What Are The Melanoma Stages And What Do They Mean
Early melanomas
Stage 0 and I are localized, meaning they have not spread.
- Stage 0: Melanoma is localized in the outermost layer of skin and has not advanced deeper. This noninvasive stage is also called melanoma in situ.
- Stage I: The cancer is smaller than 1 mm in Breslow depth, and may or may not be ulcerated. It is localized but invasive, meaning that it has penetrated beneath the top layer into the next layer of skin. Invasive tumors considered stage IA are classified as early and thin if they are not ulcerated and measure less than 0.8 mm.
Find out about treatment options for early melanomas.
Intermediate or high-risk melanomas
Localized but larger tumors may have other traits such as ulceration that put them at high risk of spreading.
- Stage II: Intermediate, high-risk melanomas are tumors deeper than 1 mm that may or may not be ulcerated. Although they are not yet known to have advanced beyond the primary tumor, the risk of spreading is high, and physicians may recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy to verify whether melanoma cells have spread to the local lymph nodes. Thicker melanomas, greater than 4.0 mm, have a very high risk of spreading, and any ulceration can move the disease into a higher subcategory of stage II. Because of that risk, the doctor may recommend more aggressive treatment.
Learn more about sentinel lymph node biopsy and melanoma treatment options.
Advanced melanomas
Detect Skin Cancer: How To Perform A Skin Self
¿Cómo se ve el cáncer de la piel? ¿Cómo puedo prevenir el cáncer de piel?¿Estoy en riesgo de desarrollar melanoma?Cáncer de piel en personas de colorCómo examinar sus manchasNoe Rozas comparte su
How to check your skin for skin cancer
Follow these tips from board-certified dermatologists to increase your chances of spotting skin cancer early, when its most treatable.
If you notice any new spots on your skin, spots that are different from others, or spots that are changing, itching or bleeding, make an appointment to see a board-certified dermatologist.
Anyone can get skin cancer, regardless of skin color. It is estimated that one in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. When caught early, skin cancer is highly treatable.
You can detect skin cancer early by following dermatologists tips for checking your skin. Download the AAD’s body mole map to document your self-examination, or the How to SPOT Skin Cancer infographic and know what to look for when checking your spots.
If you notice a spot that is different from others, or that changes, itches or bleeds, you should make an appointment to see a dermatologist.
These Apps Are Available For Both Apple And Android Phones
- Miiskin. Miiskin is a paid “aka premium” app. It uses high-res photography to take photos of large parts of your body. The app allows the user to compare individual moles over time to detect changes.
- MoleMapper. MoleMapper is the result of a cancer biologist’s efforts to help his wife. Oregon Health & Science University collaborated with Apple and Sage Bionetworks to develop this app. It’s available at no cost. OHSU guides physicians to help monitor suspicious lesions without monthly in-person visits.
- MoleScope. Users must purchase a device that attaches to their smartphone. Photos taken with the attachment are sent to a dermatologist for an online opinion.
- SkinVision. A board of dermatologists developed this paid app. The app uses a deep learning algorithm to analyze your mole photo and assess whether it is high-risk within a minute.
- UMSkinCheck. This University of Michigan Medical School app is free. UMSkinCheck allows users to do a complete skin cancer exam and track changes over time. This app provides helpful advice on how to perform a skin exam. The app stores your baseline photos for comparison. It also furnishes prompts to remind you to check your skin regularly.
Early detection of suspicious moles saves lives and helps prevent disfigurement because a patient waited too long to see a dermatologist. Be sure to incorporate a monthly skin self-exam into your routine.
Also Check: Melanoma Bone Cancer Symptoms
A Birthday Check For Your Birthday Suit
Most doctors recommend performing a monthly self-check for skin cancer. Additionally, a dermatologist should check for skin cancer on a yearly basis. Many experts advise thinking of the yearly skin check like a birthday present for a persons birthday suit.
To perform a skin check at home, find a well-lit room with a full-length mirror. Examine skin for any new moles or growths as well as for any changes in current moles or growths. Make sure to look at less common places like elbows and soles of feet. People with fair skin or many freckles are at a higher risk for skin cancer and will want to take extra care to check for new freckles or moles.
