Who Is Most At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can develop skin cancer, youre at increased risk if you:
- Spend a considerable amount of time working or playing in the sun.
- Get easily sunburned have a history of sunburns.
- Live in a sunny or high-altitude climate.
- Tan or use tanning beds.
- Have light-colored eyes, blond or red hair and fair or freckled skin.
- Have many moles or irregular-shaped moles.
- Have actinic keratosis .
- Have a family history of skin cancer.
- Have had an organ transplant.
- Take medications that suppress or weaken your immune system.
- Have been exposed to ultraviolet light therapy for treating skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
Protect Yourself & Look Great
- Avoid tanning entirely: Its the best way to safeguard against unhealthy, unsightly skin damage.
- Fake, dont bake: If you want a golden glow, consider sunless tanning products. There are many options that can give you a bronzed look, but you still need sun protection!
- Tone, dont tan: Get radiant skin by doing aerobic or high-intensity exercises. Working out feels good and boosts your mood.
- Hydrate, eat great: Drink lots of water and choose whole, unprocessed foods. Your skin will thank you!
Make healthy skin a way of life. Get the details here: Your Daily Sun Protection Guide
Reviewed by:
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form.
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells.
- Melanocytes: These are the cells that can become melanoma. They normally make a brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin protects the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Recommended Reading: Immunotherapy For Malignant Melanoma
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common kind of skin cancer. It can develop almost anywhere on the body.
BCCs typically form in sun-exposed areas. They vary greatly in how they lookpink or red bumps, open sores, or waxy patches. For people with brown or black skin, BCCs may appear brown or almost black.
How Is Melanoma Staged
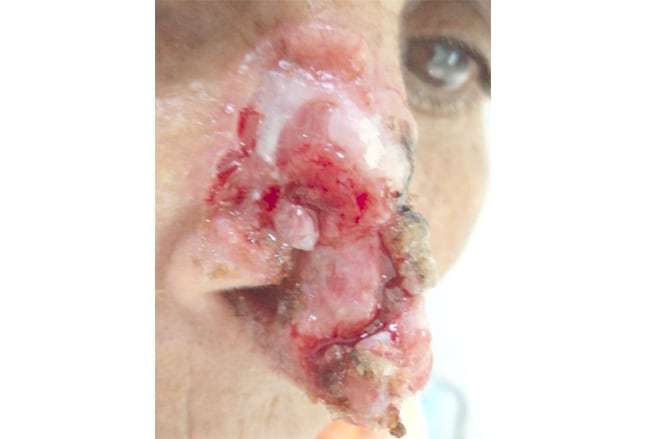
Melanoma is divided into 4 stages based on the depth of the primary tumor and how far the cancer has spread from its starting point. Melanoma staging system helps to identify the best treatment method for individual cases and also helps to identify the prognosis. In situ melanomas have an excellent prognosis after surgical excision with a sufficient surgical margin. Invasive melanomas are far more serious. Breslow thickness is the depth of the melanoma calculated perpendicularly from the skin surface, specifically from the stratum granulosum of the epidermis to the lower-most level of the melanoma .
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Three Most Common Skin Cancers
It is estimated that one in seven people in the United States will develop some form of skin cancer during their lifetime. Although anyone can get skin cancer, people who burn easily and are fair-skinned are at higher risk. Researchers believe that one serious sunburn can increase the risk of skin cancer by as much as 50%. A yearly skin exam by a doctor is the best way to detect skin cancer early, when it is most treatable. If you have a new growth or any change in your skin, be sure to see your doctor to have it examined. Remember, protecting yourself from the sun is the best way to prevent all forms of skin cancer.
Diagnosing Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The main way to diagnose squamous cell carcinoma is with a biopsy. This involves having a small piece of tissue removed from the suspicious area and examined in a laboratory.
