When Is Itching A Sign Of Skin Cancer
Itchy skin could be a sign of skin cancer if it is accompanied by:
- A new skin growth or lesion
- A change in a mole, such as a spread of pigment beyond the border
- A sore that continually crusts over but doesnt heal
- A rough or scaly skin patch
- A pink, pearly bump that bleeds easily
Because it can be difficult to distinguish between a cancerous and noncancerous skin condition, its important to promptly discuss any new, changing or unusual rashes or moles with a physician.
Can Skin Cancer Spread To Other Parts Of The Body
Yes, it can. However, it depends on the type of skin cancer and its stage.
Non-melanoma skin cancers are less likely to spread. Basal cell carcinoma usually does not migrate to other parts of the body, but there is a small chance that squamous cell cancer will do so.
Melanoma skin cancer spreads more readily than non-melanoma, making it more dangerous. It can spread to the lymph nodes and, from there, to other organs in the body.
Who Gets Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma has an estimated incidence of 0.23 per 100,000 people in Caucasian populations, which is much less common than melanoma.
- Increasing numbers of Merkel cell carcinomas have been reported by some centres in recent years.
- Merkel cell carcinoma mainly affects older people, with most cases occurring after the age of 50.
- It is slightly more common in men.
- It occurs on parts of the body commonly exposed to sunlight, most often the head and neck.
- It is also more common and more serious in those that are immune suppressed, such as patients with solidorgan transplants, human immunodeficiency virus infection, haematologicalmalignancy or on drugs such as azathioprine.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma Bone Cancer Symptoms
How Common Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the commonest type of cancer in the United States. The skin is the largest organ in the body with a surface area of around 2 sq ft in an average adult. It acts as a protective barrier against several types of harmful agents, including heat, injuries, light, and infections. Because of the crucial protective functions that the skin performs, it is vulnerable to various conditions, such as allergies, infections, burns, and even cancer.
Depending on the cell from which it originates, skin cancer can be of several types. The most common types of skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. These two types of skin cancers are curable unlike the third most common skin cancer called melanoma. Melanoma is the most dangerous skin cancer, causing many deaths. Even curable skin cancers can cause significant disfigurement to the affected person. Other types of skin cancers include lymphoma of the skin, Kaposi sarcoma, and Merkel cell skin cancer. Knowing the type of skin cancer is crucial for your doctor to decide your treatment.
Actinic Keratosis Signs And Symptoms
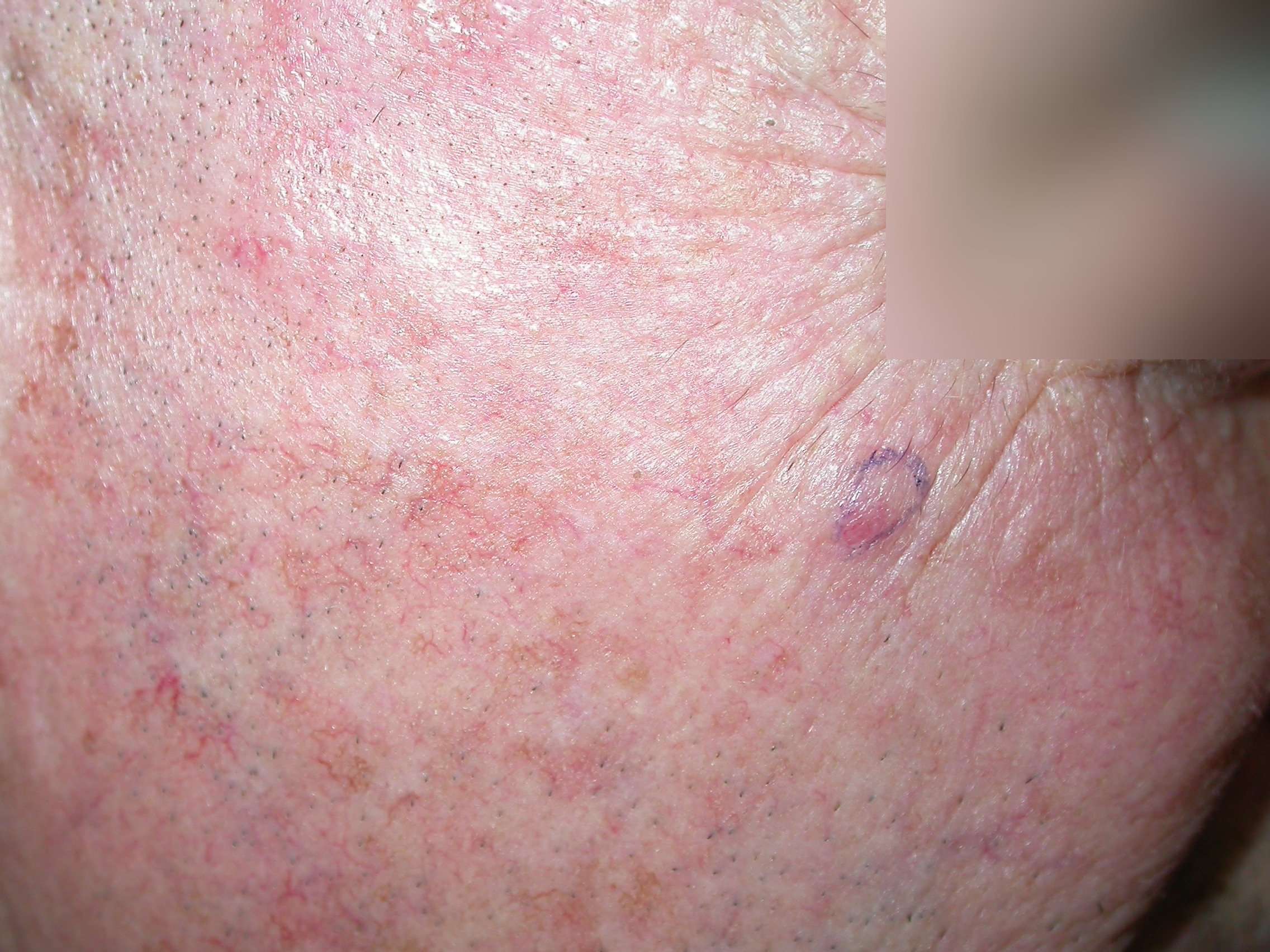
