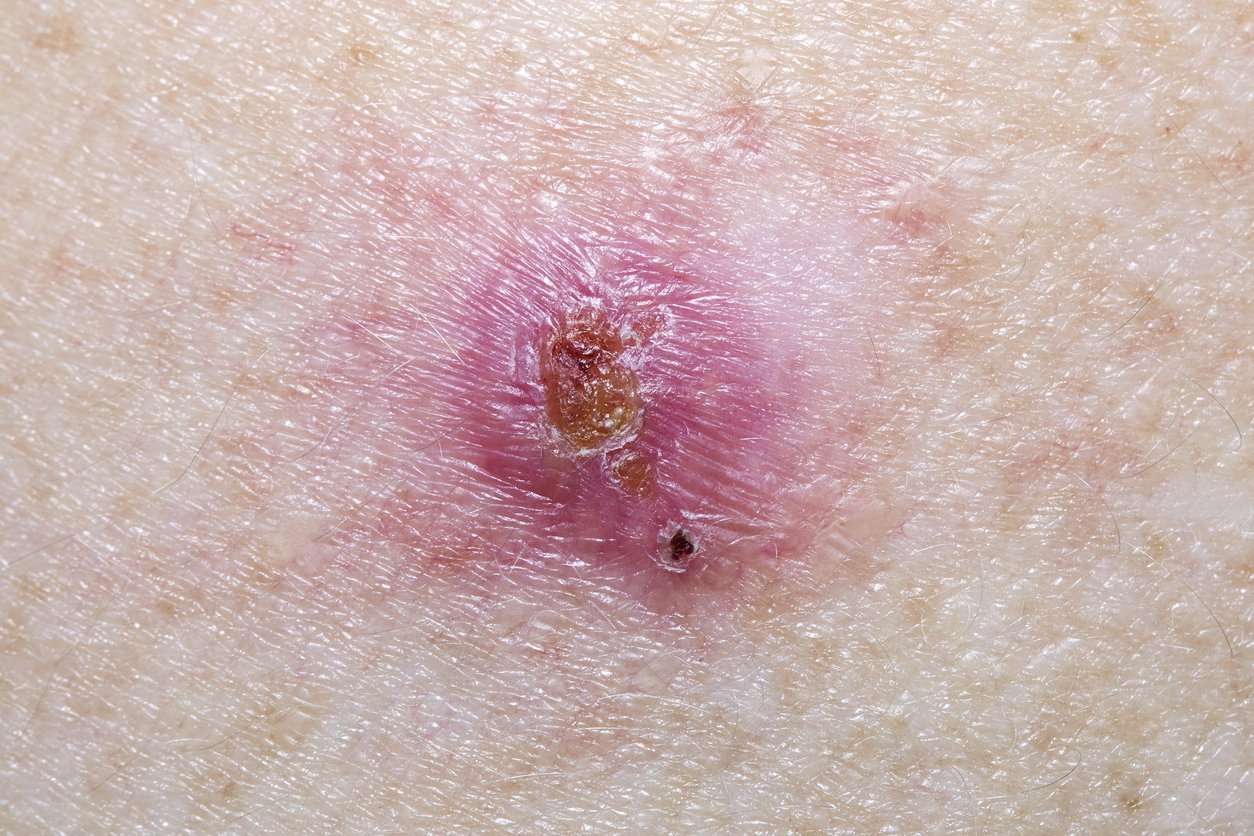
What Does A Basal Cell Carcinoma Look Like
BCCs can vary greatly in their appearance, but people often first become aware of them as a scab that bleeds and does not heal completely or a new lump on the skin. Some BCCs are superficial and look like a scaly red flat mark on the skin. Others form a lump and have a pearl-like rim surrounding a central crater and there may be small red blood vessels present across the surface. If left untreated, BCCs can eventually cause an ulcer hence the name rodent ulcer. Most BCCs are painless, although sometimes they can be itchy or bleed if caught.
What Steps Can I Take For Basal Cell Carcinoma Prevention
Basal cell carcinoma prevention always starts with sun protection. By the time you get your first basal, youve probably already had a lot of sun damage. Once youve been diagnosed, play it smart so you dont make the damage worse.
Start making adjustments to your sun habits. Dont go to the lake and sit in the sun all day. Dont go to the golf course without a hat. Its time to wear the right gear: hats, long sleeves, and sunglasses.
