Tumour Staging For Cutaneous Scc
TX: Th Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0: No evidence of a primary tumour
Tis: Carcinoma in situ
T1: Tumour 2cm without high-risk features
T2: Tumour 2cm or Tumour 2 cm with high-risk features
T3: Tumour with the invasion of maxilla, mandible, orbit or temporal bone
T4: Tumour with the invasion of axial or appendicular skeleton or perineural invasion of skull base
What Does It Mean If In Addition To A Diagnosis Of Cancer My Report Also Says Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia Squamous Dysplasia Or Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Situ
All of these are terms for pre-cancers that can be found in the lung. They are sometimes found near invasive cancer. If they are found on needle biopsy in addition to invasive cancer, it isnât really important. If they are found in a specimen from surgery to remove the entire tumor, they may be important if they are found at or near a margin .
Treating Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Skin
Treatment options for squamous cell skin cancer depend on the risk of the cancer coming back, which is based on factors like the size and location of the tumor and how the cancer cells look under a microscope, as well as if a person has a weakened immune system.
Most squamous cell skin cancers are found and treated at an early stage, when they can be removed or destroyed with local treatment methods. Small squamous cell cancers can usually be cured with these treatments. Larger squamous cell cancers are harder to treat, and fast-growing cancers have a higher risk of coming back.
In rare cases, squamous cell cancers can spread to lymph nodes or distant parts of the body. If this happens, treatments such as radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and/or chemotherapy may be needed.
Also Check: Stage 3 Cancer Symptoms
The Second Most Common Skin Cancer
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is the second most common form of skin cancer, characterized by abnormal, accelerated growth of squamous cells. When caught early, most SCCs are curable.
SCC of the skin is also known as cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma . Adding the word cutaneous identifies it as a skin cancer and differentiates it from squamous cell cancers that can arise inside the body, in places like the mouth, throat or lungs.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Pictures
Squamous cell carcinoma initially appears as a skin-colored or light red nodule, usually with a rough surface. They often resemble warts and sometimes resemble open bruises with raised, crusty edges. The lesions tend to develop slowly and can grow into a large tumor, sometimes with central ulceration.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Perineural Or Vascular Invasion
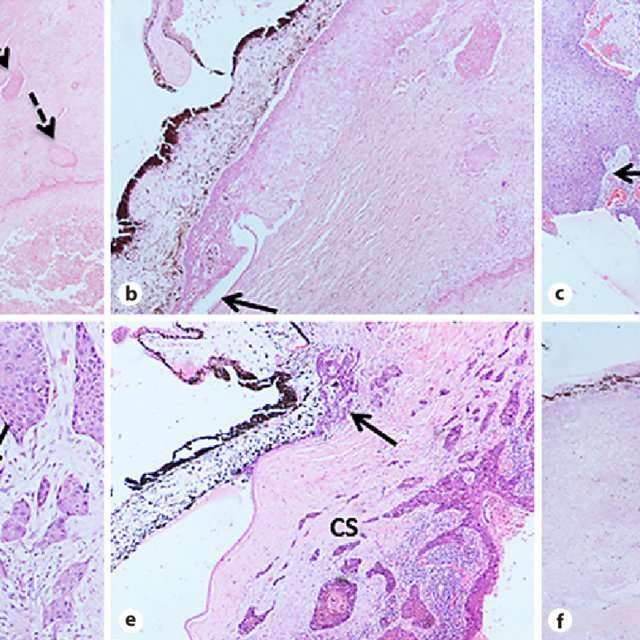
In SCC, look for any perineural invasion, and at least a quick glance for any vascular invasion.
-
Perineural invasion: the arrow indicates a large peripheral nerve that has been surrounded by tumor cells.
-
Vascular invasion: the arrow indicates a small cluster of atypical squamous cells in a small vessel.