Many people have actinic keratosis , also called solar keratosis, on their skin. It shows that youâve had enough sun to develop skin cancer, and it is considered a precursor of cancer, or a precancerous condition.
Usually AK shows up on the parts of your body that have received the most lifetime sun exposure, like the face, ears, scalp, neck, backs of the hands, forearms, shoulders and lips.
Some of the same treatments used for nonmelanoma skin cancers are used for AK to ensure it does not develop into a cancerous lesion.
Appearance
This abnormality develops slowly. The lesions are usually small, about an eighth of an inch to a quarter of an inch in size. You may see a few at a time. They can disappear and later return.
- AK is a scaly or crusty bump on the skinâs surface and is usually dry and rough. It can be flat. An actinic keratosis is often noticed more by touch than sight.
- It may be the same color as your skin, or it may be light, dark, tan, pink, red or a combination of colors.
- It can itch or produce a prickling or tender sensation.
- These skin abnormalities can become inflamed and be encircled with redness. Rarely, they bleed.
Recommended Reading: Skin Cancer Metastasis To Lymph Nodes
Risk Factors + Warning Signs = Aeiou
Since MCCs can progress rapidly and become more difficult to treat, its crucial to understand your risks and warning signs. This AEIOU summary combines key points from both to help you with early detection.
- A: ASYMPTOMATIC lesion, not painful or tender
- E: Lesion is EXPANDING rapidly
- I: You are IMMUNOsuppressed
- O: You are OLDER than 50
- U: The lesion appears on UV-exposed skin
In a study of 195 patients, 89 percent of MCC patients presented with three or more of the AEIOU characteristics.
Left photo: Merkel cell carcinoma, local recurrence, forehead
Right photo: Merkel cell carcinoma, primary tumor, lower arm
Please note: Since not all Merkel cell carcinomas have the same appearance, these photos serve as a general reference for what MCC can look like. If you see anything NEW, CHANGING or UNUSUAL on your skin, go get checked by a dermatologist.
When Should I See A Doctor
- You should see your doctor if you have any new or changing marks on your skin. Be aware of any lumps, growths, moles, or other abnormal areas on your skin. Watch for new spots or areas that are changing. This can include skin marks that grow larger, bleed, crust, or itch.
- Early diagnosis and treatment is important to prevent the cancer from spreading. Your healthcare provider may recommend you do a skin self-exam once a month or more.
Read Also: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Scalp Prognosis
Key Points About Merkel Cell Cancer
- Merkel cell cancer is a rare type of skin cancer. It forms in the Merkel cells. These cells are found in the outer layer of the skin.
- Merkel cells are very close to nerve endings. They help the skin sense light touch.
- Being exposed to a lot of UV light can raise your risk for this cancer.
