Screening For Cancerous Moles
If a mole looks or acts at all peculiarly it is best to have it evaluated by an expert. This frequently is a dermatologist. Most dermatologists can tell if the pigmented lesion is composed of melanocytes or is something quite different with no possibility of being a melanoma. Many dermatologists now use a hand-held magnifying device which produces polarized light to evaluate colored melanocytic tumors. The use of this instrument improves the doctor’s ability to identify suspicious lesions.
Treatment For Skin Cancer
If you are diagnosed with skin cancer, you may have multiple options for treatment. Based on the specifics of your case, your doctor will recommend your best course of action. The suggested methods for fighting the cancer may include:
-
Cryotherapy. In cryotherapy, a doctor freezes and kills precancerous or cancerous skin cells using liquid nitrogen. This technique is most often used to treat minor basal or squamous carcinomas or precancerous skin conditions.
-
Surgery. Different types of skin cancer may be removed by surgery. Surgery can be excisional – simply cutting out a cancerous area and the skin surrounding it – or may involve meticulous removal of layers of skin.
-
Radiation therapy. In radiation therapy, energy beams are used to kill cancerous cells. Radiation therapy may help finish off a cancer that was not fully removed by surgery, and can also be instrumental in cases that dont allow for surgery.
-
Chemotherapy. This type of therapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. To treat some cases of skin cancer, chemotherapy may be applied locally through topical creams or lotions. It may also be administered by IV to target multiple body parts at once.
-
Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy, also called biological therapy, involves boosting the immune system to fight cancer cells. With the help of strengthening medicines, the immune system may be better prepared to kill cancerous cells.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Early Stages
Basal cells are found within the skin and are responsible for producing new skin cells as old ones degenerate. Basal cell carcinoma starts with the appearance of slightly transparent bumps, but they may also show through other symptoms.
In the beginning, a basal cell carcinoma resembles a small bump, similar to a flesh-colored mole or a pimple. The abnormal growths can also look dark, shiny pink, or scaly red in some cases.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Signs And Symptoms
Generally found on the ears, face and mouth, squamous cell carcinoma can be more aggressive than basal cell. Untreated, it may push through the skin layers to the lymphatic system, bloodstream and nerve routes, where it can cause pain and symptoms of serious illness.
Appearance
Squamous cell cancer often starts as a precancerous lesion known as actinic keratosis . When it becomes cancerous, the lesion appears raised above the normal skin surface and is firmer to the touch. Sometimes the spot shows only a slight change from normal skin.
Other signs include:
- Any change, such as crusting or bleeding, in an existing wart, mole, scar or other skin lesion
- A wart-like growth that crusts and sometimes bleeds
- A scaly, persistent reddish patch with irregular borders, which may crust or bleed
- A persistent open sore that does not heal and bleeds, crusts or oozes
- A raised growth with a depression in the center that occasionally bleeds and may rapidly increase in size
Who Gets Skin Cancer And Why
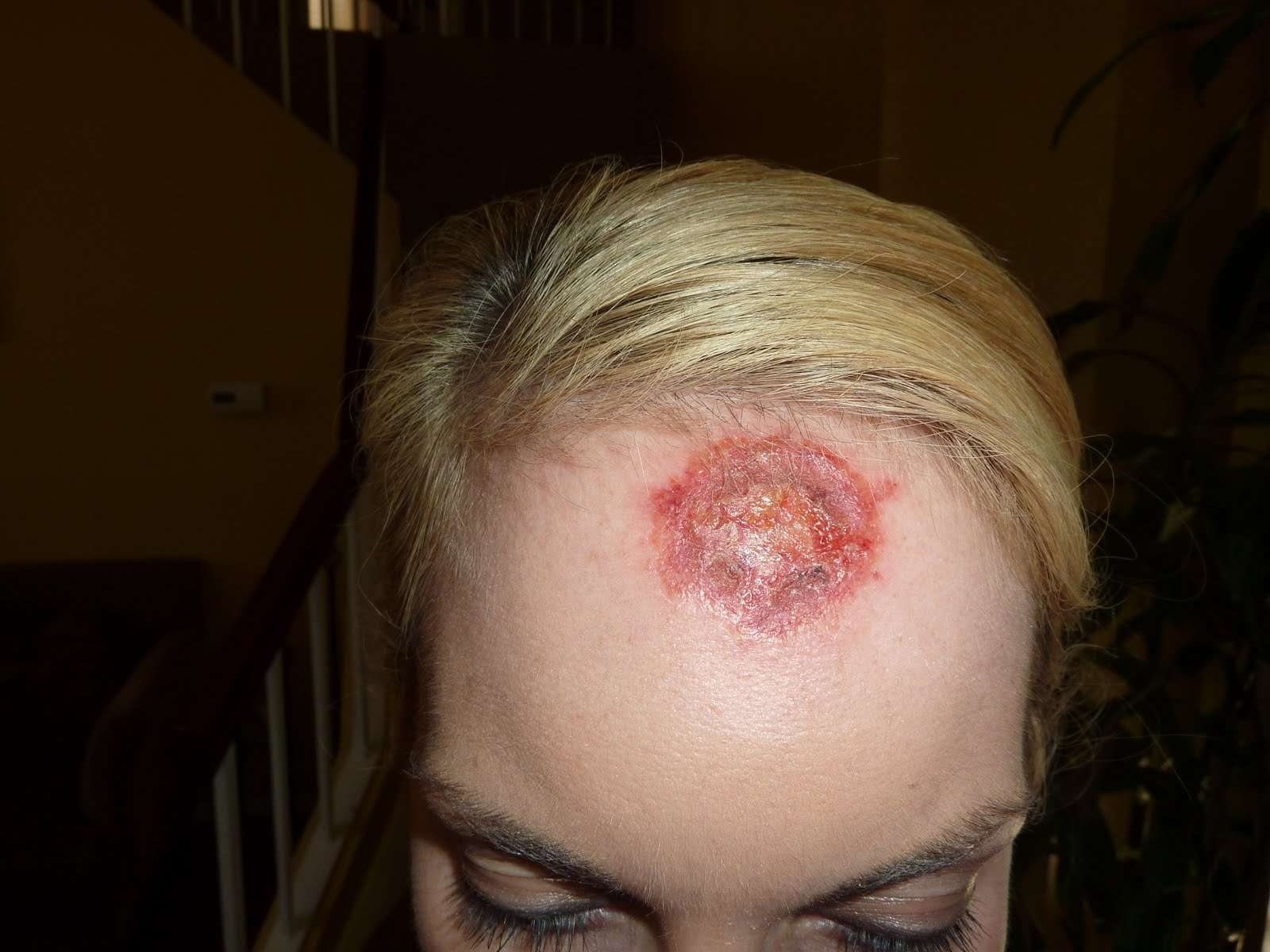
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. But it doesn’t explain skin cancers that develop on skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Exposure to environmental hazards, radiation treatment, and even heredity may play a role. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is greatest for people who have:
