What Does Squamous Cell Cancer Look Like
Squamous cell carcinomas may appear as flat reddish or brownish patches in the skin, often with a rough, scaly, or crusted surface. They tend to grow slowly and usually occur on sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and backs of the hands. Normal moles also develop from these skin cells.
What is the best treatment for squamous cell carcinoma? Squamous Cell Skin Cancer Treatment Mohs Surgery. Mohs surgery has the highest cure rate of all therapies for squamous cell carcinomas. Curettage and Electrodessication. This very common treatment for squamous cell carcinoma is most effective for low-risk tumors. Cryosurgery. Laser Surgery.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage basal cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is given a stage. For basal cell carcinoma staging, the factors are grouped and labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of basal cell carcinoma are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high-risk features.
Stage 3 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma usually begins as a painless bump or nodule that grows slowly. Later, it becomes an open ulcer with a hard edge. Nearly 90% of basal cell carcinomas occur on the face, but they can appear on any part of the body that is sometimes exposed to the sunthe face, ears, neck, back, chest, arms, and legs.
Although basal cell carcinoma almost never spreads to other organs and is rarely fatal, it can invade surrounding tissue and be disfiguring if not treated.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
More Important Skin Cancer Prevention Tips
Pay particular attention to sun protection with children For outdoor occupations, advocate sun protection and / or wear suitable sun protection clothing From the age of 35, skin cancer screening is recommended every two years Participation in cancer follow-up care: The timely detection of a recurrence of the old tumor ensures the chance of a permanent cure.
Prevention Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Because basal cell carcinoma is often caused by sun exposure, people can help prevent this cancer by doing the following:
-
Avoiding the sun: For example, seeking shade, minimizing outdoor activities between 10 AM and 4 PM , and avoiding sunbathing and the use of tanning beds
-
Wearing protective clothing: For example, long-sleeved shirts, pants, and broad-brimmed hats
-
Using sunscreen: At least sun protection factor 30 with UVA and UVB protection used as directed and reapplied every 2 hours and after swimming or sweating but not used to prolong sun exposure
In addition, any skin change that lasts for more than a few weeks should be evaluated by a doctor.
Don’t Miss: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
What Is A Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that occurs when there is damage to the DNA of basal cells in the top layer, or epidermis, of the skin. They are called basal cells because they are the deepest cells in the epidermis. In normal skin, the basal cells are less than one one-hundredth of an inch deep, but once a cancer has developed, it will spread deeper.
Warning: Graphic Image Below
If not treated it may eventually cause dramatic disfigurement yet will very rarely metastasize in even the most neglected cases.
Many years of basal cell carcinoma neglect. Apparently this patient didnt know that cancer was eating away at his face.
Squamous cell carcinoma which will likely metastasize if left untreated begins insidiously, appearing first as a faded pink and very flat patchy area on the skin.
A person can go for years without knowing that this usually slow growing skin cancer is progressing.
Many people even in industrialized nations do not check their skin monthly and never get clinical exams and may even be fully aware of a new lesion yet get so used to it that it never dawns on them that its malignant.
There may be the It cant happen to me mindset, along with those who are afraid of what the doctor might find, and those who avoid doctors because they dont have health insurance or because they are cognitively impaired.
Often, people will notice something growing on their face or scalp but chalk it up to older age or benign damage from the sun.
Its possible to have melanoma for several years without knowing it, because some kinds of melanomas grow rather slowly and spread out laterally before they begin burrowing vertically into deeper layers of skin tissue.
Melanoma on the bottom of a foot.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If You Have Skin Cancer
What To Do If You Receive A Skin Cancer Diagnosis
Once a skin biopsy confirms skin cancer, your doctor will recommend a treatment based on the stage of the cancer.
To improve your outlook, its important that you complete your treatment and schedule follow-up appointments as needed. Your doctor may want to see you every few months to make sure the cancer hasnt returned.