Vascular invasion most frequently involves a complete encircling of the nerve or vessel by tumor cells. An incomplete, crescent-like pattern of atypical cells is also commonly seen. Occasionally, tangential contact, permeation, and lamination can be observed. Invasion almost always occurs contiguous to the main body of the tumor however, it has been known on occasion to affect more distant nerve and vascular sites. Usually, tumor cells arranged in solid or sheet-like patterns are less invasive, and will pass around the nerve or vessel. In contrast, individual tumor cells will generally penetrate and track along associated structures.
What Is Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Ill start by breaking down the terminology. Carcinoma is acancer derived from epithelial cells, which are the lining cellsthat make up the skin, lining of the gastrointestinal tract, liningof the respiratory tract, etc. Squamous cell is a particular typeof epithelial cell that is flat there are only certain places inthe body that have this type of epithelial cell. Welldifferentiated means the cells, while cancerous, are still typicalin shape, size and intracellular characteristics for the type ofcell they developed from.
Putting everything back together, this is a cancer derived fromthe cells of either the skin or a body cavity lining that is stillfairly normal appearing. Interpreting this, I would guess thecancer is associated with the skin and that the cancer is notlikely to have metastasized yet.
You May Like: Stage Iii Melanoma Treatment
Types Of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Distinct clinical types of invasive cutaneous SCC include:
- Cutaneous horn the horn is due to excessive production of keratin
- Keratoacanthoma a rapidly growing keratinising nodule that may resolve without treatment
- Carcinoma cuniculatum , a slow-growing, warty tumour on the sole of the foot
- – a cutaneous SCC that has developed in a scar or chronic ulcer
- Multiple eruptive SCC/KA-like lesions arising in syndromes, such as multiple self-healing squamous epitheliomas of Ferguson-Smith and Grzybowski syndrome
The pathologist may classify a tumour as well differentiated, moderately well differentiated, poorly differentiated or anaplastic cutaneous SCC. There are other variants.
Subtypes of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
What Are Scc’s Caused By
Cumulative, long-term exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun over your lifetime causes most SCCs. Daily year-round sun exposure, intense exposure in the summer months or on sunny vacations and the UV produced by indoor tanning devices all add to the damage that can lead to SCC. Experts believe that indoor tanning is contributing to an increase in cases among young women, who tend to use tanning beds more than others do.
Read Also: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Does It Mean If My Carcinoma Is Called Small Cell Carcinoma
Small cell carcinoma is a special type of lung cancer that tends to grow and spread quickly. Since it has often spread outside the lung at the time it is diagnosed, it is rarely treated with surgery. It is most often treated with chemotherapy, which might be combined with radiation. The chemotherapy used is different from what is used for other types of lung cancers.
Meaning Of Carcinoma In Situ
In many ways, the term “carcinoma” is simply equated with cancer. Roughly 85 percent of cancers are carcinomas. Carcinomas are composed of epithelial cells the type of cells that line the skin, breast ducts, and other surfaces of organs in the body.
The subtypes of carcinomas include adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, transitional cell carcinoma , and basal cell carcinoma.
Carcinoma in situ can be further defined by the tissue type in which cancer is beginning. For example, squamous cell carcinoma in situ of the cervix would represent a cancer that had started in squamous cells which line the cervix and has not yet become invasive.
Tumors such as sarcomas arise in tissues which do not have a basement membrane so that for these types of cancer there is not a stage of carcinoma in situ. In other words, tumors such as bone cancer do not have a pre-invasive stage and the cells would either be considered normal or cancer. Likewise, blood-related cancers, such as leukemias and lymphomas, do not have a preinvasive but cancerous stage for which people can be screened. For cancers that don’t have a CIS stage, screening tests are not as effective in early detection, because once the abnormal cells are detected, it would already be considered invasive with the potential to spread .
Don’t Miss: Large Cell Cancer Of The Lung
Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma a very common form of nonmelanoma skin cancer that originates in the squamous cells becomes metastatic when it spreads beyond the primary cancer site and affects other areas of the body. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma is uncommon but can develop if the primary cancer is not surgically removed or treated in a timely manner.
