Treating Stage 3 Melanoma
If the melanoma has spread to nearby lymph nodes , further surgery may be needed to remove them.
Stage 3 melanoma may be diagnosed by a sentinel node biopsy, or you or a member of your treatment team may have felt a lump in your lymph nodes.
The diagnosis of melanoma is usually confirmed using a needle biopsy .
Removing the affected lymph nodes is done under general anaesthetic.
The procedure, called a lymph node dissection, can disrupt the lymphatic system, leading to a build-up of fluids in your limbs. This is known as lymphoedema.
Cancer Research UK has more information about surgery to remove lymph nodes.
Treating Stage 4 Melanoma
If melanoma comes back or spreads to other organs it’s called stage 4 melanoma.
In the past, cure from stage 4 melanoma was very rare but new treatments, such as immunotherapy and targeted treatments, show encouraging results.
Treatment for stage 4 melanoma is given in the hope that it can slow the cancer’s growth, reduce symptoms, and extend life expectancy.
You may be offered surgery to remove other melanomas that have grown away from the original site. You may also be able to have other treatments to help with your symptoms, such as radiotherapy and medicine.
If you have advanced melanoma, you may decide not to have treatment if it’s unlikely to significantly extend your life expectancy, or if you do not have symptoms that cause pain or discomfort.
It’s entirely your decision and your treatment team will respect it. If you decide not to receive treatment, pain relief and nursing care will be made available when you need it. This is called palliative care.
Ajcc Stage Groupings And Tnm Definitions
The American Joint Committee on Cancer has designated staging by TNM classification to define melanoma.
Cancers staged using this staging system include cutaneous melanoma. Cancers not staged using this system include melanoma of the conjunctiva, melanoma of the uvea, mucosal melanoma arising in the head and neck, mucosal melanoma of the urethra, vagina, rectum, and anus, Merkel cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
AJCC Prognostic Stage Groups-Clinical
| Stage | N Category | M Category |
|---|---|---|
| T = primary tumor N = regional lymph node M = distant metastasis c = clinical LDH = lactate dehydrogenase No. = number. | ||
| aAdapted from AJCC: Melanoma of the Skin. In: Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, et al., eds.: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York, NY: Springer, 2017, pp. 56385. | ||
| bThickness and ulceration status not applicable. | ||
| 0 | N0 = No regional metastases detected. | M0 = No evidence of distant metastasis. |
AJCC Prognostic Stage Groups-Pathological
References
Read Also: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of The Head And Neck
Tnm Categories And Subcategories For Stage Iii Melanoma
T means Tumor. This category is related to your primary melanoma tumor.
T0 means no evidence of a primary tumor.
The T1 category includes tumors that are less than 1.0 mm thick. T1 subcategories:
- T1a tumors are less than 0.8 mm thick and are not ulcerated.
- T1b tumors are less than 0.8 mm thick and are ulcerated or are 0.8 to 1.0 mm thick and can be ulcerated or not.
The T2 category includes tumors that are greater than 1.0 mm and up to 2.0 mm thick. T2 subcategories:
- T2a tumors are greater than 1.0 mm and up to 2.0 mm thick and do not have ulceration.
- T2b tumors are greater than 1.0 mm and up to 2.0 mm thick and are ulcerated.
The T3 category includes tumors that are 2.0 to 4.0 mm thick. T3 subcategories:
- T3a tumors are 2.0 to 4.0 mm thick and are not ulcerated.
- T3b tumors are 2.0 to 4.0 mm thick and are ulcerated.
The T4 category includes tumors that are greater than 4.0 mm thick. T4 subcategories:
- T4a tumors are greater than 4.0 mm thick and are not ulcerated.
- T4b tumors are greater than 4.0 mm thick and are ulcerated.
N means Node. This category is related to the regional spread of your melanoma, beyond the primary tumor.