In the laboratory, a pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope to determine if it is a skin cancer. He or she will also stage the cancer by the number of abnormal cells, their thickness, and the depth of penetration into the skin. The higher the stage of the tumor, the greater the chance it could spread to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma on sun-exposed areas of skin usually does not spread. However, squamous cell carcinoma of the lip, vulva, and penis are more likely to spread. Contact your doctor about any sore in these areas that does not go away after several weeks.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Survival Rate
How Often Does Bcc Spread
Metastasis is rare with BCC, occurring in between 0.0028 and 0.55% of all cases. When it does occur, the lymph nodes, lungs, and bone are the most common sites of metastasis.
If BCC remains localized, there is a five-year survival rate of 100%. If BCC metastasizes, the outcomes are generally poor with median survival times ranging from eight months to 3.5 years.
Prognosis And Survival For Non
If you have non-melanoma skin cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type, size and grade of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. Prognostic factors help doctors predict a prognosis and plan treatment and follow-up.
Doctors use many of the following prognostic factors to classify basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma into risk groups. The risk groups help the doctor estimate the risk that the cancer will come back . Doctors also use the risk groups to help plan the best treatment.
Prognosis and survival for most non-melanoma skin cancers is excellent. The following are prognostic factors for non-melanoma skin cancer.
Don’t Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate Stage 1
How Is Skin Cancer Treated
Treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. Stages of skin cancer range from stage 0 to stage IV. The higher the number, the more cancer has spread.
Sometimes a biopsy alone can remove all the cancer tissue if the cancer is small and limited to your skins surface only. Other common skin cancer treatments, used alone or in combination, include:
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze skin cancer. The dead cells slough off after treatment. Precancerous skin lesions, called actinic keratosis, and other small, early cancers limited to the skins top layer can be treated with this method.
Excisional surgery
This surgery involves removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy skin to be sure all cancer has been removed.
Mohs surgery
With this procedure, the visible, raised area of the tumor is removed first. Then your surgeon uses a scalpel to remove a thin layer of skin cancer cells. The layer is examined under a microscope immediately after removal. Additional layers of tissue continue to be removed, one layer at a time, until no more cancer cells are seen under the microscope.
Mohs surgery removes only diseased tissue, saving as much surrounding normal tissue as possible. Its most often used to treat basal cell and squamous cell cancers and near sensitive or cosmetically important areas, such as eyelids, ears, lips, forehead, scalp, fingers or genital area.
Curettage and electrodesiccation
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy
Tanning Facts And Risks
Skin damage starts with your very first tan. Each time you tan, the damage builds up, creating more genetic mutations and greater risk.
Indoor tanning is dangerous: Tanning beds dont offer a safe alternative to sunlight they raise the risk for skin cancers. One study observing 63 women diagnosed with melanoma before age 30 found that 61 of them thats 97 percent used tanning beds.
Tanning damages all types of skin: Even if your skin type is not fair, tanning causes DNA injury that can lead to premature aging and skin cancer.
You can easily reduce your likelihood of developing skin cancer by practicing sun safety.
Read Also: Scalp Melanoma Stages
What Happens When Skin Cancer Goes Untreated
If you notice an abnormality on your skin you may be tempted to ignore it. However, if it is skin cancer you could be putting your health at risk by waiting to get a skin and mole check. There are three main types of skin cancer in Australia with melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, and they each have their own set of unique characteristics. The most important thing to remember is that if you delay treatment of skin cancer it could have life threatening consequences:
A Dangerous Skin Cancer
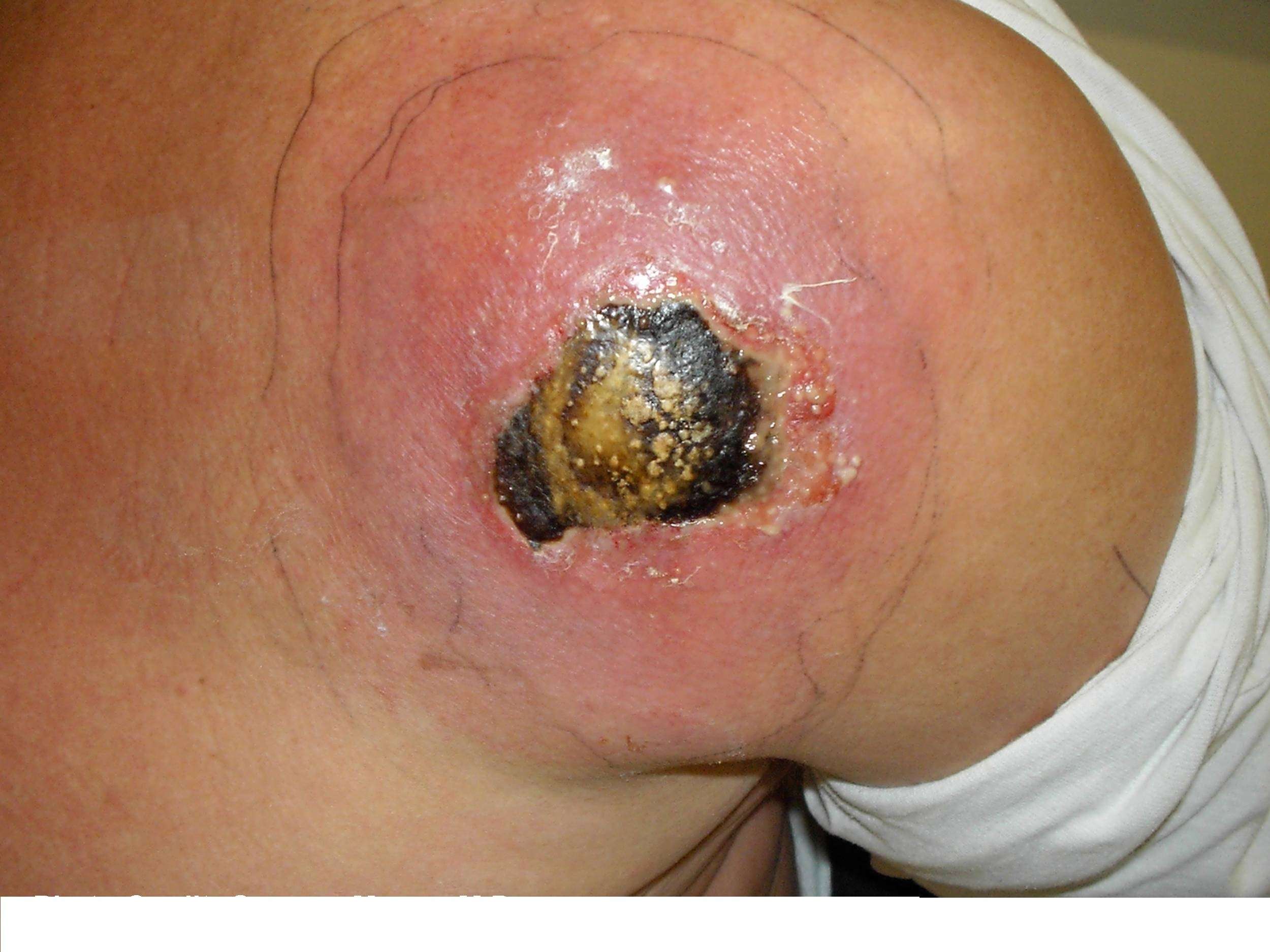
Melanoma is a serious form of skin cancer that begins in cells known as melanocytes. While it is less common than basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma , melanoma is more dangerous because of its ability to spread to other organs more rapidly if it is not treated at an early stage.
Learn more about melanoma types, risk factors, causes, warning signs and treatment.
Melanoma Fact
Only 20-30% of melanomas are found in existing moles.
While 70-80% arise on normal-looking skin.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take For Melanoma To Spread
What Are The Signs Of Skin Cancer
The most common warning sign of skin cancer is a change on your skin, typically a new growth, or a change in an existing growth or mole. The signs and symptoms of common and less common types of skin cancers are described below.
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell cancer is most commonly seen on sun-exposed areas of skin including your hands, face, arms, legs, ears, mouths, and even bald spots on the top of your head. Basal cell cancer is the most common type of skin cancer in the world. In most people, its slow growing, usually doesnt spread to other parts of the body and is not life-threatening.