Invasive Moderately Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinomawhat Does This Mean Severe Squamous Dysphasia Meaning Also Please
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Prognosis
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Symptoms
Cancer appears in numerous forms and skin carcinomas and melanomas are the most common. SCC is categorized as a non-melanoma type that develops from sun-damaged skin or excessive use of tanning beds or sunlamps. The individuals most vulnerable to SCC are those who are light skinned and easily sunburned. Adults over 40 years old and individuals with a family history of sun cancer are also at risk.
Early detection provides the best opportunity for effective treatment, so a regular routine of checking your skin for unusual growths is your best defense towards preventing the disease from spreading and causing greater harm.
You want to watch for the following signs:
- Wart-like growth on skin
- Stubborn red bump on skin
- Scaly area of skin that bleeds or has crust
- Skin sore or thick growth of skin on lower lip
While these symptoms could indicate skin cancer, you need a confirmed diagnosis from a cancer expert. By consulting with a specialist like Dr. Allison, you will have the assurance of an experienced and talented oncologist who knows the most effective treatment solutions for your needs.
Usually squamous cell carcinoma is confirmed with a biopsy. Some of the skin lesion is examined and the tissue sent to a pathologist for analysis. Once the results are confirmed, you and your doctor can discuss your treatment plan.
Can A Sphincter Preserve Surgery Be Used For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Sphincter-preserving surgery is usually feasible. Clinical judgment of tumor response after chemoradiation is not completely reliable. Immunohistochemistry suggests a common cellular origin for rectal squamous-cell carcinoma and rectal adenocarcinoma, which is different from anal squamous-cell carcinoma.
Also Check: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma And What Does It Look Like
Looking for an answer to the question: What is squamous cell carcinoma and what does it look like? On this page, we have gathered for you the most accurate and comprehensive information that will fully answer the question: What is squamous cell carcinoma and what does it look like?
Excisional surgery can be used for squamouscellcarcinomas as well as basal cellcarcinomas and melanomas. For tumors discovered at an early stage that have not spread beyond the tumor margin,excisional surgery is frequently the only treatment required.
In general,the squamous cell carcinoma survival rate is very high. Thats because a cure is often possible,especially if the cancer is detected at an early stage. Even if squamous cell carcinoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes,the cancer may be effectively treated through a combination of surgery and radiation treatment.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is usually not life-threatening,though it can be aggressive in some cases. Untreated,squamous cell carcinoma of the skin can grow large or spread to other parts of your body,causing serious complications.
What Does It Mean If My Cancer Is Called Malignant Mesothelioma
Mesotheliomas are not technically lung cancers, because they donât develop from cells in the lung. They come from the lining on the outside of the lung, called the pleura. These cancers are not carcinomas.
Mesotheliomas are often described based on how they look under the microscope with terms like epithelial, spindled, sarcomatoid, or mixed epithelial and spindle cell features. Mesotheliomas may be linked to exposure to asbestos.
Read Also: Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rates
How Common Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Over 1 million people are diagnosed with SCC in the US each year. The incidence of SCC has risen about 200 percent over the past 30 years. There are more than 15,000 deaths each year in the US from SCC. Excluding head and neck SCC and CSCC in situ, about 200,000-400,000 new cases of SCC are diagnosed in the US every year, resulting in about 3,000 deaths.
Men are about two times more likely than women to develop SCCs. People over the age of 50 are most likely to get SCCs, but the incidence has been rising in younger people.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
Certain things make you more likely to develop SCC:
- Older age
- Blue, green, or gray eyes
- Blonde or red hair
- Spend time outside, exposed to the sun’s UV Rays
- History of sunburns, precancerous spots on your skin, or skin cancer
- Tanning beds and bulbs
- Long-term exposure to chemicals such as arsenic in the water
- Bowens disease, HPV, HIV, or AIDS
Your doctor may refer you to a dermatologist who specializes in skin conditions. They will:
- Ask about your medical history
- Ask about your history of severe sunburns or indoor tanning
- Ask if you have any pain or other symptoms
- Ask when the spot first appeared
- Give you a physical exam to check the size, shape, color, and texture of the spot
- Look for other spots on your body
- Feel your lymph nodes to make sure they arent bigger or harder than normal
If your doctor thinks a bump looks questionable, theyll remove a sample of the spot to send to a lab for testing.
Continued
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
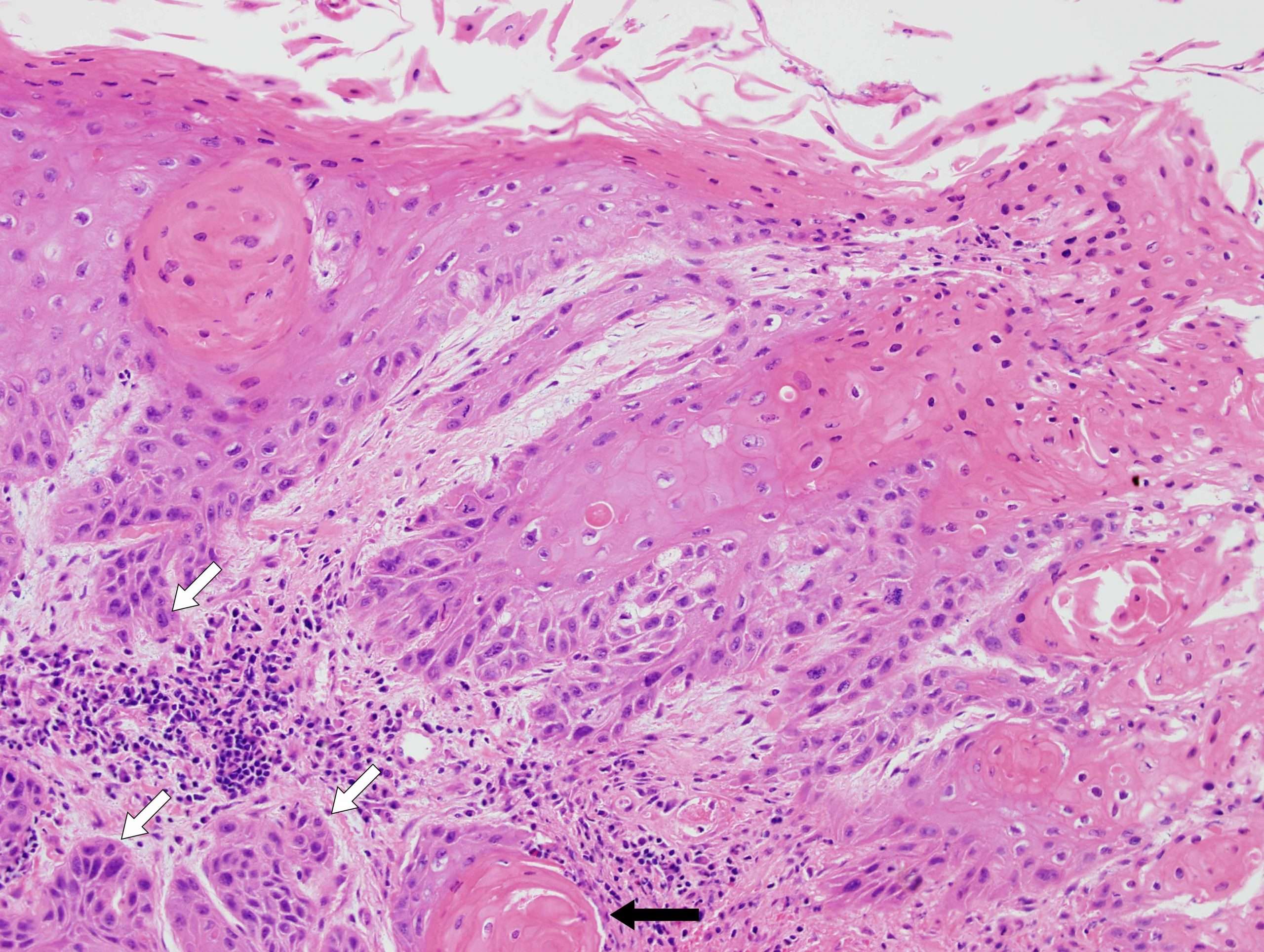
Classification Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma By Risk
Cutaneous SCC is classified as low-risk or high-risk, depending on the chance of tumour recurrence and metastasis. Characteristics of high-risk SCC include:
High-risk cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma has the following characteristics:
- Diameter greater than or equal to 2 cm
- Location on the ear, vermilion of the lip, central face, hands, feet, genitalia
- Arising in elderly or immune suppressed patient
- Histological thickness greater than 2 mm, poorly differentiated histology, or with the invasion of the subcutaneous tissue, nerves and blood vessels
Metastatic SCC is found in regional lymph nodes , lungs, liver, brain, bones and skin.
High-risk cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
How Is Squamous Cell Cancer Diagnosed
Your doctor will first perform a physical exam and inspect any abnormal areas for signs of SCC. Theyll also ask you about your medical history. If SCC is suspected, your doctor may decide to take a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
A biopsy usually involves removing a very small portion of the affected skin. The skin sample is then sent to a laboratory for testing.
In some cases, your doctor may need to remove a larger part or all of the abnormal growth for testing. Talk to your doctor about any potential scarring or biopsy concerns.
Treatment for SCC varies. Treatment is based on:
- the extent and severity of your cancer
- your age
- your overall health
- the location of the cancer
If SCC is caught early, the condition can usually be successfully treated. It becomes harder to cure once it has spread. Many treatments can be performed as in-office procedures.
Some doctors may also use photodynamic therapy, laser surgery, and topical medications to treat SCC. However, the Food and Drug Administration hasnt approved these methods for treating SCC:
Once SCC has been treated, its critical to attend all follow-up visits with your doctor. SCC can return, and its important to monitor your skin for any precancerous or cancerous areas at least once per month.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread To Organs
What Is Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Anus
- Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Anus is a malignant condition affecting the skin or mucosal membranes of the anus, which developed from in situ squamous cell carcinoma
- This malignant carcinoma, which may be present as a lesion on the anus, has the potential to metastasize , usually to the inguinal lymph nodes
- The cause of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Anus is unknown, but factors such as HPV infection, poor immunity, high-risk sexual practices, etc., are known to contribute towards its development. Middle-aged and elderly adults are at risk for the condition
- Any combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and invasive procedures are used to treat Anal Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma. The outcome depends upon many factors including the stage of the tumor earlier the diagnosis and treatment, better is the prognosis
What Is The Treatment For Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Cutaneous SCC is nearly always treated surgically. Most cases are excised with a 310 mm margin of normal tissue around a visible tumour. A flap or skin graft may be needed to repair the defect.
Other methods of removal include:
- Shave, curettage, and electrocautery for low-risk tumours on trunk and limbs
- Aggressive cryotherapy for very small, thin, low-risk tumours
- Mohs micrographic surgery for large facial lesions with indistinct margins or recurrent tumours
- Radiotherapy for an inoperable tumour, patients unsuitable for surgery, or as adjuvant
Also Check: Late Stage Basal Cell Carcinoma
Is Mohs Surgery Better Than Excision
As mentioned earlier, Mohs is more reliable and boasts a higher cure rate than standard surgical excisions. Plus, Mohs is often the cheaper of the two surgeries. For these reasons, more and more patients are directed toward Mohs micrographic surgery to eliminate their basal or squamous cell carcinoma.
How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Esophagus Treated
The treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Esophagus usually involves surgery, which is the first treatment option considered. It also includes a combination of radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
- When the tumor is confined to the surface, then endoscopic mucosal/submucosal resection is undertaken
- Esophagectomy or surgery to remove part of esophagus
- If the tumor has metastasized, then a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and invasive procedures may be used to treat the tumor
- Palliative care is provided for advanced cancer stages
- Follow-up care with regular screening and check-ups are very important and encouraged
Clinical trials: In advanced stages of cancer progression, there may be some newer treatment options currently on clinical trials, which can be considered for some patients depending on their respective risk factors.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Pictures Mayo Clinic