Cme Information And Disclosures
Statement of Need:Target Audience:AccreditationAMA PRA Credit DesignationAMA PRA Category 1 CreditsAAD Recognized CreditDisclaimer:DisclosuresEditorsPlannersResolutions of Conflicts of InterestLearning ObjectivesDate of release: November 2011Expiration date: November 2014American Academy of Dermatology:
- Supported browsers: FireFox , Google Chrome , Internet Explorer , Safari , Opera .
- JavaScript needs to be enabled.
Elsevier:
- PC: Windows NT, Windows 2000, Windows ME, or Windows XP
- Processor speed of 500MHz or higher
Confidentiality Statement:American Academy of Dermatology: POLICY ON PRIVACY AND CONFIDENTIALITYPrivacy PolicyE-mail Addresses and Other Personal InformationCookiesLinksChildren
Original Articlerisk Of Second Primary Cancer In Survivors Of In Situ Melanoma
Survivors of invasive melanoma have an increased risk of developing second primary cancers however, similar risks associated with in situ melanoma have not been established. We evaluated 39,872 survivors of first primary in situ melanoma diagnosed from 1982 through 2012 in Queensland, Australia. Relative risk of second nonmelanoma primary cancers was estimated from standardized incidence ratios with 95% confidence intervals. A total of 4,823 in situ melanoma survivors developed a second primary cancer. A small increased risk compared with the general population was found. In those younger than 50 years, risk was increased by 14% for all cancers combined. In situ melanoma survivors had significantly increased risks of developing lip, thyroid, pancreatic, and brain cancers and decreased risks of head and neck, and lung cancers. Male in situ melanoma survivors had a significantly increased risk of prostate cancer female survivors had an increased risk of thyroid cancer and lymphoid leukemia. Findings indicate that in situ melanoma may predict the diagnosis of certain second primary cancers. This altered risk may be due to biological, behavioral, or genetic factors or increased medical surveillance, and it requires further investigation, particularly among people younger than 50 years.
- Previous article in issue
Melanoma At Its Most Curable
Our authors recent research shows that melanoma in situ, the earliest form of the disease, is on the rise, especially among young men. Heres why this is bad news and good news, and what everyone needs to know to stay ahead of it.
H. WILLIAM HIGGINS II, MD, MBE, and DAVID LEFFELL, MD
Growing up in Texas, Jim was no stranger to sun exposure. A year-round athlete, he also spent many summers landscaping, and he was proud of his golden bronze tan. To achieve this look, he purposely burned during his first intense sun exposure in spring, thinking that would be a good start on maintaining a tan through the summer. He even frequented tanning salons during the winter to keep it going.
When Jims mother noticed a spot on his cheek shed never seen before, she pointed it out to him. It was dark brown, about the size of a pencil eraser, and it had an irregular shape. At first glance, it looked like a new freckle or mole. When it continued to grow, Jim became worried and visited a dermatologist. Just 29 years old, he was shocked when tests showed he had melanoma, a cancer that arises in the skins pigment-producing cells.
He was lucky, though. It was melanoma in situ: The tumor had not invaded beyond the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. The earliest form of melanoma , it is the easiest to treat and almost always curable. If Jim had waited any longer before seeing the doctor, it could have been much worse.
Don’t Miss: Basal Skin Cancer Survival Rates
Melanoma In Situ Treatment Options
Fortunately, stage 0 melanomas are, most often, easy to treat because they are the least invasive when compared to the other stages of melanoma. Typically, all that is required is excision of the affected cells and surrounding healthy tissue this type of outpatient treatment is often found to be successful. Of note, however, repeated surgical treatment may be required until all margins of the area in concern are clear.
Excision may not be ideal in the cases of malignant melanoma in situ of the head and neck due to the risk of disfiguration. Researchers at the University of Connecticut Health Center and School of Medicine have reported that the use of the 5% strength topical cream, imiquimod, healed patients suffering from facial melanoma in situ. Thus, imiquimod was found to be an effective treatment without the normal disfiguring results of excision.
