Where Does Skin Cancer Develop
Skin cancer is most commonly seen in sun-exposed areas of your skin your face , ears, neck, arms, chest, upper back, hands and legs. However, it can also develop in less sun-exposed and more hidden areas of skin, including between your toes, under your fingernails, on the palms of your hands, soles of your feet and in your genital area.
Early Stage Leg Skin Cancer
While skin cancer is most frequently found on the upper body, including the head, neck, face, and arms, skin cancer on the leg is possible as well. The best way to ward off early stage leg skin cancer is to schedule annual skin cancer screenings with a dermatologist. This yearly examination will help keep track of any major changes to your skin, and will allow you to be proactive in your skins health.
Recognizing Skin Cancer What Does Early Melanoma Look Like
It is estimated that 54,000 new cases of malignant melanoma are diagnosed each year. Unlike basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are highly curable, melanoma is a more dangerous form of skin cancer. If left unnoticed and untreated it can spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream and lymphatic vessels. As many as 7,800 deaths each year can be attributed to malignant melanoma.
While still in its early stage before the cancer has had the chance to spread, it can be treated. Wondering what does early melanoma look like? Find out what to look out for to make sure you donât have this form of skin cancer. If you might have it make sure to see your doctor right away.
You May Like: Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
How Common Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in the U.S.
Other skin cancer facts:
- Around 20% of Americans develop skin cancer sometime in their life.
- Approximately 9,500 Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer every day.
- Having five or more sunburns in your life doubles your chance of developing melanoma. The good news is that the five-year survival rate is 99% if caught and treated early.
- Non-Hispanic white persons have almost a 30 times higher rate of skin cancer than non-Hispanic Black or Asian/Pacific Islander persons.
- Skin cancer in people with skin of color is often diagnosed in later stages when its more difficult to treat. Some 25% of melanoma cases in African Americans are diagnosed when cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
How Is Skin Cancer Treated
Treatment depends upon the stage of cancer. Stages of skin cancer range from stage 0 to stage IV. The higher the number, the more cancer has spread.
Sometimes a biopsy alone can remove all the cancer tissue if the cancer is small and limited to your skins surface only. Other common skin cancer treatments, used alone or in combination, include:
Cryotherapy uses liquid nitrogen to freeze skin cancer. The dead cells slough off after treatment. Precancerous skin lesions, called actinic keratosis, and other small, early cancers limited to the skins top layer can be treated with this method.
Excisional surgery
This surgery involves removing the tumor and some surrounding healthy skin to be sure all cancer has been removed.
Mohs surgery
With this procedure, the visible, raised area of the tumor is removed first. Then your surgeon uses a scalpel to remove a thin layer of skin cancer cells. The layer is examined under a microscope immediately after removal. Additional layers of tissue continue to be removed, one layer at a time, until no more cancer cells are seen under the microscope.
Mohs surgery removes only diseased tissue, saving as much surrounding normal tissue as possible. Its most often used to treat basal cell and squamous cell cancers and near sensitive or cosmetically important areas, such as eyelids, ears, lips, forehead, scalp, fingers or genital area.
Curettage and electrodesiccation
Chemotherapy and immunotherapy
You May Like: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
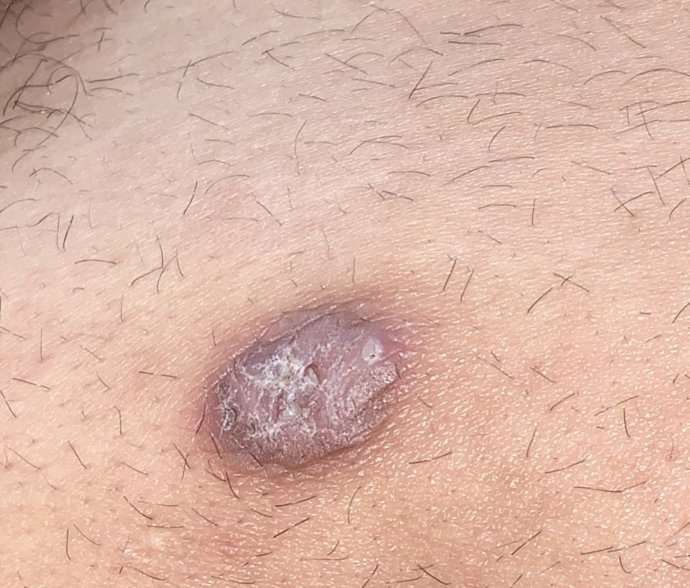
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma occurs when a tumor makes its way into the dermis via thin strands between collagen fibers. This aggressive type of skin cancer is harder to diagnose and treat because of its location. Typically, infiltrative basal cell carcinoma appears as scar tissue or thickening of the skin and requires a biopsy to properly diagnose.
