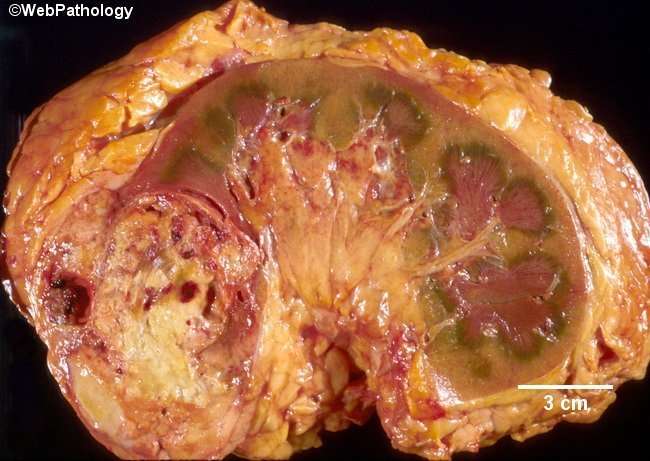
What Are The Possible Complications Of Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
The possible complications due to Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Skin could be:
- The metastasis can occur to any part of the body
- Large lesions may ulcerate and bleed resulting in superimposed bacterial or fungal infections
- Tumors that invade into nerves have higher chances of recurrence and metastasis
- Severely infiltrated or metastasized tumors may affect many body functions, depending on their location
Prognosis For Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
If carcinoma of the tongue is localized , 5-year survival is > 75%. For localized carcinoma of the floor of the mouth, 5-year survival is 75%. Lymph node metastasis decreases survival rate by about half. Metastases reach the regional lymph nodes first and later the lungs.
For lower lip lesions, 5-year survival is 90%, and metastases are rare. Carcinoma of the upper lip tends to be more aggressive and metastatic.
What Are The Risk Factors For Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Skin
Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Skin is the advanced form of SCC of skin. The chief contributing factors for squamous cell carcinoma of skin include:
- Exposure to intense sun for long periods during the course of work or due to regular participation in outdoor sports activities
- Frequent use of tanning beds, tanning parlors
- People living in geographical regions where hot-dry, desert-like climatic conditions prevail
- Radiation therapy
- Coal tar exposure
- Smoking, tobacco chewing
- Individuals with weak immune system, which could be due to cancer treatment, AIDS, or those on immunosuppressant drugs after receiving an organ transplant
- Those with sensitive skin, who get easily sunburned
- Caucasians are more vulnerable compared to other darker-toned individuals
SCC of skin in certain locations has higher chances of metastasis and they include:
- On the lips
- In the region of radiation scar
- In the region of scar due to burns
- Vulvar skin
- Perianal skin
The following subtypes are the more aggressive forms of SCC of skin, and hence, there is a greater possibility of metastasis:
- Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma of skin
- Spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma of skin
- Pseudovascular squamous cell carcinoma of skin
- Adenosquamous carcinoma of skin
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
Also Check: How Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Start
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Lungs
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lungs is one form of non-small cell lung cancer. Non-small cell lung cancers account for about 85 percent of lung cancers, and of these, roughly 30 percent are squamous cell carcinomas.
Squamous cell carcinoma begins in the tissues that line the air passages in the lungs. It is also known as epidermoid carcinoma. Most squamous cell carcinomas of the lungs are located centrally, usually in the larger bronchi that join the trachea to the lung.
Symptoms Of Squamous Papilloma
The non-cancerous growths of squamous cell papilloma rarely cause any symptoms. Wherever the growths are located, it often does not cause any pain although they can be present for a long period of time especially the ones in the mouth.
The patient can experience dysphagia which involves the difficulty in swallowing in cases when the tumors become larger, displeasing, or abnormal and affecting the throat.
Recommended Reading: Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Cure Itself
Diagnosis Of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-
Biopsy
|
Distant metastasis |
|
|
Data from Amin MB, Edge S, Greene F, Byrd DR, et al: American Joint Committee on Cancer Cancer Staging Manual, 8th edition. New York, Springer, 2017 AJCC Cancer Staging Form Supplement, 2018. For a comparison of the 7th and 8th edition, see Cramer JD, Reddy A, Ferris RL, et al: Comparison of the seventh and eighth edition American Joint Committee on Cancer oral cavity staging systems. Laryngoscope, 128:2351-2360, 2018. doi: 10.1002/lary.27205 |
Putative Genes For Basal Cell Carcinoma
BRCA1-associated protein 1
Pathogenic variants in the BAP1 gene are associated with an increased risk of a variety of cancers, including cutaneous melanoma and uveal melanoma. Although the BCC penetrance in individuals with pathogenic variants in BAP1 is not known, there are several BAP1 families that report diagnoses of BCC. In one study, pathogenic variant carriers from four families reported diagnoses of BCC. Tumor evaluation of BAP1 showed loss of BAP1 protein expression by immunohistochemistry in BCCs of two germline BAP1 pathogenic variant carriers but not in 53 sporadic BCCs. A second report noted that four individuals from families with BAP1 germline pathogenic variants were diagnosed with a total of 19 BCCs. Complete loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was observed in 17 of 19 BCCs from these individuals but none of 22 control BCC specimens. Loss of BAP1 nuclear expression was also reported in a series of 7 BCCs from individuals with loss of function BAP1 variants, but only in 1 of 31 sporadic BCCs.
Also Check: How Does Skin Cancer Occur
Scc Is Mainly Caused By Cumulative Uv Exposure Over The Course Of A Lifetime
If youve had a basal cell carcinoma you may be more likely to develop a squamous cell skin carcinoma, as is anyone with an inherited, highly UV-sensitive condition such as xeroderma pigmentosum.
Chronic infections, skin inflammation, HIV and other immune deficiency diseases, chemotherapy, anti-rejection drugs used in organ transplantation, and excessive sun exposure can all lead to a risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
Occasionally, squamous cell carcinomas arise spontaneously on what appears to be normal, healthy skin. Some researchers believe the tendency to develop these cancers can be inherited.
SCCs may occur on all areas of the body including the mucous membranes and genitals, but are most common in areas frequently exposed to the sun:
- Ears
- Previous BCC or SCC
- Chronic inflammatory skin conditions or chronic infections
But anyone with a history of substantial sun exposure is at increased risk. Those whose occupations require long hours outside or who spend their leisure time in the sun are also at risk.
What Are The Stages Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is classified into the following stages, which are partly based on how far the cancer has spread throughout the body:
- Stage 0 Squamous cell carcinoma develops in the squamous cells, which are located in the epidermis . During Stage 0, the cancer hasnt spread beyond the epidermis.
- Stage 1 When squamous cell carcinoma progresses to Stage 1, it means that the cancer has spread deeper into the skin, but not into any lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 2 A Stage 2 classification means that, in addition to progressing deeper into the skin, the cancer also displays at least one high-risk feature. This might include metastasizing to the lower skin layers or the nerves. However, at this stage, the cancer still hasnt spread to lymph nodes or healthy tissues.
- Stage 3 Once squamous cell carcinoma reaches Stage 3, the cancer has spread into lymph nodes but not any other tissues or organs.
- Stage 4 This is the final stage of squamous cell carcinoma, where the cancer has spread to at least one distant organ, whether that be the brain, the lungs or a separate area of skin.
If you think you might have squamous cell carcinoma, its important to seek prompt medical attention to minimize the risk of cancer spread. The specialists in Moffitt Cancer Centers Cutaneous Oncology Program can provide you with the comprehensive diagnostic and treatment services you need. Call or complete our new patient registration form online to request an appointment.
- BROWSE
Recommended Reading: Are There Stages Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Causes
Exposure to ultraviolet rays, like the ones from the sun or a tanning bed, affects the cells in the middle and outer layers of your skin and can cause them to make too many cells and not die off as they should. This can lead to out-of-control growth of these cells, which can lead to squamous cell carcinoma.
Other things can contribute to this kind of overgrowth, too, like conditions that affect your immune system.
Different Kinds Of Skin Cancer
There are many types of skin cancer. Some are very rare. Your doctor can tell you more about the type you have.
The two most common kinds of skin cancers are:
- Basal cell cancer, which starts in the lowest layer of the skin
- Squamous cell cancer, which starts in the top layer of the skin
Another kind of skin cancer is called melanoma. These cancers start from the color-making cells of the skin . You can read about melanoma in If You Have Melanoma Skin Cancer.
You May Like: What Are The Three Most Common Types Of Skin Cancer
How Can I Prevent Scc
Reducing ultraviolet exposure will reduce the risk of getting an SCC.
Top sun safety tips
- Protect your skin with clothing, and dont forget to wear a hat that protects your face, neck and ears, and a pair of UV protective sunglasses.
- Spend time in the shade between 11am and 3pm when its sunny. Step out of the sun before your skin has a chance to redden or burn. Keep babies and young children out of direct sunlight.
- When choosing a sunscreen look for a high protection SPF to protect against UVB, and the UVA circle logo and/or 4 or 5 UVA stars to protect against UVA. Apply plenty of sunscreen 15 to 30 minutes before going out in the sun, and reapply every two hours and straight after swimming and towel-drying.
- Sunscreens should not be used as an alternative to clothing and shade, rather they offer additional protection. No sunscreen will provide 100% protection.
- It may be worth taking Vitamin D supplement tablets as strictly avoiding sunlight can reduce Vitamin D levels. You should consult your doctor about this.
Treatment of areas of scaly sun damage may reduce your risk of an SCC.
What Is A Squamous Cell
One of three main types of cells in the top layer of the skin , squamous cells are flat cells located near the surface of the skin that shed continuously as new ones form.
SCC occurs when DNA damage from exposure to ultraviolet radiation or other damaging agents trigger abnormal changes in the squamous cells.
Read Also: What Does Stage 3b Melanoma Mean
Syndromes And Genes Associated With A Predisposition For Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Major genes have been defined elsewhere in this summary as genes that are necessary and sufficient for disease, with important pathogenic variants of the gene as causal. The disorders resulting from single-gene pathogenic variants within families lead to a very high risk of disease and are relatively rare. The influence of the environment on the development of disease in individuals with these single-gene disorders is often very difficult to determine because of the rarity of the genetic variant.
Identification of a strong environmental risk factorchronic exposure to UV radiationmakes it difficult to apply genetic causation for SCC of the skin. Although the risk of UV exposure is well known, quantifying its attributable risk to cancer development has proven challenging. In addition, ascertainment of cases of SCC of the skin is not always straightforward. Many registries and other epidemiologic studies do not fully assess the incidence of SCC of the skin owing to: the common practice of treating lesions suspicious for SCC without a diagnostic biopsy, and the relatively low potential for metastasis. Moreover, NMSC is routinely excluded from the major cancer registries such as the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results registry.
With these considerations in mind, the discussion below will address genes associated with disorders that have an increased incidence of skin cancer.
Xeroderma pigmentosum
Multiple self-healing squamous epitheliomata
Oculocutaneous albinism
How Widespread Is Scc
While SCC is less common than basal cell carcinoma , the number of reported SCC cases in the U.S. has steadily increased.
- An estimated 1.8 million cases of SCC are diagnosed each year, which translates to about 205 cases diagnosed every hour.
- SCC incidence has increased up to 200 percent in the past three decades.
Reviewed by:
Don’t Miss: Can Someone Die From Skin Cancer
Is Bowen’s Disease Serious
Bowen’s disease itself is not usually serious. It tends to grow very slowly over months or years, and there are several very effective treatments for it.
The concern is that Bowen’s disease can eventually develop into a different type of skin cancer called squamous cell skin cancer if it’s left undiagnosed or neglected.
It’s estimated this happens in up to 1 in 20 to 1 in 30 people with untreated Bowen’s disease.
Squamous cell skin cancer is often treatable, but it can spread deeper into the body and is sometimes very serious.
What About Other Treatments That I Hear About
When you have cancer you might hear about other ways to treat the cancer or treat your symptoms. These may not always be standard medical treatments. These treatments may be vitamins, herbs, special diets, and other things. You may wonder about these treatments.
Some of these are known to help, but many have not been tested. Some have been shown not to help. A few have even been found to be harmful. Talk to your doctor about anything youre thinking about using, whether its a vitamin, a diet, or anything else.
Don’t Miss: Can You Survive Stage 4 Melanoma Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages
There are certain features that are considered to make the cancer at higher risk for spreading or recurrence, and these may also be used to stage squamous cell carcinomas. These include:
- Greater than 2 mm in thickness
- Invasion into the lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Invasion into the tiny nerves in the skin
- Location on the ear or on a hair-bearing lip
After the TNM components and risk factors have been established, the cancer is assigned to one of the five squamous cell carcinoma stages, which are labeled 0 to 4. The characteristics and stages of squamous cell cancer are:
Stage 0: Also called carcinoma in situ, cancer discovered in this stage is only present in the epidermis and has not spread deeper to the dermis.
Stage 1 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is less than 2 centimeters, about 4/5 of an inch across, has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs, and has one or fewer high-risk features.
Stage 2 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer is larger than 2 centimeters across, and has not spread to nearby organs or lymph nodes, or a tumor of any size with 2 or more high risk features.
Stage 3 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer has spread into facial bones or 1 nearby lymph node, but not to other organs.
Stage 4 squamous cell carcinoma: The cancer can be any size and has spread to 1 or more lymph nodes which are larger than 3 cm and may have spread to bones or other organs in the body.
Feline Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Fact Sheet
Oral squamous cell carcinoma is a nasty disease in cats. Frequently, these tumours are not identified until the lesion has progressed significantly with associated oral pain and halitosis due to bacterial infection.
What is oral squamous cell carcinoma?
Oral squamous cell carcinoma is a cancer that arises from the cells that produce the lining of the mouth and throat including the gums, tongue, cheeks and tonsils. This cancer has an ability to grow invasively into the surrounding tissues and the visible part of the tumour is all too often just the proverbial tip of the iceberg.
Presentation
The average age for diagnosis of this disease is 11-12 years, although it has been described in cats from 2-18 years old. Presenting complaints commonly include facial deformity, loose teeth, weight loss and halitosis. Other, more subtle signs include oral pain and dribbling. Picture 1 shows an oral lesion from a patient whose only presenting complaint was a slightly reduced appetite.
Right: Oral eosinophilic granuloma in a cats mouth. An important differential diagnosis for feline oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Other conditions can affect the oral cavity that might resemble squamous cell carcinoma, such as eosinophilic granuloma complex, see picture 2. There are of course countless other causes of oral inflammation that must also be discounted.
Right: An invasive feline oral squamous cell carcinoma .
Also Check: How Young Can You Get Skin Cancer
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
Squamous cell skin cancer is mainly caused by cumulative ultraviolet exposure from the sun, according to Dr. Leffell.
Daily year-round exposure to the suns UV light and intense exposure in the summer months add to the damage that causes this type of cancer, he says. People at the highest risk for squamous cell skin cancer tend to have light or fair-colored skin blue, green or gray eyes a history of sun exposure and a tendency to sunburn quickly. Squamous cell cancers occur four times more frequently in men than in women.
Although squamous cell cancer can be more aggressive than basal cell cancer, the risk of this type of cancer spreading is lowas long as the cancer is treated early, Dr. Leffell says. He notes that the lesions must be treated with respect because they may grow rapidly and invade deeply. While it is more difficult to treat squamous cell cancer that has metastasized, up to half of cases can be cured.
In a small percentage of cases, squamous cell skin cancer can grow along the tiny nerves in the skin. In this very serious condition, the squamous cell cancer of the face or scalp can travel along the nerves and spread to the brain.
Who Is Most Likely To Have A Squamous Cell Carcinoma

The following groups of people are at greater risk of developing SCC:
- Immunosuppressed individuals either due to medical treatment, such as methotrexate, ciclosporin and azathioprine, or due to diseases which affect immune function, including inherited diseases of the immune system or acquired conditions such as leukaemia or HIV
- Patients who have had an organ transplant because of the treatment required to suppress their immune systems to prevent organ rejection
- People who are more susceptible to sunburn
- People who have had significant cumulative ultraviolet light exposure, for example:
- people who have lived in countries near to the equator, or who have been posted to work in these countries, e.g. military personnel, construction workers
- outdoor workers, such as builders, farmers
- people of advanced years, who have had a lifetime of frequent sun exposure
Also Check: What Does Advanced Skin Cancer Look Like