Recurrence In Nearby Lymph Nodes
If nearby lymph nodes werenât all removed during the initial treatment, the melanoma might come back in these lymph nodes. Lymph node recurrence is treated by lymph node dissection if it can be done, sometimes followed by adjuvant treatments such as radiation therapy and/or immunotherapy or targeted therapy . If surgery is not an option, radiation therapy or systemic treatment can be used.
Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Brain
You might have any of the following symptoms if your cancer has spread to your brain:
- headaches
- weakness of a part of the body
- fits
- personality changes or mood changes
- eyesight changes
-
J Tobias and D HochhauserJohn Wiley and Sons Ltd
-
TNM Staging ChartsLippincott Williams and Wilkins, 2009
-
Improving supportive and palliative care for adults with cancerNational Institute for Clinical Excellence , 2004
-
Oxford Textbook of Palliative MedicineEds D Doyle and othersOxford Universty Press, 3rd edition 2005
-
Cancer and its Management J Tobias and D HochhauserWiley Blackwell, 2015
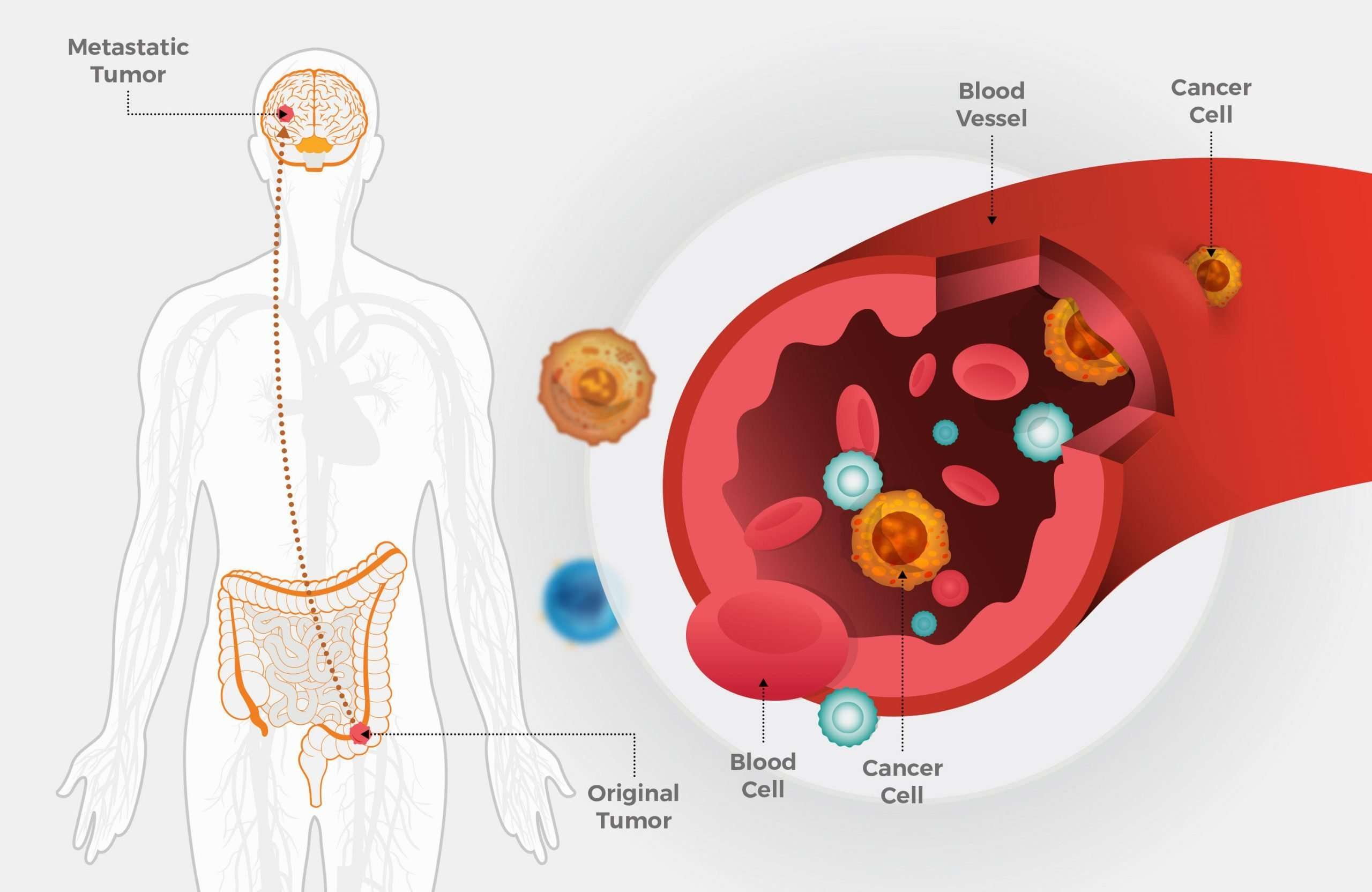
If Melanoma Skin Cancer Spreads
Cancer cells can spread from the area of skin where the cancer started to other parts of the body. This spread is called metastasis.
Understanding how a type of cancer usually grows and spreads helps your healthcare team plan your treatment and future care. If melanoma skin cancer spreads, it can spread to the following:
- lymph nodes near where the cancer started
- other areas of skin away from where the cancer started
- soft tissue
- American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC Cancer Staging Handbook. 7th ed. Chicago: Springer 2010.
- American Society of Clinical Oncology. Melanoma. 2015: .
- Canadian Dermatology Association . Malignant Melanoma . .
- Petrella T, Ernst S, Spatz A, Claveau J, Wong R, Smylie M. Canadian perspective on the clinical management of metastatic melanoma. New Evidence in Oncology. Toronto, ON: New Evidence 2012: .
- Ribas A, Slingluff Cl Jr, Rosenberg SA. Cutaneous melanoma. DeVita VT Jr, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA. Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 10th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2015: 94:1346-1394.
Also Check: Stage Iii Melanoma
What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma, also called malignant melanoma or cutaneous melanoma, is a type of skin cancer. It develops when there is an uncontrolled growth of the cells that give the skin its tan or brown color . Usually, the melanoma tumors are brown or black since most melanoma cells can make melanin. Some melanomas, however, do not make melanin. Such melanoma tumors can appear pink, tan, or even white.Melanoma can occur on the skin of any part of the body. They usually start developing on the chest and back in men and on the legs in women. Melanomas also commonly occur on the neck and face. The less common sites for melanomas include the eyes, mouth, genitals, and anal area. Although melanomas are far less common than the other types of skin cancers, they are more dangerous since they spread rapidly to other parts of the body . Thus, they need to be diagnosed and treated at early stages.
What Is The Most Effective Treatment For Melanoma
Wide excision The main treatment for melanoma is surgical removal, or excision, of the primary melanoma on the skin. The extent of the surgery depends on the thickness of the melanoma. Most melanomas are found when they are less than 1.0 mm thick, and outpatient surgery is often the only treatment needed.
Also Check: Idc Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What To Ask Your Doctor About Stage I Melanoma
When your doctor tells you that you have Stage I melanoma, it can be overwhelming. But it is important to use the time with your doctor to learn as much about your cancer as you can. S/he will provide you important information about your diagnosis.
The following questions are those you may want to ask your doctor. Remember, it is ALWAYS okay to ask your doctor to repeat or clarify something s/he said so that you can better understand it. You may find it helpful to print out these questions and bring them with you to your next appointment.
Common Places For Melanoma To Spread
Melanoma can spread from the original site on your skin and form a tumor in any organ or body tissue, but its most likely to metastasize to the lymph nodes, liver, brain, lungs, and less commonly, the bones. Melanoma really likes the brain and the liver, says Lisa Zaba, M.D., dermatologic oncologist at Stanford Medical Center in San Jose, CA. If you notice any of the following red flags, it might mean your melanoma has spread and warrants a call to your doctor right away.
Also Check: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Risk Factors For Metastatic Melanomas
You cannot get metastatic melanoma without first having melanoma, though the primary melanoma may be so small its undetectable. Major risk factors for melanomas include:
- Light skin, light-colored hair or light-colored eyes
- Skin prone to burning easily
- Multiple blistering sunburns as a child
- Family history of melanoma
- Frequent exposure to sun or ultraviolet radiation
- Certain genetic mutations
- Exposure to environmental factors, such as radiation or vinyl chloride
Other factors have been connected with increased metastasis. In a 2018 study in the Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia and a 2019 study in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, the following factors were associated with higher levels of metastasis:
- Male gender
- Primary tumor thickness of more than 4 mm
- Nodular melanoma, which is a specific subtype that a care team would identify
- Ulceration of the primary tumor
What Happens If Melanoma Gets Into Lymph Nodes
If the melanoma has spread into the lymph nodes, it means cancer has spread beyond its original site . It will need a more aggressive line of management.
Melanoma is a rapidly progressive type of skin cancer. The treatment of melanoma depends on the stage of the disease. Lymph nodes are small glands that are part of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is involved in the formations of the white blood cells or WBCs. It is also the site where lymph, a clear fluid containing the white blood cells, is filtered. When melanoma begins to spread, it often first goes to the lymph node near the melanoma. The first lymph nodes that drain lymph fluid from the primary tumor are called sentinel lymph nodes. If the melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes, it means that the person has stage III melanoma. Knowing the stage of melanoma helps the doctor plan the appropriate treatment. If the tumor has spread to the lymph nodes, the person may need a major surgery that involves the removal of the affected lymph nodes besides the primary tumor.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Spreading To The Organs
After the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes, the lymph nodes and/or blood vessels help the cancer move to other areas of the body, like the organs. Which organ it will spread to first, varies depending on where the cancer started, the type and the person, but the liver, lungs, and brain are common sites for metastases.
Once its in the organs, it is known as stage four melanoma.
Melanoma Of The Head And Neck Treatment
Surgical resection with wide margins and often sentinel lymph node biopsy is required for melanoma that has not spread. Thin tumors, up to 1 millimeter thick, can be resected with 1-centimeter margins around the tumor. The greater the depth of invasion, the larger the margin required, up to 2 centimeters. Mohs surgery is not suitable for melanoma because the diagnosis often requires special pathologic staining that is not part of the Mohs technique.
To obtain a sentinel lymph node biopsy, a preoperative sentinel node localization study is performed: A radionuclide tracer is injected in the melanoma, then a radionuclide uptake SPECT or SPECT-CT scan shows which nodes the tracer spreads to first. These sentinel nodes may or may not contain melanoma: They are the nodes that a melanoma that has spread would first encounter, and contain melanoma cells when melanoma has spread to lymph nodes. Because there are hundreds of lymph nodes in the head and neck, your surgeon will use a gamma probe at surgery to identify and confirm that the nodes selected for removal are the sentinel nodes.
When enlarged lymph nodes are present, a neck dissection is performed at the time of surgery. If distant spread is detected during the workup that is, melanoma has spread to other organs immunotherapy and sometimes radiation therapy are used for treatment.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery
Recommended Reading: Cancer All Over Body Symptoms
When Melanoma Can’t Be Cured
If your cancer has spread and it is not possible to cure it by surgery, your doctor may still recommend treatment. In this case, treatment may help to relieve symptoms, might make you feel better and may allow you to live longer.
Whether or not you choose to have anti-cancer treatment, symptoms can still be controlled. For example, if you have pain, there are effective treatments for this.
General practitioners, specialists and palliative care teams in hospitals all play important roles in helping people with cancer.
Keeping An Eye On Moles
Sometimes groups of melanocytes make moles, also called nevi. Most people have some moles on their bodies. These moles are often pink, tan, or brown. They can be flat or raised, and are often round or oval. Most moles are on the chest or the upper part of the body.
Moles don’t often grow or change very much. Moles can fade in older adults. Most moles are not cancer . And they don’t lead to cancer. Some abnormal moles, called dysplastic nevi, have an increased risk of melanoma. These should be checked regularly by a doctor.
Recommended Reading: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
What Does Serious Melanoma Look Like
Melanoma borders tend to be uneven and may have scalloped or notched edges, while common moles tend to have smoother, more even borders. C is for Color. Multiple colors are a warning sign. While benign moles are usually a single shade of brown, a melanoma may have different shades of brown, tan or black.
Symptoms If Cancer Has Spread To The Bone
You might have any of the following symptoms if your cancer has spread to the bones:
- pain from breakdown of the bone the pain is continuous and people often describe it as gnawing
- backache, which gets worse despite resting
- weaker bones they can break more easily
- raised blood calcium , which can cause dehydration, confusion, sickness, tummy pain and constipation
- low levels of blood cells blood cells are made in the bone marrow and can be crowded out by the cancer cells, causing anaemia, increased risk of infection, bruising and bleeding
Cancer in the spinal bones can cause pressure on the spinal cord. If it isn’t treated, it can lead to weakness in your legs, numbness, paralysis and loss of bladder and bowel control . This is called spinal cord compression. It is an emergency so if you have these symptoms, you need to contact your cancer specialist straight away or go to the accident and emergency department.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer 1st Stage
Mouse Models Mimic Metastasis Of Human Melanoma
Metastasis is a highly inefficient process in that the vast majority of cancer cells that try to migrate die before they ever have an opportunity to form a tumor, Dr. Morrison said.
Dr. Morrisons team found previously that one factor limiting the survival of melanoma cells circulating in the blood is that the cells experience a high level of oxidative stress. Oxidative stressan imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the bodycauses chemical reactions that can damage proteins, DNA, and lipids in cells and disrupt normal cell processes. However, precisely how oxidative stress kills circulating melanoma cells was not known.
For their studies, the team used a mouse model of metastasis created by transplanting melanoma cells from humans beneath the skin of specially bred mice with weakened immune systems. These mice were used to avoid having the transplanted human cells seen as foreign and attacked by the immune system. The team also used a second mouse model created by transplanting mouse melanoma cells into mice with normal immune systems.
Comparing these two mouse models let the researchers control for potential effects of the immune system on the spread of melanoma, Dr. Salnikow explained.
The study was supported in part by NCIs Patient-Derived Models of Cancer program, which promotes the development of animal models that more closely mirror how tumor cells behave in humans.
What Causes Metastatic Melanoma
Anyone can get melanoma, but most cases of melanoma are caused by UV radiation from sunlight some studies even put incidences of skin cancer caused by sun exposure at around 95%. The UV rays from the sun damage skin cells ability to repair DNA. When this happens, gene mutations can occur and the risk of cancer increases.
The risk of melanoma is higher in fair-skinned people as they have less melanin in their skin to protect from the suns rays. Risk is also higher if there is a history of melanoma in the family as gene mutations are often passed down from one generation to the next.
Don’t Miss: Well Differentiated
Are There Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
There are many types of skin cancer. Your doctor can tell you more about the type of skin cancer you have.
Basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers are much more common than melanoma and dont often spread to other parts of the body. Melanoma is more deadly because it is more likely to spread to other parts of the body.
What Will Happen After Treatment
Youll be glad when treatment is over. For years after treatment, you will see your cancer doctor. Be sure to go to all of these follow-up visits. You will have exams, blood tests, and maybe other tests to see if the cancer has come back.
At first, your visits may be every few months. Then, the longer youre cancer-free, the less often the visits are needed. After 5 years, they may be done once a year.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health. Call us at 1-800-227-2345 or talk to your cancer care team to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as good as you can.
Recommended Reading: Ductal Invasive Carcinoma Survival Rate
Metastasis To Lymph Nodes
The first non-contiguous sites to which melanoma cells are thought to spread are lymph nodes . The first lymph node encountered by fluid draining from the cutaneous site where the primary melanoma resides is referred to as the sentinel lymph node. The presence or absence of tumor cells in this lymph node is generally determined in melanoma patients with tumors > 1 mm thick in a procedure called a sentinel lymph node biopsy. If the sentinel node is negative histologically, it is likely that other regional nodes are also free of metastasis . The presence of melanoma cells in the lymph node is the single most powerful predictor of recurrence and survival in melanoma patients , and if it is positive, it is possible that tumor cells have already gained access to the systemic circulation. In fact, removal of the sentinel node or even the entire draining nodal basin does not appear to significantly extend survival in melanoma patients .
Melanoma Formation And Progression
Progression from normal melanocytes to melanoma has classically been divided into a series of progressive steps . Although there are several histologic subtypes of melanoma, this model best describes superficial spreading melanoma, the most common variant, but is useful in understanding other subtypes as well. Melanoma is thought to arise in one of two ways: with no visible precursor lesion or in association with a benign melanocytic proliferation called a nevus . Although only 2030% of melanomas are thought to arise in association with a nevus precursor , this model is also useful in understanding the progression of de novo melanoma .
Although the model described above provides a foundation for understanding melanoma formation and progression, the critical events that occur between local tumor expansion and metastatic spread are complex and not addressed by the model. Additionally, there is compelling evidence that progression does not always occur in such a neat, step-wise fashion. In fact, there is evidence to support the notion that melanocytic cells can spread to distant sites in earlier stages of tumor progression. Lastly, melanomas show a predilection for metastasis to particular organs. Much work has been done to explain these phenomena at a molecular level and these issues will be the focus of this review.
Recommended Reading: Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rate
Red Flag #: Unexplained Weight Loss And Loss Of Appetite
Unintentional weight loss is a common side effect of any cancer. When it comes to melanoma, extreme weight loss usually only happens after the cancer has spread from the skin to other parts of the body. Dr. Zaba says she can sometimes tell if a patients melanoma has metastasized because it looks like they have cachexia, a syndrome marked by drastic loss of fat and muscle and increased weakness. Cachexia can also cause loss of appetite, which further contributes to the problem.