To remove this type of basal cell carcinoma, a specific form of surgery, called Mohs, is used. During a Mohs surgery, also called Mohs micrographic surgery, thin layers of skin are removed until there is no cancer tissue left.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Superficial basal cell carcinoma, also known as in situ basal-cell carcinoma, tends to occur on the shoulders or the upper part of the torso, but it can also be found on the legs and arms. This type of cancer isnt generally invasive because it has a slow rate of growth and is fairly easy to spot and diagnose. It appears reddish or pinkish in color and may crust over or ooze. Superficial basal cell carcinoma accounts for roughly 15%-26% of all basal cell carcinoma cases.
What Is My Skin Type
Skin types that are more sensitive to ultraviolet radiation burn more quickly and are at a greater risk of skin cancer.
All skin types can be damaged by too much UV radiation. Skin types that are more sensitive to UV radiation burn more quickly and are at a greater risk of skin cancer.
People with naturally very dark skin still need to take care in the sun even though they may rarely, if ever, get sunburnt. The larger amount of melanin in very dark skin provides natural protection from UV radiation. This means the risk of skin cancer is lower.
Eye damage can occur regardless of skin type. High levels of UV radiation have also been linked to harmful effects on the immune system.
Vitamin D deficiency may be a greater health concern for people with naturally very dark skin, as it is more difficult for people with this skin type to make vitamin D.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Stage 3 Survival Rate
What Causes Skin Cancer
The main cause of skin cancer is overexposure to sunlight, especially when it results in sunburn and blistering. Ultraviolet rays from the sun damage DNA in your skin, causing abnormal cells to form. These abnormal cells rapidly divide in a disorganized manner, forming a mass of cancer cells.
Another cause of skin cancer is frequent skin contact with certain chemicals, such as tar and coal.
Many other factors can increase your risk of developing skin cancer. See question, Who is most at risk for skin cancer?
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Make an appointment to see your healthcare provider or dermatologist as soon as you notice:
- Any changes to your skin or changes in the size, shape or color of existing moles or other skin lesions.
- The appearance of a new growth on your skin.
- A sore that doesnt heal.
- Spots on your skin that are different from others.
- Any spots that change, itch or bleed.
Your provider will check your skin, take a biopsy , make a diagnosis and discuss treatment. Also, see your dermatologist annually for a full skin review.
You May Like: Skin Cancer Metastasis To Lymph Nodes
Abcde Melanoma Detection Guide
A is for Asymmetry
Look for spots that lack symmetry. That is, if a line was drawn through the middle, the two sides would not match up.
B is for Border
A spot with a spreading or irregular edge .
C is for Colour
Blotchy spots with a number of colours such as black, blue, red, white and/or grey.
D is for Diameter
Look for spots that are getting bigger.
E is for Evolving
Spots that are changing and growing.
These are some changes to look out for when checking your skin for signs of any cancer:
- New moles.
- Moles that increases in size.
- An outline of a mole that becomes notched.
- A spot that changes colour from brown to black or is varied.
- A spot that becomes raised or develops a lump within it.
- The surface of a mole becoming rough, scaly or ulcerated.
- Moles that itch or tingle.
- Moles that bleed or weep.
- Spots that look different from the others.
Squamous Cell Skin Cancers
Squamous cell skin cancers can vary in how they look. They usually occur on areas of skin exposed to the sun like the scalp or ear.
Thanks to Dr Charlotte Proby for her permission and the photography.
You should see your doctor if you have:
- a spot or sore that doesn’t heal within 4 weeks
- a spot or sore that hurts, is itchy, crusty, scabs over, or bleeds for more than 4 weeks
- areas where the skin has broken down and doesn’t heal within 4 weeks, and you can’t think of a reason for this change
Your doctor can decide whether you need any tests.
-
Cancer and its management J Tobias and D HochhauserBlackwell, 2015
-
Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology VT De Vita, TS Lawrence and SA RosenbergWolters Kluwer, 2018
Read Also: Late Stage Basal Cell Carcinoma
Explore Your Treatment Options In Advance
When it comes to treating skin cancer, especially on the face, many patients worry about the invasiveness of common procedures like Mohs surgery, which could leave a scar. Fortunately, there are other, less invasive treatment methods to consider. Knowing your options ahead of time will help you to feel better prepared to make a decision. Image Guided Superficial Radiotherapy is a non-invasive alternative for treating non-melanoma skin cancers like Basal cell carcinoma and Squamous cell carcinoma. If you would like to learn more about how IG-SRT works, please call GentleCure at 312-987-6543 to speak with a skin cancer information specialist.
