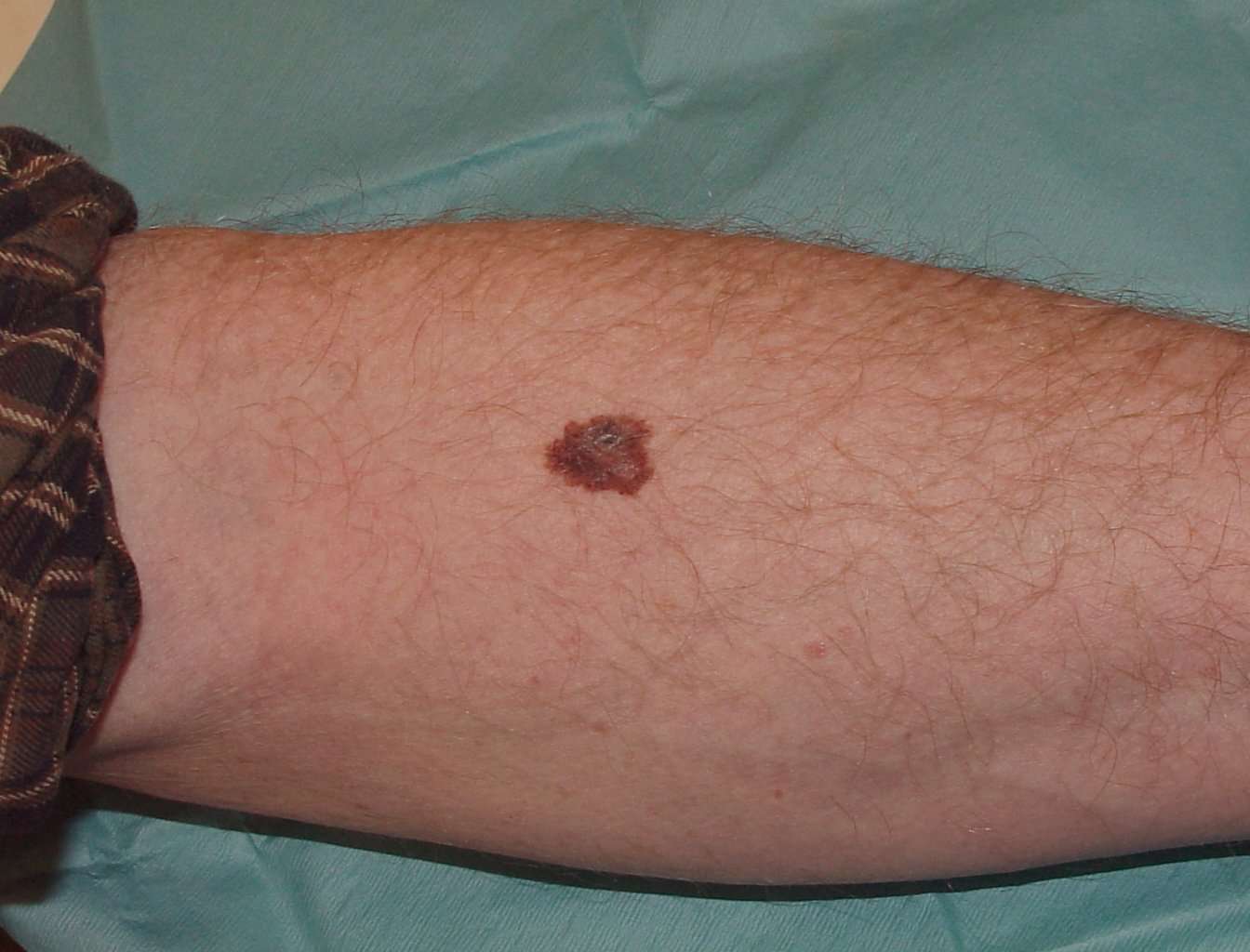
Melanoma in situ is an early stage type of melanoma. In situ means that the cancer cells may not have had the opportunity to spread to anywhere else in the body. The cancer cells are in the top layer of the skin and they are all contained in the area in which they began to develop, they have not become invasive to the lower layers of skin . If not treated, melanoma in situ can develop into an invasive cancer. It may be referred to as a precancerous lesion.
Recommended Reading: Can Cancer Cause Skin Rash
Abcdef Guidelines For Pigmented Nail Lesions
Levit et al described ABCDEF guidelines to assess pigmented nail lesions .
