Unusual Skin Patch Or Sore
If you noticed a skin growth or sore pop up that doesn’t seem to be going away, it could be non-melanoma skin cancer, says the Cancer Treatment Centers of America . Just keep an eye on it: if it’s changing size and color with time, it might be more than an everyday skin condition that just goes away on its own and should be checked out before it goes deeper into the skin. And for more things to keep an eye on, don’t miss the 20 Skin Symptoms That Indicate More Serious Health Issues.
What Is The Staging For Skin Cancer
There is no specific staging system for basal cell carcinoma. If the tumor is wider than 2 cm , it is probably a more serious tumor. Basal cell carcinomas of the ears, nose, and eyelid may also be of more concern, regardless of the size.
There is a staging system for squamous cell carcinoma. Large tumors that are thicker than 2 mm, invade the nerve structures of the skin, occur on the ear, and have certain worrisome characteristics under the microscope are of more concern. If the tumor metastasizes to a site at some distance from the primary tumor, the cancer is likely to be a dangerous tumor.
What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer And Their Symptoms
Think about the parts of your body that get the most sun exposure: Your face, ears, scalp, lips, neck, chest, hands, and arms. On women, that also includes the legs. Skin cancer usually develops in those places, but can also show up in other areaseven your groin or in between your toes.
Keep an eye out for these signs of skin cancer, which vary depending on the type you’ve developed.
The rarest, yet deadliest form of skin cancer. It is most often characterized by asymmetrical moles with irregular borders. Learn more about the melanoma symptoms you should tell your doctor about ASAP.
Also called solar keratosis, actinic keratosis is a precancer or a premalignant lesion. These lesions are usually rough, red, and scaly, and vary in size, and often occur on the face, lips, ears, back of the hands, and arms. They may also be itchy or painful.
The most common type of skin cancer. It tends to be slow growing and is very treatable. These lesions are pearly or shiny bumps or spots that often develop on the face, neck, and ears. They tend to form scabs or sores, be scaling and flaky, or bleed easily.
The second most common type of skin cancer, squamous cell carcinoma is similar to basal cell carcinoma in that it tends to be a pink bump or patch that won’t go away. Relatively easy to treat when spotted early.
Read Also: What Is Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Signs And Symptoms Of Cancer
Signs and symptoms are ways the body lets you know that you have an injury, illness, or disease.
- A sign, such as fever or bleeding, can be seen or measured by someone else.
- A symptom, such as pain or fatigue, is felt or noticed by the person who has it.
Signs and symptoms of cancer depend on where the cancer is, how big it is, and how much it affects nearby organs or tissues. If a cancer has spread , signs or symptoms may appear in different parts of the body.
Signs And Symptoms Of Non
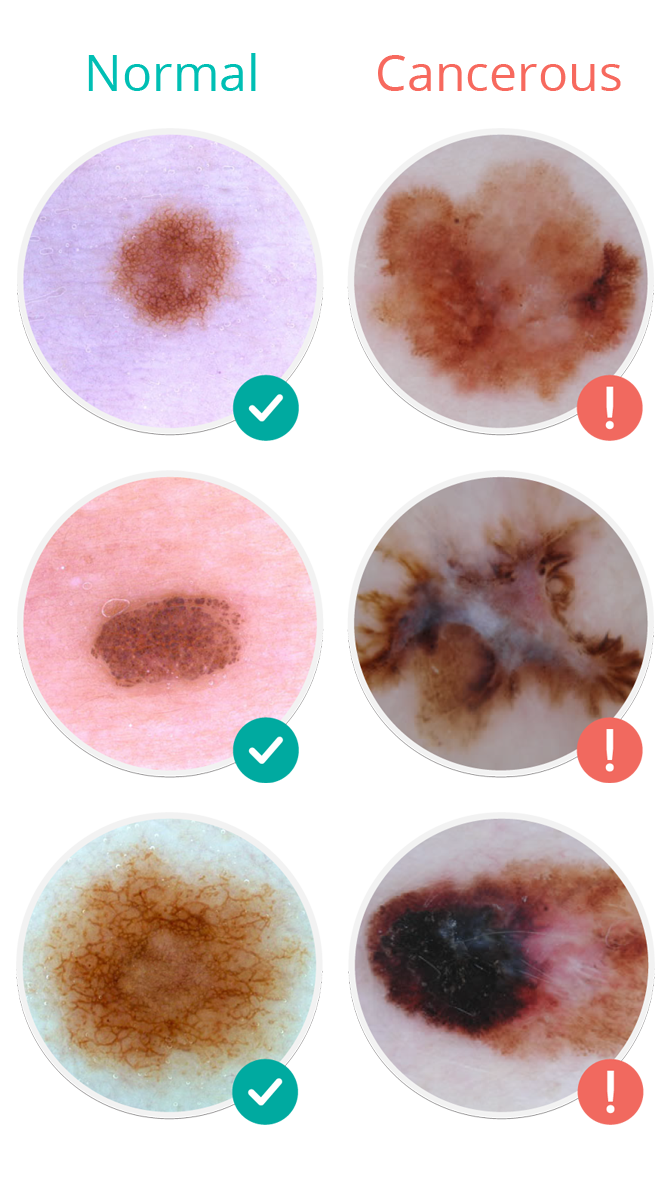
Non-melanoma skin cancer usually starts as an abnormal area or change on any part of the skin. How non-melanoma skin cancer looks often depends on the type of cancer. Other health conditions can also look like non-melanoma skin cancer. See your doctor if you have any changes on your skin.