Signs and symptoms of basal cell carcinoma include:
- A small, smooth, pearly or waxy bump on the face, ears, and neck.
- A flat, pink/red- or brown-colored lesion on the trunk or arms and legs.
- Areas on the skin that look like scars.
- Sores that look crusty, have a depression in the middle or bleed often.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell cancer is most commonly seen on sun-exposed areas of skin including your hands, face, arms, legs, ears, mouths, and even bald spots on the top of your head. This skin cancer can also form in areas such as mucus membranes and genitals.
Signs and symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma include:
- A firm pink or red nodule.
- A rough, scaly lesion that might itch, bleed and become crusty.
Melanoma
Signs and symptoms of melanoma include:
- A brown-pigmented patch or bump.
- A mole that changes in color, size or that bleeds.
How Often Does Mcc Spread
Around one-third to one-half of people with MCC will experience metastasis, most commonly to the brain, lungs, liver, or bones.
Treatment options for MCC vary based on the stage of the disease and how healthy a patient is overall. Treatment options include:
- Surgical removal of the tumor
- Radiation
- Chemotherapy
Also Check: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Common In Sun
Squamous cell carcinoma, also called squamous cell cancer, is the second most common type of skin cancer. It accounts for about 20 percent of cases.
This type of cancer starts in flat cells in the outer part of the epidermis. It commonly crops up on sun-exposed areas, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and hands. It can also develop on scars or chronic sores.
Squamous cell carcinomas may develop from precancerous skin spots, known as actinic keratosis .
These cancers might look like:
- A firm, red bump
- A flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface
- A sore that heals and then reopens
People with lighter skin are more at risk for developing squamous cell carcinoma, but the skin cancer can also affect those with darker skin.
Other risk factors include:
- Having light eyes, blond or red hair, or freckles
- Being exposed to the sun or tanning beds
- Having a history of skin cancer
- Having a history of sunburns
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having the genetic disorder xeroderma pigmentosum
RELATED: 10 Things You May Know Cause Skin Cancer
Factors That Increase Your Risk Of Developing Melanoma
A risk factor is anything that affects the likelihood that you develop a disease. Some skin cancer risk factors are within your control, such as how much sun youre exposed to. Others are outside of your control, like your age or familys medical history.
Are you at a high risk of developing skin cancer? On the #LiveWellHealthy blog, Dr. McCarron shares 7 factors that can increase your risk of #SkinCancer, including #Melanoma, you can do to decrease your odds: https://bit.ly/3du6xif.
Don’t Miss: Stage 4 Basal Cell Carcinoma Life Expectancy
What Is The Staging For Skin Cancer
There is no specific staging system for basal cell carcinoma. If the tumor is wider than 2 cm , it is probably a more serious tumor. Basal cell carcinomas of the ears, nose, and eyelid may also be of more concern, regardless of the size.
There is a staging system for squamous cell carcinoma. Large tumors that are thicker than 2 mm, invade the nerve structures of the skin, occur on the ear, and have certain worrisome characteristics under the microscope are of more concern. If the tumor metastasizes to a site at some distance from the primary tumor, the cancer is likely to be a dangerous tumor.
Leaving Basal Cell Carcinoma Untreated
Basal cell carcinoma is a slow growing cancer, but this doesnt mean it can be ignored. This is the least dangerous form of skin cancer and rarely spreads to other internal parts of the body. While death is a rare consequence there is the potential for disfigurement. Over time basal cell carcinoma can expand and cause ulcers and damage the skin and tissues.
Any damage could be permanent and have an impact on the way you look. Depending on how long the basal cell carcinoma has been present, radiotherapy may be required. This is the most common form of skin cancer and is often found on the face. You may notice a small lump which is shiny or pearl like and this is a sign you should get checked. This type of cancer generally does not cause any pain.