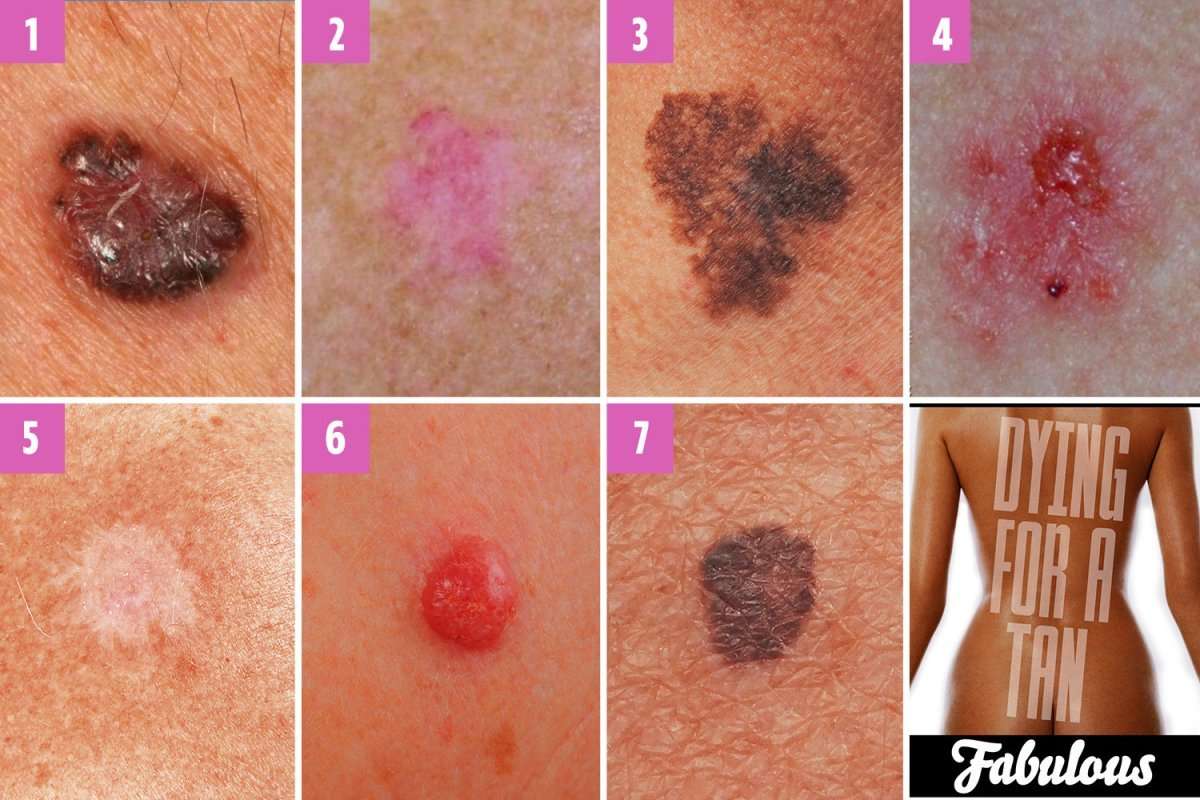
What Are Some Early Clues Of Skin Cancer What Does The Beginning Of Skin Cancer Look Like
Skin cancer is actually the most prevalent of all cancers, as more an instance of skin cancer ought to have diagnosed than any other. The consensus sentiment is that the identification of early clues of skin cancer will dramatically increase the chances of defeating it, since management can be applied more promptly and effectively. Because early spotting is critical, it is very important to learn what the early ratifies of skin cancer are. Therefore, you will know exactly what to look for, you will be able to check your skin sporadically to see if any of these clues are present.
Should you realise early signalings of skin cancer, you will then be able to take action immediately before it gets out of hand.
Five Primary Characteristics
When reading the early signals of skin cancer, you need to focus primarily on five peculiarities. Each one can be easily retained by appointing the first 5 letters of the alphabet to each one. The first early signal of skin cancer characteristic that corresponds with the word A is asymmetry, which refers to the malignant emergence being shaped irregularly, making it will be presented disproportionate.
The character D represents the word diameter, which references the cancerous tumors diameter. If these tumors are often larger than 1/4 inch, then it should be recognized as one of the early indicates of skin cancer. Elevation is the final quality, and refers to the skin skin-deep being hoisted or unbalanced,
Additional Signs
Also Check: Stage 4 Basal Cell Carcinoma Life Expectancy
What Are The Early Signs Of Skin Cancer On Your Face
Approximately 85% of skin cancer spots are found on a patients head, face, eyelids, and neck region. Detection in the early stages of skin cancer is key to treatment success, but do you know how to spot the early signs of skin cancer on your face? Before we review how to discern a potentially cancerous spot in the guide below, we will first need to discuss the most common types of skin cancer and how they might present on your skin.
