Meaning Of Carcinoma In Situ
In many ways, the term “carcinoma” is simply equated with cancer. Roughly 85 percent of cancers are carcinomas. Carcinomas are composed of epithelial cells the type of cells that line the skin, breast ducts, and other surfaces of organs in the body.
The subtypes of carcinomas include adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma , and basal cell carcinoma.
Carcinoma in situ can be further defined by the tissue type in which cancer is beginning. For example, squamous cell carcinoma in situ of the cervix would represent a cancer that had started in squamous cells which line the cervix and has not yet become invasive.
Tumors such as sarcomas arise in tissues which do not have a basement membrane so that for these types of cancer there is not a stage of carcinoma in situ. In other words, tumors such as bone cancer do not have a pre-invasive stage and the cells would either be considered normal or cancer. Likewise, blood-related cancers, such as leukemias and lymphomas, do not have a preinvasive but cancerous stage for which people can be screened. For cancers that don’t have a CIS stage, screening tests are not as effective in early detection, because once the abnormal cells are detected, it would already be considered invasive with the potential to spread .
Carcinoma In Situ Vs Cancer
A million-dollar question lately, especially with controversy over the treatment of ductal carcinoma in situ or in situ breast cancer, is whether or not carcinoma in situ is really cancer. The answer is that it depends on who you talk to. Some physicians classify carcinoma in situ as non-invasive cancer and others may prefer calling it pre-cancer. The distinction would lie in knowing whether or not the CIS would progress to invasive cancer, and that, by definition, is not known. Nor are we apt to get answers soon, as it wouldn’t be ethical to simply watch large numbers of carcinoma in situ’s to see if they became invasive cancer and spread.
Path To Improved Health
The following are terms that you might hear during the diagnosis and treatment of cancer:
Adjuvant therapy: Therapy used to kill remaining cancer cells left behind after primary treatment, usually surgery. Could include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or hormone therapy.
Advance Directive: Instructions on what kind of care you would like to receive if you become unable to make medical decisions. Includes living wills and do-not-resuscitate orders.
Benign: Noncancerous. Any tumor, growth, or cell abnormality that is not cancerous. The growth will not spread to deeper tissues or other parts of the body. Also called nonmalignant.
Biological Therapy: Therapy that uses substances made from living organisms to attack cancer cells. The substances may occur naturally in the body. They also may be made in a laboratory. Some therapies affect the immune system. Others attack specific cancer cells.
Biopsy: Removal of a small portion of tissue to see if it is cancerous.
Carcinoma In Situ : A group of abnormal cells that remain in the place where they first formed. The cells may become cancer and spread to nearby tissue.
Chemotherapy: Therapy that uses special medicines to damage and kill cancer cells.
Clinical Trials: Research studies that involve actual patients. They help find better ways to manage cancer . They study prevention, detection, diagnosis, and treatment.
Colposcopy: Procedure where a lighted, magnifying instrument is used to look for problems in the vagina and cervix.
Also Check: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
Tissue Changes That Are Not Cancer
Not every change in the bodys tissues is cancer. Some tissue changes may develop into cancer if they are not treated, however. Here are some examples of tissue changes that are not cancer but, in some cases, are monitored because they could become cancer:
- Hyperplasia occurs when cells within a tissue multiply faster than normal and extra cells build up. However, the cells and the way the tissue is organized still look normal under a microscope. Hyperplasia can be caused by several factors or conditions, including chronic irritation.
- Dysplasia is a more advanced condition than hyperplasia. In dysplasia, there is also a buildup of extra cells. But the cells look abnormal and there are changes in how the tissue is organized. In general, the more abnormal the cells and tissue look, the greater the chance that cancer will form. Some types of dysplasia may need to be monitored or treated, but others do not. An example of dysplasia is an abnormal mole that forms on the skin. A dysplastic nevus can turn into melanoma, although most do not.
- Carcinoma in situ is an even more advanced condition. Although it is sometimes called stage 0 cancer, it is not cancer because the abnormal cells do not invade nearby tissue the way that cancer cells do. But because some carcinomas in situ may become cancer, they are usually treated.
When Should I See A Healthcare Provider About Basal Cell Carcinoma

It is important to contact a healthcare provider any time you have a skin problem that does not resolve. This means developing any new or larger mole, lump or sore, or new symptoms such as pain or itchiness. If you have had BCC or another type of skin cancer, you will probably be given a recommended schedule of needed appointments. You should follow up on these appointments as directed.
Don’t Miss: Soderstrom Skin Cancer Screening
The Second Most Common Skin Cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is the second most common form of skin cancer, characterized by abnormal, accelerated growth of squamous cells. When caught early, most SCCs are curable.
SCC of the skin is also known as cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma . Adding the word cutaneous identifies it as a skin cancer and differentiates it from squamous cell cancers that can arise inside the body, in places like the mouth, throat or lungs.
Outlook After An Rcc Diagnosis
The outlook after being diagnosed with RCC depends largely on whether the cancer has spread and how soon treatment is started. The sooner its caught, the more likely you are to have a full recovery.