Read Also: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
Survival Rates For Melanoma Skin Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
Skin Cancer Symptoms And Signs
Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer and has a predilection for sun-exposed skin. Tumors may appear as a pearly or waxy bumps usually with visible blood vessels , or as a flat scaly reddish patch with a brown border, or as a hard or scar-like lesion . Frequently BCCs can be itchy, often bleed, or in more advanced cases, ulcerate.
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 3 Melanoma Look Like
Is Skin Cancer Life Threatening
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
Ask U.S. doctors your own question and get educational, text answers â it’s anonymous and free!
HealthTap doctors are based in the U.S., board certified, and available by text or video.
How Is Melanoma Diagnosed
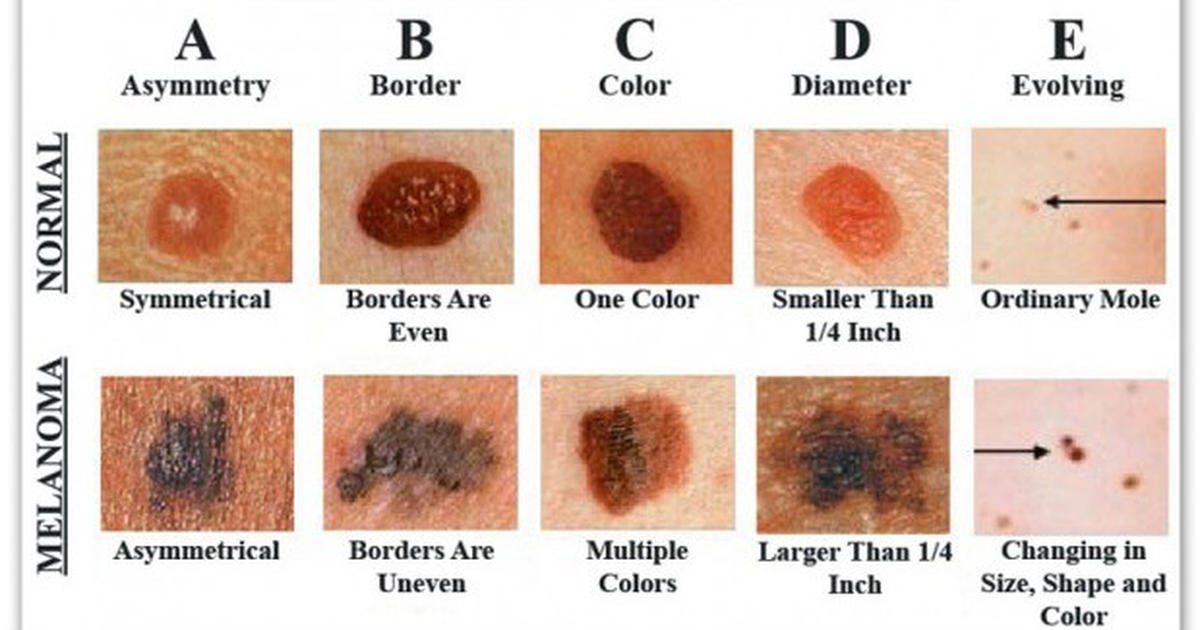
Moles, also called nevi, are groups of normal-appearing cells of melanocytic origin in the dermis. They are harmless brown spots on the skin. Melanoma usually looks different from the ordinary moles. The best way to find any suspicious moles on your body is to do a skin examination to look for the ABCDEs of melanoma. The first sign of melanoma is often a change in the size, shape, or color of a mole.
Melanoma also may appear as a new, black, abnormal or “ugly-looking” mole. Rarely, melanoma is not pigmented and is more difficult to diagnose. It may also appear as a non-healing ulcer or a new scar-like lump in the skin.
Melanoma checklist:Examine yourself from head to toe and check for the following changes in your mole
| Melanoma has a diameter of 6mm or more. | ||
| E | EVOLUTION | There is a history of change in the lesion size, shape, color, elevation or any symptoms such as bleeding, ulceration, itching or crusting. |
If you see one or more, make an appointment with a dermatologist immediately.
You May Like: Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma