Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Squamous cell carcinoma in situ, also known as Bowens disease, is a precancerous condition that appears as a red or brownish patch or plaque on the skin that grows slowly over time. The patches are often found on the legs and lower parts of the body, as well as the head and neck. In rare cases, it has been found on the hands and feet, in the genital area, and in the area around the anus.
Bowens disease is uncommon: only 15 out of every 100,000 people will develop this condition every year. The condition typically affects the Caucasian population, but women are more likely to develop Bowens disease than men. The majority of cases are in adults over 60. As with other skin cancers, Bowens disease can develop after long-term exposure to the sun. It can also develop following radiotherapy treatment. Other causes include immune suppression, skin injury, inflammatory skin conditions, and a human papillomavirus infection.
Bowens disease is generally treatable and doesnt develop into squamous cell carcinoma. Up to 16% of cases develop into cancer.
How Dangerous Is Bcc
While BCCs rarely spread beyond the original tumor site, if allowed to grow, these lesions can be disfiguring and dangerous. Untreated BCCs can become locally invasive, grow wide and deep into the skin and destroy skin, tissue and bone. The longer you wait to have a BCC treated, the more likely it is to recur, sometimes repeatedly.
There are some highly unusual, aggressive cases when BCC spreads to other parts of the body. In even rarer instances, this type of BCC can become life-threatening.
What Is A Basal Cell
One of three main types of cells in the top layer of the skin, basal cells shed as new ones form. BCC most often occurs when DNA damage from exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or indoor tanning triggers changes in basal cells in the outermost layer of skin , resulting in uncontrolled growth.
You May Like: Stage 3 Lobular Breast Cancer
What Does It Mean If The Following Terms Are Used To Describe The Adenocarcinoma: Papillary Micropapillary Acinar Mucinous Or Solid
These terms describe different types of lung adenocarcinoma, which are based on how the cells look and are arranged under the microscope . Some tumors look basically the same throughout the tumor, and some can look different in different areas of the tumor. Some growth patterns have a better prognosis than others. Since some tumors can have a mixture of patterns, the pathologist canât always tell all the types contained in a tumor just based on a biopsy that samples only a small part of the tumor. To know what types a tumor contains, the entire tumor must be removed.
I Think I Have An Actinic Keratosis What Should I Do
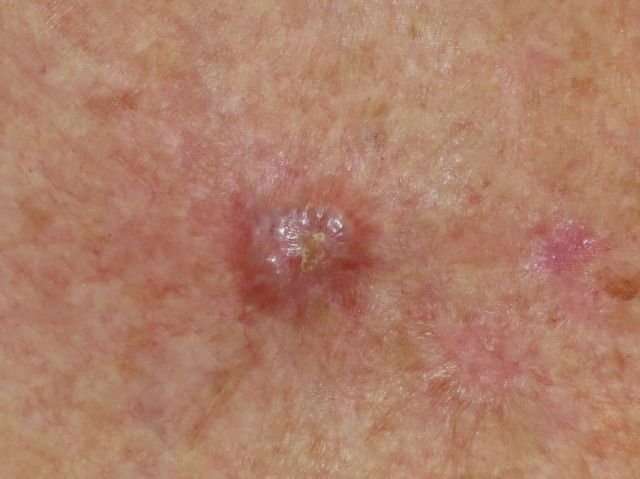
If detected early, actinic keratoses can be treated before they develop into skin cancer.
See your dermatologist, who can accurately diagnose the lesion and recommend an effective treatment. Its best to diagnose and treat AKs early, before they become cancerous. This is especially true for AKs that arise on the head or neck, where skin cancers may be more aggressive.
Protect yourself to help prevent further sun damage. Seek shade and protect your skin against UV exposure every day, even when its cloudy, using broad-spectrum sunscreen and sun safe clothing, hats and eyewear. Avoid indoor tanning entirely and do not get sunburned.
Reviewed by:
Also Check: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rates
What Is A Biopsy
A proper diagnosis of cancer in the skin is made possible through biopsy. We will remove a skin tissue sample and send it to a laboratory. A pathologist will then examine your samples and look for abnormal cells that could be cancerous. Through a biopsy, you can also get accurate information about the stage of skin cancer you might have.
For advanced melanoma, we request imaging tests and lymph node biopsy to see whether cancer has affected other parts of the body. Additional evaluation is made possible using any or a combination of the following methods:
- Computed tomography
- Measurement of lactate dehydrogenase levels
Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
These are the classic form of basal cell carcinoma, and is the type most often described in textbooks. Nodular basal cell carcinoma often has a red, rounded appearance, and vessels may be seen on their surface. In certain lights, nodular basal cell carcinomas may have a slight sheen to them, described as pearliness.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
Prognosis Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma is nearly always successful, and the cancer is rarely fatal. However, almost 25% of people with a history of basal cell carcinoma develop a new basal cell cancer within 5 years of the first one. Thus, anyone with one basal cell carcinoma should have a yearly skin examination.
Looking For Signs Of Skin Cancer
Non melanoma skin cancers tend to develop most often on skin that’s exposed to the sun.
To spot skin cancers early it helps to know how your skin normally looks. That way, you’ll notice any changes more easily.
To look at areas you cant see easily, you could try using a hand held mirror and reflect your skin onto another mirror. Or you could get your partner or a friend to look. This is very important if you’re regularly outside in the sun for work or leisure.
You can take a photo of anything that doesn’t look quite right. If you can it’s a good idea to put a ruler or tape measure next to the abnormal area when you take the photo. This gives you a more accurate idea about its size and can help you tell if it’s changing. You can then show these pictures to your doctor.
You May Like: Does Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Most skin cancers can be cured if diagnosed and treated early. Aside from protecting your skin from sun damage, it is important to recognize the early signs of skin cancer.
The ABCDEs of melanoma are a helpful guide: Asymmetry Borders Color Diameter Evolution. The symptoms of melanoma skin cancer include:
Symptoms of non-melanoma skin cancer include:
- Itchy patches of skin that may crust over or are very painful
- Bumps or skin spots that bleed easily or crust over frequently
- Nodules that do not go away. These may be clear, a pearl-like color, or even red, pink, or white.
- Skin sores that do not heal
- A scar-like bump that was not caused by injury or trauma
Another Skin Cancer In 2021
Ron knows that a history of two or more skin cancers puts him at a much higher risk of developing further skin cancers. In October 2021, he noticed something new on his scalp a scaly lesion that occasionally bled. He immediately went to see his dermatologist. The biopsy showed that this time, Ron had squamous cell carcinoma . While the majority of SCCs can be successfully treated, if left to grow, this common skin cancer can become invasive, penetrate deeper layers of skin and spread to other parts of the body.
Rons lesion was removed with Mohs surgery, the most effective technique for treating SCCs. It is often recommended for SCCs located in cosmetically or functionally important areas, including the scalp. Mohs is done in stages while the patient waits. After removing a layer of tissue, the surgeon examines it under a microscope in an on-site lab. If any cancer cells remain, the surgeon removes another layer from that precise location, sparing as much healthy tissue as possible. This process is repeated until no cancer cells remain.
After two layers were removed, Rons scalp was clear of cancer cells. Im glad I got it checked out and taken care of right away, he explained.
SCC removed by Mohs surgery on the scalp.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread
Basal Cell Carcinoma: The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma, or BCC, is a form of skin cancer that arises from basal cells deep in the lining of the skins top layer, the epidermis.
Its common: According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, over 4 million cases of BCC are diagnosed each year in the U.S. alone. As most people know, its associated with frequent or prolonged sun exposure.
If theres something good to say about BCC, its that most cases are manageable. Its a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads. Also, BCCs occur on the skin, usually where they can be readily seen. Surgical removal is an effective treatment.
But when a BCC grows undetected, it can become more serious.