The N1 category comprises spread to only one lymph node OR there is in-transit, satellite, or microsatellite metastasis. N1 subcategories:
The N2 category comprises spread to two or three lymph nodes OR that there is in-transit, satellite, or microsatellite metastases AND one positive lymph node. N2 subcategories:
Treating Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage IV melanomas have already spread to distant lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
Metastases in internal organs are sometimes removed, depending on how many there are, where they are, and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab are typically the first drugs tried, especially in people whose cancer cells do not have BRAF gene changes. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Ipilimumab , a different type of checkpoint inhibitor, is not typically used by itself as the first treatment, although it might be combined with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. This slightly increase the chances that the tumor will shrink, although itâs also more likely to result in serious side effects, which needs to be considered carefully. People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects..
Itâs important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.
You May Like: Skin Cancer Prognosis
Treatments For Stage Iii Melanoma
Stage III melanoma has multiple treatment options and can include surgery , neo-adjuvant therapy, adjuvant therapy, radiation therapy, and clinical trials. You will likely see a surgical oncologist for the surgery-related treatments and a medical oncologist for the drug-related treatments. If you have any radiation treatments, you will see a radiation oncologist.
It is important to know whether all of your Stage III melanoma has been completely removed with surgery , or if it was not possible to remove all of the melanoma . These two types of Stage III melanoma are treated very differently. Unresectable Stage III patients are treated similarly to Stage IV melanoma patients. Read about Stage IV melanoma.
Order of Treatment
Patients with melanoma often receive more than one type of treatment, and certain terms are used to describe the order of treatments given. Neo-adjuvant treatment is what is given before primary treatmentin melanoma, primary treatment is generally surgeryto shrink tumors. For Stage III patients, neo-adjuvant treatment is mostly given in clinical trials. Primary treatment is the main treatment to remove cancer. Adjuvant treatment is given after primary treatment to kill any remaining cancer cells. FDA-approved adjuvant therapies for Stage III are noted below.
Surgery
The standard treatment for all primary melanoma is a surgery called wide local excision. The purpose of the surgery is to remove any cancer remaining after the biopsy of the primary tumor.
Historic Progress New Options More Hope
While melanoma is one of the most dangerous forms of skin cancer, promising new treatment options are improving quality of life and increasing survival rates for patients with advanced melanoma.
If youve been diagnosed, your treatment choices depend on the stage of the disease, the location of the tumor and your overall health. Options include:
You May Like: Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rates
Terapiji Li Juaw Medikazzjoni
L-uu ta ‘mediini biex joqtlu -elloli tal-kaner huwa magruf bala trattament sistemiku. Din it-tip ta droga tii injettata fid-demm biex tilaq i-elloli tal-kaner madwar il-isem kollu. Onkologu mediku, kliniista li jispejalizza fl-uu ta ‘mediini gall-kura tal-kaner, normalment jippreskrivi terapija sistemika.
Tubu ol-vini imdaal o vina b’labra, jew pillola jew kapsula li tittiekel, huma ew modi komuni kif jiu amministrati mediini sistemii.
It-tipi ta terapiji sistemii uati gall-melanoma jinkludu:
- immunoterapija
- Terapija mmirata
- kimoterapija
Kull wada minn dawn it-tipi ta ‘terapija hija koperta aktar fil-fond aktar ‘l isfel. Forma wada ta ‘terapija sistemika tista’ tingata kull darba, jew trattamenti sistemii varji jistgu jiu pprovduti simultanjament. Jistgu jintuaw ukoll ma ‘kirurija u terapija bir-radjazzjoni.
Il-mediini uati gall-kura tal-kaner qed jiu ttestjati l-in kollu. L-ajar appro biex tifhem il-preskrizzjonijiet mogtija galik, l-iskop taghom, u kwalunkwe effett negattiv potenzjali jew kombinazzjoni ma ‘mediini ora huwa li tkellem mat-tabib tiegek. Huwa wkoll krujali li tinforma lit-tabib tiegek jekk qed tieu xi mediini jew supplimenti addizzjonali, rietta jew mingajr rietta. It-trattamenti tal-kaner jistgu jinteraixxu ma ‘xejjex aromatii, vitamini, u mediini ora.
immunoterapija
Inibituri PD-1 u PD-L1
Inibituri CTLA-4
Jikkombinaw inibituri PD-1 u CTLA-4
Interleukin-2
Terapija tal-virus
Interferon
Treatment By Stage Of Melanoma
Different treatments may be recommended for each stage of melanoma. General descriptions by stage are below. Your doctor will recommend a specific treatment plan for you based on the stage and other factors. Detailed descriptions of each type of treatment are provided earlier on this page. Clinical trials may also be a treatment option for each stage.