If the cancer has spread to other organs, the survival rate is much lower than if its caught before spreading.
According to the National Cancer Institute, the five-year survival rate for RCC is over
You May Like: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
How Can You Prevent Basal Cell Carcinoma
Being safe in the sun is the best way to prevent BCC and other skin cancers. Here are some tips:
- Avoid being in the sun from 10 am to 4 pm.
- Avoid tanning beds.
- Use a broad spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher each day. If you will be outside for longer periods of time, use a broad spectrum sunscreen that is water-resistant and has an SPF of 30 or higher. Put the sunscreen on 30 minutes before going outside. Put sunscreen on again every two hours, or more frequently if you have been swimming or sweating a lot.
- Use protective clothing that has built-in sun protection, which is measured in UPF. Also, use broad-brimmed hats and sunglasses.
- Do your own skin self-exam about once per month and see a dermatologist about one time per year for a professional skin exam.
- Have any skin changes examined as soon as possible by a healthcare provider.
Hormone Therapy After Surgery
If the DCIS is hormone receptor-positive , treatment with tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor for 5 years after surgery can lower the risk of another DCIS or invasive cancer developing in either breast. If you have hormone receptor-positive DCIS, discuss the reasons for and against hormone therapy with your doctors.
Don’t Miss: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Components Of Medical Words
Most medical terms are compound words made up of root wordswhich are combined with prefixes andsuffixes . Thus medical terms that may atfirst seem very complex can be broken down into their componentparts to give you a basic idea of their meaning. For example theword neuroblastoma
- neuro- means nerve
- blast- relates to immature cells
- -oma means tumour.
Therefore by breaking down a complex word we can see thatneuroblastoma literally means a tumour made up of immature nervecells.
To take another type of tumour: osteogenic sarcoma
- osteo- means bone
- -genic means creating / causing
Thus we can see that this is a bone forming tumour.
All medical terms have a root word. They may also have aprefix, a suffix, or both a prefix and a suffix.
Prefixes have a droppable “o”, which acts to connect the prefix to root words which begin with a consonant. As a general rule, the “o” is dropped when connecting to a root word beginning with a vowel .
Etymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time. Most medical words derive from ancient Greek and Latin.
Some examples of root words:-
| component |
What Does The Term ‘carcinoma’ Mean
Dr. Susan Love answers the question: ‘What Does Carcinoma Mean?’
— Question: What does the term “carcinoma” mean?
Answer: Carcinoma is a really broad term to mean a cancer that starts in an epithelial cell, in one of the cells that line our body — in the skin, you can have carcinoma of the brain, you can have carcinoma of the colon, so it’s not defined just as breast. Cancer means not only is there abnormal growth, but those cells can spread to other parts of the body and start invading, almost as terrorists, into other areas — and that’s what really kills you when you get cancer. It’s not the cells in the original organ, but the cells that get into more important places, like the lungs, or the liver, or the brain.
Read Also: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Are The Complications/side Effects Of The Treatments For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Most of the complications related to BCC treatments other than the hedgehog inhibitors are cosmetic, such as scarring or redness.
People who use sonidegib or vismodegib should make sure to use effective birth control to avoid pregnancy due to the risk of birth defects. In addition, sonidegib has other potential risks, including problems with nerves and muscles.
Carcinoma Treatment And Therapy Options

Treatment for carcinoma varies depending on the type, location and extent of the disease, but may include:
Surgery: Depending on the type of cancer, carcinoma may be treated with the surgical removal of cancerous tissue, as well as some surrounding tissue. Minimally invasive surgical treatment methods may help to reduce healing time and reduce the risk of infection after surgery.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy may be used in combination with surgery and/or chemotherapy. Advanced radiation therapies use image guidance before and during treatment on target tumors, and are designed to help spare healthy tissues and surrounding organs.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy treats carcinoma with drugs designed to destroy cancer cells, either throughout the whole body, or in a specific area. In some cases, chemotherapy may be used in combination with other treatments, such as radiation therapy or surgery.
Expert
Recommended Reading: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
DCIS is the earliest form of breast cancer. It develops in the lining of the breast ducts and is noninvasive, which means the cells do not spread to other parts of the body. Because of this, the survival rate for DCIS is .
Although DCIS itself is noninvasive, it can in some cases turn into an invasive form of cancer.
What Is The Prognosis For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Based on individual markers and prognostic factors, including the staging of your tumor, your physician will work to give you a prognosis. At Johns Hopkins Medicine, our team of breast cancer specialists is dedicated to developing cutting-edge techniques for surgery, breast reconstruction, chemotherapy, biologic targeted therapy, radiation therapy and other hormonal therapies. Our research allows us to make great strides forward for patients with breast cancer.
You May Like: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
What Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
It’s the most common type of kidney cancer. Although itâs a serious disease, finding and treating it early makes it more likely that youâll be cured. No matter when youâre diagnosed, you can do certain things to ease your symptoms and feel better during your treatment.