How Is Melanoma In Situ Diagnosed
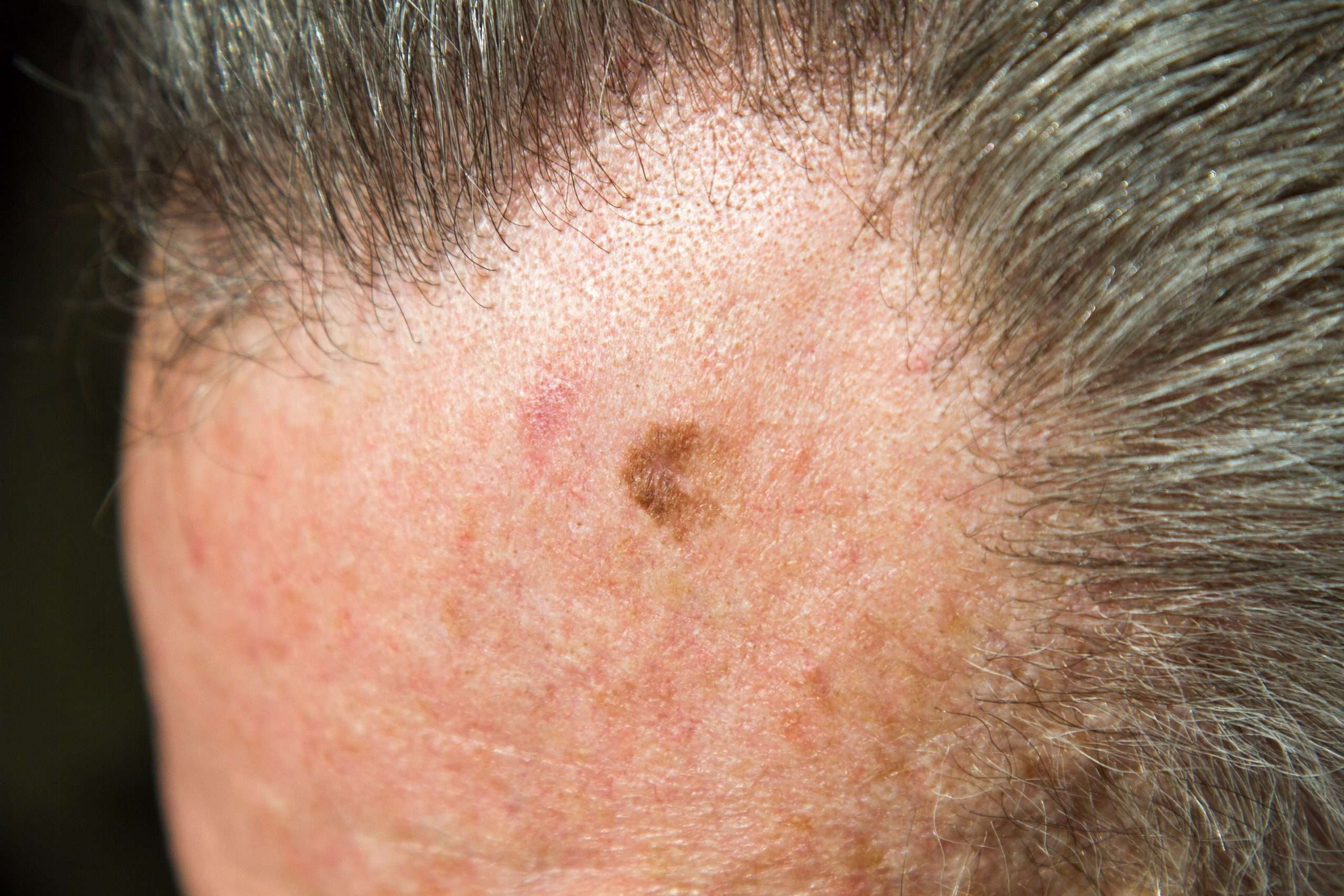
Melanoma in situ may be suspected clinically or by dermoscopy.
Diagnosis is confirmed by histological examination of the tumour and finding malignant melanocytes confined to the epidermis and epidermaladnexal structures. Breslow thickness is not reported for melanoma in situ.
- Melanoma in situ is often reported as a Clark level 1 melanoma.
- Melanoma in situ is considered Stage 0 in the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging guidelines.
Multiple sections through the specimen should be examined to ensure there are no areas of invasive disease. Immunohistochemical stains, such as micropthalmia-associated transcription factor and Sry-related HMG-BOX gene 10 , may aid diagnosis .
- In sun-damaged skin, it can be difficult to differentiate benign forms of atypical melanocytic hyperplasia and lichenoidinflammation from melanoma in situ.
- The morphology may differ between subtypes of melanoma.
- An initial diagnosis of melanoma in situ may be upstaged to invasive melanoma upon evaluating the deeper sections of a complete excision specimen.
Read Also: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
Questions To Ask Your Physician
Patients with melanoma of less than 1 millimeter should ask their physicians whether or not their melanoma demonstrated any evidence of ulceration, vertical growth phase, regression, or whether it is Clark level IV. Patients should also inquire about the treatment results achieved at the cancer center or institution where they are considering treatment.
Characteristics Of Stage 0 Melanoma
Stage 0 melanoma is a tumor limited to the epidermis. There are no subgroups for Stage 0 melanoma. In the TNM system , its described as TisN0M0:
- Tis: means Tumorin situ cancer cells are found only in the outer layer of skin , not the second layer of skin
- N0: means melanoma has not spread to the lymph nodes
- M0: means melanoma has not spread to distant sites
Risk: Patients with Stage 0 melanoma are considered at very low risk for local recurrence or for regional and distant metastases.
Recommended Reading: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Skin Checks In Future
- detect any evidence of the melanoma returning or spreading to other organs, and
- identify new melanomas.
If the original melanoma returns, it is likely to be in the first 1-2 years after diagnosis . People who have had a melanoma have an increased risk â as much as 5 to 10 fold â of developing a new melanoma in future. This increased risk persists lifelong .
The usual follow-up for a patient with melanoma in situ is:
- full body skin cancer check for melanoma and other skin cancers, plus examination of lymph nodes and abdomen for signs of spread: 6-monthly for two years, then 12-monthly for the next three years and then
- a full body skin cancer check for melanoma and other skin cancers every year for life .
Dont Use Tanning Beds Or Sunlamps
Tanning equipment like tanning beds or lamps give off the same damaging UVA and UVB rays as the sun. As a result, people who use tanning equipment have at least a 20% increased risk of melanoma.
In Ontario, the Skin Cancer Prevention Act , 2013 banned the sale and marketing of tanning services to people under 18 years of age.
Also Check: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
Treatment For Stage 0 Melanoma
The standard treatment for Stage 0 melanoma is surgery.
The purpose of the surgery is to remove any cancer remaining after the biopsy. This procedure is called a wide local excision. The surgeon removes any remaining tumor from the biopsy site, the surgical margin , and the underlying subcutaneous tissue, to make certain the whole tumor has been removed. This procedure may be done in a doctors office under local anesthetic. The width of the margin taken depends upon the thickness of the primary tumor. The surgical margin for in situ melanoma is 0.5 to 1.0 cm, based on National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines.
Some Are More Dangerous
The physician will tell you whether the melanoma is early or advanced by describing it as either in situ or invasive. In situ is Latin and means in one site or localized. Melanomas in situ occupy only the uppermost part of the epidermis, the top layers of the skin.
Invasive melanomas are the more serious, as they have penetrated more deeply into the skin and may have traveled from the original tumor through the body.
Read Also: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
What Is Stage 0 Melanoma
In Stage 0 melanoma, the malignant tumor is still confined to the upper layer of the skinthe epidermiswhich means the cancer cells are only in the outer layer of the skin and have not grown into the second layer of skin, called the dermis. Stage 0 melanoma is not considered invasive melanoma the other stages are invasive. In Stage 0 melanoma, there is no evidence the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or to distant sites . Stage 0 is local melanoma, meaning it has not spread beyond the primary tumor. Another term for Stage 0 melanoma is in situ, which means in place in Latin.
Be Aware Of Products That Increase Sun Sensitivity
Some medications or products can make your skin more sensitive to the sun . When you start a new prescription, over-the-counter medication or herbal remedy, read the product information and talk with your pharmacist. Ask if this product has been reported to make people more sensitive to the sun. If it has, you should be careful to protect yourself whenever you are in the sun.
Transplant patients have special sun protection needs. You can learn more at the Kidney Foundation of Canada.
Recommended Reading: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treatments For Early Stage Melanoma Skin Cancer
The following are treatment options for early stage melanoma skin cancer. Early stage melanoma skin cancer is only in the skin, including stage 0 , stage 1A, stage 1B, stage 2A, stage 2B and stage 2C. Your healthcare team will suggest treatments based on your needs and work with you to develop a treatment plan.
Skin Exam And Physical
If youve been diagnosed with melanoma, youve already had a skin biopsy. This biopsy was taken when you had part of the suspicious spot removed. After it was removed, a doctor looked at the spot under a microscope to find out if it contained cancer cells. This is currently the only way to tell if someone has skin cancer.
After getting the diagnosis, the next step is to get a complete skin exam and physical.
During the physical, your dermatologist will feel your lymph nodes. This is where melanoma usually goes when it begins to spread. It usually travels to the lymph nodes closest to the melanoma.
If there is a risk the cancer could have spread, your dermatologist may recommend that you have a lymph node biopsy. If a sentinel lymph node biopsy is recommended, it can be performed at the time of your surgery for melanoma.
After the skin exam and physical, your dermatologist may recommend testing, such as a CAT scan, MRI, or a blood test. These can also help detect spread.
Recommended Reading: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Is The Outcome For Melanoma In Situ
Patients with melanoma in situ have the same life expectancy as the general population. Further problems are rare from melanoma in situ because the malignant cells within the epidermis have no metastatic potential. However, a small focus of invasive disease may have beeen missed due to the impracticability of evaluating every part of a large skin lesion.
Melanoma in situ occasionally recurs at the same site, requiring further surgery.
What Is Melanoma In Situ
Melanoma is an uncontrolled growth of melanocytes, the pigment producing cells in the skin. If untreated, melanoma can spread to remote sites in the body, causing serious illness or death. Melanoma in situ is melanoma in its earliest form. The “in situ” part of the name is there because at this early stage, the cancer has not spread beyond that location. It is confined to the epidermis, an upper layer of the skin, and has not yet penetrated deeper into the skin. Melanoma in situ must be diagnosed by a skin pathologist examining the cells under a microscope to examine how far into the skin the melanoma as penetrated.
Read Also: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
Treating Stage Ii Melanoma
Wide excision is the standard treatment for stage II melanoma. The width of the margin depends on the thickness and location of the melanoma.
Because the melanoma may have spread to nearby lymph nodes, many doctors recommend a sentinel lymph node biopsy as well. This is an option that you and your doctor should discuss.
If an SLNB is done and does not find cancer cells in the lymph nodes, then no further treatment is needed, although close follow-up is still important.
If the SLNB finds that the sentinel node contains cancer cells, then a lymph node dissection will probably be done at a later date. Another option might be to watch the lymph nodes closely by getting an ultrasound of the nodes every few months.
If the SLNB found cancer, adjuvant treatment with an immune checkpoint inhibitor or targeted therapy drugs might be recommended to try to lower the chance the melanoma will come back. Other drugs or perhaps vaccines might also be options as part of a clinical trial.
Health Literacy To Empower Patients
With the right information, patients can make the best decisions about their care. By partnering with patients, healthcare providers, and hospitals, we hope to provide all patients with the tools and knowledge to understand their pathology report.
For more information about this site, contact us at .
Disclaimer: The articles on MyPathologyReport are intended for general informational purposes only and they do not address individual circumstances. The articles on this site are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment and should not be relied on to make decisions about your health. Never ignore professional medical advice in seeking treatment because of something you have read on the MyPathologyReport site. MyPathologyReport is independently owned and operated and is not affiliated with any hospital or patient portal. The articles on MyPathologyReport.ca are intended for use within Canada by residents of Canada only.
Copyright © 2020. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
Our work is generously supported by:
Don’t Miss: Does Insurance Cover Skin Cancer Screening
How Is Melanoma In Situ Treated
Melanoma in situ is treated by excision biopsy. A special tissue-sparing technique may be used for a large melanoma in situ, such as Mohs micrographic surgery or staged mapped excisions .
When surgical margins are narrow, a second surgical procedure is undertaken, including a 510mm clinical margin of normal skin, to ensure complete removal of the melanoma. This is known as wide local excision.
Non-surgical options may be considered in selected cases of melanoma in situ where surgery is contraindicated, including imiquimod cream , intralesional interferon-alpha, radiation therapy, and laser therapy. Recurrence rates are high with these second-line treatments.
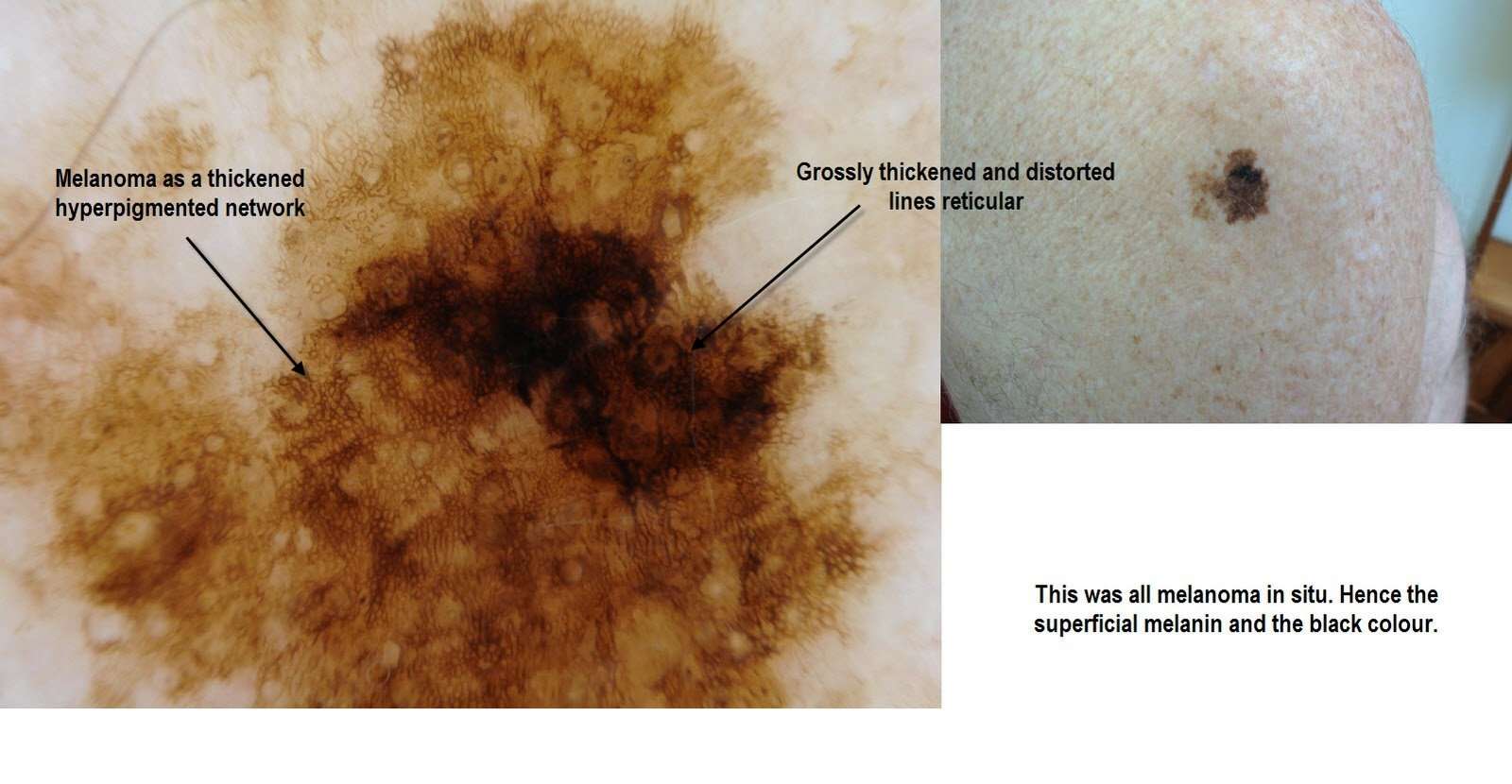
What Are The Complications Of Melanoma In Situ
Untreated, melanoma in situ slowly enlarges. Some in-situ melanomasdevelop foci or a more potentially dangerous, invasive form of melanoma.
- It is thought that less than 5% of lentigo maligna and lentiginous melanoma transform into invasive melanoma.
- The risk of melanoma in situ evolving into invasive melanoma over time is greater in superficial spreading melanoma, acral lentiginous melanoma and other forms of melanoma, but the exact risk is unknown.
You May Like: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
Recurrence In Nearby Lymph Nodes
If nearby lymph nodes werenât all removed during the initial treatment, the melanoma might come back in these lymph nodes. Lymph node recurrence is treated by lymph node dissection if it can be done, sometimes followed by adjuvant treatments such as radiation therapy and/or immunotherapy or targeted therapy . If surgery is not an option, radiation therapy or systemic treatment can be used.
What They Look Like
Melanomas in situ tend to be flat and asymmetric with irregular borders. They can be black, brown, tan, gray or even pink if the person has very fair skin. Areas that receive the greatest sun exposure, such as the scalp, face and neck, are more likely to develop melanoma in situ than the arms or legs. However, non-sun exposed areas, such as the buttocks, are also at risk. We dont always understand the causes of these melanomas, though heredity can play a role. To detect melanoma in situ as early as possible, it helps to monitor your own skin. Head-to-toe self-examinations are a good place to start, including the areas where the sun doesnt shine. When evaluating your skin, focus on the ABCDEs of melanoma detection. A stands for asymmetry B for irregular borders C for more than one color D for diameter greater than 6mm , or the size of a pencil eraser and E for evolving, meaning any lesion that is new or changing. View helpful photos showing the ABCDEs of melanoma.
You May Like: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like On Your Head
Treating Stage 0 Melanoma
Stage 0 melanoma has not grown deeper than the top layer of the skin . It is usually treated by surgery to remove the melanoma and a small margin of normal skin around it. The removed sample is then sent to a lab to be looked at with a microscope. If cancer cells are seen at the edges of the sample, a second, wider excision of the area may be done.
Some doctors may consider the use of imiquimod cream or radiation therapy instead of surgery, although not all doctors agree with this.
For melanomas in sensitive areas on the face, some doctors may use Mohs surgery or even imiquimod cream if surgery might be disfiguring, although not all doctors agree with these uses.