The Prognosis For Microinvasive Carcinoma Of The Breast Is Very Good
There is universal agreement that the prognosis for ductal carcinoma discovered and intervened at a microinvasive stage, is very good. Patients with microinvasive breast cancer can typically expect a cure rate very close to 100%, with local treatment alone. Most microinvasive breast cancers will be treated by breast conserving surgery or by radical mastectomy . Adjuvant treatment is still a bit controversial, but radiotherapy is very common , while chemical and endocrine treatments are much common and will likely depend on the hormone receptor status of individual patients.
What Does Stage Ia Mean For Breast Cancer
In general, stage IA describes invasive breast cancer in which: the tumor measures up to 2 centimeters and. the cancer has not spread outside the breast no lymph nodes are involved.
In an invasive carcinoma, the tumor cells can spread to other parts of your body. What does it mean if my carcinoma is called invasive ductal carcinoma, invasive lobular carcinoma, or carcinoma with ductal and lobular features?
What Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Invasive lobular carcinoma is a cancer that starts in the breasts lobules and invades surrounding tissue. ILC is the second most common form of invasive breast cancer, accounting for 10 to 15% of breast cancer cases. ILC doesnt always form a lump, but women who have it may notice a thick or full area that doesnt feel like the rest of the breast.
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 3 Melanoma Mean
Understanding Your Pathology Report: Breast Cancer
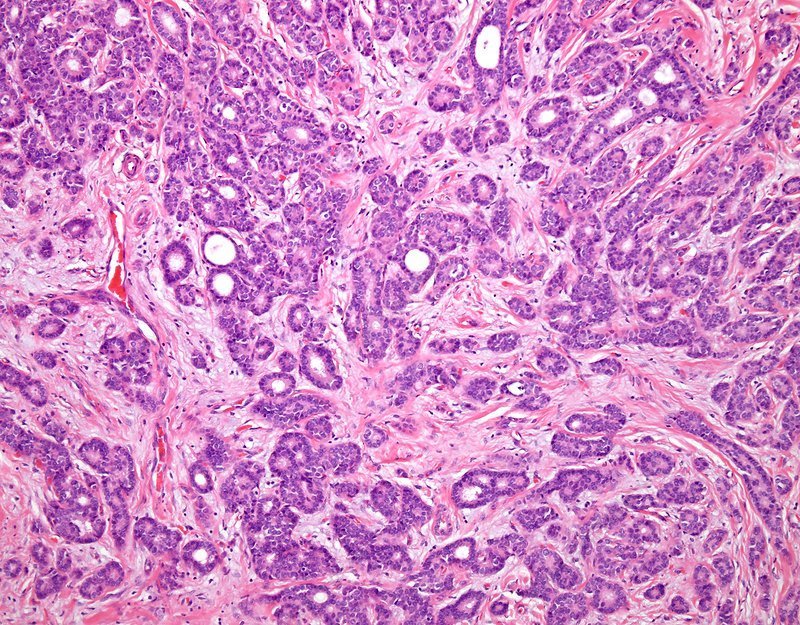
When your breast was biopsied, the samples taken were studied under the microscope by a specialized doctor with many years of training called a pathologist. The pathologist sends your doctor a report that gives a diagnosis for each sample taken. Information in this report will be used to help manage your care. The questions and answers that follow are meant to help you understand medical language you might find in the pathology report from a breast biopsy, such as a needle biopsy or an excision biopsy.
In a needle biopsy, a needle is used to remove a sample of an abnormal area. An excision biopsy removes the entire abnormal area, often with some of the surrounding normal tissue. An excision biopsy is much like a type of breast-conserving surgery called a lumpectomy.
Symptoms Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Symptoms of invasive breast cancer include:
- A lump or thickening of the breast tissue
- A change in the size or shape of the breast
- A change of skin texture such as puckering or dimpling of the skin
- A lump or swelling under the arm
- Changes to the nipple, for example it has become pulled in
- Discharge from the nipple
- Less commonly, a type of rash involving the nipple known as Pagets disease of the breast
Routine breast screening can often pick up cancer before a woman notices any symptoms. Therefore, some women will be diagnosed with invasive breast cancer after attending breast screening without having any of the symptoms above.
Don’t Miss: Who Can Diagnose Skin Cancer
Risk Factors For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Age and gender are the two greatest risk factors for developing invasive ductal carcinoma. Women over the age of 55 are more likely to develop invasive breast cancer than any other group of people.
Some other risk factors that doctors have identified are:
- Weight weight gain and obesity in adulthood play a role due to changes in hormones.
- Breast tissue women with less fatty tissue in their breasts have an increased risk of the disease.
- Family history those with family members who also had breast cancer are more likely to develop the disease.