How Are Moles Evaluated
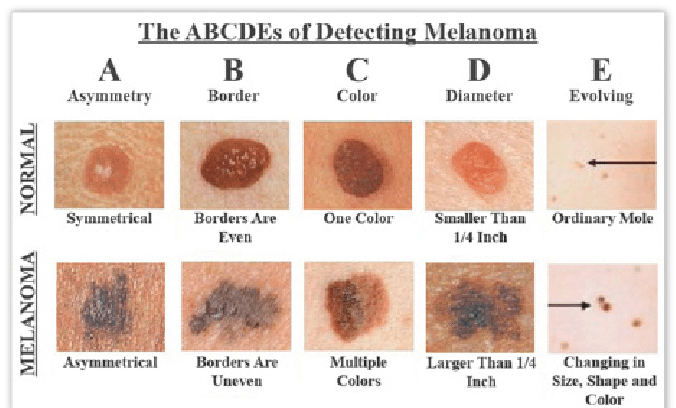
If you find a mole or spot that has any ABCDEâs of melanoma â or one thatâs tender, itching, oozing, scaly, doesnât heal or has redness or swelling beyond the mole â see a doctor. Your doctor may want to remove a tissue sample from the mole and biopsy it. If found to be cancerous, the entire mole and a rim of normal skin around it will be removed and the wound stitched closed. Additional treatment may be needed.
Also Check: Tumor Calcification
Five Apps That Can Help You Track Skin Changes
There are several ways that you could keep track of your moles and other skin changes. The old-school way was to have a paper body map that you used to mark moles, growths, or other suspicious spots. Many people choose to continue using the paper method and thats perfectly fine. However, there are also other options if youd prefer to keep your records digitally — including smartphone apps.
Several smartphone apps can help you keep track of skin changes and changes in specific moles. These apps are helpful, but they do not take the place of seeing a dermatologist when you detect moles that look suspicious. Always remember that it’s better to err on the side of getting a dermatologist to look at any skin growth that looks different or pops up and quickly grows.
Subtypes Of Melanoma Defined By Gene Mutations
Melanoma cells are usually classified by histologic types , which are based on how the cells appear under a microscope. Recent information has shown that melanoma can also be classified into molecular subtypes. These molecular subtypes are based on the specific genetic changes in the melanoma cells, called mutations. These genetic changes include:
-
BRAF mutations. The most common genetic change in melanoma is found in the BRAF gene, which is mutated in about 50% of cutaneous melanomas.
-
NRAS mutations. NRAS is mutated in the tumors of around 20% of people with melanoma.
-
NF-1 mutations. NF-1 mutations are present in the tumors of around 10% to 15% of people with melanoma.
-
KIT mutations. These mutations occur more commonly in melanomas that develop from mucus membranes, melanomas on the hands or feet, or melanomas that occur in chronically sun-damaged skin, such as lentigo maligna melanoma.
Some melanomas do not have mutations in the BRAF, NRAS, NF-1, or KIT genes. These tumors have other genetic changes that cause them to grow. Researchers are trying to target other mutations found in these tumors in clinical trials.
The classification of melanoma into different subtypes based on genetic changes can have a major effect on the types of treatment used for advanced melanoma. Targeting specific mutated genes is an important way of treating invasive melanoma, called targeted therapy. Learn more about targeted therapy in the Types of Treatment and Latest Research sections.
You May Like: Stage 2 Carcinoma
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
Melanoma is a skin cancer that can show up on the skin in many ways. It can look like a:
-
Changing mole
-
Spot that looks like a new mole, freckle, or age spot, but it looks different from the others on your skin
-
Spot that has a jagged border, more than one color, and is growing
-
Dome-shaped growth that feels firm and may look like a sore, which may bleed
-
Dark-brown or black vertical line beneath a fingernail or toenail
-
Band of darker skin around a fingernail or toenail
-
Slowly growing patch of thick skin that looks like a scar
Early melanoma
This early melanoma could be mistaken for a mole, so its important to look carefully at the spots on your skin.