- Merkel cell cancer often looks like firm, shiny lumps on your skin that dont hurt. They may be red, pink, or blue.
- This cancer grows and spreads quickly.
- Treatment includes surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. One type of treatment or a combination of treatments may be used.
Mcc Arising On The Abdomen
The abdomen is a relatively sun protected area but MCC can develop in these areas also.The square-shaped rash around the tumor is a reaction to a bandage. There are cherry angiomas , that are 2-3mm red bumps scattered on the abdomen. Cherry angiomas are common benign skin lesions that are unrelated to the MCC.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma 3b
One Location For Coordinated Merkel Cell Carcinoma Care
Patients with Merkel cell carcinoma often require a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. Because of this, a team approach which can coordinate all care is the best way to manage these complicated cases.
At Brigham and Womens Hospital , our surgical oncologists are among the worlds leading surgical specialists treating complex and advanced-stage Merkel cell carcinoma. They are the surgical team at the Center for Cutaneous Oncology at the Dana-Farber/Brigham and Womens Cancer Center. Working together as one singularly-focused team, we help Merkel cell carcinoma patients get better faster with improved outcomes and fewer post-operative problems. From diagnosis to treatment, our multidisciplinary team of surgical oncologists, dermatologists, pathologists, medical oncologists, plastic and reconstructive surgeons and radiation oncologists work collaboratively with patients and families.
- The dermatopathologists at Dana-Farber/Brigham and Womens Cancer Center are among the best in the world with special expertise in diagnosing rare cases. This is extremely important as the patients treatment plan is guided by the diagnosis. For the ten percent of cases that are not routine, this is especially relevant.
- The BWH plastic and reconstructive surgeons are pioneers in ground-breaking procedures. The size and experience of our group allow us to tailor specific, individual care to each patient.
Diagnosing Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma may be detected during a physical exam by your doctor or dermatologist. Your doctor will check for lumps, lesions, or irregularly shaped moles. They may also ask you for a detailed medical history, history of sun exposure, and if anyone in your family has had skin cancer.
If your doctor finds anything abnormal, they may perform a skin biopsy to check for cancer. During a skin biopsy, a tiny amount of the lump is removed and viewed under a microscope.
If the biopsy is positive for Merkel cell carcinoma, your doctor will run additional tests to determine the stage and extent of the cancer. These tests may include:
- a sentinel lymph node biopsy, to find out if the cancer has spread to your lymph nodes
Depending on the stage of the cancer and your overall health, your treatment options may include one or more of the following:
- surgery to remove the tumor and any affected lymph nodes
- radiation treatment, which directs high energy beams at the cancer cells
- chemotherapy drugs
Your doctors will discuss the benefits of each option, as well as the possible risks and side effects.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Cancer Prognosis
Clinical Photos Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
For more examples of MCC tumors, visit the Clinical Photos page.
A Closer Look
A study2 of 195 Merkel cell carcinoma patients was carried out to determine the features that doctors or patients typically find associated with this cancer. AEIOU summarizes the features that are usually associated with MCC. 89% of MCC tumors have three or more of these five features:A: Asymptomatic88% of MCCs are not tender.E: Expanding rapidly63% of MCCs have grown significantly within the past 3 monthsI: Immunosuppression*MCC patients are 16-times more likely to be immunosuppressed*O: Older than 5090% of MCC patients are over age 50 & MCC risk keeps increasing with ageU: UV exposed fair skin81% of MCCs arise on sun-exposed skin and 98% of MCCs arise in people whose skin tone is light* The relationship between immune suppression & MCC is tricky to understand. While only 8% of MCC patients have severe, long-term immune suppression , this is a 16-fold over-representation compared to the general population. Such long-term immunosuppressed patients have a higher risk of developing MCC and of later having their MCC recur.