- A: Age 4070 years of age African, Japanese, Chinese, and Native American heritage
- B: Brown-black band 3mm with variegated borders
- C: Change or lack of change in the nail band or nail morphology
- D: Digit most commonly involved
- E: Extension of discolouration into the skin surrounding the nail
- F: Family or personal history of melanoma
What Is A Lentigo Maligna
Lentigo malignaLentigo maligna
Lentigo maligna melanoma is a type of invasive skin cancer. It develops from lentigo maligna, which is sometimes called Hutchinson’s melanotic freckle.
Beside above, is lentigo maligna curable? Lentigo maligna can be cured with surgery. However, if the whole area is not removed completely with the appropriate surgery, some may develop into an invasive melanoma. It is therefore important to have it removed with a rim of normal skin .
Additionally, what is the difference between lentigo maligna and lentigo maligna melanoma?
Lentigo maligna is an early form of melanoma in which the malignant cells are confined to the tissue of origin, the epidermis, hence it is often reported as ‘in situ’ melanoma. Lentigo maligna melanoma is diagnosed when the malignant melanoma cells have invaded into the dermis and deeper layers of skin.
What is a lentigo?
nËta?go?/) is a small pigmented spot on the skin with a clearly defined edge, surrounded by normal-appearing skin. It is a harmless hyperplasia of melanocytes which is linear in its spread.
You May Like: Does Melanoma Skin Cancer Itch
Who Gets Nodular Melanoma
Nodular melanoma accounts for about 15% of melanoma in Australia and New Zealand. Although more common in very fair skin , it may also occur in those who tan quite easily , and occasionally in brown or black skin .
Nodular melanoma is more common in males than in females. Most are over the age of 50 when it is diagnosed.
The main risk factors for nodular melanoma are:
- Increasing age
- Previous invasive melanoma or melanoma in situ
- Many melanocyticnaevi
- Multiple atypical naevi
- Fair skin that burns easily
It is less strongly associated with sun exposure than superficial spreading and lentigo maligna types of melanoma.
Can Changing My Diet Help Prevent Melanoma
The American Cancer Society advocates eating a plant-based diet over an animal-based diet as part of a healthy plan to avoid all cancers. Growing evidence suggests that plants pack a powerful punch in any fight against cancer because they’re nutritious, cholesterol-free and fiber-rich.
Theres no doubt that a healthy diet can protect your immune system. Having a strong immune system is important to help your body fight disease. Some research has shown that a Mediterranean diet is a healthy choice that may help prevent the development of cancer. Talk to your healthcare provider about the role food plays in lowering your cancer risks.
Some skin and immune-system healthy foods to consider include:
- Daily tea drinking: The polyphenols in tea help strengthen your immune system. Green tea contains more polyphenols than black tea.
- High vegetable consumption: Eating carrots, cruciferous and leafy vegetables is linked to the prevention of cutaneous melanoma.
- Weekly fish intake: Study participants who ate fish weekly seemed to avoid developing the disease when compared to those who did not eat fish weekly.
You May Like: What Is The Treatment For Lobular Carcinoma In Situ
When Is A Mole A Problem
If a new or existing mole begins to change shape, color, size, or becomes flaky, crusty, or begins to bleed, it’s time to make an appointment with your dermatologist to get it checked out. A mole can turn into melanoma on rare occasions. In early melanoma, the shape of a mole becomes asymmetrical and uneven.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
Nodular basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that is most often found on the head. This type of cancer starts in basal cells, which are tasked with making new skin cells to push the old ones toward the surface of the skin. Nodular basal cell carcinoma is responsible for 60%-80% of all basal cell carcinomas. In the United States, its estimated that 4.3 million cases of basal cell carcinoma are diagnosed every year, with 2.5 to 3.4 million of those cases being nodular basal cell carcinoma.
This type of cancer appears as a pearl-like papule that is round and surrounded by threadlike red lines on the skin made up of tiny blood vessels. The risk of developing nodular basal cell carcinoma can be increased by spending a lot of time out in the sun, living in high-altitude and sunny locations, and radiation therapy.
Other risk factors include:
- Prolonged exposure to arsenic
- Certain rare genetic disorders such as basal cell nevus syndrome
Although this type of cancer is common, it is highly treatable, and the five-year relative survival rate is 100%.