Also schedule annual skin exams with a dermatologist. Get into the habit of checking your own skin for abnormal growths, too. This includes your back, scalp, soles of feet, and ears.
You can also ask your doctor about local support groups for those with skin cancer, or search for support programs in your area.
What You Should Know About Basal Cell Carcinoma
Although sunshine and outdoor activity aregenerally good for your health and well-being, the fact is that too much exposureto sunlight can be harmful. Skin cancer is one of the most common conditions inAmerica, with around 20 percent of the adult population suffering from a formof skin cancer at some point during their lives.
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for manyof these cases, with over four million cases diagnosed every year. Fortunately,while basal cell carcinoma is common, its rarely fatal. Despite that fact,its imperative to understand as much about this disease as possible, as earlytreatment can ensure it doesnt overtly affect your body.
So, with that in mind, lets take a closerlook at BCC what it is, how it affects the body and what to expectafter a diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know You Have Skin Cancer
Diagnosing Squamous Cell Carcinoma
The main way to diagnose squamous cell carcinoma is with a biopsy. This involves having a small piece of tissue removed from the suspicious area and examined in a laboratory.
In the laboratory, a pathologist will examine the tissue under a microscope to determine if it is a skin cancer. He or she will also stage the cancer by the number of abnormal cells, their thickness, and the depth of penetration into the skin. The higher the stage of the tumor, the greater the chance it could spread to other parts of the body.
Squamous cell carcinoma on sun-exposed areas of skin usually does not spread. However, squamous cell carcinoma of the lip, vulva, and penis are more likely to spread. Contact your doctor about any sore in these areas that does not go away after several weeks.
Be Smart About Sun Protection
If you already have skin cancer, your risk of getting other skin cancers later is higher. But you can help keep that from happening by protecting your skin from harmful UV rays. Staying out of the sun entirely is the best way to do it, but thatâs not always an option. Instead, depend on these defenses:
Stay in during peak sun hours. The UV index is highest from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. every day, even when itâs cloudy. When you can, choose times outside this window to enjoy the great outdoors.
Wear sun-protective clothing. Cover up when you go out with wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, long sleeves, and pants. You can also buy clothing with UV protection in the fabric.
Slather on sunscreen. âChoose a SPF 30+ broadband sunscreen that contains zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, and reapply every 2-3 hours,â Torbeck says.
Ditch tanning beds forever. Theyâre never safe, and their UV rays are stronger than those from the sun.
Also Check: How Bad Is Basal Cell Carcinoma
Which Is Worse Basal Cell Or Squamous Cell Cancer
Akashbasal cellsquamous cell
Can SCC turn into melanoma? Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer . Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
What Causes Basal Cell Carcinoma
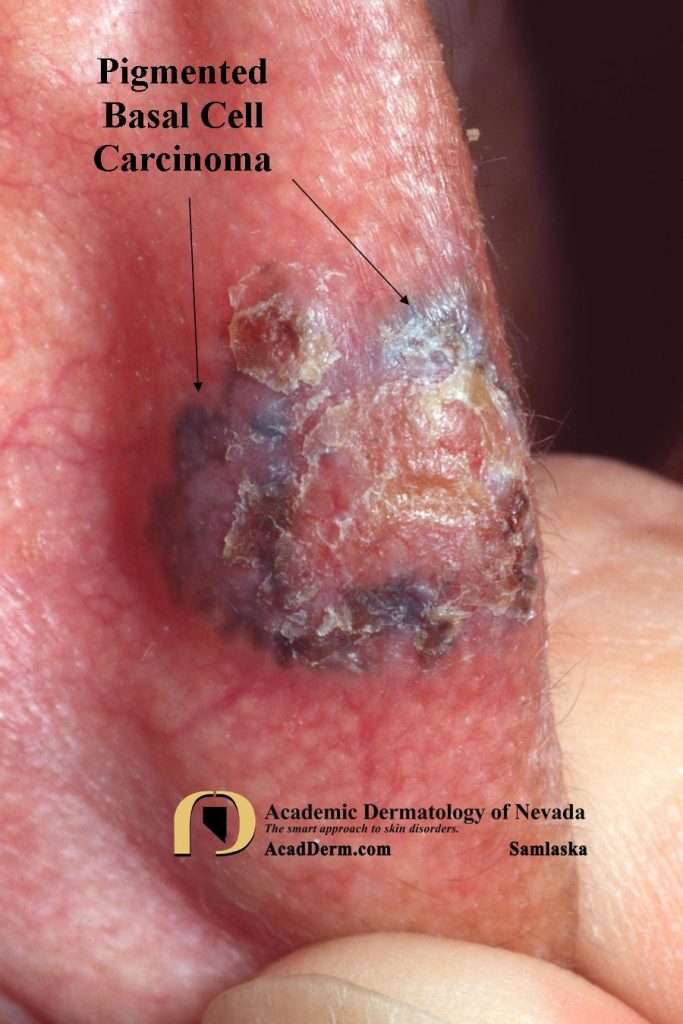