I cant even say how phenomenal Dr. Desai was. He was so down-to-earth and helped me understand everything that was happening to me. Every time I went, he encouraged me and was honest, but positive.
-Jen
You May Like: How Do You If You Have Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet Light And Other Potential Causes
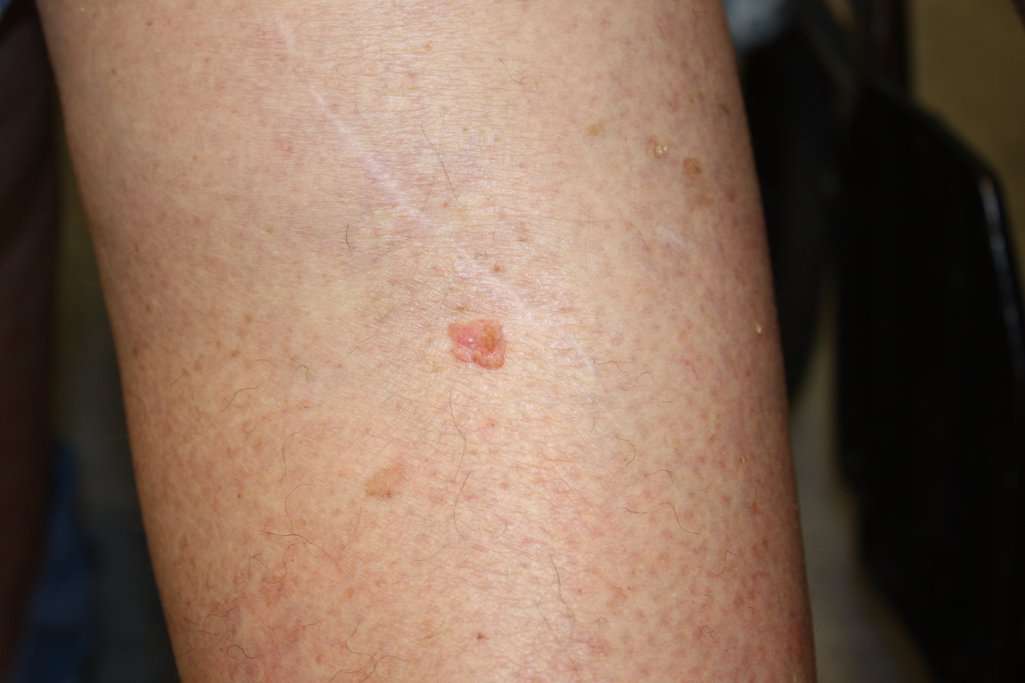
Much of the damage to DNA in skin cells results from ultraviolet radiation found in sunlight and in the lights used in tanning beds. But sun exposure doesnt explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. This indicates that other factors may contribute to your risk of skin cancer, such as being exposed to toxic substances or having a condition that weakens your immune system.
Also Check: Show Me What Skin Cancer Looks Like
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Stage 4 Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Pictures
Squamous cell carcinoma also appears in areas most exposed to the sun and, as indicated in the pictures below, often presents itself as a scab or sore that doesnt heal, a volcano-like growth with a rim and crater in the middle or simply as a crusty patch of skin that is a bit inflamed and red and doesnt go away over time.
Any lesion that bleeds or itches and doesnt heal within a few weeks may be a concern even if it doesnt look like these Squamous cell carcinoma images.
The Five Stages Of Skin Cancer
Cancer in the skin thats at high risk for spreading shares features with basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Some of these features are:
- Not less than 2 mm in thickness
- Has spread into the inner layers of the skin
- Has invaded skin nerves
Stage 0
In the earliest stage, cancer is only present in the upper layer of the skin. You may notice the appearance of blood vessels or a dent in the center of the skin growth. There are no traces of malignant cells beyond this layer.
Stage 1
At stage 1, cancer has not spread to muscles, bone, and other organs. It measures roughly 4/5 of an inch. Theres a possibility that it may have spread into the inner layer of the skin.
Stage 2
In this stage, cancer has become larger than 4/5 of an inch. Cancer still has not spread to muscles, bone, and other organs.
Stage 3
At stage 3, the cancer is still larger than 4/5 of an inch. Facial bones or a nearby lymph node may have been affected, but other organs remain safe. It may also spread to areas below the skin, such as into muscle, bone, and cartilage but not far from the original site.
Stage 4
Cancer can now be of any size and has likely spread into lymph nodes, bones, cartilage, muscle, or other organs. Distant organs such as the brain or lungs may also be affected. In rare cases, this stage might cause death when allowed to grow and become more invasive.
Read Also: What Does Melanoma In Situ Look Like
Can Skin Cancer Spread To Other Parts Of The Body
Yes, it can. However, it depends on the type of skin cancer and its stage.
Non-melanoma skin cancers are less likely to spread. Basal cell carcinoma usually does not migrate to other parts of the body, but there is a small chance that squamous cell cancer will do so.
Melanoma skin cancer spreads more readily than non-melanoma, making it more dangerous. It can spread to the lymph nodes and, from there, to other organs in the body.
Biopsy And Gross Examination
A biopsy is a sample of potentially diseased or cancerous tissue. Your surgeon might take a biopsy before or during tumor removal surgery.
Healthcare providers take biopsies in several different ways based on the type of tumor theyre sampling:
- The simplest biopsy is a needle guided either by touch or an imaging test to find the tumor. The needle can be thin, as in a fine-needle aspiration biopsy, or a little thicker, as in a core biopsy.
- Skin can be biopsied directly by cutting away pieces of skin that may be diseased.
- An endoscopic biopsy is when the healthcare provider uses a flexible tube through your mouth or rectum to see and sample the various parts of the respiratory tract and digestive tract.
- Getting more invasiveyour healthcare provider might need to do a laparoscopic biopsy, in which a surgeon passes a small tube into the abdomen through a small cut in the skin.
Samples for analysis may also be obtained during surgery aimed at locating and removing the tumor, such as a laparotomy or lobectomy. Nearby lymph nodes may also be removed to see if cancer has spread or metastasized locally.
The most interesting thing about a biopsy is what happens after its takenthe analysis. The sample, which may include the tumor and the surrounding normal tissues, is sent to a histology and pathology lab for evaluation by a pathologist.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
Basal Cell Carcinoma Screening
Diagnosis and management of Basal Cell Carcinoma is best performed via a Full Body Scan.
In the first incidence, this process includes
- Digitally Mapping a patients entire body for any suspicious skin damage or lesion
- Followed by a detailed Dermoscopic Examination by a trained skin cancer specialist
- Recording and combining all images and skin metrics into the patient record
Our expert Doctors at Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic will then clearly identify and diagnose any skin disease.
Dont Miss: Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Dangerous
What If My Report Says Squamous Carcinoma
The inner lining of the esophagus is known as the mucosa. In most of the esophagus the top layer of the mucosa is made up of squamous cells. This is called squamous mucosa. Squamous cells are flat cells that look similar to fish scales when viewed under the microscope. Squamous carcinoma of the esophagus is a type of cancer that arises from the squamous cells that line the esophagus.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
The Most Common Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer and the most frequently occurring form of all cancers. In the U.S. alone, an estimated 3.6 million cases are diagnosed each year. BCCs arise from abnormal, uncontrolled growth of basal cells.
Because BCCs grow slowly, most are curable and cause minimal damage when caught and treated early. Understanding BCC causes, risk factors and warning signs can help you detect them early, when they are easiest to treat and cure.
What Is Squamous Cell Cancer
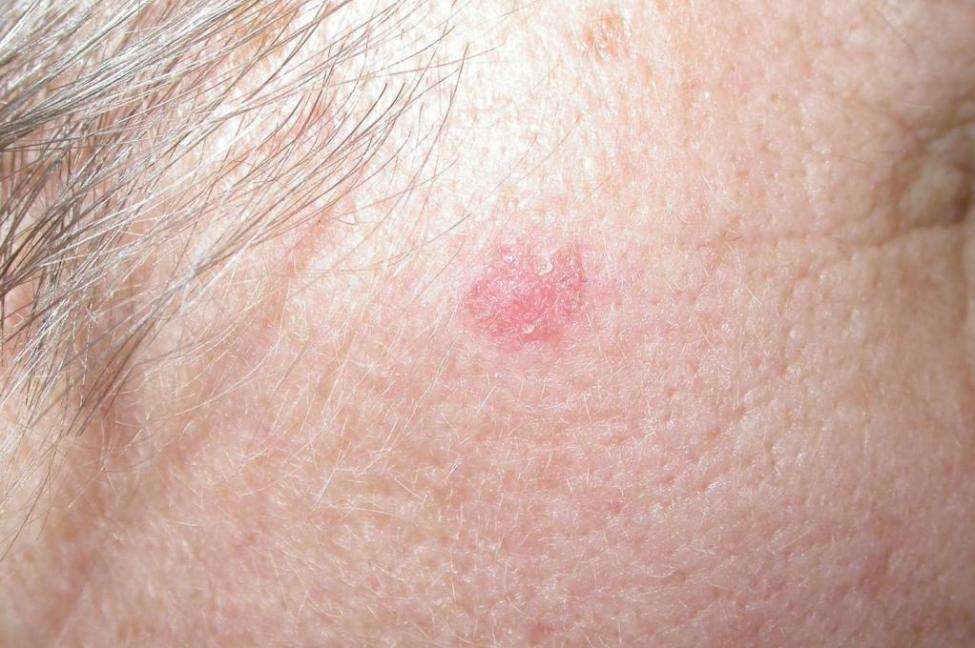
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is a common skin cancer that typically develops in chronic sun-exposed areas of your body. This type of skin cancer is usually not nearly as aggressive as melanoma and is uncontrolled growth of cells in the epidermis of your skin.
It can become disfiguring and sometimes deadly if allowed to grow. Squamous cell carcinomas are at least twice as frequent in men as in women. They rarely appear before age 50 and are most often seen in individuals in their 70s.
An estimated 700,000 cases of SCC are diagnosed each year in the United States, resulting in approximately 2,500 deaths.
Recommended Reading: Stage 4 Basal Cell Carcinoma Life Expectancy
What Do Actinic Keratoses Look Like
AKs often appear as small dry, scaly or crusty patches of skin. They may be red, light or dark tan, white, pink, flesh-toned or a combination of colors and are sometimes raised. Because of their rough texture, actinic keratoses are often easier to feel than see. For photos, go to our warning signs page.
Who Gets Skin Cancer And Why
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation treatment, and even heredity may play a role. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive sun exposure or blistering sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
Recommended Reading: Clear Cell Carcinoma Symptoms
Changes In Existing Spots
Warts and moles are rarely cause to worry. Though they may cause some irritation, most warts and moles are completely harmless. Because squamous cell carcinoma sometimes develops in existing skin lesions, its important to monitor moles, warts, or skin lesions for changes. Any observable change should raise a red flag and warrant a trip to the doctor for further examination.
The prognosis for SCC depends on a few factors, including:
- how advanced the cancer was when it was detected
- the location of the cancer on the body
- whether the cancer has spread to other areas of the body
The sooner SCC is diagnosed, the better. Once found, treatment can begin quickly, which makes a cure more likely. Its important to treat precancerous lesions, like Bowens disease or actinic keratosis, early before they develop into cancer. See your doctor right away if you notice any new or unusual skin lesions.
Make regular appointments with your doctor for a skin check. Perform a self-examination once every month. Ask a partner or use a mirror to check places you cant see, like your back or the top of your head.
This is especially important for higher risk individuals, such as those with light skin, blond hair, and light-colored eyes. Anyone who spends prolonged time in the sun unprotected is also at risk.