Signs Of Melanoma In Situ
According to the American Cancer Society, the most important warning sign of melanoma is an existing mole or spot on the skin that is changing in shape, color, or size. This spot may look vastly different from the other spots on your skin. A new lesion on the skin can also indicate melanoma. If you notice any of these warning signs, see your physician at once.
The ABCDE rule is an easy-to-remember guide to help you identify melanoma. When performing your monthly at home skin check, look for:
- Asymmetry: A birthmark or mole that is not symmetrical. That means that one-half does not match the other.
- Border: Look for edges that are blurred, notched, ragged or otherwise irregular.
- Color: The color may include different shades of black or brown. It will usually not have the same color all over. It may sometimes appear with patches of blue, white or pink.
- Diameter: Any spot or mole larger than about ¼ inch should be checked by a physician.
- Evolving: A spot or mole that is changing in color, shape or size.
If you notice any of the above symptoms, contact a dermatologist right away. Additionally, keep in mind that a dermatologist’s eye is going to be much more advanced at detecting cancers. Keep up with your annual or biannual skin checks for maximum protection.
Read Also: Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Contagious
Diagnostic Excision Of A Lesion Suspicious Of Nodular Melanoma
If the skin lesion is suspected to be a nodular melanoma, it should be urgently cut out . A small biopsy is best avoided, except in unusually large lesions. An incisional or punch biopsy could be misleading.
The pathological diagnosis of melanoma can be challenging. Nodular melanomas have little or no spread of malignant cells within the epidermis the melanoma cells are found within the dermis or subcutaneous fat. Extra tests using immunohistochemical stains may be necessary.
Surgery To Remove Melanoma That Has Spread
You might have surgery to remove melanoma that has spread to other areas of the skin or body, such as the lungs, skin and bowel. Cancer that has spread to another area of the body is called secondaries or metastases. The operation you have depends on which part of the body the melanoma has spread to.
For example, you might have surgery to remove a secondary melanoma in the skin. Or it might be possible for some people to have an operation to remove a secondary melanoma in their lung or bowel. This operation is more likely if there are no other signs of melanoma elsewhere in the body. And you need to be reasonably fit and well to have this operation.
It is not usually possible to cure the melanoma. But some people can stay well for months or sometimes years after having several different treatments such as surgery to remove metastases, targeted cancer drugs or immunotherapies.
Read Also: When Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spreads
What Tests Are Used To Stage Melanoma
There are several tests your doctor can use to stage your melanoma. Your doctor may use these tests:
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Patients with melanomas deeper than 0.8 mm, those who have ulceration under the microscope in tumors of any size or other less common concerning features under the microscope, may need a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes to determine if the melanoma has spread. Patients diagnosed via a sentinel lymph node biopsy have higher survival rates than those diagnosed with melanoma in lymph nodes via physical exam.
- Computed Tomography scan: A CT scan can show if melanoma is in your internal organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan: An MRI scan is used to check for melanoma tumors in the brain or spinal cord.
- Positron Emission Tomography scan: A PET scan can check for melanoma in lymph nodes and other parts of your body distant from the original melanoma skin spot.
- Blood work: Blood tests may be used to measure lactate dehydrogenase before treatment. Other tests include blood chemistry levels and blood cell counts.
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma occurs when a tumor makes its way into the dermis via thin strands between collagen fibers. This aggressive type of skin cancer is harder to diagnose and treat because of its location. Typically, infiltrative basal cell carcinoma appears as scar tissue or thickening of the skin and requires a biopsy to properly diagnose.
To remove this type of basal cell carcinoma, a specific form of surgery, called Mohs, is used. During a Mohs surgery, also called Mohs micrographic surgery, thin layers of skin are removed until there is no cancer tissue left.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Superficial basal cell carcinoma, also known as in situ basal-cell carcinoma, tends to occur on the shoulders or the upper part of the torso, but it can also be found on the legs and arms. This type of cancer isnt generally invasive because it has a slow rate of growth and is fairly easy to spot and diagnose. It appears reddish or pinkish in color and may crust over or ooze. Superficial basal cell carcinoma accounts for roughly 15%-26% of all basal cell carcinoma cases.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Know If I Got Skin Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ, also known as Bowens disease, is a precancerous condition that appears as a red or brownish patch or plaque on the skin that grows slowly over time. The patches are often found on the legs and lower parts of the body, as well as the head and neck. In rare cases, it has been found on the hands and feet, in the genital area, and in the area around the anus.