Most people who have renal cell carcinoma are older, usually between ages 50 and 70. It often starts as just one tumor in a kidney, but sometimes it begins as several tumors, or itâs found in both kidneys at once. You might also hear it called renal cell cancer.
Doctors have different ways to treat renal cell carcinoma, and scientists are testing new ones, too. Youâll want to learn as much about your disease as you can and work with your doctor so you can choose the best treatment.
Examples Of Carcinoma In A Sentence
carcinomacarcinomaCondé Nast TravelercarcinomaCNNcarcinoma PEOPLE.comcarcinoma BostonGlobe.comcarcinomaCNNcarcinomaNew York Timescarcinoma EssencecarcinomaHarper’s Magazine
These example sentences are selected automatically from various online news sources to reflect current usage of the word ‘carcinoma.’ Views expressed in the examples do not represent the opinion of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback.
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
What Is A Squamous Cell
One of three main types of cells in the top layer of the skin , squamous cells are flat cells located near the surface of the skin that shed continuously as new ones form.
SCC occurs when DNA damage from exposure to ultraviolet radiation or other damaging agents trigger abnormal changes in the squamous cells.
Carcinoma Of Unknown Primary Site
The term carcinoma has also come to encompass malignant tumors composed of transformed cells whose origin or developmental lineage is unknown , but that possess certain specific molecular, cellular, and histological characteristics typical of epithelial cells. This may include the production of one or more forms of cytokeratin or other intermediate filaments, intercellular bridge structures, keratin pearls, and/or tissue architectural motifs such as stratification or pseudo-stratification.
Don’t Miss: Basal Skin Cancer Survival Rates
How Is Renal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed
If your doctor suspects that you may have RCC, theyll ask about your personal and family medical history. Theyll then do a physical exam. Findings that can indicate RCC include swelling or lumps in the abdomen, or, in men, enlarged veins in the scrotal sac .
If RCC is suspected, your doctor will order a number of tests to get an accurate diagnosis. These may include:
- complete blood count a blood test conducted by drawing blood from your arm and sending it to a lab for evaluation
- CT scan an imaging test that allows your doctor to take a closer look at your kidneys to detect any abnormal growth
- abdominal and kidney ultrasounds a test that uses sound waves to create a picture of your organs, allowing your doctor to look for tumors and problems within the abdomen
- urine examination tests used to detect blood in the urine and to analyze cells in the urine looking for evidence of cancer
- biopsy the removal of a small piece of kidney tissue, done by inserting a needle into the tumor and drawing out a tissue sample, which is then sent to a pathology lab to rule out or confirm the presence of cancer
If you are found to have RCC, more tests will be done to find out if and where the cancer has spread. This is called staging. RCC is staged from stage 1 to stage 4, in order of ascending severity. Staging tests can include a bone scan, PET scan, and chest X-ray.
Approximately one-third of individuals with RCC have cancer that has spread at the time of diagnosis.
Patient Discussion About Carcinoma
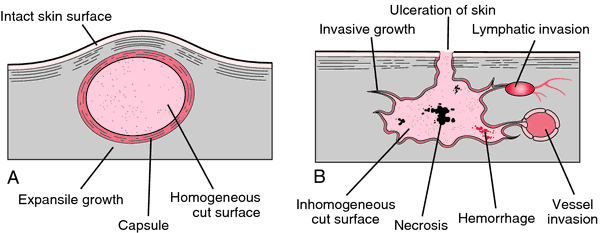
Q. Can any one give me information about Carcinoma of the pancreas? What is the prognosis for carcinoma of the pancreas? I want to know as much as I can information on carcinoma of the pancreas.
A.
Q. Do japanese in the US still have high risk of stomach cancer? I was born in the US to parents that emigrated from Japan when they were in their late twenties. I know that people in Japan have a very high risk of stomach cancer. Does that mean that as an individual of Japanese origin I also have high risk, although I never were in Japan?
A.
Q. what is the most accurate pathological test to identify the primary source of a cystic mass in the neck? the mass was removed. Pathologist was unable to identify the source and diagnosed the mass as a branchilogic carcinmoa . Therefore, I am looking for the most updated test and examinations that can be applied to blocks of the mass and determine their origin
A.
Don’t Miss: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Treatment
Most women with IDC have surgery to remove the cancer. The treatment options are usually:
- Lumpectomy: The surgeon only removes the tumor and a bit of the tissue around it to help make sure all the cancer cells have been removed. You might hear it called breast-conserving surgery
- Mastectomy: The surgeon removes an entire breast.
Which one you get depends on the size of your tumor and how much it has spread throughout your breast and surrounding lymph nodes.
In addition to surgery, other treatments may include:
- Radiation: This usually follows your surgery.
- Hormone therapy: Youll get it if your cancer is hormone receptor-positive . These drugs block or lower the amount of estrogen in your body.
- Chemotherapy: These medications target cancer cells throughout your body. Doctors may also use It before surgery to shrink tumors and after to kill any cancer cells left behind.
- Targeted therapy: These medications block cancer cell growth. You might get them along with chemotherapy.
You might get one treatment or a combination.