The following are common signs and symptoms of basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma , the most common types of non-melanoma skin cancer.
Basal cell carcinoma usually develops on areas of skin exposed to the sun, especially the head, face and neck. It can also develop on the central part of the body . BCC may appear on the skin as:
- a sore that doesnt heal or comes back after healing
- pale white or yellow flat areas that look like scars
- raised and scaly red patches
- small, smooth and shiny lumps that are pearly white, pink or red
- a pink growth with raised edges and indents in the centre
- a growth that has small blood vessels on the surface
- a sore that bleeds
- a growth or area that is itchy
Squamous cell carcinoma usually develops on areas of skin exposed to the sun, but it can also be found on the skin around the genitals and anus. It can occur on the skin of scars, sores, ulcers and burns. SCC may appear on the skin as:
- a sore that doesnt heal or comes back after healing
- rough or scaly red patches with irregular borders
- raised lumps that indent in the centre
- a growth that looks like a wart
- a sore that is crusty or bleeds easily
- a growth or area that is itchy, irritated or sore
Don’t Miss: Why Do You Get Skin Cancer
How To Give Yourself A Skin Exam
Skin cancers are almost always curable when they’re found earlyand although an annual visit to a dermatologist for a skin exam will help, scanning your own skin head-to-toe monthly may help you spot new or changing lesions. Keep an eye out for the changing moles that are the hallmark sign of melanoma, as well as other signs of skin cancer.
When Is A Mole A Problem
A mole is a benign growth of melanocytes, cells that gives skin its color. Although very few moles become cancer, abnormal or atypical moles can develop into melanoma over time. “Normal” moles can appear flat or raised or may begin flat and become raised over time. The surface is typically smooth. Moles that may have changed into skin cancer are often irregularly shaped, contain many colors, and are larger than the size of a pencil eraser. Most moles develop in youth or young adulthood. It’s unusual to acquire a mole in the adult years.
You May Like: How Fast Can Skin Cancer Kill You
Tips For Screening Moles For Cancer
Examine your skin on a regular basis. A common location for melanoma in men is on the back, and in women, the lower leg. But check your entire body for moles or suspicious spots once a month. Start at your head and work your way down. Check the “hidden” areas: between fingers and toes, the groin, soles of the feet, the backs of the knees. Check your scalp and neck for moles. Use a handheld mirror or ask a family member to help you look at these areas. Be especially suspicious of a new mole. Take a photo of moles and date it to help you monitor them for change. Pay special attention to moles if you’re a teen, pregnant, or going through menopause, times when your hormones may be surging.
Who Gets Skin Cancer And Why
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation treatment, and even heredity may play a role. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive sun exposure or blistering sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
You May Like: What Can Skin Cancer Do
Moles That Change Size
While normal moles are generally smaller than 6 millimeters , seeing something bigger than that is a key warning sign that you could have melanoma. If your spot is bigger than the size of a pencil eraser, check it out to make sure nothing funky is going on with your skin, says the ACA. But don’t rule out smaller spots, either: melanoma can be tinier than 6 millimeters, too.
Basal Cell Skin Cancer Warning Signs
Basal cell cancer tends to develop on parts of the body that get a lot of sun exposure, like the face, head, and neck, but they can appear anywhere.
Some are flat and look a lot like normal skin. Others have more distinctive characteristics, says the American Cancer Society , including:
- Flat, firm, pale, or yellow areas that resemble a scar
- Raised, reddish patches of skin that might be itchy or irritated
- Small bumps that might be pink, red, pearly translucent, or shiny, possibly with areas of blue, brown, or black
- Pink growths with slightly raised edges and an indentation in the center tiny blood vessels might run through it like the spokes of a wheel
- Open sores, possibly with oozing or crusted areas, that dont heal or that go through cycles of healing and bleeding
- Delicate areas that bleed easily. For instance, having a sore or cut from shaving that lingers longer than one week.
These slow-growing skin cancers can be easy to ignore unless they become big and begin to itch, bleed, or even hurt, according to the ACS.
You May Like: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
Signs Of Dying From Cancer
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death in the United States. Although mortality rates are dropping, cancer is common enough that most people in the United States know someone who has had cancer in their lifetime.
However, not as much is known about the end-of-life signs of cancer, and what one should expect at the end. Furthermore, many are unaware of the ways in which hospice can help patients in dealing with the stages of death from cancer.
Identifying Skin Cancer: 37 Photos You Need To See
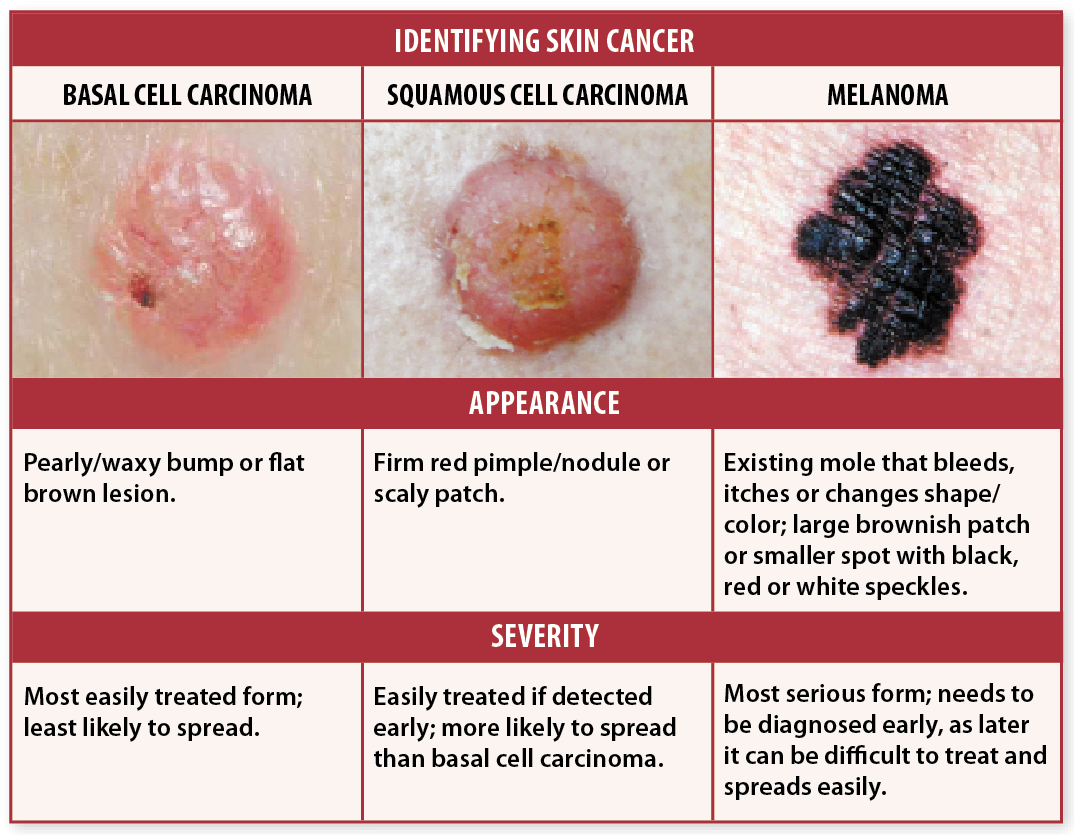
As we head into summer, its time to kick your safe skin practices into high gear. All individuals should apply a broad spectrum SPF every day, and watch their local UV forecast for daily updates when outside activities are planned.
Why? Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States. One in five Americans will be diagnosed with the disease in his or her lifetime. There are more new cases of skin cancer every year than breast, prostate, lung and colon cancers combined, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Although family history and your natural skin pigmentation play a role in your risk, the number-one thing that causes skin cancer is exposure to UV rays.
Erin Gilbert, M.D., Ph.D., a spokesperson for the Skin Cancer Foundation, offered these guidelines to weather.com in 2014: Avoid the sun when its at its peak wear sun-protective clothes, such as a hat always wear a broad-spectrum SPF. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or after swimming or sweating.
Its a myth that most sun damage occurs in childhood, so theres nothing you can do about it as an adult, Dr. Gilbert said.
Twenty-three percent of sun damage happens before youre 18, but it is cumulative. Its never too late to start protecting yourself, she said. Your melanoma risk doubles if youve had more than five severe sunburns at any age. Dont let a sunburn or a tan deter you from seeing your dermatologist or wearing sun screen the next day.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Treatment For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Talk to your doctor if you notice changes in your skin such as a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, a change in an old growth, or any of the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma.
A change in your skin is the most common sign of skin cancer. This could be a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, or a change in a mole.external icon Not all skin cancers look the same.