- No children women who have never had children are at increased risk. At the same time, women who breastfeed reduce their risk of developing breast cancer.
- Genetic mutations mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are the most common causes of invasive breast cancer.
How Is It Diagnosed
There are a variety of tests to diagnose invasive breast cancer. These include:
- Breast exam: During a breast exam, a healthcare professional will carefully feel your breasts for signs of lumps or other changes.
- Mammogram: During a mammogram, a device presses your breasts between two plates. X-ray images of the breast tissue are then taken and evaluated for signs of cancer.
- Imaging tests: A healthcare professional may order additional imaging tests to help them better visualize breast tissue. Some examples include ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging .
- Biopsy: During a biopsy, a sample of breast tissue is carefully removed and checked under a microscope for signs of cancer.
- Blood tests: Blood tests use a sample your blood to check for various markers of disease or illness.
If cancer is detected, additional tests can be used to help characterize the cancer and determine its stage. These tests can include things like:
- Receptor testing: Various tests can check for estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors, and HER2 status.
- Lymph node biopsy: A lymph node biopsy can determine if the cancer has spread to the nearby lymph nodes.
- Imaging tests: Imaging tests can look to see if cancer has spread to other areas. Some that may be used include bone scans, X-rays, CT scans, and positron emission tomography scans.
CE MM 4/8/2021: resolved
Treatment for invasive breast cancer depends on the stage of the cancer as well as other factors. Lets examine the most common treatment options.
Also Check: What Is The Cause Of Malignant Melanoma
Kinds Of Breast Cancer
The most common kinds of breast cancer are
- Invasive ductal carcinoma. The cancer cells grow outside the ducts into other parts of the breast tissue. Invasive cancer cells can also spread, or metastasize, to other parts of the body.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma. Cancer cells spread from the lobules to the breast tissues that are close by. These invasive cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body.
When To Contact A Doctor
A person not diagnosed with cancer should see a doctor regularly for routine health checks. This can include cancer screenings to check for early signs of potential cancer.
A person diagnosed with non-invasive cancer should see a doctor more frequently for checks. A doctor can check to see if the cancer has progressed or come back.
A person in treatment for invasive cancer should work with a doctor to determine how often they need medical appointments. They should do their best to keep all appointments and follow treatments as prescribed.
A person should contact a doctor if they notice any side effects from treatment. A doctor may be able to help them cope with the side effects.
Also Check: How To Treat Melanoma Under Toenail
How Is Invasive Breast Cancer Treated
Different things will determine the type of breast cancer treatment your doctor recommends, including:
- Size of the tumor
- Results of lab tests done on the cancer cells
- Stage of the cancer
- Your age and general health
- If youâve been through menopause
- Your own feelings about the treatment options
- Family history
What Is Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare and very aggressive disease in which cancer cells block lymph vessels in the skin of the breast. This type of breast cancer is called inflammatory because the breast often looks swollen and red, or inflamed.
Inflammatory breast cancer is rare, accounting for 1 to 5 percent of all breast cancers diagnosed in the United States. Most inflammatory breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas, which means they developed from cells that line the milk ducts of the breast and then spread beyond the ducts.
Inflammatory breast cancer progresses rapidly, often in a matter of weeks or months. At diagnosis, inflammatory breast cancer is either stage III or IV disease, depending on whether cancer cells have spread only to nearby lymph nodes or to other tissues as well.
Additional features of inflammatory breast cancer include the following:
- Compared with other types of breast cancer, inflammatory breast cancer tends to be diagnosed at younger ages.
- Inflammatory breast cancer is more common and diagnosed at younger ages in African American women than in white women.
- Inflammatory breast tumors are frequently hormone receptor negative, which means they cannot be treated with hormone therapies, such as tamoxifen, that interfere with the growth of cancer cells fueled by estrogen.
- Inflammatory breast cancer is more common in obese women than in women of normal weight.
Recommended Reading: Why Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Keep Coming Back
What Increases The Risk Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Thereâs no way to know if youâll develop an invasive form of breast cancer, but there are things that increase your chances, many of which you canât change.
Older women are at higher risk. About 10% of women diagnosed with invasive breast cancer are under age 45. And 2 out of every 3 women with invasive breast cancer are age 55 or older when theyâre first diagnosed.
Your genetics and family history of breast cancer play roles. Itâs more common among white women than black, Asian, or Hispanic women.
Also, youâre at higher risk if youâre obese, your breasts are dense, you didnât have children, or you became pregnant after the age of 35.
