How Common Is It
Overall, skin cancers are the most common cancers in the United States. But melanoma is less common than the other two major types, basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma.
Each year about 91,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with melanoma of the skin, according to the American Cancer Society. By comparison, about 3.3 million are diagnosed with one or more basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas.
How Is Melanoma Treated
Melanoma treatment can include:
- surgery to remove the cancerous lesion
- chemotherapy: tumor-killing medicines are given by mouth, through an injection , or intravenously
- targeted therapy: specific medicines that find and attack cancer cells without hurting normal cells
- immunotherapy : when doctors stimulate the body’s own immune system to fight cancer cells
The treatment chosen depends on:
- how big and how deep the lesion is
- what part of the body it is on
- whether the cancer has spread
Can You Get Rid Of Flat Moles
Some moles can be removed using lasers. This is most commonly done with small, flat, non-cancerous moles. During laser removal, your doctor will use bursts of light radiation to destroy the mole tissue. To fully remove a mole using laser therapy, you may need to have two or three treatments.
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer In A Child
Symptoms of basal cell carcinoma appear on areas exposed to the sun, such as the head, face, neck, arms, and hands. The symptoms can include:
-
A small, raised bump that is shiny or pearly, and may have small blood vessels
-
A small, flat spot that is scaly, irregularly shaped, and pale, pink, or red
-
A spot that bleeds easily, then heals and appears to go away, then bleeds again in a few weeks
-
A growth with raised edges, a lower area in the center, and brown, blue, or black areas
Symptoms of squamous cell carcinoma appear on areas exposed to the sun, such as the head, face, neck, arms, and hands. They can also appear on other parts of the body, such as skin in the genital area. The symptoms can include:
-
A rough or scaly bump that grows quickly
-
A wart-like growth that may bleed or crust over.
-
Flat, red patches on the skin that are irregularly shaped, and may or may not bleed
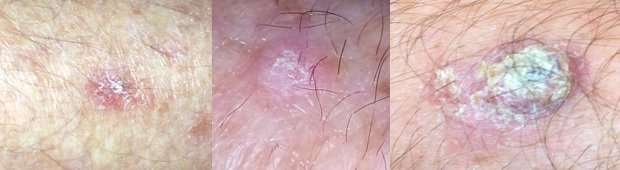
Symptoms of melanoma include a change in a mole, or a new mole that has ABCDE traits such as:
-
Asymmetry. One half of the mole does not match the other half.
-
Border irregularity. The edges of the mole are ragged or irregular.
-
Color. The mole has different colors in it. It may be tan, brown, black, red, or other colors. Or it may have areas that appear to have lost color.
-
Diameter. The mole is bigger than 6 millimeters across, about the size of a pencil eraser. But some melanomas can be smaller.
-
Evolving. A mole changes in size, shape, or color.
Other symptoms of melanoma can include a mole that:
What Can I Do To Prevent Skin Cancer In My Child
The American Academy of Dermatology and the Skin Cancer Foundation advise you to:
-
Limit how much sun your child gets between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
-
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF 30 or higher that protects against both UVA and UVB rays. Put it on the skin of children older than 6 months of age who are exposed to the sun.
-
Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours, even on cloudy days. Reapply after swimming.
-
Use extra caution near water, snow, and sand. They reflect the damaging rays of the sun. This can increase the chance of sunburn.
-
Make sure your child wears clothing that covers the body and shades the face. Hats should provide shade for both the face, ears, and back of the neck. Wearing sunglasses will reduce the amount of rays reaching the eye and protect the lids of the eyes, as well as the lens.
-
Dont let your child use or be around sunlamps or tanning beds.
The American Academy of Pediatrics approves of the use of sunscreen on babies younger than 6 months old if adequate clothing and shade are not available. You should still try to keep your baby out of the sun. Dress the baby in lightweight clothing that covers most surface areas of skin. But you also may use a small amount of sunscreen on the babys face and back of the hands.