For melanoma specifically, a simple way to remember the warning signs is to remember the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma
- A stands for asymmetrical. Does the mole or spot have an irregular shape with two parts that look very different?
- B stands for border. Is the border irregular or jagged?
- C is for color. Is the color uneven?
- D is for diameter. Is the mole or spot larger than the size of a pea?
- E is for evolving. Has the mole or spot changed during the past few weeks or months?
Talk to your doctor if you notice changes in your skin such as a new growth, a sore that doesnt heal, a change in an old growth, or any of the A-B-C-D-Es of melanoma.
Flat Red Patches And Rashes
One type of cancer that affects the skin, T-cell lymphoma, often begins with very itchy, flat, red patches and plaques that are easily mistaken for eczema or psoriasis.
One type of T-cell lymphoma, mycosis fungoids, transitions from these patches to dome-shaped nodules, and then to extensive reddened areas on multiple areas of the body. It may spread to lymph nodes and other regions of the body such as the lungs, liver, and bones. T-cell lymphomas most often begin on the buttocks, groin, hips, armpits, and chest.
Other cancers, such as breast cancer, may spread to the skin and initially be mistaken for a benign rash. Inflammatory breast cancer is a type of breast cancer that originates in the skin and appears, at first, to be an eczematous type of rash.
You May Like: Can People Die From Skin Cancer
Distinguishing Benign Moles From Melanoma
To find melanoma early, when it is most treatable, it is important to examine your skin on a regular basis, and become familiar with moles, and other skin conditions, in order to better identify changes. Certain moles are at a higher risk for changing into malignant melanoma. Large moles that are present at birth , and atypical moles , have a greater chance of becoming malignant.
Recognizing changes in your moles, is crucial in detecting malignant melanoma at its earliest stage. The warning signs are:
Normal mole / melanoma
The Abcde Rule For Melanoma
The ABCDE rule is a useful guide to the common signs of melanoma:
- Asymmetry: For example, one half of a mole or birthmark does not match the other.
- Border: The edges of the spot are irregular or blurred.
- Color: The color varies and may include different shades of brown or black, or even patches of pink, red, white or blue.
- Diameter: The spot is larger than the size of pencil eraser.
- Evolving: The spot is changing in size, shape or color.
Early recognition of possible melanoma skin cancer symptoms can result in earlier diagnosis, as well as more treatment options and a higher likelihood of cure.
Read Also: How To Say Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Do Lumps In My Breast Mean
Many conditions can cause lumps in the breast, including cancer. But most breast lumps are caused by other medical conditions. The two most common causes of breast lumps are fibrocystic breast condition and cysts. Fibrocystic condition causes noncancerous changes in the breast that can make them lumpy, tender, and sore. Cysts are small fluid-filled sacs that can develop in the breast.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Signs And Symptoms
Like basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma usually occurs because of repeated sun exposure over time. This skin cancer is a slow-developing skin cancer that can spread to other areas of the skin, although it is still considered uncommon to spread widely.
Squamous cell carcinoma normally takes the form of:
- wart-like bumps that often have crusted surfaces
- rough, scaly patches that may bleed
- an open sore that bleeds or develops a crust
- red, dome-like nodules
Bowens disease, also known as squamous cell carcinoma in situ, is an early form of squamous cell carcinoma. It usually appears as a red, itchy scaly patch that can often be confused for psoriasis or eczema. It is easily treated, but if left undiagnosed, it can pose a risk.
Recommended Reading: Where Can Skin Cancer Spread
How Can I Help Prevent Sun Damage And Ultimately Skin Cancer
Nothing can completely undo sun damage, although the skin can sometimes repair itself. So, it’s never too late to begin protecting yourself from the sun. Your skin does change with age for example, you sweat less and your skin can take longer to heal, but you can delay these changes by limiting sun exposure.
Maintaining healthy skin
- Stop smoking: People who smoke tend to have more wrinkles than nonsmokers of the same age, complexion, and history of sun exposure. The reason for this difference is unclear. It may be because smoking interferes with normal blood flow in the skin.
- Apply sunscreen with a sun protection factor of 30 or greater 30 minutes before sun exposure and then every 2 to 3 hours thereafter. Reapply sooner if you get wet or perspire significantly.
- Select cosmetic products and contact lenses that offer UV protection.
- Wear sunglasses with total UV protection.
- Avoid direct sun exposure as much as possible during peak UV radiation hours between 10 am and 4 pm.
- Perform skin self-exams regularly to become familiar with existing growths and to notice any changes or new growths.
- Relieve dry skin using a humidifier at home, bathing with soap less often , and using a moisturizing lotion.
- Become a good role model and foster skin cancer prevention habits in your child. Eighty percent of a person’s lifetime sun exposure is acquired before age 18.
Understanding UV index
0-2: Low
3-5: Moderate
6-7: High
8-10: Very high
11 or higher : Extreme