How Often Does Stage 1 Breast Cancer Come Back After Treatment

If stage 1 cancer is treated comprehensively, it rarely comes back. A new, unrelated breast cancer is more likely to emerge after stage 1 breast cancer is treated than a recurrence. Your healthcare provider will recommend a surveillance schedule for you so that new breast cancer or a recurrence can be identified and treated as quickly as possible.
Also Check: What Is Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
What Does It Mean If My Report Mentions Estrogen Receptor Or Progesterone Receptor
Receptors are proteins on cells that can attach to certain substances, such as hormones, that circulate in the blood. Normal breast cells and some breast cancer cells have receptors that attach to the hormones estrogen and progesterone. These 2 hormones often fuel the growth of breast cancer cells.
An important step in evaluating a breast cancer is to test a portion of the cancer removed during the biopsy to see if they have estrogen and progesterone receptors. Cancer cells may contain neither, one, or both of these receptors. Breast cancers that contain estrogen receptors are often referred to as ER-positive cancers, while those containing progesterone receptors are called PR-positive cancers. Women with hormone receptor-positive cancers tend to have a better prognosis and are much more likely to respond to hormone therapy than women with cancers without these receptors.
All breast cancers and pre-cancers, with the exception of lobular carcinoma in situ , should be tested for these hormone receptors when they have the breast biopsy or surgery.
Results for ER and PR are reported separately and can be reported in different ways:
- Negative, weakly positive, positive
- Percent positive
- Percent positive and whether the staining is weak, moderate, or strong.
How the results of your tests will affect your therapy is best discussed with your doctor.
Causes Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Unfortunately, doctors have yet to figure out the exact cause of invasive ductal carcinoma. When you get this type of cancer, it means something damaged your cells’ DNA and caused it to change. The result is that the cells grow abnormally and uncontrollably in your breast tissue.
Doctors are still looking for genetic and environmental factors that damage the DNA. They have determined that caffeine, deodorant, microwaves and cell phone use do not lead to this type of cancer.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Melanoma Skin Cancer Naturally
What Is The Prognosis Of Patients With Inflammatory Breast Cancer
The prognosis, or likely outcome, for a patient diagnosed with cancer is often viewed as the chance that the cancer will be treated successfully and that the patient will recover completely. Many factors can influence a cancer patients prognosis, including the type and location of the cancer, the stage of the disease, the patients age and overall general health, and the extent to which the patients disease responds to treatment.
Because inflammatory breast cancer usually develops quickly and spreads aggressively to other parts of the body, women diagnosed with this disease, in general, do not survive as long as women diagnosed with other types of breast cancer.
It is important to keep in mind, however, that survival statistics are based on large numbers of patients and that an individual womans prognosis could be better or worse, depending on her tumor characteristics and medical history. Women who have inflammatory breast cancer are encouraged to talk with their doctor about their prognosis, given their particular situation.
Ongoing research, especially at the molecular level, will increase our understanding of how inflammatory breast cancer begins and progresses. This knowledge should enable the development of new treatments and more accurate prognoses for women diagnosed with this disease. It is important, therefore, that women who are diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer talk with their doctor about the option of participating in a clinical trial.
Hormonal Therapy For Idc
If the cancer tested positive for hormone receptors, your doctor likely will recommend some form of hormonal therapy. Hormonal therapy, also called anti-estrogen therapy or endocrine therapy, works by lowering the amount of estrogen in the body or blocking the estrogen from signaling breast cancer cells to grow. Because hormonal therapy affects your whole body, its sometimes called a systemic treatment.
In some cases of advanced-stage IDC, hormonal therapy can be given before surgery to help shrink the cancer . Still, it’s more common for hormonal therapy to start after other treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, unless these treatments arent needed.
Hormone receptors are special proteins found on the surface of certain cells throughout the body, including breast cells. These receptor proteins are the eyes and ears of the cells, receiving messages from the hormones in the bloodstream and then telling the cells what to do. In other words, the receptors act like an on-off switch for a particular activity in the cell. If the right substance comes along that fits into the receptor like a key fitting into a lock the switch is turned on and a particular activity in the cell begins.
You and your doctor will work together to decide which form of hormonal therapy is best in your situation. Two types of hormonal therapy are most frequently used:
Read Also: Does The Sun Cause Skin Cancer
Symptoms Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Invasive breast cancer doesn’t always have obvious signs or symptoms that affect your daily life. This is why regular screenings are essential to detect this type of cancer in its early stages.
Common symptoms of invasive ductal carcinoma include:
- Lump in the breast
- Red skin or rash on the breast
- Pain or changes in the appearance of the nipple
What Are The Symptoms Of Lobular Carcinoma
Often, in the earliest stages, lobular carcinoma causes no signs or symptoms. Lobular invasive breast cancer may cause an area of thickening in the breast. Likewise, there may be an area of fullness or swelling in the breast.