Radiation Treatments For Merkel Cell Carcinoma
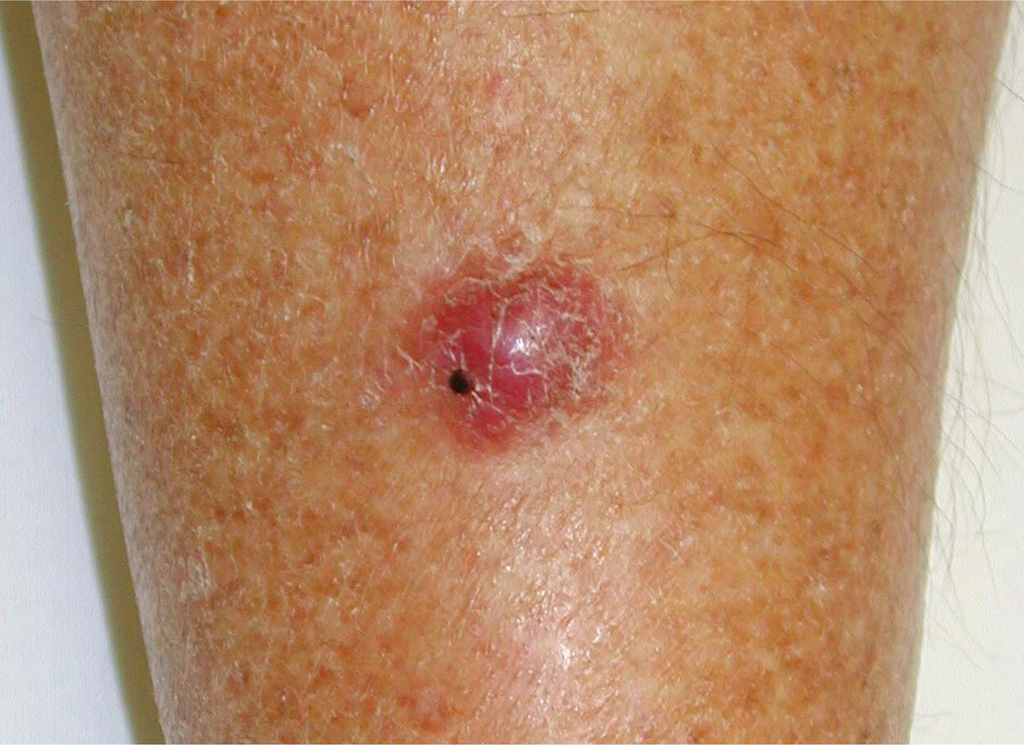
Some patients may undergo radiation a few weeks after surgery to lower the risk of the cancer returning. The radiation destroys any cancerous cells left behind after surgery.
If you have stage IV Merkel cell carcinoma or cannot have surgery, radiation or immunotherapy may be the first treatment step.
Common side effects of radiation include skin irritation, changes in skin color or texture, hair loss, and fatigue.
Also Check: Tumor Calcification
Skin Cancer Can Cause Itching However Itching Alone Doesnt Mean A Thing Learn Other Symptoms Of Skin Cancer And How You Can Take Action To Prevent It
The most common type of cancer among Americans is skin cancer, with melanoma being the deadliest. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun, tanning beds, and sunlamps are the leading causes of melanoma. In 2013 the American Cancer Society did a study that revealed almost 77,000 Americans have skin cancer, with 60% of those people being men. Are there any signs that can be observed? Such questions can be frequently asked. Here the article will give you perfect help about that. Read on to find these answers!
Also Check: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
Basal Cell Carcinoma Signs And Symptoms
This type of cancer is usually found on sun-exposed areas of the skin like the scalp, forehead, face, nose, neck and back.
Basal cell carcinomas may bleed after a minor injury but then scab and heal. This can happen over and over for months or years with no visible growth, making it easy to mistake them for wounds or sores. They rarely cause pain in their earliest stages.
Appearance
In addition to the bleeding and healing, these are other possible signs of a basal cell cancer:
- A persistent open sore that does not heal and bleeds, crusts or oozes.
- A reddish patch or irritated area that may crust or itch.
- A shiny bump or nodule that is pearly or translucent and often pink, red or white. It can also be tan, black or brown, especially in dark-haired people, and easy to confuse with a mole.
- A pink growth with a slightly elevated, rolled border and a crusted indentation in the center. Tiny blood vessels may appear on the surface as the growth enlarges.
- A scar-like lesion in an area that you have not injured. It may be white, yellow or waxy, often with poorly defined borders. The skin seems shiny and tight sometimes this can be a sign of an aggressive tumor.
You May Like: Skin Cancer Spreading To Lymph Nodes
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers do not know why certain cells become cancerous. However, they have identified some risk factors for skin cancer.
The most important risk factor for melanoma is exposure to UV rays. These damage the skin cellsâ DNA, which controls how the cells grow, divide, and stay alive.
Most UV rays come from sunlight, but they also come from tanning beds.
Some other risk factors for skin cancer include:
- A lot of moles: A person with more than 100 moles is more likely to develop melanoma.
- Fair skin, light hair, and freckles: The risk of developing melanoma is higher among people with fair skin. Those who burn easily have an increased risk.
- Family history:Around 10% of people with the condition have a family history of it.
- Personal history: Melanoma is likelier to form in a person who has already had it. People who have had basal cell or squamous cell cancers also have an increased risk of developing melanoma.
