Basal Cell Skin Cancer
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. About 75 out of every 100;non melanoma skin cancers are BCCs. They develop from basal cells and these are found in the deepest part of the outer layer of the skin .
They develop mostly in areas of skin exposed to the sun, including parts of the face such as the nose, forehead and cheeks. Also, on your back or lower legs.
They are;most often diagnosed in people who are middle aged or older.
Doctors might also call;a basal cell cancer;a rodent ulcer.
There are;a number of different types of BCC.;Each type can look and behave differently. They;include:
- nodular basal cell skin cancer
- superficial basal cell skin cancer
- morphoeic basal cell skin cancer – also known as sclerosing or infiltrating basal cell skin cancer
- pigmented basal cell skin cancer
Nodular basal cell cancer is the most common subtype.
It’s very rare for basal cell skin cancer to spread to another part of the body to form a;secondary cancer. It’s possible to have more than one basal cell cancer at any one time and having had one does increase your risk of getting another.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Prognosis
Most basal cell carcinoma causes are preventable; diagnosis at sufficiently early stages is associated with a high cure rate. This means that BCC is rarely fatal. Similarly, rodent ulcers are rare as most treatments are curative.
Mohs micrographic surgery has the highest cure rate only 2.5% of patients experience recurrence after a term of five years, although not all tumors are eligible for this procedure. High-heat treatments are associated with a 7.7% five-year recurrence rate.
Patients who refuse surgery or have tumors in difficult-to-reach areas can expect control of tumor growth in 85% 95% of cases with radiotherapy. This option is usually only recommended for frailer, older patients.
In cases that have not metastasized, basal cell cancer is 100% curable. When metastasis occurs , basal cancer cells are most likely to settle in the lungs.
Metastatic basal cell carcinoma prognosis is poor with death occurring within four and a half years for most patients. However, it is extremely rare to find cases of advanced BCC. Today, targeted therapies can increase overall survival rates even for locally advanced and metastatic BCCs.
How Is Basal Cell Cancer Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Basal cell cancers are staged by size and extent of growth. These cancers rarely metastasize to lymph nodes or other organs, but they can grow quite large and invade small nerves and local structures.
Biopsy can help determine if the basal cell cancer is a low-risk tumor or a high-risk tumor that requires more aggressive treatment. Low-risk tumors are often nodular and do not have nerve involvement. High-risk tumors in the head and neck are those that involve the central face, nose and eye area, as well as those tumors that are greater than or equal to 10 millimeters on the cheeks, scalp and neck; tumors that are recurrent or arising from previously radiated tissue; and tumors arising in patients who are immunosuppressed. An aggressive growth pattern on the pathology evaluation and perineural invasion are also features of high-risk basal cell cancers.
Also Check: How Does Skin Cancer Feel
How Dangerous Is Bcc
While BCCs rarely spread beyond the original tumor site, if allowed to grow, these lesions can be disfiguring and dangerous. Untreated BCCs can become locally invasive, grow wide and deep into the skin and destroy skin, tissue and bone. The longer you wait to have a BCC treated, the more likely it is to recur, sometimes repeatedly.
There are some highly unusual, aggressive cases when BCC spreads to other parts of the body. In even rarer instances, this type of BCC can become life-threatening.
Treatment Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
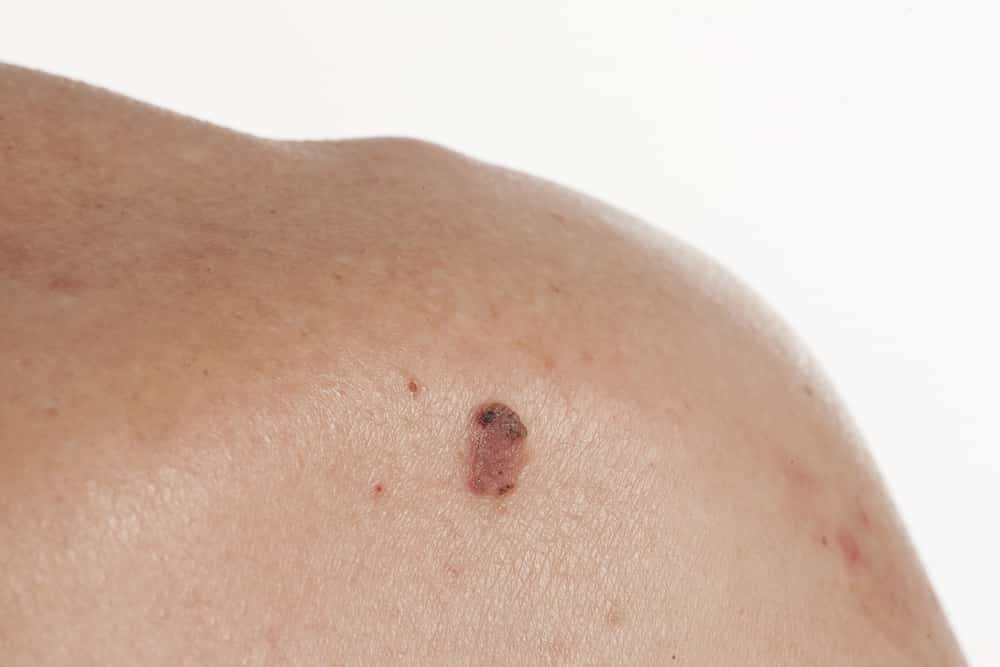
-
Removal of the tumor
Doctors may remove the cancer in the office by scraping and burning it with an electric needle or by cutting it out. Doctors may destroy the cancer by using extreme cold .
Certain chemotherapy drugs may be applied to the skin. Photodynamic therapy , in which chemicals and a laser are applied to the skin, also may be used. Occasionally, radiation therapy is used.
A technique called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery may be required for some basal cell carcinomas that are large or regrow or occur in certain areas, such as around the nose and eyes.
People whose cancer has spread to nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body and who are not candidates for surgery or radiation therapy may be given the drug vismodegib or sonidegib taken by mouth.
Recommended Reading: How Quickly Does Renal Cell Carcinoma Grow
Answer: Basal Cell Carcinoma Growth Rate Difficult To Generalize
Well, typically BCCs grow very slowly, but there are occasions when they grow fast. If a person’s immune system is compromised , BCC can grow faster. If the cancer has been there for 5 years, typically it’s bigger than a dime, but again it’s hard to say. Each person’s BCC grow as different rates. I’m a Mohs surgeon and have seen thousands of BCCs.
What Is The Prognosis Of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
- In general, the prognosis of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is excellent, if it is detected and treated early. However, if it metastasizes to the local lymph nodes, the prognosis is guarded or unpredictable
- In such cases of metastatic BCC, its prognosis depends upon a set of several factors that include:
- Stage of tumor: With lower-stage tumors, when the tumor is confined to site of origin, the prognosis is usually excellent with appropriate therapy. In higher-stage tumors, such as tumors with metastasis, the prognosis is poor
- The surgical resectability of the tumor
- Overall health of the individual: Individuals with overall excellent health have better prognosis compared to those with poor health
- Age of the individual: Older individuals generally have poorer prognosis than younger individuals
- Whether the tumor is occurring for the first time, or is a recurrent tumor. Recurring tumors have a poorer prognosis compared to tumors that do not recur
- Response to treatment: Tumors that respond to treatment have better prognosis compared to tumors that do not respond so well to treatment
You May Like: What Does Skin Cancer On The Hand Look Like
Alternative Treatment Options: Radiation Therapy
For Squamous and Basal cell cancer, Mohs surgery is often not the only viable treatment option. The invasive nature of Mohs surgery coupled with the possibility of scarring and the need for antibiotics following the procedure makes some patients uneasy.;
If you are searching for a non-invasive alternative, youll want to learn more about Image Guided Superficial Radiotherapy . IG-SRT uses Ultrasound Imaging and Superficial Radiotherapy to treat Basal and Squamous cell cancers with a precise, measured dose of radiation delivered directly under the patients skin surface. It is completely non-invasive and has less of an effect on the patients daily life post-treatment, with no scarring, no need for antibiotics, and no requirement to stop taking certain medications prior to the procedure.
Where Does Bcc Develop
As the above pictures show, this skin cancer tends to develop on skin that has had lots of sun exposure, such as the face or ears. Its also common on the bald scalp and hands. Other common areas for BCC include, the shoulders, back, arms, and legs.
While rare, BCC can also form on parts of the body that get little or no sun exposure, such as the genitals.
Recommended Reading: Can I Donate Blood If I Had Melanoma
Mohs Microscopically Controlled Surgery
|
Because skin cancer cells often have spread beyond the edges of the visible patch on the skin, doctors sometimes use a special surgical technique to make sure they remove all of the cancer. In this technique, called Mohs microscopically controlled surgery or Mohs micrographic surgery, doctors first remove the visible tumor and then begin cutting away the edges of the wound bit by bit. During surgery, doctors examine pieces of tissue to look for cancer cells. Tissue removal from the area continues until the samples no longer contain cancer cells. This procedure enables doctors to limit the amount of tissue removed and thus is especially useful for cancers near such important sites as the eye. After removing all of the cancer, doctors decide how best to replace the skin that has been cut away. They may bring the edges of the remaining skin together with sutures or use a skin graft or skin flap. Or they may place dressings on top of the wound and let the skin heal on its own. Mohs surgery reduces recurrence rates for skin cancers. This surgery is useful for basal cell and squamous cell cancers but is less often used for melanoma. |
Pigment Basal Cell Carcinoma
The pigmentation can be found in different clinical versions of basal cell carcinoma including nodular, micronodular, multifocal and superficial BCC, and the color varies from dark brown to black . Histology showed nests of basaloid cells, abundance of melanin and melanophages, and moderate inflammatory infiltrate. The melanocytes are located among tumor nests, while the melanophages are present in the stroma. The differential diagnosis has to be made with malignant melanoma.
An irregular, periphery spreading erosive pigmented plaque on head of a 78 years old woman
Donât Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Basal Cell Carcinoma
Don’t Miss: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma Recurrence
Doctors at the Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic have seen a significant increase in the number of patients in their twenties and thirties are being treated for Basal Cell Carcinoma over the last 17 years.
Men with Basal Cell Carcinoma have outnumbered women with the disease, but more women are getting Basal Cell Carcinomas than in the past.
Regular checks at the Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic should be performed so that not only the site previously treated, but the entire skin surface can be examined, and mapped digitally and compared to the images taken at subsequent skin checks.
Basal Cell Carcinomas on the scalp and nose are especially troublesome, with higher rates of recurrence and with these recurrences typically taking place within the first two to three years following surgery.
Should a cancer recur, your Doctor might recommend a different type of treatment. Some methods, such as Mohs micrographic surgery, may be highly effective for recurrences.
What Are The Causes Of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
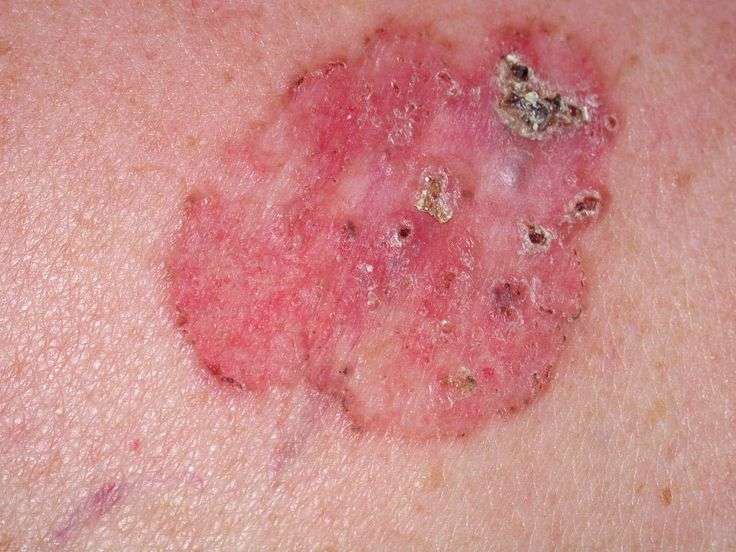
- The exact cause of development of Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma of Skin is not completely known, in a majority of cases
- Although, genetic mutations have been detected in Basal Cell Carcinomas, which are currently being characterized
- Most BCCs are sporadic in origin i.e., they occur in a random fashion
You May Like: What Are The Risk Factors Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
The Risks The Causes What You Can Do
Basal cell carcinoma is caused by damage and subsequent DNA changes to the basal cells in the outermost layer of skin. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun and indoor tanning is the major cause of BCCs and most skin cancers.
Understanding what causes BCC and the factors that increase your risk of getting it can help you prevent the disease or detect it in its earliest stages, when its easiest to treat.
These factors increase your BCC risk:
Mohs Micrographically Controlled Excision
This is a type of excision that uses a microscope to remove the lesion layer by layer until no signs of cancer are present. The microscope allows the doctor to pinpoint the cancerous areas of skin to better target removal and save healthy skin. This is a very effective form of removal with a success rate of 99 percent or higher.
Donât Miss: Is Basal Cell Carcinoma Malignant
Read Also: Can Melanoma Be Treated Successfully
How Fast Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Grow
From what I have read, basal cell carcinoma tends to be slow growing. What exactly does that mean? I am 43 years old and have a BCC located just below my nose and scheduled for Mohs surgery on Tuesday. I have had the BCC for at least 5 years, probably longer.;My surgeon tells me that there is no way to know how much tissue will be removed until surgery. Immediately following the Mohs surgery, I will see a plastic surgeon to repair the wound. My bcc is pink slightly elevated with a rolled border and a crusted indentation in the center. When i went to the dermatologist, he knew right away just from looking at it that it was a BCC, biopsy confirmed. Do they grow at a certain rate? I just want to be prepared. Any information will be helpful.
What Do Basal Cell Carcinomas Look Like
BCCs often appear as a change in your skin, such as a lump or a sore that does not heal.;
The main features are:
- slow growing ;months to years
- a pearly white, skin-coloured or pink bump;that is translucent
- waxy, small, raised lesions that may have a dent in the centre
- brown or blue-black areas, in some cases
- a scaly red flat mark on the skin, in some cases
- a tendency to bleed or turn into an ulcer
- scaly, oozing or crusted areas
- varying in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter.
You May Like: What Are The Types Of Skin Cancer
Recommended Reading: What Does Melanoma Look Like On The Leg
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
According to the Moffitt Cancer Center, squamous cell carcinoma is classified into stages from 0-4 according to how far it has spread throughout the body. Stage 0 means it hasnt spread beyond the top layer of skin. Stage 1 squamous cell has spread deeper into the skin but has not spread into healthy tissue or lymph nodes. Stage 2 squamous cells have grown deeper into the skin and have spread to additional skin layers or nerves. Stage 3 means that the cancer has spread to lymph nodes, and Stage 4 squamous cell has spread to at least one organ, such as a separate area of the skin, the lungs, or the brain.
Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma usually begins as a painless bump or nodule that grows slowly. Later, it becomes an open ulcer with a hard edge. Nearly 90% of basal cell carcinomas occur on the face, but they can appear on any part of the body that is sometimes exposed to the sunthe face, ears, neck, back, chest, arms, and legs.
Although basal cell carcinoma almost never spreads to other organs and is rarely fatal, it can invade surrounding tissue and be disfiguring if not treated.
Read Also: How Long Does Melanoma Take To Spread
Combination Therapy For Basal Cell Carcinoma
At the Bondi Junction Skin Cancer Clinic we may recommend combination therapy to treat the Basal Cell Carcinoma. Some combinations are:
Radiation And Immunologic Origins
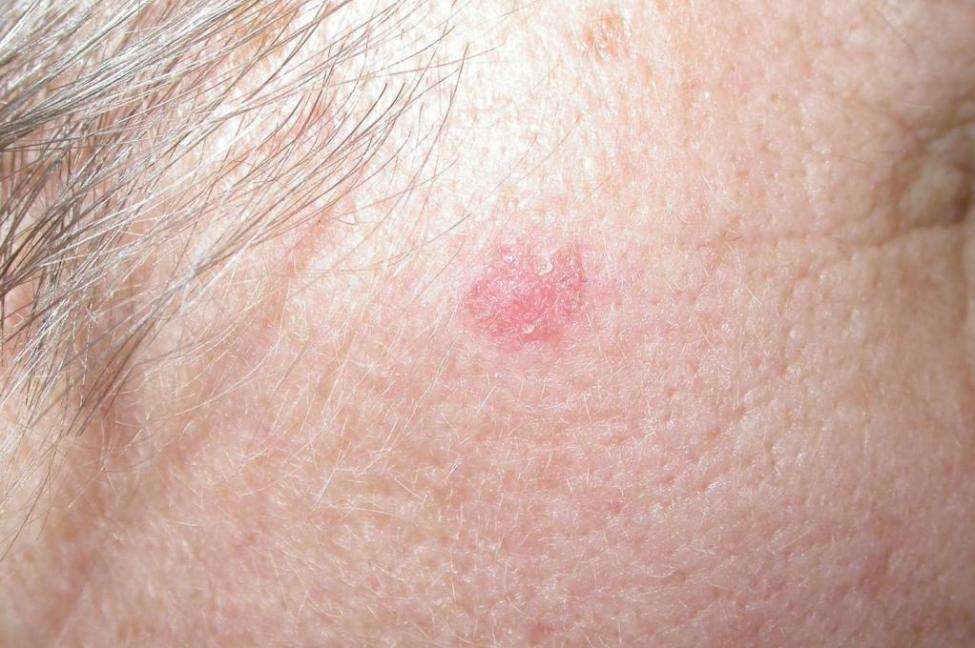
Radiation has proven to be tumorigenic by two mechanisms. The first entails the initiations of prolonged cellular proliferation, thereby increasing the likelihood of transcription errors that can lead to cellular transformation. The second mechanism is direct damage of DNA replication, leading to cellular mutation that may activate proto-oncogenes or deactivate tumor suppressor genes.
Immunologically, the mechanism by which prolonged ultraviolet radiation exposure leads to the development of BCC includes suppression of the cutaneous immune system and immunologic unresponsiveness to cutaneous tumors. This local effect includes a decrease in Langerhans cells, dendritic epidermal T cells, and Thy1+ cells. Furthermore, systemic proliferation of suppressor T cells and the release of immunosuppressive factors are believed to be pathogenic to the development of BCC.
Read Also: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
Dna Mismatch Repair Proteins
DNA mismatch repair proteins are a group of proteins that physiologically stimulate G2 cell cycle checkpoint arrest and apoptosis. Failure of MMR proteins to detect induced DNA damage results in the survival of mutating cells. MMR protein levels have been found to be higher in nonmelanoma skin cancers than in normal skin, and there is also some evidence of MMR dysregulation.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
An evidence-based approach to basal cell cancer
Basal cell cancer is relatively common. Patients often first present to the primary care provider with complaints of an abnormal skin lesion. When diagnosed early, it has an excellent prognosis, but if there is a delay in diagnosis, the tumor can advance and lead to significant morbidity. Basal cell cancer is best managed by an interprofessional team that includes a dermatologist, mohs surgeon, plastic surgeon, nurse practitioner, primary care provider, and a dermatopathologist. Basal cell carcinomas typically have a slow growth rate and tend to;be locally invasive. Tumors around the nose and eye can lead to vision loss. In most cases, surgical excision is curative. However, because recurrences can occur, these patients need long-term follow;up.
Don’t Miss: Can Skin Cancer Be Cured With Cream
Where Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Originate
Basal cell carcinoma is one of the most common forms of skin cancer worldwide. According to the American Cancer Society, about 5.4 million basal and squamous cell skin cancers are diagnosed each year and approximately 8 out of 10 of those are basal cell carcinoma. But where does it originate and how does it form?