What Could Be The Harm In Trying Home Remedies For Skin Cancer First
First, you may not know exactly what kind of lesion you are self-treating. Accurate diagnosis of skin cancer requires examination by a healthcare professional. There are three main types of skin cancer, and several subtypes of each. Although there are typical features of each type, cancerous lesions may have atypical features. Even dermatologists use special magnifying glasses and handheld imaging devices. These tools help them to identify suspicious lesions. A skin biopsy is needed to confirm that a lesion is cancerous.
Second, delaying effective treatment for skin cancer can lead to worse outcomes. One risk of using a home remedy is that it will not work, giving the cancer time to grow. Of the three major skin cancers, melanoma is the most likely to invade and spread if it is not treated early.1 About 5% to 10% of squamous cell carcinoma is aggressive.2 Squamous cell carcinoma is difficult to treat once it spreads. Although basal cell carcinoma rarely spreads to distant parts of the body, it can grow into bone or the tissue below the skin if left untreated.3
Basal Cell Carcinoma Signs And Symptoms
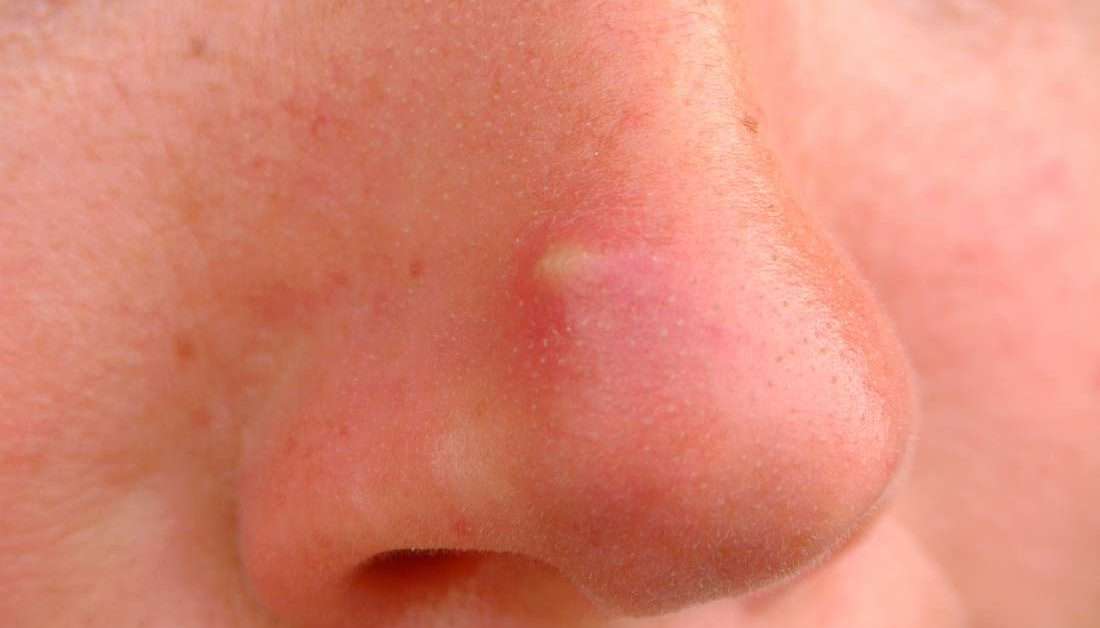
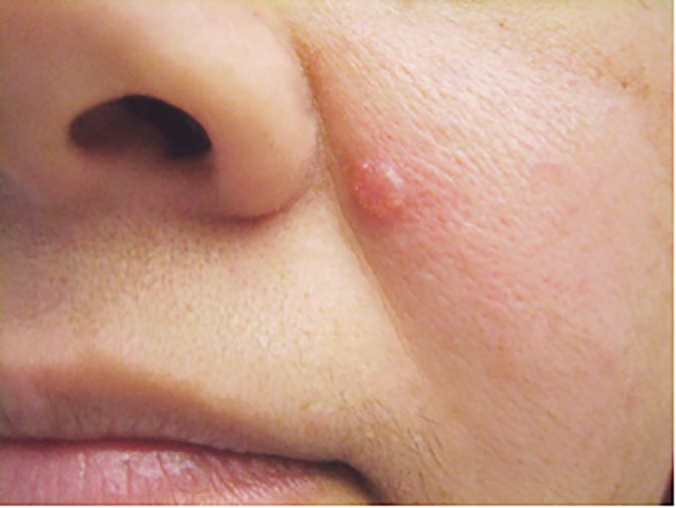
This type of cancer is usually found on sun-exposed areas of the skin like the scalp, forehead, face, nose, neck and back.
Basal cell carcinomas may bleed after a minor injury but then scab and heal. This can happen over and over for months or years with no visible growth, making it easy to mistake them for wounds or sores. They rarely cause pain in their earliest stages.
Appearance
In addition to the bleeding and healing, these are other possible signs of a basal cell cancer:
- A persistent open sore that does not heal and bleeds, crusts or oozes.
- A reddish patch or irritated area that may crust or itch.
- A shiny bump or nodule that is pearly or translucent and often pink, red or white. It can also be tan, black or brown, especially in dark-haired people, and easy to confuse with a mole.
- A pink growth with a slightly elevated, rolled border and a crusted indentation in the center. Tiny blood vessels may appear on the surface as the growth enlarges.
- A scar-like lesion in an area that you have not injured. It may be white, yellow or waxy, often with poorly defined borders. The skin seems shiny and tight sometimes this can be a sign of an aggressive tumor.
Closure With 2 Suture Layers
The scar on the cheek is nicely hidden along the nasolabial crease and is almost imperceptible after healing in many patients. There are two layers of stitches. The underlying stitches cannot be seen in this picture because they are deeper below the surface. They will dissolve on their own. The top layer of sutures are the visible blue sutures and they are removed in approximately 1 week. If sutures are left in the surface too long, a railroad track type of scarring can occur. If sutures are taken out too early then some scars can spread and widen. With strong supporting stitches in the deep layer, removing top stitches 1 week after surgery usually yields the optimal result. After top stitch removal we often reinforce the healing skin by placing steristrips across the surface. These are like small pieces of reinforced tape that usually stay on for about one week and provide a little more support for optimal scar healing. More
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
Stage Ivb And Ivc Ethmoid Sinus Cancers
Stage IVB: For tumors that cannot be removed with surgery or for people who can’t have or dont want surgery, the first treatment is usually radiation therapy. Sometimes chemo is given with the radiation treatments. In some cases, if the person is healthy enough, chemotherapy can be given first then radiation or chemo with radiation. If someone is too weak for those treatment options, radiation alone or one chemotherapy drug might be tried.
Stage IVC: The goal of treatment for cancers that have spread to distant parts of the body, like the lungs or bones, is to stop or slow the growth of the cancer for as long as possible and to help relieve any symptoms it may be causing.
Treatment for this stage depends on where the cancer is, the problems it’s causing, and a persons general health. Chemo is often the main treatment if a person can tolerate it because it reaches almost all parts of the body. Another option might be immunotherapy, either alone or along with chemo. Radiation therapy may be directed at areas of cancer that are causing problems. Because these cancers are hard to treat, clinical trials of newer treatments are a good option for some people.
What Is The Process Of Liquid Nitrogen Skin Cancer Treatment
With this process, a dermatologist will destroy the skin cancer cells by freezing the lesion with liquid nitrogen. The liquid nitrogen is applied to the cells with a cotton applicator or a spray. The method is also known for being used to remove warts, so it may sound familiar. This method can call for numbing prior to the process, depending on how large the lesion is and how sensitive the individual is.
Read Also: Cell Cancer Symptoms
Treating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Several types of treatment can be used to remove or destroy basal cell skin cancers. The options depend on factors such as the tumor size and location, and a persons age, general health, and preferences. These cancers very rarely spread to other parts of the body, although they can grow into nearby tissues if not treated.
All of the treatments listed here can be effective when used in appropriate situations. The chance of the cancer coming back ranges from less than 5% after Mohs surgery to up to 15% or higher after some of the others, but this depends on the size of the tumor. Small tumors are less likely to recur than larger ones. Even if a tumor does recur, it can often still be treated effectively.
The Cosmetic Effects Of Mohs Surgery On The Nose
Mohs surgery, while effective, is not always the best option for treating skin cancer on the nose. Because Mohs requires a doctor to surgically remove multiple layers of skin from the cancerous spot, patients will be left with a wound when the treatment is over. Once the wound heals, there will likely be a scar. Depending on the size of the wound, some patients may even need to have a skin graft or undergo reconstructive surgery to heal.
Don’t Miss: Metastatic Skin Cancer Pictures
Ask The Expert: Why Am I Having Surgery To Remove A Small Basal Cell Carcinoma
Although the nonmelanoma skin cancer basal cell carcinoma is rarely life-threatening, it can be troublesome, especially because 80 percent of BCCs develop on highly visible areas of the head and neck. These BCCs can have a substantial impact on a persons appearance and can even cause significant disfigurement if not treated appropriately in a timely manner.
The fact is, BCCs can appear much smaller than they are. On critical areas of the face such as the eyes, nose, ears and lips, they are more likely to grow irregularly and extensively under the skins surface, and the surgery will have a greater impact on appearance than might have been guessed. Even a small BCC on the face can be deceptively large and deep the extent of the cancer cannot be seen with the naked eye.
If such a BCC is treated nonsurgically , the chance of the cancer recurring is high. Unfortunately, treating a BCC that has returned is usually much more difficult than treating it precisely and completely when initially diagnosed.
BCCs on the trunk, arms and legs that cause concern are typically larger in size, but even a small BCC in these areas can have an irregular growth pattern under the skin if the initial biopsy shows the tumor is aggressive. In addition, a small BCC in an area previously treated with radiation may be much more aggressive than it appears on the surface. Again, treating such a tumor nonsurgically is likely to leave cancer cells behind.
About the Expert:
How Do You Treat Skin Cancer On The Nose
The nose is a relatively common spot for skin cancer to develop. Skin cancer often starts on the face because it’s usually the body part that’s exposed to the sun. The two most common types of skin cancer that develop on the nose are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma . While both types of skin cancer should be addressed right away, BCC is usually slow-growing and SCC grows more quickly. Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer ,with about 80% of cases occurring on the face and 25 to 30% on the nose.
The third type of skin cancer, melanoma, is rare and much more serious. It almost always requires excisional surgery to remove it. Fortunately, most forms of skin cancer are very treatable, especially when caught early. Treatment may include surgery, radiation, topical treatments, and more.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma On Face Prognosis
Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma: The most common type of skin cancer, a disease in which the cancer cells resemble the basal cells of the epidermis, the outer layer of the skin.
Basal cell carcinomas usually appear as the classic sore that doesnt heal. A bleeding or scabbing sore that seems to get somewhat better, then recurs and starts to bleed, may be a basal cell carcinoma.
Most basal cell carcinomas are on the face and neck where the skin is exposed to sunlight. However, a fair number show up on parts of the body such as the abdomen, leg, and scalp exposed to little or no sunlight.
Basal cell carcinomas typically are locally invasive. They tend to burrow in locally and not metastasize to distant locations.
Small basal cell carcinomas can be removed by being scraped and burned . Larger basal cells can be removed by surgery. Basal cell carcinomas on the scalp, ears, and sides of the nose, as well as those which have come back after being treated, are treated best by Mohs surgery.
One basal cell carcinoma means an increased risk of developing another. Prudent sun precautions and annual skin checkups by the doctor are advisable.
When Is Radiation Therapy Used
If a tumor is very large or is on an area of the skin that makes it hard to remove with surgery, radiation therapy may be used as the main treatment. Radiation therapy can also be useful for some patients who, for other health reasons, cant have surgery. Radiation therapy can often cure small basal or squamous cell skin cancers and can delay the growth of more advanced cancers.
Radiation is also useful when combined with other treatments. For example, radiation can be used after surgery as an adjuvant treatment to kill any small areas of remaining cancer cells that may not have been visible during surgery. This lowers the risk of cancer coming back after surgery. Radiation may also be used to help treat skin cancer that has spread to lymph nodes or other organs.
Don’t Miss: Well-differentiated
What Are Treatment Options For Recurrent Nasal Cavity Or Paranasal Sinus Cancer
Cancer is called recurrent when it comes back after treatment. Recurrence can be local , regional , or distant . Options for treating recurrences depend on the location and type of cancer, as well as the treatment used the first time.
For a local recurrence, if radiation was the first treatment for the cancer, surgery may be used. If the first treatment was surgery without radiation, radiation therapy may be tried. Chemo and/or targeted therapy may be used with radiation, or it may be used by itself to treat recurrences that are not controlled by radiation therapy or surgery.
In a regional recurrence, the cancer comes back in the lymph nodes in the neck. This is often treated with surgery to remove many lymph nodes in the neck that are on the same side as the cancer. This may be followed with radiation to the neck, sometimes combined with chemo and/or targeted therapy.
Recurrent melanomas or sarcomas of the nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses are treated by surgery, if possible. Depending on the exact type of cells forming the cancers, chemo or other treatments may also be given.
When a nasal cavity or paranasal sinus cancer comes back in other organs, it’s often treated with chemo, targeted therapy, and/or immunotherapy, although radiation could also be an option if it wasnt given before.
Because these cancers are hard to treat, clinical trials of new treatments are a good option for some people.
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers do not know why certain cells become cancerous. However, they have identified some risk factors for skin cancer.
The most important risk factor for melanoma is exposure to UV rays. These damage the skin cellsâ DNA, which controls how the cells grow, divide, and stay alive.
Most UV rays come from sunlight, but they also come from tanning beds.
Some other risk factors for skin cancer include:
- A lot of moles: A person with more than 100 moles is more likely to develop melanoma.
- Fair skin, light hair, and freckles: The risk of developing melanoma is higher among people with fair skin. Those who burn easily have an increased risk.
- Family history:Around 10% of people with the condition have a family history of it.
- Personal history: Melanoma is likelier to form in a person who has already had it. People who have had basal cell or squamous cell cancers also have an increased risk of developing melanoma.
The best way to reduce the risk of skin cancer is to limit oneâs exposure to UV rays. A person can do this by using sunscreen, seeking shade, and covering up when outdoors.
People should also avoid tanning beds and sunlamps to reduce their risk of skin cancer.
It can be easy to mistake benign growths for skin cancer.
The following skin conditions have similar symptoms to skin cancer:
Also Check: What Is Pigmented Basal Cell Carcinoma
Read Also: Large Cell Carcinoma Lung Cancer
What You Can Do
If youve already had a BCC, you have an increased chance of developing another, especially in the same sun-damaged area or nearby.
A BCC can recur even when it has been carefully removed the first time, because some cancer cells may remain undetectable after surgery and others can form roots that extend beyond whats visible. BCCs on the nose, ears and lips are more likely to recur, usually within the first two years after surgery.
Heres what you can do to detect a recurrence and safeguard yourself against further skin damage that can lead to cancer:
Reviewed by:
Treating Skin Cancer On The Nose
The nose is one of the most common areas for patients to develop skin cancer as it is frequently exposed to the suns harmful rays. If you have a case of non-melanoma skin cancer on your nose and your doctor recommends an invasive treatment like Mohs surgery, you may understandably be worried about the cosmetic side effects, like scarring. Thankfully, for cases of Basal cell and Squamous cell carcinoma, there is a non-surgical alternative to consider in Image Guided Superficial Radiotherapy . Learn more about IG-SRT as a less invasive treatment method with the team at GentleCure, below.
Also Check: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Patients May Want To Think About Taking Part In A Clinical Trial
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today’s standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
Causes Of Skin Lesions
Facial skin cancer is the result of mutations in the skin cells that cause them to grow out of control. The biggest risk factor for skin cancer is ultraviolet radiation from sunlight and tanning beds. Those with fair skin, a history of sunburns and excessive sun exposure, moles, or a family history of skin cancer are more prone to developing it.
You May Like: Body Cancer Symptoms
Stages 0 I And Ii Maxillary Sinus Cancer
The first step in treating most stage 0, I, or II maxillary sinus cancers is surgery to remove the cancer. In most cases, a maxillectomy is done. Lymph nodes in the neck aren’t removed.
Radiation might be needed after surgery for people with stage I and II cancers, if the cancer has features that make it more likely to come back, such as positive margins , or cancer growing into the area around the nerves .
Radiation is often recommended after surgery for adenoid cystic cancers, even if the margins are negative and there’s no perineural invasion, because they have a high chance of coming back after treatment.
For some aggressive types of maxillary sinus tumors, such as undifferentiated cancer or esthesioneuroblastoma, chemotherapy might be recommended along with radiation treatment.
In cases where surgery to remove the cancer would be risky because of other medical problems, treatment may be radiation therapy alone or chemo given with the radiation.