Also Check: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
How To Detect Melanoma
You must know how to detect melanoma so that you can identify any concerns early in case you need to visit a dermatologist for a professional mole check. In knowing how to do self mole checks and self-skin checks you can give yourself every opportunity to keep your moles and skin safe both during and after sun exposure.
These are the main melanoma checks you should do to stay on top of your skin safety:
Also Check: Skin Cancer 1st Stage
Lymph Node Dissection Or Completion Lymphadenectomy
An operation to remove the remaining lymph nodes in the group is known as a completion lymph node dissection or completion lymphadenectomy. Again, you should discuss the pros and cons of the procedure with your surgeon.
Other tests you may have include:
Cancer Research UK has more information about test to diagnose melanoma and tests to stage melanoma.
What Tests Are Used To Stage Melanoma
There are several tests your doctor can use to stage your melanoma. Your doctor may use these tests:
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy: Patients with melanomas deeper than 0.8 mm, those who have ulceration under the microscope in tumors of any size or other less common concerning features under the microscope, may need a biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes to determine if the melanoma has spread. Patients diagnosed via a sentinel lymph node biopsy have higher survival rates than those diagnosed with melanoma in lymph nodes via physical exam.
- Computed Tomography scan: A CT scan can show if melanoma is in your internal organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging scan: An MRI scan is used to check for melanoma tumors in the brain or spinal cord.
- Positron Emission Tomography scan: A PET scan can check for melanoma in lymph nodes and other parts of your body distant from the original melanoma skin spot.
- Blood work: Blood tests may be used to measure lactate dehydrogenase before treatment. Other tests include blood chemistry levels and blood cell counts.
Recommended Reading: What Is Braf Melanoma
How Is Melanoma Treated
Your melanoma treatment will depend on the stage of the melanoma and your general health.
Surgery is usually the main treatment for melanoma. The procedure involves cutting out the cancer and some of the normal skin surrounding it. The amount of healthy skin removed will depend on the size and location of the skin cancer. Typically, surgical excision of melanoma can be performed under local anesthesia in the dermatologist’s office. More advanced cases may require other types of treatment in addition to or instead of surgery.
Treatments for melanoma:
- Melanoma Surgery: In the early stages, surgery has a high probability of being able to cure your melanoma. Usually performed in an office, a dermatologist numbs the skin with a local anesthetic and removes the melanoma and margins .
- Lymphadenectomy: In cases where melanoma has spread, removal of the lymph nodes near the primary diagnosis site may be required. This can prevent the spread to other areas of your body.
- Metastasectomy: Metastasectomy is used to remove small melanoma bits from organs.
- Targeted cancer therapy: In this treatment option, drugs are used to attack specific cancer cells. This targeted approach goes after cancer cells, leaving healthy cells untouched.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy includes treatments with high-energy rays to attack cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Immunotherapy: immunotherapy stimulates your own immune system to help fight the cancer.
What Are The Signs Of Melanoma
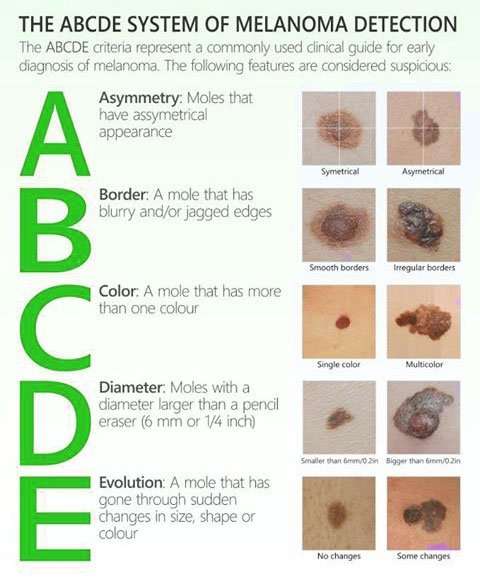
Knowing how to spot melanoma is important because early melanomas are highly treatable. Melanoma can appear as moles, scaly patches, open sores or raised bumps.
Use the American Academy of Dermatology’s “ABCDE” memory device to learn the warning signs that a spot on your skin may be melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half does not match the other half.
