Thyroid Cancer Is A Disease In Which Malignant Cells Form In The Tissues Of The Thyroid Gland
The thyroid is a gland at the base of the throat near the trachea . It is shaped like a butterfly, with a right lobe and a left lobe. The isthmus, a thin piece of tissue, connects the two lobes. A healthy thyroid is a little larger than a quarter. It usually cannot be felt through the skin.
The thyroid uses iodine, a mineral found in some foods and in iodized salt, to help make several hormones. Thyroid hormones do the following:
- Control heart rate, body temperature, and how quickly food is changed into energy .
- Control the amount of calcium in the blood.
Association With Clinicopathologic Characteristics
After histopathological review, the diagnosis of PRCC was confirmed in a total of 52 patients, including 38 males and 14 females . The mean tumor size was 4.8±2.5cm. There were 24 patients with type 1 PRCC and 28 patients with type 2 PRCC. The age at surgery ranged from 17 to 86years old . According to Table , patients with type 2 PRCC were more likely to have a higher WHO/ISUP grade and an advanced tumor stage . Moreover, patients with type 2 PRCC were more likely to receive radical nephrectomy . Other clinical characteristics demonstrated no statistically significant differences across the two groups.
Table 1 Clinical characteristics between type 1 and type 2 papillary renal cell carcinomaFig. 1
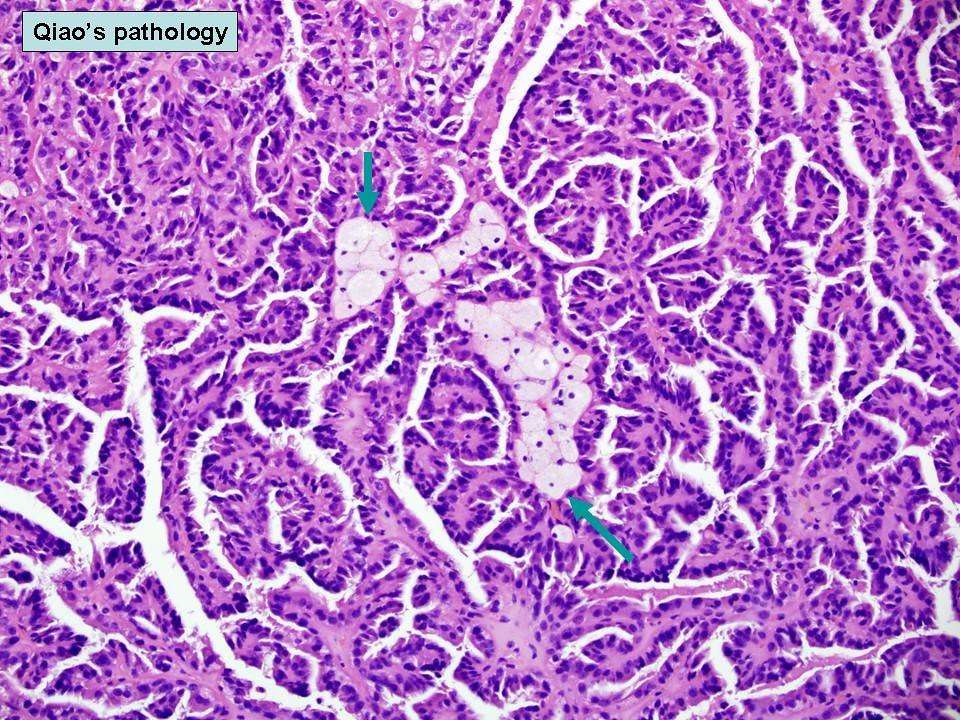
Papillary renal cell carcinoma grading and types. a, type 1 b, type 2 Papillary renal cell carcinoma graded as nucleolar grade 1, 2, 3, 4. Hematoxylin and eosin stains, original magnification ×400
Table displays the pathologic characteristics of the patients. Presence of foamy macrophages was more frequent in type 1 than in type 2 . In contrast, eosinophils and microvascular angiolymphatic invasion were more frequent in type 2 PRCC . There were no statistically significant differences across the two groups in terms of hemosiderin laden macrophages, necrosis, sarcomatoid differentiation, hyaline cells, classic papillary architecture, solid architecture, tubular architecture, and perinephric/renal sinus fat invasion.
Comprehensive Molecular Characterization Of Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
Previously published next-generation sequencing studies have identified several mutated genes associated with pRCC including: MET, NF2, SETD2, and Nrf2 pathway genes . However, these mutations were found in only ~10â15% of pRCC tumors in these studies . The investigators of The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, in an attempt to improve our understanding and classification of pRCC, performed comprehensive molecular analysis, including whole-exome sequencing, identification of copy number alterations , micro- and messenger-RNA sequencing, protein expression and DNA methylation analysis of 161 primary pRCC tumors .
Of these tumors, 75 were classified as papillary type 1 and 60 as type 2. As expected, the type 1 tumors were more likely to be lower grade than type 2 tumors. Analysis of CNAs resulted in the identification of three patterns: predominantly type 1 tumors with frequent gain of chromosomes 7 and 17 type 2 tumors with few CNAs and type 2 tumors with aneuploidy, including frequent loss of chromosome 9p . Whole-exome sequencing identified 11 significantly mutated genes, including previously identified genes such as MET, SETD2, NF2 and BAP1, among others. These mutations, many of which are part of known cancer-associated pathways, were present in a higher percentage of tumors than was reported by previous studies.
Recommended Reading: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
What Is The Outlook For People With Renal Cell Carcinoma
The earlier RCC is detected, the better. Overall, about 75% of people with kidney cancer are alive five years after their diagnosis. When cancer hasnt spread beyond the kidney, survival rates are high as 93%.
Even if your treatment is successful, RCC can come back. This is called recurrence. Its important to have a follow-up plan with your doctor after treatment for RCC to detect a recurrence as soon as possible.
From the community:I have metastatic renal cell cancer–first diagnosed December, 2008–which has been well treated with multiple surgeries and multiple systemic treatments over the years–you name it, I’ve probably had it! So don’t lose hope. There have been 2 or 3 dark periods for me over the past 11 years, when I thought this is it, the end, but some new treatment or clinical trial or surgery has always come up that either removed or reduced my tumors or at the very least stabilized their growth for a year or more, giving me time until the next best treatment appeared on the horizon. I’m now age 70, doing well, physically quite active and enjoying my recent retirement. For all practical purposes, my renal cell cancer has become a chronic disease and theres a reasonable chance I’ll ultimately beat this. – Inspire member
What Gets Stored In A Cookie
This site stores nothing other than an automatically generated session ID in the cookie no other information is captured.
In general, only the information that you provide, or the choices you make while visiting a web site, can be stored in a cookie. For example, the site cannot determine your email name unless you choose to type it. Allowing a website to create a cookie does not give that or any other site access to the rest of your computer, and only the site that created the cookie can read it.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take Melanoma To Metastasize
Therapies For Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
While all the pivotal trials leading to the approval of targeted therapies for RCC have focused on clear cell histology thus far, recent studies have investigated the optimal treatment regimens in non-clear cell RCC. Sunitinib was tested in pRCC in the SUPAP trial and was found to be active in both type 1 and type 2 pRCC . The RAPTOR trial evaluated everolimus as monotherapy in pRCC and found that it was beneficial, with a median OS of 21 months and a similar difference between type 1 and type 2 . ASPEN and ESPN are two recently published phase 2 trials comparing sunitinib and everolimus as first line therapy in patients with metastatic non-clear cell RCC. Of note, there were significant differences in the trial populationsâthe ESPN trial included sarcomatoid clear cell RCC and 39.7% pRCC whereas ASPEN did not allow any clear cell RCC and 66% of subjects had pRCC. The ESPN trial was not able to show superiority of everolimus over sunitinib while the ASPEN trial concluded that sunitinib improved progression-free survival when compared to everolimus for non-clear cell RCC. Both trials, however, are limited by the significant heterogeneity of the non-clear cell RCC groups they studied and noted the need for improved patient stratification by molecular and genetic characteristics.
Treatment Options Under Clinical Evaluation For Patients With Any T Any N M1 Disease
Prognosis is poor in patients with stage IV disease and consideration of entry into a clinical trial is appropriate.
Other chemotherapy regimens appear to be active in the treatment of metastatic disease. Chemotherapy agents that have shown activity in metastatic bladder cancer include paclitaxel, docetaxel, ifosfamide, gallium nitrate, and pemetrexed.
Also Check: Can Melanoma Be Treated Successfully
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Stage 4 Cancer
Cystectomy Cystoprostatectomy And Pelvic Exenteration Specimens
Processing of these specimens may be summarized in three steps: orientation of the specimen and identification of relevant anatomic structures , fixation of the specimen and dissection of the specimen. Peritoneum covering the surface of the bladder is a reliable anatomic landmark. In both male and female patients, the peritoneum descends further along the posterior wall of the bladder than it does along the anterior wall. Other pelvic organs, if present, may also be used to orient the specimen. In the male, the bladder adjoins the rectum and seminal vesicles posteriorly, the prostate inferiorly, and the pubis and peritoneum anteriorly. In the female, the vagina is located posteriorly, and the uterus is located superiorly. Once the specimen is oriented, both ureters and, when present, the vasa deferentia should be identified. Location and dissection of the ureters is easier after fixation. The outer dimensions of the urinary bladder, as well as the length and diameter of ureters, should be recorded. The external surface of the bladder should be inked.
The minimum number of sections to be taken are as follows: tumor bladder neck , trigone , anterior wall , posterior wall , lateral walls , dome , ureteral orifices , margins , any abnormal appearing bladder mucosa and any perivesical lymph nodes .
Figure 18
Papillary Vs Flat Cancer
Bladder cancers are also divided into 2 subtypes, papillary and flat, based on how they grow .
- Papillary carcinomas grow in slender, finger-like projections from the inner surface of the bladder toward the hollow center. Papillary tumors often grow toward the center of the bladder without growing into the deeper bladder layers. These tumors are called non-invasive papillary cancers. Very low-grade , non-invasive papillary cancer is sometimes called papillary urothelial neoplasm of low-malignant potential and tends to have a very good outcome.
- Flat carcinomas do not grow toward the hollow part of the bladder at all. If a flat tumor is only in the inner layer of bladder cells, itâs known as a non-invasive flat carcinoma or a flat carcinoma in situ .
If either a papillary or flat tumor grows into deeper layers of the bladder, itâs called an invasive urothelial carcinoma.
Donât Miss: What Is Papillary Urothelial Carcinoma
Recommended Reading: Well-differentiated Meaning
Symptoms Of Hereditary Papillary Renal Carcinoma
The only symptom of hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma is the development of kidney cancer, which usually happens just after turning 40 .
So far, all reported HPRC patients have developed kidney cancer, according to the National Cancer Institute .
When the tumors are small, they dont usually cause symptoms. If they grow larger, symptoms may include:
- Pain in the upper abdomen, back or sides
- Blood in the urine
- Lump in the abdomen or lower back
When HPRC kidney tumors become large, they may metastasize, most commonly to the lungs, and cause additional symptoms.
Changes To This Summary
The PDQ cancer information summaries are reviewed regularly and updated as new information becomes available. This section describes the latest changes made to this summary as of the date above.
Inheritance and Risk of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Added text about the results of several studies in which patients with renal cell carcinoma were found to have pathogenic variants in genes not previously associated with hereditary RCC .
This summary is written and maintained by the PDQ Cancer Genetics Editorial Board, which iseditorially independent of NCI. The summary reflects an independent review ofthe literature and does not represent a policy statement of NCI or NIH. Moreinformation about summary policies and the role of the PDQ Editorial Boards inmaintaining the PDQ summaries can be found on the About This PDQ Summary and PDQ® – NCI’s Comprehensive Cancer Database pages.
Also Check: Survival Rates For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Will My Doctor Test For It
Youll need a few different tests to see if a nodule is cancer.
Physical exam. Your doctor will feel for unusual growths in your neck and ask about any symptoms you might have.
Blood tests. You may get your thyroid hormone levels checked. This wont tell you if you have cancer, but it gives more information about how your thyroid is working.
Ultrasound. Youll get this test, which uses sound waves to make a picture of things inside your body, to learn more about nodules you have. Your doctor will find out about their shape, size, and other features. That will give important clues to decide how much of a problem they are.
Biopsy. Your doctor will use a very fine needle to take a sample of the nodule to test for cancer. Typically, the most youll feel during it is a small pinch.
Youll likely get this done for any nodule thats bigger than 1 centimeter . Nodules with calcium buildup, lots of blood vessels, or without clear borders raise red flags. So do unusual-looking nearby lymph nodes bean-shaped organs that help fight infections.
Return to: Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Overview
Papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Tall Cell Variant
Follicular Variant
Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma
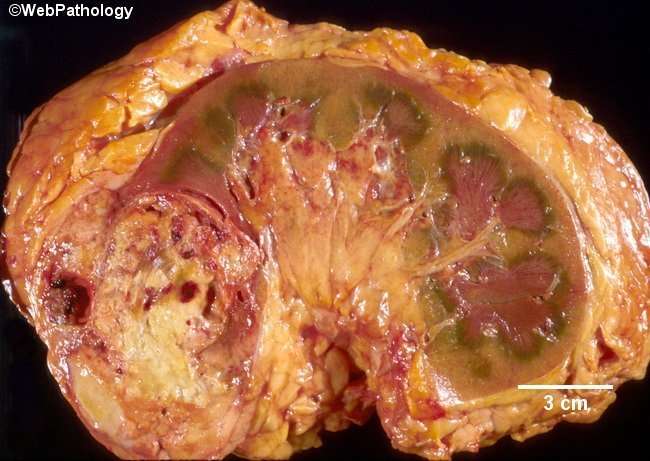
Jianping Zhao, Eduardo Eyzaguirre Clear Cell Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1 September 2019 143 : 11541158. doi:
Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma is a recently recognized entity and represents the fourth most common variant of renal cell carcinoma . It has unique morphologic and immunohistochemical features and demonstrates an indolent clinical behavior. Microscopically, it may mimic other RCCs with clear cell features, such as clear cell RCC, translocation RCC, and papillary RCC with clear cell changes. A high index of suspicion is required to keep ccpRCC in the differential diagnosis of RCCs with features of clear cell and/or papillary architecture. In equivocal cases, immunohistochemistry is generally sufficient to substantiate the diagnosis of ccpRCC. In this review, we discuss the clinical, gross, and histopathologic features, immunohistochemical and genetic profiling, and prognosis of ccpRCC.