The appearance of the skin over the affected breast may change and appear dimpled. The nipple can become inverted.
Please note, however, that lobular breast cancer is less likely than other types to cause a firm breast lump.
You May Like: What Is Melanoma Skin Cancer
What Is The Prognosis For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Based on individual markers and prognostic factors, including the staging of your tumor, your physician will work to give you a prognosis. At Johns Hopkins Medicine, our team of breast cancer specialists is dedicated to developing cutting-edge techniques for surgery, breast reconstruction, chemotherapy, biologic targeted therapy, radiation therapy and other hormonal therapies. Our research allows us to make great strides forward for patients with breast cancer.
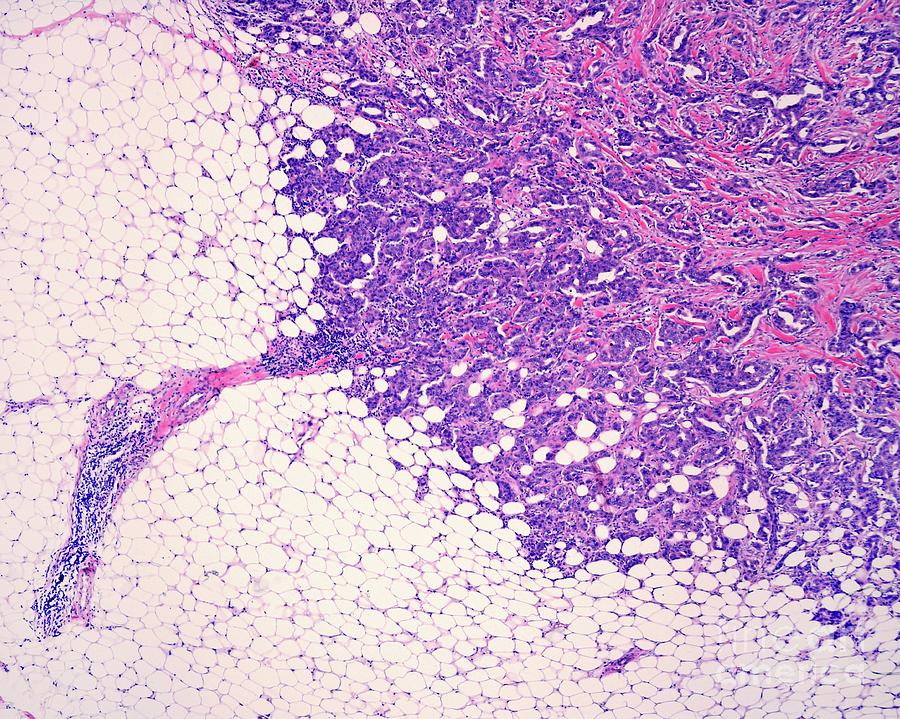
What If My Report Mentions Margins Or Ink
When an entire tumor is removed, the outside edges of the specimen are coated with ink, sometimes even with different colors of ink on different sides of the specimen. The pathologist looks at slides of the tumor under the microscope to see how close the cancer cells get to the ink . If cancer cells are touching the ink , it can mean that some cancer was left behind, and more surgery or other treatments may be needed. Sometimes, though, the surgeon has already removed more tissue to help make sure that this isnt needed.
Sometimes, all of the invasive cancer is removed, but there may be pre-cancer or another serious condition at or near the margin, such as ductal carcinoma in situ or lobular carcinoma in situ .
If your pathology report shows positive margins, your doctor will talk to you about what treatment is best.
Recommended Reading: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
What Does It Mean If In Addition To Cancer My Report Also Mentions Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia Atypical Lobular Hyperplasia Ductal Carcinoma In Situ Intraductal Carcinoma Lobular Carcinoma In Situ Or In
These are terms for certain atypical or pre-cancer changes that can sometimes be seen on biopsy that arent as serious as invasive cancer. If they are found in a needle biopsy that also shows invasive cancer, they are typically not important. They may, however, need to be removed completely as a part of treatment. If they are seen on an excisional biopsy at or near a margin , more tissue may need to be removed .
Key Differences Between Invasive And Metastatic Breast Cancer
Metastatic breast cancer isnt a specific type of breast cancer, but is the most advanced stage of breast cancer. Both invasive and metastatic breast cancer have spread beyond the exact point where they started. Invasive breast cancers may have spread within the breast only, or to nearby lymph nodes or tissues, or may have spread to distant body parts. All metastatic breast cancers have spread outside of the breast and nearby lymph nodes to distant body parts. If a cancer is only invasive within the breast, its usually easier for doctors to treat than metastatic disease.
Continued
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Basal Cell Carcinoma