- Border: The edges are not smooth.
- Color: The color is mottled and uneven, with shades of brown, black, gray, red or white.
- Diameter: The spot is greater than the tip of a pencil eraser .
- Evolving: The spot is new or changing in size, shape or color.
Some melanomas don’t fit the ABCDE rule, so tell your doctor about any sores that won’t go away, unusual bumps or rashes or changes in your skin or in any existing moles.
Another tool to recognize melanoma is the ugly duckling sign. If one of your moles looks different from the others, its the ugly duckling and should be seen by a dermatologist.
You May Like: Precursor To Skin Cancer
How To Check For Skin Cancer
This article was medically reviewed by . Dr. Litza is a board certified Family Medicine Physician in Wisconsin. She is a practicing Physician and taught as a Clinical Professor for 13 years, after receiving her MD from the University of Wisconsin-Madison School of Medicine and Public Health in 1998.There are 15 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 788,620 times.
Early detection of skin cancer is important and can be lifesaving, especially for certain types of skin cancer such as melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma. It is estimated that 76,380 new cases of melanoma will be diagnosed in 2016 and over 13,000 will die from the skin cancer.XTrustworthy SourceAmerican Cancer SocietyNonprofit devoted to promoting cancer research, education, and supportGo to source Given that timing is so crucial to diagnosing and treating skin cancer, you should follow a few simple steps to learn how to detect skin cancer on your skin.
How To Check Yourself For Skin Cancer
The SCF recommends that people conduct skin self-exams at least once a month or more if you have risk factors such as an inherited gene that predisposes toward skin cancer, or if you have spent a lot of time in the sun.
This check, which should be done in a well-lit room with a floor-length mirror and a hand mirror, should not take long once you get the hang of it.
Youll need to examine every inch of your skin, from your scalp to the bottoms of your feet and nails. A self-exam body map can help keep track of whats normal for you and whats not.
The more often you do these self-exams, the more familiar you will be with every freckle, mole, sore, lump, and blemish on your body and the better you will be at recognizing potential trouble in the form of new markings or changes in the size, shape, or color of existing spots.
Overall, heres the bottom line on what you should be looking for, according to the American Academy of Dermatology : a mole or skin lesion that changes in size, shape, or color, as well as spots that itch or bleed. Also watch for a new growth or a sore that doesnt heal.
Knowing your body and all of its unique spots is the first step in knowing what to look for when it comes to early signs and symptoms of skin cancer.
You May Like: How Do You Cure Melanoma
Also Check: What Does Cancer Look Like Outside The Body
Who Gets Skin Cancer And Why
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesnât explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation treatment, and even heredity may play a role. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive sun exposure or blistering sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
What To Do If You Think You Have Melanoma
The first thing you should do is contact a doctor or visit a dermatologist to get your moles and skin checked. When it comes to skin cancer, you want peace of mind so swift action can either help determine if a mole is benign or identify early-stage melanoma and begin treatment to help you fight the skin disease.
Mole checks donât take too long and there are other examination and identification techniques such as mole mapping and biopsy, which is something a dermatologist can do in line with an ABCDE check to ascertain whether or not a mole is benign.
Additionally, mole mapping can be carried out annually to keep moles in check and identify any changes to your moles over time. Mole mapping takes digital pictures of your mole-to-body profile and matches the pictures each time you get a mole map to identify any changes to your moles. This is a quicker way to identify potentially troublesome moles so that a dermatologist can have a further look into the specific mole and qualify if itâs benign or not.
Recommended Reading: Show Me What Skin Cancer Looks Like
Be Attuned To Any Visible Change
A change in a moles shape, size, or color indicates that melanoma may be brewing, notes Dr. Harvey. An uptick in mole elevation raises red flags, too, since that suggests vertical growth beneath the surface of the skin. In fact, a new bump may point to nodular melanoma, the second most common type of melanoma, accounting for 10% to 30% of all cases. Remember, skin cancer can resemble something as nondescript as a pimple or red patch, so its important to check your skin often and take note of all changes, says Dr. McNeill.
Also Check: How Often Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Spread