The best way to reduce the risk of skin cancer is to limit oneâs exposure to UV rays. A person can do this by using sunscreen, seeking shade, and covering up when outdoors.
People should also avoid tanning beds and sunlamps to reduce their risk of skin cancer.
It can be easy to mistake benign growths for skin cancer.
The following skin conditions have similar symptoms to skin cancer:
Dont Miss: What Is Melanoma In The Brain
What Are Merkel Cells
Merkel cells are found in the top layer of the skin. They are very close to the nerve endings that receive the sensation of touch. Merkel cell carcinoma occurs when Merkel cells grow out of control.
The prognosis for Merkel cell carcinoma depends on several factors, including the size of the tumor, if the cancer cells have spread to other areas of the body, where on the body the tumor is, whether it has recurred, and your overall health and age.
In this article, we will discuss the various treatment options for Merkel cell carcinoma, as well as possible side effects and prognosis.
Dont Miss: What To Do When You Get Skin Cancer
Read Also: Braf And Melanoma
Are There Risk Factors For Developing Merkel Cell Carcinoma
- Merkel cell polyomavirus infection This virus was first discovered in 2008, and its still somewhat of a mystery. This virus is found in the cancer cells of 80 percent of people with Merkel cell carcinoma.
- UV light exposure Exposure to the ultraviolet rays is the major risk factor . This exposure can come from the sun, tanning beds, or from UV light treatments for psoriasis.
- Fair skin Nearly 90 of Merkel cell carcinomas occur in white people.
- Old age This form of skin cancer is very rare in people under the age of 50. Over 80 percent of cases form in those over 70. This is probably due to a combination of accumulating UV exposure and a weakening immune system.
- Males Men are twice as likely to get this skin cancer, although again that can simply be a factor that men get more sun exposure.
- Weakened immune system Our immune systems not only fight germs and viruses, they also help the body fight cancer. When these systems are weakened, the patient becomes more likely to develop some types of cancer, including Merkel cell carcinoma.
Stages Of Merkel Cell Carcinoma
After receiving a cancer diagnosis, your doctor will run tests to find out if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body. This is referred to as staging. Staging is important for determining what types of treatment are needed.
In general, a higher number stage means the further a cancer has spread. There are five main stages in MCC :
- stage 0: the cancer is only in the epidermis and hasnt spread to the lymph nodes
- stage 1: the cancer is less than 2 centimeters across and hasnt grown into the lymph nodes
- stage 2: the cancer is more than 2 cm across and hasnt spread to the lymph nodes
- stage 3: the cancer has grown into lymph nodes as well as nearby tissues
- stage 4: the cancer has spread to nearby tissues, the lymph nodes, and distant sites, such as the lungs, bones, or brain
The main symptom of Merkel cell carcinoma is the appearance of a single lump or nodule on the skin. The lump is typically:
- red or violet in color
- firm to the touch
- fast-growing
- painless
The nodule can form anywhere on the body, but most often appears on areas regularly exposed to sunlight, such as the:
- face
- neck
- arms
If the cancer spreads to the lymph nodes, the nodes may grow large enough to be seen as lumps under the skin.
Merkel cell carcinoma can look like many other types of skin cancer at first, so a definitive diagnosis usually isnt made until after a biopsy. Other types of skin cancers often present with:
Don’t Miss: Rare Cancer Symptoms
When Is A Mole A Problem
If a new or existing mole begins to change shape, color, size, or becomes flaky, crusty, or begins to bleed, it’s time to make an appointment with your dermatologist to get it checked out. A mole can turn into melanoma on rare occasions. In early melanoma, the shape of a mole becomes asymmetrical and uneven.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
Nodular basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that is most often found on the head. This type of cancer starts in basal cells, which are tasked with making new skin cells to push the old ones toward the surface of the skin. Nodular basal cell carcinoma is responsible for 60%-80% of all basal cell carcinomas. In the United States, its estimated that 4.3 million cases of basal cell carcinoma are diagnosed every year, with 2.5 to 3.4 million of those cases being nodular basal cell carcinoma.
This type of cancer appears as a pearl-like papule that is round and surrounded by threadlike red lines on the skin made up of tiny blood vessels. The risk of developing nodular basal cell carcinoma can be increased by spending a lot of time out in the sun, living in high-altitude and sunny locations, and radiation therapy.
Other risk factors include:
- Prolonged exposure to arsenic
- Certain rare genetic disorders such as basal cell nevus syndrome
Although this type of cancer is common, it is highly treatable, and the five-year relative survival rate is 100%.