Tips For Screening Moles For Cancer
Examine your skin on a regular basis. A common location for melanoma in men is on the back, and in women, the lower leg. But check your entire body for moles or suspicious spots once a month. Start at your head and work your way down. Check the “hidden” areas: between fingers and toes, the groin, soles of the feet, the backs of the knees. Check your scalp and neck for moles. Use a handheld mirror or ask a family member to help you look at these areas. Be especially suspicious of a new mole. Take a photo of moles and date it to help you monitor them for change. Pay special attention to moles if you’re a teen, pregnant, or going through menopause, times when your hormones may be surging.
Recommended Reading: Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
Scaly Red Patches Of Skin
Scaly red patches of skin are a telltale early warning sign of squamous cell carcinoma. After basal cell carcinoma, it is one of the most commonly diagnosed types of skin cancer in the United States. A patch of skin like this on your body should be monitored closely. If you’ve been diagnosed with eczema, you may be having a flare-up. But if you’ve ruled out any kind of eczema and your scaly patch of skin isn’t going away, it may be time to see your doctor. In addition, these patches of skin may bleed or ooze and then crust back over repeatedly.
Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Be Prevented
The best way to prevent SCC is to avoid sunburn. Avoid going outin the sun when the UV Index is higher than 3, such as in the middle of theday. Seek shade, wear a hat, sunglasses and clothing that protects you from thesun, and always use an SPF30+ sunscreen. Do not go to tanningsalons.
If you are at very high risk of developing another skin cancer, yourdoctor may prescribe you specific vitamins.
Also Check: Small Blue Cell Tumor Prognosis
Tracking Changes To Your Skin With An App
Some people find it helpful to photograph areas of their skin such as the back or individual lesions to be able to better spot any future changes.
Over the past years, smartphone apps that can help consumers track moles and skin lesions for changes over time have become very popular and can be a very helpful tool for at-home skin checks.
This page does not replace a medical opinion and is for informational purposes only.
Please note, that some skin cancers may look different from these examples. See your doctor if you have any concerns about your skin.
It might also be a good idea to visit your doctor and have an open talk about your risk of skin cancer and seek for an advice on the early identification of skin changes.
* Prof. Bunker donates his fee for this review to the British Skin Foundation , a charity dedicated to fund research to help people with skin disease and skin cancer.
Make a difference. Share this article.
What Do The Early Stages Of Skin Cancer Look Like
Early stage skin cancer may resemble a small spot or discolored blemish significantly smaller than the size of a fingernail. It may be reddish or brown, though sometimes white with flaking skin cells surrounded by a small blotch of darker skin.
If you have concerns about the recent appearance of unusual spots on your skin, schedule an appointment right away with a board-certified dermatologist.
Skin cancer is the abnormal growth of skin cells. Skin cancer develops when mutations occur in the DNA of skin cells. The mutations can quickly cause cells to grow out of control and turn into a mass of cancer cells, which then attack healthy cells.
The most common cause of skin cancer is prolonged overexposure to the sun, sometimes over a period of years, but skin cancer can also develop on areas of your skin not exposed to sunlight.
There are three main types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma. Other, rare forms of skin cancer also exist.
Skin cancer starts in the epidermis, which is the top layer of your skin. This top layer contains three main types of cells:
Research has shown that patients with skin of color are less likely to survive melanoma. Late detection is one of the critical reasons for this higher mortality rate. On average, 2 people die of skin cancer in the United States every hour, reports the Skin Cancer Foundation.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Bone Cancer Symptoms
What Are Some Of The Lesser
Some of the less common skin cancers include the following:
Kaposi sarcoma is a rare cancer most commonly seen in people who have weakened immune systems, those who have human immunodeficiency virus /AIDS and people who are taking immunosuppressant medications who have undergone organ or bone marrow transplant.
Signs and symptoms of Kaposi sarcoma are:
- Blue, black, pink, red or purple flat or bumpy blotches or patches on your arms, legs and face. Lesions might also appear in your mouth, nose and throat.
Merkel cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare cancer that begins at the base of the epidermis, the top layer of your skin. This cancer starts in Merkel cells, which share of the features of nerve cells and hormone-making cells and are very close to the nerve ending in your skin. Merkel cell cancer is more likely to spread to other parts of the body than squamous or basal cell skin cancer.
Signs and symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma are:
- A small reddish or purplish bump or lump on sun-exposed areas of skin.
- Lumps are fast-growing and sometimes open up as ulcers or sores.
Sebaceous gland carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma is a rare, aggressive cancer that usually appears on your eyelid. This cancer tends to develop around your eyes because theres a large number of sebaceous glands in that area.
Signs and symptoms of sebaceous gland carcinoma are:
- A painless, round, firm, bump or lump on or slightly inside your upper or lower eyelid.
Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans