Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage 3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Squamous cell carcinoma rarely metastasizes , and when spreading does occur, it typically happens slowly. Indeed, most squamous cell carcinoma cases are diagnosed before the cancer has progressed beyond the upper layer of skin. There are various types of squamous cell carcinoma and some tend to spread more quickly than others.
Continue Learning About Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Important: This content reflects information from various individuals and organizations and may offer alternative or opposing points of view. It should not be used for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. As always, you should consult with your healthcare provider about your specific health needs.
Dont Miss: How Common Is Renal Cell Carcinoma
You May Like: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rates
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Squamous cell skin cancer is mainly caused by cumulative ultraviolet exposure from the sun, according to Dr. Leffell.
Daily year-round exposure to the suns UV light and intense exposure in the summer months add to the damage that causes this type of cancer, he says. People at the highest risk for squamous cell skin cancer tend to have light or fair-colored skin blue, green or gray eyes a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Squamous cell cancers occur four times more frequently in men than in women.
Although squamous cell cancer can be more aggressive than basal cell cancer, the risk of this type of cancer spreading is lowas long as the cancer is treated early, Dr. Leffell says. He notes that the lesions must be treated with respect because they may grow rapidly and invade deeply. While it is more difficult to treat squamous cell cancer that has metastasized, up to half of cases can be cured.
In a small percentage of cases, squamous cell skin cancer can grow along the tiny nerves in the skin. In this very serious condition, the squamous cell cancer of the face or scalp can travel along the nerves and spread to the brain.
Also Check: What Can Happen If Skin Cancer Is Left Untreated
When Skin Cancer Spreads
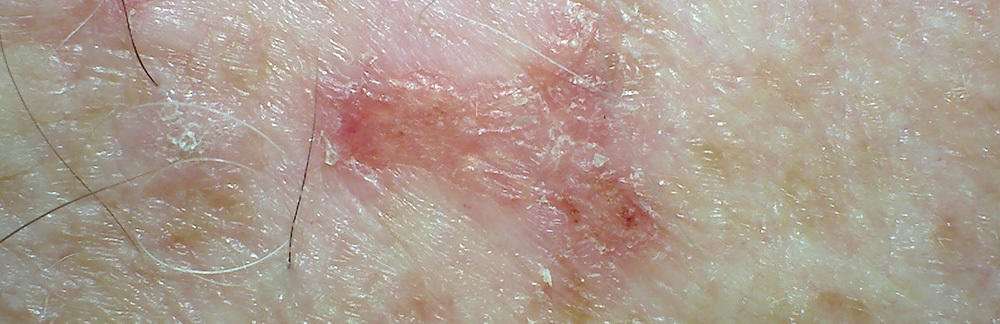
If squamous cell carcinoma spreads it first moves to nearby lymph nodes. From the lymph nodes it can metastasize to other organs. In most cases the cancer spreads to the lungs, although it can travel elsewhere.
The risk of metastasis is low. It is estimated that from two to six percent of cases metastasize. Generally, it is the high-risk cases of the disease that have this problem, when they are left untreated. Factors such as age, sun exposure, and fair skin increase risk. Once the cancer has reached the lymph nodes the morbidity rate is significant. If squamous cell carcinoma reaches the lungs it cannot be cured.
Also Check: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
The Science Of Lung Cancer Cell Growth
A normal lung cell becomes a cancer cell after a series of mutations in genes that control cell growth, often both oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. This means the cell no longer works like a normal cell. The genetic changes do not usually all happen at once, but they add up as the cells divide into the billions over a period of timeâsometimes decades. Even then, lung cancer still may be missed by a chest X-ray and the cells continue growing without anyone knowing.
Treatment Options: Mohs Surgery
Minor cases of skin cancer can often be treated with a simple excision, but in about half of all cases more significant intervention is needed. In these more significant cases, most dermatologic practices either offer Mohs surgery in-house or refer patients for Mohs surgery to a practice offering the procedure. While Mohs surgery effectively treats non-melanoma skin cancer 95 percent of the time or more, the side effects of Mohs surgery can be significant with bleeding, pain, and healing time being the most common. Theres also a need for reconstructive surgery in about 1 third of cases.
You May Like: Stage 3 Lobular Breast Cancer
Risks Associated With Untreated Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. This type of cancer has a variable growth rate. Some squamous cell carcinomas grow slowly, while others can grow rapidly. Smaller squamous cell carcinomas have a lower risk of metastasis, however, if they are large, they are at higher risk for spreading to other organs, including the lymph nodes. In certain locations, such as the ear, lip, and temple, there is a higher risk of spread as well. As with all skin cancers, treatment in earlier stages is always recommended to prevent cancer from spreading. Squamous cell carcinomas can be life-threatening if left untreated.
According to Dr. Truong, We recommend patients keep a close eye on any changes to their skin color, texture, or sensation by completing self-exams at home every month or every other month. With squamous cell carcinoma, the first thing patients notice is red, rough, and scaly patches of skin. This type of skin cancer can be asymptomatic, but can also be painful to the touch. Some patients experience abnormal sensations in the areas . The feelings of pain and numbness may be the first sign that squamous cell carcinoma is spreading and impacting surrounding nerves, therefore it is important to let your dermatologist know if you are experiencing these symptoms.
What Is A Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma also referred to as is a malignant skin cancer that arises from the flat cells in the uppermost layers of the skin known as the epidermis
It appears in the upper layer of the epidermis and usually on the most sun exposed areas .
It is one of the most common cancers in Australia, and accounts for around 15-20% of non-melanoma skin cancers.
In 2016 there were 120,000 cases in Australia. This equates to 499 Squamous Cell Carcinomas per 100,000 people per year – which is equal to all forms of other major malignancies combined .
When treated early the vast majority of Squamous Cell Carcinomas are not life-threatening.
Also Check: Web Md Skin Cancers
How To Tell Whether Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has Spread
at the last stage of the disease, cancer can spread to the brain. Since it is not typical for squamous cell carcinoma to spread at a high rate, it is essential to be careful of the signs displayed on your skin.
There are those common signs which one can see some of the risk factors which shows that squamous cell carcinoma has spread include the tumor growing more than two millimeters, cancer moving to the lower dermis of the skin, cancer has grown to the nerves in the skin, and when the cancer is present of the skin hair.
At this point, knowing the stage of your squamous cell carcinoma will help in understanding the rate at which the squamous cell carcinoma has spread and the proper medication you need to reduce the spread of cancer to other parts of the body. Staging squamous cell carcinoma includes doing a physical exam, skin biopsy, more history, lymph nodes biopsy, and developing studies.
Many diagnostic tests will help your doctor know the stage your cancer has reached. Removing some samples of your skin and doing tests in the lab can help determine the level of the tumor in your body. You can also understand whether squamous cell carcinoma has spread more in your body you can go for medications as early as the first stage. Nowadays, a computed tomography scan is used to see the stage at which squamous cell carcinoma has spread in the body.
How To Improve Your Odds
Even if youve exhausted all of your treatment options, you dont have to give up. Researchers are always testing new SCC treatments in clinical trials. Getting into one of these studies could give you access to a drug or therapy that might slow or stop your cancer.
To avoid the worsening of your skin cancer or a new cancer in a different area, protect yourself from the suns damaging UV rays. Wear sun-protective clothing and a wide-brimmed hat whenever you go outdoors. Apply a layer of broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays.
Also check your own skin for any new growths on a regular basis. Report any skin changes to your doctor right away.
Also Check: Can Malignant Neoplasm Be Cured
Treatment Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
-
Removal of the tumor
Doctors may remove the cancer in the office by scraping and burning it with an electric needle or by cutting it out. Doctors may destroy the cancer by using extreme cold .
Certain chemotherapy drugs may be applied to the skin. Photodynamic therapy , in which chemicals and a laser are applied to the skin, also may be used. Occasionally, radiation therapy is used.
A technique called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery may be required for some basal cell carcinomas that are large or regrow or occur in certain areas, such as around the nose and eyes.
People whose cancer has spread to nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body and who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy may be given the drug vismodegib or sonidegib taken by mouth.
You May Like: What Happens If I Have Skin Cancer
How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Grow
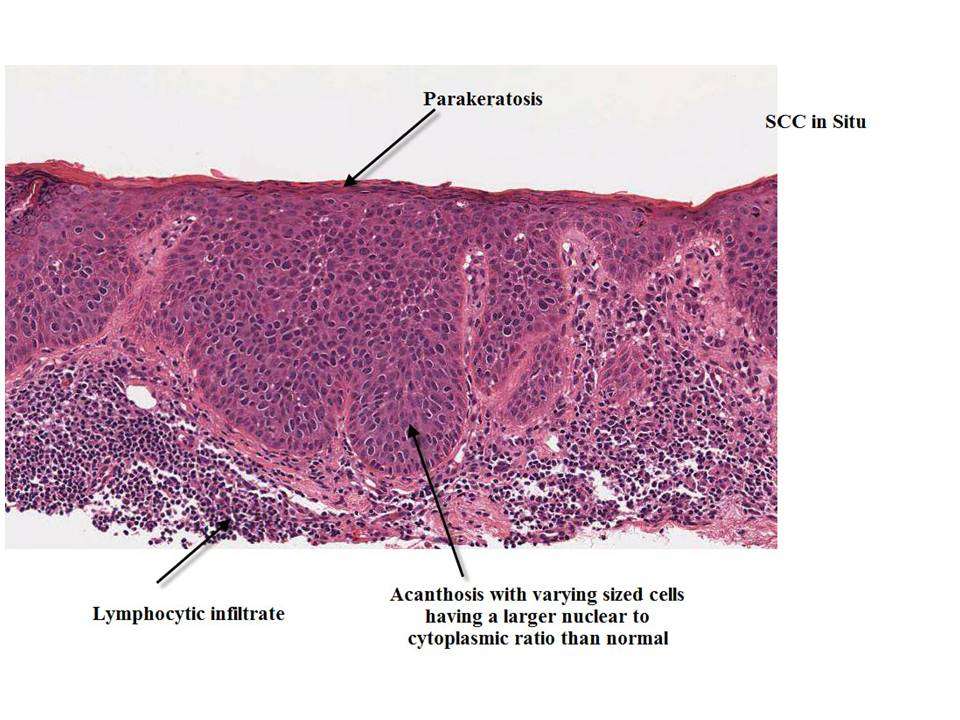
Results: Rapidly growing SCC occurred most commonly on the head and neck, followed by hands and extremities, and had an average duration of 7 weeks before diagnosis. The average size of the lesions was 1.29 cm and nearly 20% occurred in immunosuppressed patients. Conclusions: Some SCCs may grow rapidly.
You May Like: Survival Rates For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Metastatic Squamous Neck Cancer With Occult Primary Is A Disease In Which Squamous Cell Cancer Spreads To Lymph Nodes In The Neck And It Is Not Known Where The Cancer First Formed In The Body
Squamous cells are thin, flat cells found in tissues that form the surface of the skin and the lining of body cavities such as the mouth, hollow organs such as the uterus and blood vessels, and the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Some organs with squamous cells are the esophagus, lungs, kidneys, and uterus. Cancer can begin in squamous cells anywhere in the body and metastasize through the blood or lymph system to other parts of the body.
When squamous cell cancer spreads to lymph nodes in the neck or around thecollarbone, it is called metastatic squamous neck cancer. The doctor will try to find the primary tumor , because treatment for metastatic cancer is the same as treatment for the primary tumor. For example, when lung cancer spreads to the neck, the cancer cells in the neck are lung cancer cells and they are treated the same as the cancer in the lung. Sometimes doctors cannot find where in the body the cancer first began to grow. When tests cannot find a primary tumor, it is called anoccult primary tumor. In many cases, the primary tumor is never found.
Endoscopic Procedures: Panendoscopy Narrow Band Imaging Transoral Robotic Surgery And Transoral Laser Microsurgery
In NCUP of levels I, II, III, and VA of the neck, the next step in the traditional algorithm is the panendoscopy or triple endoscopy, including direct laryngoscopy, rigid or flexible bronchoscopy, and rigid or flexible esophagoscopy . Due to the exceedingly low incidence of clinically occult primary in the lung or esophagus with a metastatic node in the neck, many centers have now abandoned the practice of bronchoscopy and esophagoscopy in the search of the unknown primary. Bronchoscopy and esophagoscopy as endoscopic screening for second primaries, not causative of the neck mass, also remains controversial, but has its advocates . On the other hand direct laryngoscopy and careful endoscopy of the nasopharynx is clearly warranted. Examination under anesthesia is far superior to the office examination at identifying a primary tumor, because of relaxation of the pharyngeal musculature and ability to palpate base of tongue, tonsils and nasopharynx. Any firm nodularity, or bleeding on palpation requires biopsy of these suspicious areas .
The literature prior to the era of HPV-related cancer showed increased survival associated with the initial identification of the primary tumor in patients with NCUP . However more recent publications have not been able to show statistically improved survival rates, although other benefits occur with identification of primary tumors, such as precision in planning radiation ports .
Don’t Miss: Does Skin Cancer Burn And Itch
How Can You Tell If A Spot Is Cancerous
Redness or new swelling beyond the border of a mole. Color that spreads from the border of a spot into surrounding skin. Itching, pain, or tenderness in an area that doesn’t go away or goes away then comes back. Changes in the surface of a mole: oozing, scaliness, bleeding, or the appearance of a lump or bump.
Diagnosing Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The main way to diagnose squamous cell carcinoma is with a biopsy. This involves having a small piece of tissue removed from the suspicious area and examined in a laboratory.
In the laboratory, a pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope to determine if it is a skin cancer. He or she will also stage the cancer by the number of abnormal cells, their thickness, and the depth of penetration into the skin. The higher the stage of the tumor, the greater the chance it could spread to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma on sun-exposed areas of skin usually does not spread. However, squamous cell carcinoma of the lip, vulva, and penis are more likely to spread. Contact your doctor about any sore in these areas that does not go away after several weeks.
Recommended Reading: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
Chemotherapy For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Superficial Squamous Cell Carcinoma may be able to be treated with topical chemotherapy that is applied to the skin as an ointment or cream. This type of treatment is only for skin cancers that biopsy-proven to affect only the top layer of skin.
5-fluorouracil is approved for the treatment of Superficial Squamous Cell Carcinoma, however, invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma should not be treated topically due to the risk of spread.
Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Dogs Painful
Erosive and ulcerated skin lesion, rather than a lump. Growths on the nose, toes, legs, scrotum, or anus. Inflamed, crusty or bleeding sore that do not heal, even with antibiotics or creams. Swelling and pain of the nailbed.
Recommended Reading: Grade 3 Cancer Treatment
Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Most of squamous cell carcinomas can be cured if they are treated early. Once squamous cell carcinoma has spread beyond the skin, though, less than half of people live five years, even with aggressive treatment.
There are many ways to treat squamous cell carcinoma that has not spread. These include:
- cutting away the cancer and a small amount of healthy tissue around it. If a large area of skin is removed, a skin graft may be necessary.
- scraping away the cancer with a surgical tool. An electric probe is used to kill any cancerous cells left behind.
- freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen. This treatment is usually used only for very small tumors or for a patch of skin that looks abnormal but isnt yet cancerous.
- destroying the tumor with radiation.
- shaving away the cancer, one thin layer at a time. Each layer is examined under the microscope as it is removed. This technique helps the doctor preserve as much healthy skin as possible.
- applying drugs directly to the skin or injecting them into the tumor
- using a narrow laser beam to destroy the cancer.
The treatment that is best for you depends on the size and location of the cancer, whether it has returned after previous treatment, your age, and your general health.
Once your treatment is finished, its important to have regular follow-up skin exams. Your doctor may want to see you every three months for the first year, for example, and then less often after that.
Read Also: What Is Malignant Melanoma Skin Cancer
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
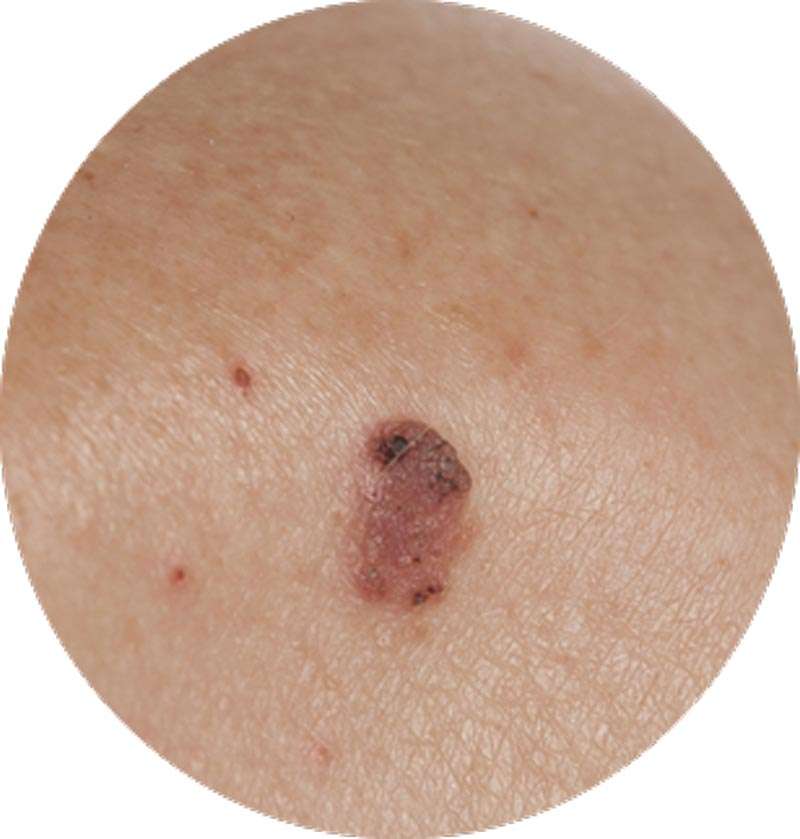
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common form of skin cancer. Its usually found on areas of the body damaged by UV rays from the sun or tanning beds. Sun-exposed skin includes the head, neck, chest, upper back, ears, lips, arms, legs, and hands.
SCC is a fairly slow-growing skin cancer. Unlike other types of skin cancer, it can spread to the tissues, bones, and nearby lymph nodes, where it may become hard to treat. When caught early, its easy to treat.
SCC can show up as:
- A dome-shaped bump that looks like a wart
- A red, scaly patch of skin thats rough and crusty and bleeds easily
- An open sore that doesnt heal completely
- A growth with raised edges and a lower area in the middle that might bleed or itch
Read Also: Prognosis Of Skin Cancer