Recommended Reading: How Can You Detect Skin Cancer
Don’t Miss: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Can Skin Cancer Be Prevented
In most cases, skin cancer can be prevented. The best way to protect yourself is to avoid too much sunlight and sunburns. Ultraviolet rays from the sun damage the skin, and over time lead to skin cancer.
Here are ways to protect yourself from skin cancer:
- Seek shade. Don’t spend long periods of time in direct sunlight.
- Wear hats with wide brims to protect your face and ears.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants to protect your arms and legs.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreens with an SPF of 30 or higher that protect against burning and tanning rays. Apply the sunscreen 30 minutes before you go outside.
- Wear sunglasses to protect your eyes.
- Use a lip balm with sunscreen.
- Avoid the sun between 10:00 a.m. and 4:00 p.m.
- Show any changing mole to your healthcare provider.
Risk Factors And Causes Of Skin Cancer
Despite the fact that high melanin content confers better photo protection, significant photo damage in the form of epidermal atypia and atrophy, dermal collagen and elastin damage and pigmentary disorders can cause skin cancer which could be fatal due to delay in detection in skin of color . Skin cancer is skin growth with varying degrees of malignancy . It is not yet very clear why skin cancer incidence has grown so dramatically over the past decades but the reason is likely to be multi factorial which includes increased UV exposure, environmental, hereditary risk factors and improved surveillance and earlier recognition . In addition, genetic polymorphisms also modulate the susceptibility to skin cancer .
Organ transplant receivers especially kidney and HIV patients have an increased frequency of skin cancers . Some treatments, including radiation therapy, phototherapy, psoralen and long-wave ultraviolet radiation can also predispose to skin malignancies . Viral infections such as the human papilloma virus can cause cancer. Patients with familial genetic patterns are vulnerable to particular types of skin cancers . Certain drugs, from common antibiotics to heart medications, can increase the skins sensitivity to sunlight, causing the skin to burn in less time and may increase the incidence of skin cancer .
Recommended Reading: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
Should Lymph Nodes Be Removed
If a melanoma spreads beyond its site of origin , the surrounding lymph nodes may become enlarged. In such cases, the lymph nodes should be surgically removed under a general anaesthetic .
Normal, unenlarged lymph nodes may also be tested to identify microscopic spread of melanoma this test is called a sentinel node biopsy and may help in cancer staging .
What Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most prevalent form of all cancers in the United States and is identified when the cells that make up our skin begin to grow and rapidly divide in a disorganized manner. There are 3 main types of skin cancer:
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Melanoma
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of skin cancer and may also sometimes be referred to as “non-melanoma skin cancer.”
Melanoma is not as common as basal cell or squamous cell carcinomas, but is the most dangerous form of skin cancer. If left untreated or caught in a late stage, melanomas are more likely to spread to organs beyond the skin, making it difficult to treat and increasing the chances of death from skin cancer.
Fortunately, if skin cancer is identified and treated early, most are cured. This is why it is important to take a few safeguards and to talk with your healthcare provider if you think you are showing any signs of skin cancer.
Read Also: What Is Braf Testing In Melanoma
What Are Possible Complications Of Skin Cancer In A Child
Possible complications depend on the type and stage of skin cancer. Melanoma is more likely to cause complications. And the more advanced the cancer, the more likely there will be complications.
Complications may result from treatment, such as:
-
Loss of large areas of skin and underlying tissue
-
Scarring
-
Problems with the area healing
-
Infection in the area
-
Return of the skin cancer after treatment
Melanoma may spread to organs throughout the body and cause death.
Warning Signs Of Basal Cell Carcinoma That You Could Mistake As Harmless
Warning sign: A pink or reddish growth that dips in the centerCan be mistaken for: A skin injury or acne scar
A pink or reddish growth that dips in the center
The BCC on this patients cheek could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the earCan be mistaken for: Scaly, dry skin, minor injury, or scar
A growth or scaly patch of skin on or near the ear
BCC often develops on or near an ear, and this one could be mistaken for a minor skin injury.