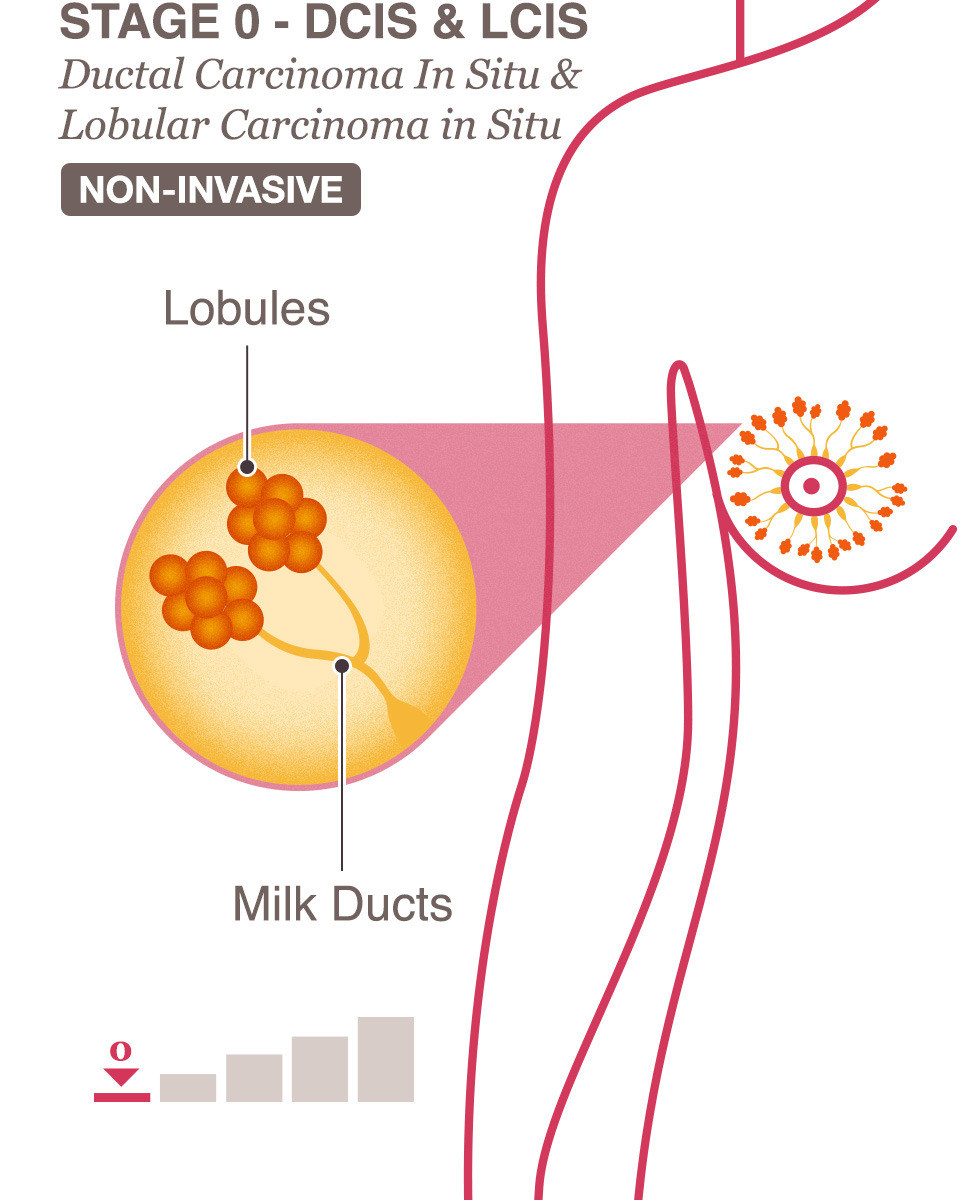
Stage 0 melanoma
Stage 0 melanoma is almost always treated with surgery alone, usually a wide excision.
Stage I melanoma
Stage I melanoma is usually treated with surgical removal of the tumor and some of the healthy tissue around it. The doctor may recommend lymph node mapping, and some lymph nodes may be removed.
Stage II melanoma
The standard treatment for stage II melanoma is surgery to remove the tumor and some of the healthy tissue around it. While this surgery is being done, lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy may also be done. In some people with stage II melanoma, treatment with interferon may be recommended after surgery to lower the chances of the cancer coming back. Treatment in a clinical trial for stage II melanoma may also be an option. Ask your doctor about what clinical trials may be available for you.
Stage III melanoma that can be removed with surgery
Advanced melanoma
-
The persons age and overall health
-
The locations and number of metastases
-
How fast the disease is spreading
-
The presence of specific genetic mutations in the tumor
-
The patients preferences
Treating brain metastases
Don’t Miss: Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch
What Are The Treatment Options For Melanoma
Treatment of stage II melanoma may include the following:
- Surgery to remove the tumor and some of the normal tissue around it.
- Surgery followed by immunotherapy with interferon if there is a high risk that the cancer will come back.
- A clinical trial of new types of treatment to be used after surgery.
Write Your Answer
If Treatment Does Not Work
Recovery from melanoma is not always possible. If the cancer cannot be cured or controlled, the disease may be called advanced or terminal.
This diagnosis is stressful, and for many people, advanced cancer is difficult to discuss. However, it is important to have open and honest conversations with your health care team to express your feelings, preferences, and concerns. The health care team has special skills, experience, and knowledge to support patients and their families and is there to help. Making sure a person is physically comfortable, free from pain, and emotionally supported is extremely important.
People who have advanced cancer and who are expected to live less than 6 months may want to consider hospice care. Hospice care is designed to provide the best possible quality of life for people who are near the end of life. You and your family are encouraged to talk with the health care team about hospice care options, which include hospice care at home, a special hospice center, or other health care locations. Nursing care and special equipment can make staying at home a workable option for many families. Learn more about advanced cancer care planning.
After the death of a loved one, many people need support to help them cope with the loss. Learn more about grief and loss.
Don’t Miss: Metastatic Skin Cancer Pictures
Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
Melanoma and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Palliative care focuses on improving how you feel during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after a cancer diagnosis. People who receive palliative care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, and report that they are more satisfied with treatment.
Palliative treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies. You may also receive palliative treatments similar to those meant to get rid of the cancer, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Learn more about the importance of tracking side effects in another part of this guide. Learn more about palliative care in a separate section of this website.
What Is Melanoma Cancer
Melanoma is a serious type of skin cancer. Most melanoma is treated surgically, and in many cases this surgery is curative. Through numerous clinical trials, the surgery that is required to treat melanoma has become less invasive. A number of these less radical procedures were pioneered at the Saint Johns Cancer Institute Melanoma Program.
100,350people in the U.S. will be diagnosed with melanoma in 2020 and the American Cancer Society estimates that number will continue to increase year after year.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
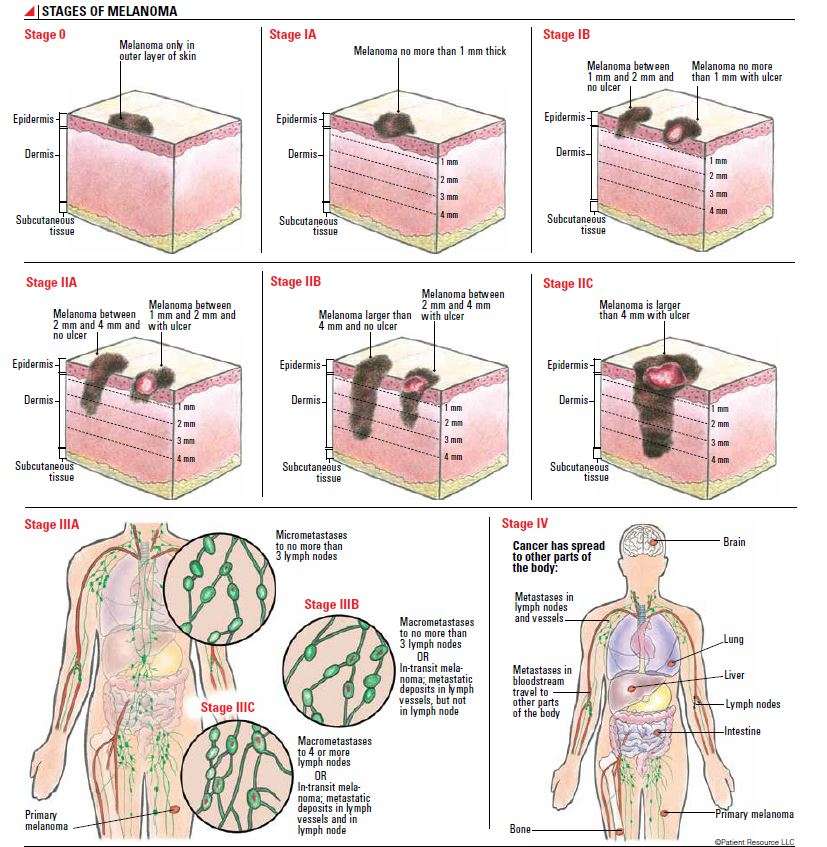
Stages Of Melanoma Skin Cancer
Staging describes or classifies a cancer based on how much cancer there is in the body and where it is when first diagnosed. This is often called the extent of cancer. Information from tests is used to find out the size of the tumour, which parts of the skin have cancer, whether the cancer has spread from where it first started and where the cancer has spread. Your healthcare team uses the stage to plan treatment and estimate the outcome .
The most common staging system for melanoma skin cancer is the TNM system. For melanoma skin cancer there are 5 stages stage 0 followed by stages 1 to 4. Often the stages 1 to 4 are written as the Roman numerals I, II, III and IV. Generally, the higher the stage number, the more the cancer has spread. Talk to your doctor if you have questions about staging.
When describing the stage, doctors often use the words early stage, locoregional or metastatic.
Early stage means that the cancer is only in where it started and has not spread to other parts of the body. It includes stage 0, stage 1A, stage 1B, stage 2A, stage 2B and stage 2C melanoma skin cancers.
Locoregional means the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, or it has spread to nearby areas of skin or lymph vessels. It includes stage 3 melanoma skin cancer.
Metastatic means that the cancer is in a part of the body farther from where it started. It includes stage 4 melanoma skin cancer.
Find out more about .
Treatments For Stage I Melanoma
Your doctor will most likely treat stage 1 melanoma with surgery called wide excision, which cuts out the melanoma along with a margin of healthy surrounding skin. The amount of healthy skin removed is determined by the location and the thickness of the melanoma being treated.
While wide excision surgery is often the only treatment necessary, in some cases a doctor may also choose to check for cancer in nearby lymph nodes by performing a sentinel lymph node biopsy. If cancer cells are found in the lymph nodes, further treatment will become necessary, such as a lymph node dissection , chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapies.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Survival Rate Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Complementary And Alternative Treatments
It’s common for people with cancer to seek out complementary or alternative treatments. When used alongside your conventional cancer treatment, some of these therapies can make you feel better and improve your quality of life. Others may not be so helpful and in some cases may be harmful.
It is important to tell all your healthcare professionals about any complementary medicines you are taking. Never stop taking your conventional treatment without consulting your doctor first.
All treatments can have side effects. These days, new treatments are available that can help to make many side effects much less severe than they were in the past.
Treatments For Early Stage Melanoma Skin Cancer
The following are treatment options for early stage melanoma skin cancer. Early stage melanoma skin cancer is only in the skin, including stage 0 , stage 1A, stage 1B, stage 2A, stage 2B and stage 2C. Your healthcare team will suggest treatments based on your needs and work with you to develop a treatment plan.
You May Like: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
Characteristics Of Stage I Melanoma
Stage I melanomas are defined by two primary characteristics: tumor thickness and ulceration.
Tumor thickness : how deeply the tumor has penetrated the skin. Thickness is measured in millimeters . These comparisons will give you an idea of size:
- 1 mm = .04 inch, or less than 1/16 inchabout equal to the edge of a penny
- 2 mm = between 1/16 and 1/8 inchabout equal to the edge of a nickel
Ulceration: when the epidermis that covers a portion of the primary melanoma is not intact. Ulceration can only be seen under a microscope, not by the naked eye.