You May Like: Invasive Breast Cancer Prognosis
Who Might Have Thyroid Cancer
Women are three times more likely than men to get thyroid cancer. The disease is commonly diagnosed in women in their 40s and 50s, and men in their 60s and 70s. Even children can develop the disease. Risk factors include:
- Exposure to radioactive fallout from nuclear weapons or a power plant accident.
Dont Miss: How Often Does Melanoma Spread To Lymph Nodes
Automated Classification Of Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma And Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma Based On A Small Computed Tomography Imaging Dataset Using Deep Learning
- 1Department of Urology, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou, China
- 2Institute for Empirical Social Science Research, Xian Jiaotong University, Xian, China
- 3School of Statistics and Mathematics, Central University of Finance and Economics, Beijing, China
- 4School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, United States
- 5Department of Radiology, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou, China
- 6Department of Pathology, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou, China
- 7School of Medicine, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China
- 8School of Medicine, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
Objectives: This study was conducted in order to design and develop a framework utilizing deep learning to differentiate papillary renal cell carcinoma from chromophobe renal cell carcinoma using convolutional neural networks on a small set of computed tomography images and provide a feasible method that can be applied to light devices.
Results: The CT image sequences of 70 patients were segmented and validated by two experienced abdominal radiologists. The best model achieved 96.8640% accuracy in the validation set and 100% and 93.3333% in the test set. The manual classification achieved 85% accuracy in the test set.
This framework demonstrates that DL models could help reliably predict the subtypes of PRCC and ChRCC.
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate
Risk Prevention And Early Detection Of Rcc
Individuals with inherited syndromes that predispose to RCC and long-term dialysis patients are at high risk but account for a minority of RCC cases. Algorithms of relative risk of RCC according to smoking status, body mass index and blood pressure have been investigated and a decrease in risk was observed for men who had stopped smoking for 30 years or more . The only evidence for the potential of chemoprevention for RCC are studies which show diets rich in fruit and vegetables as well as high vitamin D levels to be preventive . Candidates for a future chemopreventive strategy would be inherited RCC, ESRD patients and also RCC patients at high risk of recurrence.
Molecular early detection strategies must be designed with careful regard to the abundance of tumor cells in the clinical specimen as well as the frequency and timing of the alteration to be detected . LOH of 3p and point mutation of VHL are frequent and early in clear cell RCC but urine or blood contain a low ratio of DNA from renal tumor cells to DNA from normal cells that is insufficient for the robust detection of these alterations by polymorphic marker and sequencing analysis respectively. Because point mutations occur throughout the VHL gene, rather than at hotspots of particular codons like RAS, the design of more sensitive oligonucleotide molecular tests is very complicated. However, if a tumor cell-rich biopsy specimen is available, LOH and point mutation can be assessed as prognostic markers.
Treatment For Hereditary Papillary Renal Carcinoma
Patients who have tested positive for mutations linked to hereditary papillary renal carcinoma will typically get regular computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging scans of their kidneys to monitor for the development of tumors.
If these screenings find tumors developing in the kidneys, doctors may not take a biopsy or remove them. Instead, they may wait and monitor the tumors.
Tumors that grow to be bigger than 3 cm wide, or about the size of a grape, need to be surgically removed, which is done by excising part of the kidney. Your care team will try to keep as much of the kidney as possible.
If the cancer spreads to other areas of your body, doctors may discuss chemotherapy and radiation options. Treatment with drugs that block the activity of the MET receptor are currently being tested in clinical trials.
Expert
Don’t Miss: How Long Until Melanoma Spreads
What Are The Symptoms
Often, you wont have any. You might only find out about it because of an imaging test for another problem. Or, during a routine physical, your doctor might just happen to feel a lump, called a nodule, on your thyroid.
Nodules are growths that may be solid or filled with fluid. Theyre very common and often dont cause any trouble. But about 1 in 20 are cancer.
As a nodule gets bigger, you may start to have symptoms like:
- Lump in your neck that you can see or feel
- Hard time swallowing
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck
- Trouble breathing, especially when you lie down