Basal Cell Carcinoma Pictures
Basal cell carcinoma usually appears in areas of the skin previously exposed to high levels of UV radiation such as the head, neck, ears and the back of the arms and hands. It is common in exposed skin of outdoor workers or people who have used sun tanning beds in the past.
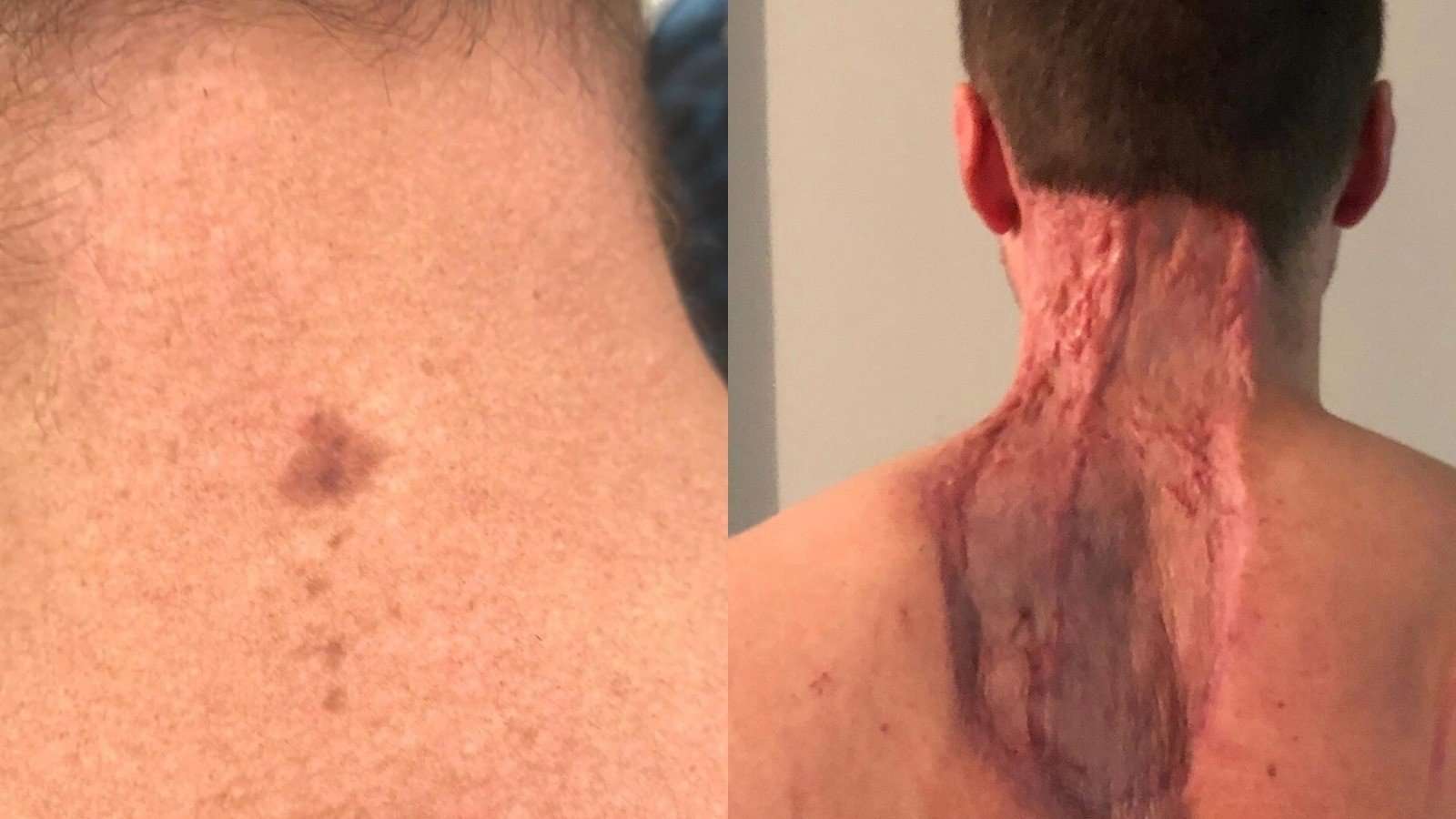
As the basal cell carcinoma pictures below indicate, this type of skin cancer usually shows as a fleshy coloured bump that does not disappear over time and tends to grow slowly in size, eventually breaking down and ulcerating.