Apply sunscreen to the areas still exposed to the sun.
Related: How to Choose the Best Sunscreen for Your Skin
If youre a parent, start instilling good sun protection practices at an early age to prevent skin cancer from the start. Just like parents should be teaching their children to brush their teeth morning and night to prevent cavities, parents should also be pointing out ways to protect our skin from sun damage to prevent skin cancer. Teach kids to wear their hats and apply their sunscreen for any extended time outdoors.
Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome
In addition to basal cell carcinoma, this autosomal dominant disorder can result in the early formation of multiple odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies. Various tumors such as medulloblastomas, meningioma, fetal rhabdomyoma, and ameloblastoma also can occur.
Odontogenic keratocysts, palmoplantar pitting, intracranial calcification, and rib anomalies may be seen. Mutations in the hedgehog signaling pathway, particularly the patched gene, are causative.
Go to Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome to see more complete information on this topic.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Prognosis
What Causes Skin Cancer
The main cause of skin cancer is overexposure to sunlight, especially when it results in sunburn and blistering. Ultraviolet rays from the sun can damage the skin and, over time, lead to skin cancer. The UV light damages DNA in the skin and causes it to grow abnormally. Exposure to certain chemicals such as tar and coal can cause skin cancer for those with jobs that require them to frequently be in contact with these chemicals. Those with a weakened immune system also have an increased risk for skin cancer.
You May Like: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
What Is The Best Medication For Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment for basal cell carcinoma will be highly individualized. Surgery is the mainstay, and most cases wont require drug treatment. Only a limited number of medications are prescribed for basal cell carcinoma, but there is no best medication.
| Best medications for basal cell carcinoma |
|---|
| Drug Name |
* Prescription savings vary by prescription and by pharmacy, and may reach up to 80% off cash price.
Pharmacy names, logos, brands, and other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
This article is not medical advice. It is intended for general informational purposes and is not meant to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. If you think you may have a medical emergency, immediately call your physician or dial 911.
Read Also: Last Stage Of Cancer Symptoms
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
JONATHON M. FIRNHABER, MD, East Carolina University, Brody School of Medicine, Greenville, North Carolina
Am Fam Physician. 2012 Jul 15 86:161-168.
Nonmelanoma skin cancer, which includes basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, is the most common cancer in the United States. Approximately 80 percent of nonmelanoma skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma and 20 percent are squamous cell carcinoma. Although the National Cancer Institute does not formally track the incidence and prevalence of nonmelanoma skin cancers, multiple longitudinal studies indicate that the incidence has risen sharply over the past two decades.1
Ask The Expert: Why Am I Having Surgery To Remove A Small Basal Cell Carcinoma
Although the nonmelanoma skin cancer basal cell carcinoma is rarely life-threatening, it can be troublesome, especially because 80 percent of BCCs develop on highly visible areas of the head and neck. These BCCs can have a substantial impact on a persons appearance and can even cause significant disfigurement if not treated appropriately in a timely manner.
The fact is, BCCs can appear much smaller than they are. On critical areas of the face such as the eyes, nose, ears and lips, they are more likely to grow irregularly and extensively under the skins surface, and the surgery will have a greater impact on appearance than might have been guessed. Even a small BCC on the face can be deceptively large and deep the extent of the cancer cannot be seen with the naked eye.
If such a BCC is treated nonsurgically , the chance of the cancer recurring is high. Unfortunately, treating a BCC that has returned is usually much more difficult than treating it precisely and completely when initially diagnosed.
BCCs on the trunk, arms and legs that cause concern are typically larger in size, but even a small BCC in these areas can have an irregular growth pattern under the skin if the initial biopsy shows the tumor is aggressive. In addition, a small BCC in an area previously treated with radiation may be much more aggressive than it appears on the surface. Again, treating such a tumor nonsurgically is likely to leave cancer cells behind.
About the Expert:
You May Like: How Long Does It Take Melanoma To Metastasize
Prognosis Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma is nearly always successful, and the cancer is rarely fatal. However, almost 25% of people with a history of basal cell carcinoma develop a new basal cell cancer within 5 years of the first one. Thus, anyone with one basal cell carcinoma should have a yearly skin examination.
Recommended Reading: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rates
What Are The Risks Of Mohs Surgery
Mohs surgery is performed with local anesthesia. This removes the common surgical risks that come with using general anesthesia.