Warning sign: A sore that doesnt heal and may bleed, ooze, or crust overCan be mistaken for: Sore or pimple
A sore that doesnt heal, or heals and returns
This patient mistook the BCC on his nose for a non-healing pimple.
Warning sign: A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin, which could be red, pink, or another colorCan be mistaken for: Dry, irritated skin, especially if its red or pink
A scaly, slightly raised patch of irritated skin
This BCC could be mistaken for a patch of dry, irritated skin.
Warning sign: A round growth that may be pink, red, brown, black, tan, or the same color as your skinCan be mistaken for: A mole, wart, or other harmless growth.
A round growth that may be same color as your skin
Would you recognize this as a skin cancer, or would you dismiss it as a harmless growth on your face?
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
What Are The Symptoms Of Skin Cancer In Black People
The main symptom of skin cancer is a change in an area of skin. This sounds very general, so lets dive deeper into some general qualities to look for.
Not all skin cancers appear the same. Its possible that a cancerous area could have one, a few, or all the characteristics listed below.
Whats important is that you make an appointment with a dermatologist if you have concerns about a certain area. They can evaluate the area to help determine whether it may be skin cancer.
Naevi Of Special Sites
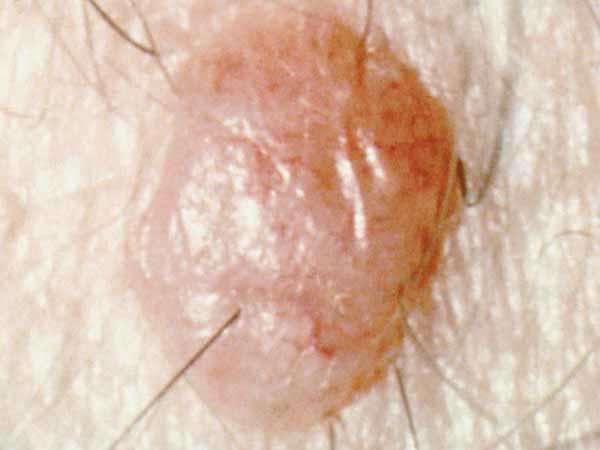
Naevi of special sites are naevi that develop in atypical areas, including the genitals, breasts, palms, soles of the feet and flexural regions . While benign, they may show a histological structure similar to melanoma. This diagnosis should particularly be considered in skin of colour, as these naevi occur in sites where melanoma commonly occurs in these skin types .
Dont Miss: Do You Need Chemo For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Don’t Miss: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Should A Very Small Melanoma Be Taken Seriously
Melanoma does not have the reputation it deserves. It is an aggressive and deadly cancer with an almost innocuous presence belying the potential gravity of the situation. A small melanoma can hide its depth and extent beneath the skin, always get them inspected by a doctor.
- What is Parastomal Hernia: Symptoms, Repair
A parastomal hernia is best explained by initially understanding
- Reducible and non-reducible hernia
The medical explanation of a hernia is the escape
- Remove Skin Tags during pregnancy: genital,
Pregnancy, a period of great joy, the nine months
- Do Skin Tags, Moles, Genital and
Itching or, to award it the correct medicinal name,
- Doterra and Oregano Oils to remove
Doterra, a memorable and unusual name, derived from the
- Over the Counter Wart, Skin Tag
Warts, always have a bit of a bad press
- Rectal Skin Tags & Warts removing:
Rectal skin tags, also termed, anal skin tags or
Polar Regions Vitamin D And Diet
Polar regions of the Northern Hemisphere receive little UV radiation, and even less vitamin D-producing UVB, for most of the year. These regions were uninhabited by humans until about 12,000 years ago. Areas like Scandinavia and Siberia have very low concentrations of ultraviolet radiation, and indigenous populations are all light-skinned. However, dietary factors may allow vitamin D sufficiency even in dark skinned populations. Many indigenous populations across Eurasia survive by consuming reindeer, which they follow and herd. Reindeer meat, organs, and fat contain large amounts of vitamin D which the reindeer get from eating substantial amounts of lichen. Some people of the polar regions, like the Inuit , retained their dark skin they ate Vitamin D-rich seafood, such as fish and sea mammal blubber. Furthermore, these people have been living in the far north for less than 7,000 years. As their founding populations lacked alleles for light skin colour, they may have had insufficient time for significantly lower melanin production to have been selected for by nature. “This was one of the last barriers in the history of human settlement,” Jablonski states. “Only after humans learned fishing, and therefore had access to food rich in vitamin D, could they settle regions of high latitude.” Additionally, in the spring, Inuit would receive high levels of UV radiation as reflection from the snow, and their relatively darker skin then protects them from the sunlight.
Also Check: Basaloid Tumor
What Causes Skin Cancer In Black People
In general, skin cancer is caused by genetic changes that occur in the DNA of our cells. Sometimes, these changes can be harmful, causing cells to begin to grow and divide out of control.
UV radiation from the sun can cause damage to DNA. Because of this, frequent exposure to UV rays in the form of sunlight or UV lamps is associated with an increased risk of skin cancer.
However, not all types of skin cancer may be linked to sun exposure. Indeed, some skin cancers in Black people occur in areas that arent exposed to much sunlight, such as the soles of the feet, palms of the hands, and nails.
This type of skin cancer is called acral lentiginous melanoma . Some dermatologists have reported that ALM makes up 30 to 70 percent of melanomas seen in People of Color visiting their practice.
Doctors dont yet know what causes ALM. However, its believed that genetic factors may play a role.
Make A Difference: Start Checking Your Skin Today
People of color have a lower risk than whites of getting skin cancer. But they still have a risk. Monthly skin self-exams can help you find skin cancer early when a cure is likely.
ImagesImages 3 11: Used with permission of Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology:
-
Images 3, 4, 9, 10, and 11: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 70:748-62.
-
Images 5, 6, 7, and 8: J Am Acad Dermatol. 2006 55:741-60.
Image 12: Image used with permission of the American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
ReferencesAgbai ON, MD, Buster K, et al. Skin cancer and photoprotection in people of color: A review and recommendations for physicians and the public. J Am Acad Dermatol 2014 70:748-62.
American Academy of Dermatology. Dermatologists provide recommendations for preventing and detecting skin cancer in people of color. News release issued February 4, 2014.
Gloster HM and Neal K. Skin cancer in skin of color. J Am Acad Dermatol 2006 55:741-60.
Recommended Reading: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Melanoma
Melanoma is a skin cancer that can show up on the skin in many ways. It can look like a:
-
Changing mole
-
Spot that looks like a new mole, freckle, or age spot, but it looks different from the others on your skin
-
Spot that has a jagged border, more than one color, and is growing
-
Dome-shaped growth that feels firm and may look like a sore, which may bleed
-
Dark-brown or black vertical line beneath a fingernail or toenail
-
Band of darker skin around a fingernail or toenail
-
Slowly growing patch of thick skin that looks like a scar
Early melanoma
This early melanoma could be mistaken for a mole, so its important to look carefully at the spots on your skin.
Major Types Of Treatments
Although surgical modalities remain the mainstay of treatment, new research and fresh innovation are still required to reduce morbidity and mortality . There has been innovation in skin cancer treatment in the last few years than in the previous 30 years . Here, we are not discussing treatment methodology in details but just an outline of currently applicable standard treatments for skin cancer is given .
Surgery: Most basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers can be successfully treated with surgery and early-stage melanomas are also cured. Thin layers are removed until no more cancer cells are seen.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays or particles to kill cancer cells or prevent them from growing. It is used when cancer is widely spread, recurred and surgery is not possible.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapeutic drugs are usually given as injection or taken by mouth as a pill. They travel through the bloodstream to all parts of the body and attack cancer cells and stop their growth by killing them or by stopping them from dividing.
Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is the emerging new type of treatment that stimulates a persons own immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to attack cancer cells. Targeted therapies usually cause less harm to normal cells than chemotherapy or radiation therapy do.
Recommended Reading: What Is Braf Testing In Melanoma