Below are pictures of skin cancer on the neck, face and trunk . These images show common areas where basal cell carcinoma develops, but it can develop anywhere.
Basal cell carcinoma. The skin cancer pictures in this article were licensed from DermNet NZ
Signs & Symptoms Of Ear Cancer
The symptoms of ear cancer depend on the location of the tumor. Swelling of cervical lymph nodes can be seen in some patients. The most common symptom of cancer in the middle ear is a discharge from the ear that can be stained with blood. Other symptoms of ear cancer include earache and hearing loss. Some patients are not able to move their face on the side where the ear cancer is. Symptoms of cancer in the inner ear include pain, hearing loss, headache, dizziness and tinnitus.
Treatment For Ear Cancer
Surgery to remove the cancer from the ear is the most common treatment. You may have radiation after surgery as well. How much of the ear is removed depends on the type, size and location of the ear canal tumor. After surgery for inner ear cancer, you may have partial or total hearing loss and struggle with balance.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Cancer Is Skin Cancer
What To Expect From Your Doctor
Your doctor is likely to ask you a number of questions. Being ready to answer them may allow time to cover other points you want to address. Your doctor may ask:
- When did you first notice your skin changes?
- Have you noticed a skin lesion that has grown or changed?
- Do you have a skin lesion that bleeds or itches?
- How severe are your symptoms?
Signs And Symptoms Of Less Common Skin Cancers
Other, less common types of skin cancer include:
-
Kaposi sarcoma. This rare form of skin cancer develops in the skin’s blood vessels and causes red or purple patches on the skin or mucous membranes.
Kaposi sarcoma mainly occurs in people with weakened immune systems, such as people with AIDS, and in people taking medications that suppress their natural immunity, such as people who’ve undergone organ transplants.
Other people with an increased risk of Kaposi sarcoma include young men living in Africa or older men of Italian or Eastern European Jewish heritage.
- Merkel cell carcinoma. Merkel cell carcinoma causes firm, shiny nodules that occur on or just beneath the skin and in hair follicles. Merkel cell carcinoma is most often found on the head, neck and trunk.
- Sebaceous gland carcinoma. This uncommon and aggressive cancer originates in the oil glands in the skin. Sebaceous gland carcinomas which usually appear as hard, painless nodules can develop anywhere, but most occur on the eyelid, where they’re frequently mistaken for other eyelid problems.
Don’t Miss: What Are Some Treatments For Melanoma
Follow Up For Ear Cancer/ear Tumor
Patient needs to have regular checkups after the treatment of ear cancer is completed. During these checkups, the doctor asks about the patientâs general health and examines the patientâs ear. During these checkups, the patient can ask the doctor if he/she has any concern. The frequency of the checkups will depend on the patientâs situation. The follow up checkups will be every 2 or 3 months and the frequency will reduce as time passes.
| Written, Edited or Reviewed By:Pramod Kerkar, M.D., FFARCSI, DA Pain Assist Inc.This article does not provide medical advice. See disclaimerLast Modified On: April 6, 2018 |
When Is A Mole A Problem
A mole is a benign growth of melanocytes, cells that gives skin its color. Although very few moles become cancer, abnormal or atypical moles can develop into melanoma over time. “Normal” moles can appear flat or raised or may begin flat and become raised over time. The surface is typically smooth. Moles that may have changed into skin cancer are often irregularly shaped, contain many colors, and are larger than the size of a pencil eraser. Most moles develop in youth or young adulthood. It’s unusual to acquire a mole in the adult years.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Melanoma Under Toenail
Less Common Skin Cancers
Uncommon types of skin cancer include Kaposi’s sarcoma, mainly seen in people with weakened immune systems sebaceous gland carcinoma, an aggressive cancer originating in the oil glands in the skin and Merkel cell carcinoma, which is usually found on sun-exposed areas on the head, neck, arms, and legs but often spreads to other parts of the body.
The Warning Signs Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancers — including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma — often start as changes to your skin. They can be new growths or precancerous lesions — changes that are not cancer but could become cancer over time. An estimated 40% to 50% of fair-skinned people who live to be 65 will develop at least one skin cancer. Learn to spot the early warning signs. Skin cancer can be cured if it’s found and treated early.
Read Also: How Do You Detect Skin Cancer
Tips For Screening Moles For Cancer
Examine your skin on a regular basis. A common location for melanoma in men is on the back, and in women, the lower leg. But check your entire body for moles or suspicious spots once a month. Start at your head and work your way down. Check the “hidden” areas: between fingers and toes, the groin, soles of the feet, the backs of the knees. Check your scalp and neck for moles. Use a handheld mirror or ask a family member to help you look at these areas. Be especially suspicious of a new mole. Take a photo of moles and date it to help you monitor them for change. Pay special attention to moles if you’re a teen, pregnant, or going through menopause, times when your hormones may be surging.
Health & Wellness7 Skin Cancer Warning Signs To Never Ignore
Ultimately, it’s not the patients job to biopsy themselves. It’s the patients job to see something and say something, Gastman said.
With some of my patients, I call it whack a mole. Theyve had melanoma and I say, look you may get a mole and it may be high risk of turning into melanoma, but we’ll just keep cutting them out. When you’re 100 years old, you’ll tell your great-grandchildren about all the scars you have on your body, but you’ll never die of your disease.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know You Have Melanoma
Ultraviolet Light And Other Potential Causes
Much of the damage to DNA in skin cells results from ultraviolet radiation found in sunlight and in the lights used in tanning beds. But sun exposure doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. This indicates that other factors may contribute to your risk of skin cancer, such as being exposed to toxic substances or having a condition that weakens your immune system.
What Causes Non
Overexposure to ultraviolet light is the main cause of non-melanoma skin cancer. UV light comes from the sun, as well as from artificial tanning sunbeds and sunlamps.
Other risk factors that can increase your chances of developing non-melanoma skin cancer include:
- a previous non-melanoma skin cancer
- a family history of skin cancer
- pale skin that burns easily
- a large number of moles or freckles
- taking medicine that suppresses your immune system
- a co-existing medical condition that suppresses your immune system
Recommended Reading: How Is Skin Cancer Inherited
What You Can Do
If youve already had a BCC, you have an increased chance of developing another, especially in the same sun-damaged area or nearby.
A BCC can recur even when it has been carefully removed the first time, because some cancer cells may remain undetectable after surgery and others can form roots that extend beyond whats visible. BCCs on the nose, ears and lips are more likely to recur, usually within the first two years after surgery.
Heres what you can do to detect a recurrence and safeguard yourself against further skin damage that can lead to cancer:
Reviewed by:
Radiation Therapy For Ear Cancer
This is a cancer treatment which utilizes high energy beams that are focused on the region of the cancer to kill or destroy the cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be done as the primary ear cancer treatment or it may be used when the surgeon has not been able to have clear margin of tissue surrounding the tumor. In such cases radiation therapy decreases the risk of recurrence of cancer. Patient is given radiation therapy usually every day for around 4 and 7 weeks.
You May Like: What Is Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma
What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Although the number of skin cancers in the United States continues to rise, more and more skin cancers are being caught earlier, when they are easier to treat. Thus, illness and death rates have decreased.
When treated properly, the cure rate for both basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma approaches 95%. The remaining cancers recur at some point after treatment.
- Recurrences of these cancers are almost always local , but they often cause significant tissue destruction.
- Less than 1% of squamous cell carcinomas will eventually spread elsewhere in the body and turn into dangerous cancer.
In most cases, the outcome of malignant melanoma depends on the thickness of the tumor at the time of treatment.
- Thin lesions are almost always cured by simple surgery alone.
- Thicker tumors, which usually have been present for some time but have gone undetected, may spread to other organs. Surgery removes the tumor and any local spread, but it cannot remove distant metastasis. Other therapies, new targeted agents or older approaches such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy, are used to treat the metastatic tumors.
- Malignant melanoma causes more than 75% of deaths from skin cancer.
- Of the approximately 70,000 malignant melanomas diagnosed in the United States in 2007, the vast majority were cured. Still, thousands of people die of melanoma each year.
Knowledge Is Your Best Defense
What Is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is the out-of-control growth of abnormal cells in the epidermis, the outermost skin layer, caused by unrepaired DNA damage that triggers mutations. These mutations lead the skin cells to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumors. The main types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma , squamous cell carcinoma , melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma .
The two main causes of skin cancer are the suns harmful ultraviolet rays and the use of UV tanning beds. The good news is that if skin cancer is caught early, your dermatologist can treat it with little or no scarring and high odds of eliminating it entirely. Often, the doctor may even detect the growth at a precancerous stage, before it has become a full-blown skin cancer or penetrated below the surface of the skin.
Americans will develop skin cancer by age 70.
You May Like: What Is Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
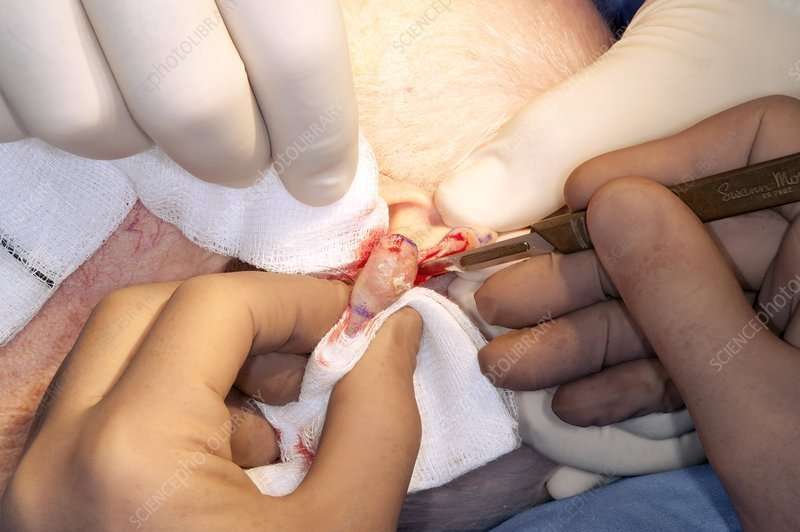
Surgery For Ear Cancer
The type of surgery and the amount of surgery which the patient needs depends on the location of the cancer in the patientâs ear. Surgical procedure also depends on the how much and where the cancer has spread to the surrounding tissues or to the adjacent structures. During surgery the surgeon will remove the entire tumor along with the surrounding tissue, so that the patient is completely free from cancer cells. This is known getting clear margins of the tissue and it needs to be a minimum 5 mm surrounding the tumor/cancer. Getting clear margins will decrease the risk of cancer recurrence.
Surgery for ear cancer involves having to remove a part or all of the following:
- The ear canal.
- A part or the entire temporal bone.
- The inner ear.
Mastoidectomy: The temporal bone is a bone that is present near the ear, at the side of the skull. Temporal bone resection or mastoidectomy is the surgical procedure where the temporal bone is removed.
Removal of facial nerve and lymph nodes: In rare cases, the facial nerve may need to be removed by the surgeon. The facial nerve travels down the side of the face and passes through the salivary gland. The surgeon may also need to remove the adjacent lymph nodes, which are present near the patientâs neck and the salivary gland that is present on the side of the patientâs head.
How Your Doctor Decides On Treatment
The treatment you have depends on:
- where in the ear the cancer is
- the type of cancer you have
- the size of the tumour
- whether it’s spread beyond the area it started in
- your general health
This page is about treatment for cancer that starts in the skin flap of your outer ear. Although the ear canal is part of the outer ear, its treatment is different.
You can read about treatment for cancer that starts in the ear canal on the pages about cancer of the ear canal, middle ear and inner ear.
You May Like: Does Sunburn Cause Skin Cancer
Exam By A Health Care Professional
Some doctors and other health care professionals do skin exams as part of routine health check-ups.
Having regular skin exams is especially important for people who are at high risk of skin cancer, such as people with a weakened immune system or people with conditions such as basal cell nevus syndrome or xeroderma pigmentosum . Talk to your doctor about how often you should have your skin examined.
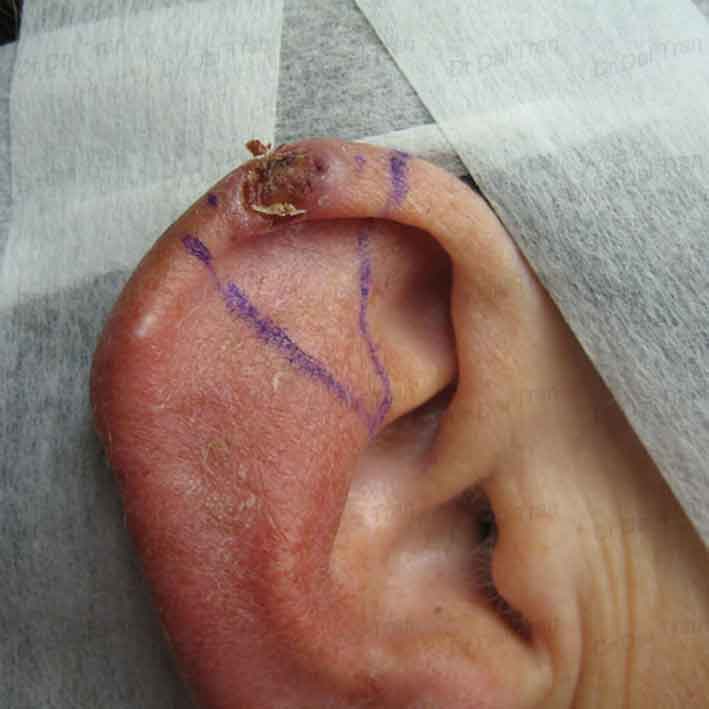
What Is Ear Cancer
Ear cancer is cancer which develops in the ear, the ear canal or middle ear and inner ear. Ear cancer is a rare cancer. Most of the cancers of the ear develop in the skin of the outer ear. Around 5 of 100 skin cancers occur on the ear. It is very rare for cancer to develop inside the ear. Majority of the ear cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. There are other types of ear cancers, which include basal cell cancer, adenoid cystic, melanoma and adenocarcinoma.
Read Also: Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Make You Tired
Can You Get A Spot In Your Ear
A pimple will form in your ear if the oil is unable to escape or bacteria grows in a clogged pore. A buildup in bacteria can be caused by a few things, such as sticking your finger in your ear or using earbuds or headphones that arent cleaned often. Other causes of acne include stress and a hormonal imbalance.
Determining The Extent Of The Skin Cancer
If your doctor determines you have skin cancer, you may have additional tests to determine the extent of the skin cancer.
Because superficial skin cancers such as basal cell carcinoma rarely spread, a biopsy that removes the entire growth often is the only test needed to determine the cancer stage. But if you have a large squamous cell carcinoma, Merkel cell carcinoma or melanoma, your doctor may recommend further tests to determine the extent of the cancer.
Additional tests might include imaging tests to examine the nearby lymph nodes for signs of cancer or a procedure to remove a nearby lymph node and test it for signs of cancer .
Doctors use the Roman numerals I through IV to indicate a cancer’s stage. Stage I cancers are small and limited to the area where they began. Stage IV indicates advanced cancer that has spread to other areas of the body.
The skin cancer’s stage helps determine which treatment options will be most effective.
You May Like: How To Tell If You Have Skin Cancer
Skin Cancer On Outer Ear Pictures : Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Eyelid
Cancer of the ear is rare. In the united states, it’s estimated that doctors diagnose over 100,000 new skin cancer cases each year. Most of these cancers start in the skin of the outer ear. The strongest risk factor for developing skin cancer is ultraviolet ray exposure, typically from the sun. Read about the symptoms, types, stages and tests for outer ear cancer.
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed In A Child
The healthcare provider will examine your child’s skin. Tell the healthcare provider:
-
When you first noticed the skin problem
-
If it oozes fluid or bleeds, or gets crusty
-
If its changed in size, color, or shape
-
If your child has pain or itching
Tell the healthcare provider if your child has had skin cancer in the past, and if other your family members have had skin cancer.
Your child’s healthcare provider will likely take a small piece of tissue from a mole or other skin mark that may look like cancer. The tissue is sent to a lab. A doctor called a pathologist looks at the tissue under a microscope. He or she may do other tests to see if cancer cells are in the sample. The biopsy results will likely be ready in a few days or a week. Your child’s healthcare provider will tell you the results. He or she will talk with you about other tests that may be needed if cancer is found.
Read Also: How Do You Get Basal Cell Carcinoma
How Do You Treat Ear Cartilage Pimples
A warm compress or heat pad may reduce inflammation and irritation. This can soften a pimple to bring the pus to the surface. If a pimple drains in this way, the individual should clean up the discharge and gently wash the area with a mild soap. Cleansers, such as witch hazel or alcohol, may prevent infections.