Risks that are associated with Mohs surgery include temporary bleeding, pain, and tenderness around the area being removed. More serious problems can occur, but they are rare. These include keloid scarring and permanent or temporary numbness or weakness in and around the affected area.
Mohs surgery requires extensive training and skill. The surgeon needs to accurately map out the tumor and analyze each layer of tissue removed during surgery. Working with a highly experienced dermatologist is important. They should be fellowship-trained and certified by the American College of Mohs Surgery. Trained physicians are not only experts in reading slides, but also in closing the wound as beautifully as possible. When choosing a surgeon, ask them about their level of training, if they are fellowship-trained, and the number of procedures like yours that they have personally performed.
Read Also: Melanoma On Nose Prognosis
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Cancer Prognosis
How Dermatologists Diagnose Basal Cell Carcinoma
When you see a board-certified dermatologist, your dermatologist will:
-
Examine your skin carefully
-
Ask questions about your health, medications, and symptoms
If your dermatologist finds a spot on your skin that could be any type of skin cancer, your dermatologist will first numb the area and then remove all of it. This can be done during an office visit and is called a skin biopsy. This is a simple procedure, which a dermatologist can quickly, safely, and easily perform.
Having a skin biopsy is the only way to know for sure whether you have any type of skin cancer. After your dermatologist removes the spot, a doctor, such as your dermatologist or a dermatopathologist, will examine it under a high-powered microscope. The doctor is looking for cancer cells.
If the doctor sees cancerous basal cells, the diagnosis is BCC.
After the doctor examines the removed skin under a microscope, the doctor writes a report. Called a biopsy report or a pathology report, this document explains in medical terms what was seen under the microscope.
If the diagnosis is any type of skin cancer, the information in this report will tell your dermatologist the key facts needed to treat the cancer, including:
-
The type of BCC you have
-
How deeply the cancer has grown
Your dermatologist will carefully consider your health and the findings in the report before choosing how to treat the cancer.
Treatments For Basal Cell Carcinoma
The following are treatment options for basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Your healthcare team will suggest treatments based on the . They will work with you to develop a treatment plan.
BCC is most often treated with local therapy. This means that only the cancer on the skin and the area around it are treated.
But if BCC has spread to other parts of the body, systemic therapy may be used. Systemic therapy travels through the bloodstream to reach and destroy cancer cells all over the body.
Don’t Miss: What Does Cancer Tissue Look Like
When Should I See A Healthcare Provider About Basal Cell Carcinoma
It is important to contact a healthcare provider any time you have a skin problem that does not resolve. This means developing any new or larger mole, lump or sore, or new symptoms such as pain or itchiness. If you have had BCC or another type of skin cancer, you will probably be given a recommended schedule of needed appointments. You should follow up on these appointments as directed.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 07/05/2019.
References
Targeted Therapy Or Immunotherapy For Advanced Basal Cell Cancers
In rare cases where basal cell cancer spreads to other parts of the body or cant be cured with surgery or radiation therapy, a targeted drug such as vismodegib or sonidegib can often shrink or slow its growth.
If these drugs are no longer working , the immunotherapy drug cemiplimab can sometimes be helpful.
You May Like: Can You Have Cancer Without A Tumor
Where Does Bcc Develop
As the above pictures show, this skin cancer tends to develop on skin that has had lots of sun exposure, such as the face or ears. Its also common on the bald scalp and hands. Other common areas for BCC include, the shoulders, back, arms, and legs.
While rare, BCC can also form on parts of the body that get little or no sun exposure, such as the genitals.
Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas may appear and grow so slowly that you may not detect them initially. It is important to see your dermatologist when you notice a change in your skin that might indicate basal cell carcinoma, such as:
- A smooth, pale growth that may have a dent or dimple in the middle
- A small, pearly or waxy bump
- A red patch or irritated area
- A sore that scabs, heals, and regrows
- A bleeding or oozing sore
You May Like: Well-differentiated
Assessment Of Risk Factors For Recurrence
Outcomes of surgical excision can be studied in terms of completeness of excision or of tumor recurrence rates. Factors affecting these outcomes may be categorized as:
Tumor-related factors, which include location, size, histologic types, borders, and primary or previously excised lesions.
Patient-related factors, which include patients immunity , coexisting medical conditions, and site of previous radiotherapy.
Operator-related factors, which can be analyzed in terms of personnel experience, surgical techniques , and surgical margin width .
Although there are a considerable number of studies in the literature addressing these issues, good-quality research in terms of randomized controlled trials is scarce.
Answer: Risk Of Not Treating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma is a locally destructive type of skin cancer that is notorious for recurrence when not adequately treated. It can become quite disfiguring if left untreated, especially when located in cosmetically sensitive areas such as the nose. Typically this type of skin biopsy is performed for diagnosis and is not adequate treatment for a skin cancer. Biopsies sample a portion of the lesion, leaving some behind. This type of sampling biopsy is not intended to remove the entire lesion. It is not advisable to leave a known skin cancer untreated as it will likely grow and become more of a problem to remove in the future. Mohs micrographic surgery allows for 100% margin control and is tissue-sparing, which means it offers the highest cure rate while preserving as much normal tissue as possible.
Don’t Miss: Well-differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
Treating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Several types of treatment can be used to remove or destroy basal cell skin cancers. The options depend on factors such as the tumor size and location, and a persons age, general health, and preferences. These cancers very rarely spread to other parts of the body, although they can grow into nearby tissues if not treated.
All of the treatments listed here can be effective when used in appropriate situations. The chance of the cancer coming back ranges from less than 5% after Mohs surgery to up to 15% or higher after some of the others, but this depends on the size of the tumor. Small tumors are less likely to recur than larger ones. Even if a tumor does recur, it can often still be treated effectively.
Cryosurgery: For Patients Who Cant Tolerate Surgery
This procedure may be used to treat small basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma, or actinic keratoses .
The physician applies liquid nitrogen to the growth with a swab or as spray, repeating several times if necessary to freeze and kill cells.
The lesion eventually blisters, crusts over, and falls off, notes the ACS.
Cryotherapy may be the right choice for patients who cant have surgery because of bleeding disorders or an intolerance to local anesthetic. But it has a lower overall cure rate than surgical methods.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Perineural Invasion
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Whether you are thinking about treatment, getting treatment, or not being treated at all, you can still get supportive care to help with pain or other symptoms. Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life.
Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help.
The American Cancer Society also has programs and services including rides to treatment, lodging, and more to help you get through treatment. Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists.
How Is Basal Cell Skin Cancer Treated When It Grows Deep Or Spreads
While this skin cancer tends to grow slowly, early treatment is recommended. Without treatment, BCC can grow deep, destroying what lies in its way. This can be disfiguring. The medical term for this is advanced basal cell carcinoma.
Its also possible for BCC to spread to other parts of your body, but this is rare. When the cancer spreads, it typically travels first to the lymph nodes closest to the tumor. From there, it tends to spread through the blood to bones, the lungs, and other parts of the skin. When this skin cancer spreads, it is called metastatic basal cell carcinoma.
For cancer that has grown deep or spread to the closest lymph nodes, treatment may involve:
-
Surgery to remove the tumor
-
Follow-up treatment with radiation to kill any remaining cancer cells
For some patients, medication that works throughout the body may be an option. Medication may also be used to treat cancer that:
-
Returns after surgery or radiation treatments
-
Has spread to another part of the body
Two such medications have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration . Both come in pill form and are taken every day. A patient only stops taking the medication if the cancer starts to grow, or the side effects become too severe.
The two medications are:
-
Sonidegib
-
Vismodegib
In clinical trials, these medications have been shown to stop or slow down the spread of the cancer and shrink the cancerous tumors in some patients.
Cemplimab may be an option if sonidegib or vismodegib:
Don’t Miss: Stage 2 Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Do I Need Medical Treatment
While basal cell carcinoma is a relatively mild form of skin cancer that is unlikely to metastasize or cause secondary health concerns, medical supervision is advised for any type of cancer. A qualified professional can help you determine the severity of your condition and suggest an appropriate course of treatment.
Health & Wellnesshow To Avoid Squamous Cell Carcinoma This Summer
This type of cancer is much more common in people who have light skin. One of the things thats tricky about basal cell carcinoma is that it can show up as skin-colored or pink, said Dr. Ivy Lee, a board-certified dermatologist with Pasadena Premier Dermatology in California and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology. A lot of patients mistake them as warts or witchs moles.
According to the ACS, you should watch for:
- Scar-like flat, firm areas
Recommended Reading: Well Differentiated Carcinoma