Bowens disease is uncommon: only 15 out of every 100,000 people will develop this condition every year. The condition typically affects the Caucasian population, but women are more likely to develop Bowens disease than men. The majority of cases are in adults over 60. As with other skin cancers, Bowens disease can develop after long-term exposure to the sun. It can also develop following radiotherapy treatment. Other causes include immune suppression, skin injury, inflammatory skin conditions, and a human papillomavirus infection.
Bowens disease is generally treatable and doesnt develop into squamous cell carcinoma. Up to 16% of cases develop into cancer.
The Four Main Types Of Cutaneous Melanoma
Cutaneous melanoma is the most common of these categories, and the four main types of cutaneous melanoma include:
All types of melanoma require immediate attention, as they are more successfully treated when caught in their early stages. If you suspect you may have a form of skin cancer, call or complete our new patient registration form online. No referral is necessary to meet with the multispecialty team of oncologists who specialize in skin cancer.
- BROWSE
Recommended Reading: How To Stop Basal Cell Carcinoma
Many Melanomas Dont Require Immediate Treatment
Many people have this concept that all melanomas are extremely rapidly growing cancers, says Dr. Marghoob. They think that waiting even one day after the diagnosis of melanoma can be fatal.
While some subtypes of melanoma do grow extremely fast, says Dr. Marghoob, most early melanomas dont require immediate treatment, allowing ample time to detect, treat, and cure them. Dr. Marghoob advises checking your skin on a monthly basis. If you notice a changing spot on your skin, dont delay in getting it checked out by a dermatologist, he says. And if your doctor does think you may have a melanoma, know that for most people its not necessary to rush to treatment. Most people can take the time they need to meet with doctors and understand their options.
Skin Checks In Future
- detect any evidence of the melanoma returning or spreading to other organs, and
- identify new melanomas.
If the original melanoma returns, it is likely to be in the first 1-2 years after diagnosis . People who have had a melanoma have an increased risk â as much as 5 to 10 fold â of developing a new melanoma in future. This increased risk persists lifelong .
The usual follow-up for a patient with melanoma in situ is:
- full body skin cancer check for melanoma and other skin cancers, plus examination of lymph nodes and abdomen for signs of spread: 6-monthly for two years, then 12-monthly for the next three years and then
- a full body skin cancer check for melanoma and other skin cancers every year for life .
Also Check: How Does Skin Cancer Feel
What Are The Signs Of Melanoma
Knowing how to spot melanoma is important because early melanomas are highly treatable. Melanoma can appear as moles, scaly patches, open sores or raised bumps.
Use the American Academy of Dermatology’s “ABCDE” memory device to learn the warning signs that a spot on your skin may be melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half does not match the other half.
- Border: The edges are not smooth.
- Color: The color is mottled and uneven, with shades of brown, black, gray, red or white.
- Diameter: The spot is greater than the tip of a pencil eraser .
- Evolving: The spot is new or changing in size, shape or color.
Some melanomas don’t fit the ABCDE rule, so tell your doctor about any sores that won’t go away, unusual bumps or rashes or changes in your skin or in any existing moles.
Another tool to recognize melanoma is the ugly duckling sign. If one of your moles looks different from the others, its the ugly duckling and should be seen by a dermatologist.
Precancerous Conditions Of The Skin
Lentigo maligna is a very early form of melanoma skin cancer called melanoma in situ. Cancer cells are only found in the top or outer layer of the skin . It tends to grow slowly. If lentigo maligna isnt treated, it may become a type of invasive melanoma skin cancer called lentigo maligna melanoma. It could take 10 years or more to happen.
Some doctors describe lentigo maligna as a precancerous skin condition because the cancer cells havent grown into deeper layers of skin or surrounding tissue.
Lentigo maligna usually develops on areas of skin that are regularly exposed to the sun without protection, especially the face, head and neck. It most often happens in people in their 70s or 80s.
Recommended Reading: What Does Early Squamous Skin Cancer Look Like
Treating Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage IV melanomas have already spread to distant lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
Metastases in internal organs are sometimes removed, depending on how many there are, where they are, and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab are typically the first drugs tried, especially in people whose cancer cells do not have BRAF gene changes. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Ipilimumab , a different type of checkpoint inhibitor, is not typically used by itself as the first treatment, although it might be combined with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. This slightly increase the chances that the tumor will shrink, although itâs also more likely to result in serious side effects, which needs to be considered carefully. People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects..
Itâs important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.