BCC develops from exposure to damaging ultraviolet sunlight and tanning beds. This cancer starts in the basal cell layer of the skin and grows very slowly. It develops mainly on the areas exposed to the sun, such as the:
- Head and face
Risk factors for basal cell carcinoma include:
- Exposure to UV radiation
- Older age
- Long-term skin inflammation or injury
- Treatment for psoriasis using psoralens and ultraviolet light treatments
- History of skin cancer
- Basal cell nevus syndrome, a rare inherited disorder
You May Like: How To Detect Skin Cancer On Face
What Happens When Skin Cancer Goes Untreated
If you notice an abnormality on your skin you may be tempted to ignore it. However, if it is skin cancer you could be putting your health at risk by waiting to get a skin and mole check. There are three main types of skin cancer in Australia with melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, and they each have their own set of unique characteristics. The most important thing to remember is that if you delay treatment of skin cancer it could have life threatening consequences:
Questions To Ask The Doctor
- Do you know the stage of the cancer?
- If not, how and when will you find out the stage of the cancer?
- Would you explain to me what the stage means in my case?
- What will happen next?
There are many ways to treat skin cancer. The main types of treatment are:
- Surgery
- Immunotherapy
- Chemotherapy
Most basal cell and squamous cell cancers can be cured with surgery or other types of treatments that affect only the spot on the skin.
The treatment plan thats best for you will depend on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Your age and overall health
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Recommended Reading: Can Melanoma Skin Cancer Kill You
Ask Your Doctor For A Survivorship Care Plan
Talk with your doctor about developing a survivorship care plan for you. This plan might include:
- A suggested schedule for follow-up exams and tests
- A schedule for other tests you might need in the future, such as early detection tests for other types of cancer, or tests to look for long-term health effects from your cancer or its treatment
- A list of possible late- or long-term side effects from your treatment, including what to watch for and when you should contact your doctor
- Diet and physical activity suggestions
Leaving Basal Cell Carcinoma Untreated
Basal cell carcinoma is a slow growing cancer, but this doesnt mean it can be ignored. This is the least dangerous form of skin cancer and rarely spreads to other internal parts of the body. While death is a rare consequence there is the potential for disfigurement. Over time basal cell carcinoma can expand and cause ulcers and damage the skin and tissues.
Any damage could be permanent and have an impact on the way you look. Depending on how long the basal cell carcinoma has been present, radiotherapy may be required. This is the most common form of skin cancer and is often found on the face. You may notice a small lump which is shiny or pearl like and this is a sign you should get checked. This type of cancer generally does not cause any pain.
Also Check: What Does In Situ Melanoma Mean
Leaving Squamous Cell Carcinoma Untreated
The third type of skin cancer we have to be cautious of in Australia is squamous cell carcinoma. This is potentially life threatening and is most dangerous when found on the face, lips, ears or neck. As it grows, there is the chance it may spread to the lymph nodes and internal organs, and while it isnt as fast growing as melanoma, it still requires treatment.
You may notice squamous cell carcinoma in the top layer of your skin and it will likely be red and scaly. Surgery is often used for removal, but if it has progressed significantly some reconstruction to the face may be needed. This is the second most common form of skin cancer, and can be quite painful to touch.
All skin cancer has the potential to be fatal, and regular checks and any necessary treatment is recommended. Melanoma is by far the most serious form of skin cancer, and if suspected you should seek an urgent skin check. Please contact My Skin Centre to book your appointment in the Perth region.
What Are The Survival Rates For Melanoma
The 5-year overall survival rate for melanoma is 92.7 percent, based on the most recent data from the National Cancer Institute from 2010-2016. That means that 5 years after being diagnosed with melanoma of any type, about 92 out of 100 people are still alive. This estimate includes people of both genders, all races, and all stages at diagnosis.4
Cancer stage. One important factor in estimating survival is how far the cancer has spread by the time it is diagnosed. Local melanoma is melanoma that has not spread beyond the original tumor. About 83 percent of melanomas are caught at this early stage. The 5-year survival rate for local melanoma is 99 percent.5
If cancer cells have spread to a nearby lymph node, it is called regional metastasis. In 9 percent of cases, the melanoma has spread to regional lymph nodes at diagnosis. The 5-year survival for regional melanoma is 66.2 percent.5
Distant spread is when cancer cells have traveled to distant parts of the body. About 4 percent of melanoma cases have metastasized to distant locations at the time of diagnosis. The 5-year survival for distant metastatic melanoma is 27.3 percent.5
Gender. Skin cancer survival rates in women are higher than survival rates in men at all ages and stages of cancer. Five years after diagnosis, 92.5 percent of women were alive compared to 87.3 percent of men.4,6
Read Also: How To Remove Skin Cancer Yourself
Moffitt Cancer Centers Approach To Squamous Cell Carcinoma
At Moffitt Cancer Center, our multispecialty team of cancer experts takes a highly individualized approach to squamous cell carcinoma treatment. We offer the latest diagnostic and treatment options, and we work closely with each patient to offer customized guidance and help ensure the best possible outcome. For instance, there are many steps a patient can take to improve his or her own squamous cell carcinoma prognosis regardless of the general survival rate such as:
- Performing self-examinations from head to toe, including parts of the body that are not regularly exposed to UV rays, at least monthly, and promptly reporting any suspicious or unusual changes in skin texture or appearance to a physician
- Seeing a physician for a professional skin cancer examination yearly
- Avoiding exposure to the suns ultraviolet rays while outdoors, preventive measures include seeking shade, wearing sunglasses and a brimmed hat, covering up with clothing and using a broad spectrum sunscreen with both UVA and UVB protection
- Never using indoor tanning beds
If youd like to learn more about the squamous cell carcinoma survival rate, the experts at Moffitt can put this information into the proper context for you and help you take appropriate steps to achieve the best possible outcome. Call or complete a new patient registration form online. We see patients with and without referrals.
Tests That May Be Done
The doctor will ask you questions about when the spot on your skin first showed up and if it has changed in size or the way it looks or feels. The rest of your skin will be checked. During the exam your doctor will check the size, shape, color and texture of any skin changes. If signs are pointing to skin cancer, more tests will be done.
Skin biopsy
In a biopsy, the doctor takes out a small piece of tissue to check it for cancer cells. A biopsy is the only way to tell for sure if you have skin cancer and what kind it is.
There are many types of skin biopsies. Ask your doctor what kind you will need. Each type has pros and cons. The choice of which type to use depends on your own case.
In rare cases basal and squamous cell skin cancer can spread to the nearby lymph nodes Ask your doctor if your lymph nodes will be tested.
Basal and squamous cell cancers don’t often spread to other parts of the body. But if your doctor thinks your skin cancer might spread, you might need imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans.
Don’t Miss: What Is Liver Cell Carcinoma