- Fair skin or light-colored eyes
- An abundance of large and irregularly-shaped moles
- A family history of skin cancer
- A history of excessive sun exposure or blistering sunburns
- Lived at high altitudes or with year-round sunshine
- Received radiation treatments
Also Check: Cancer Lesion Pictures
What Are Squamous Cell Carcinomas
The Cancer Council describes Squamous cell carcinoma as the second most common form of skin cancer and can develop on any part of the body that receives sun exposure. Squamous cell carcinoma isnt as dangerous as melanoma but can spread to other parts of the body if not treated. Squamous cell carcinoma usually develops when the cells in the top layer of the skin grow and divide in an uncontrolled way.
It takes more than typical exposure to the radiation of the sun to develop this disease and using tanning beds, tanning oil or forgoing sun protection can increase the risk of contracting squamous cell carcinoma exponentially. Squamous cell carcinoma can be aggressive cancer if left untreated and has a risk of spreading quickly to other parts of the body such as the lymph nodes.
How Your Skin Works
Your skin works as a barrier to protect your body against things like water loss, bacteria, and other harmful contaminants. The skin has two basic layers: a deeper, thicker layer and an outer layer . The epidermis contains three main types of cells. The outermost layer is composed of squamous cells, which are constantly shedding and turning over. The deeper layer is called the basal layer and is made of basal cells. Lastly, melanocytes are cells that make melanin, or the pigment that determines your skin color. These cells produce more melanin when you have more sun exposure, causing a tan. This is a protective mechanism by your body, and its actually a signal that you are getting sun damage.
The epidermis is in constant contact with the environment. While it sheds skin cells regularly, it can still sustain damage from the sun, infection, or cuts and scrapes. The skin cells that remain are constantly multiplying to replace the sloughed skin, and they can sometimes begin to replicate or multiply excessively, creating a skin tumor that may either be benign or skin cancer.
Here are some common types of skin masses:
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate
Does Skin Cancer Look Like A Scab
4.6/5doWhat it looks likeskinfull detail here
“Squamous cell cancers, which can metastasize if left untreated, are often reddish marks that will scab, flake off, then scab again,” Bank says. If you draw a line through the middle of a benign mole, the two halves will line up. Cancerous cells don’t grow evenly.
Subsequently, question is, what does early signs of skin cancer look like? Melanoma signs include: A large brownish spot with darker speckles. A mole that changes in color, size or feel or that bleeds. A small lesion with an irregular border and portions that appear red, pink, white, blue or blue-black.
Just so, does skin cancer scab and bleed?
The skin features that frequently develop are listed below. For basal cell carcinoma, 2 or more of the following features may be present: An open sore that bleeds, oozes, or crusts and remains open for several weeks. A reddish, raised patch or irritated area that may crust or itch, but rarely hurts.
What is a scab that won’t heal?
Chronic wounds, by definition, are sores that don’t heal within about three months. They can start small, as a pimple or a scratch. They might scab over again and again, but they don’t get better.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that can show up on the skin in many ways. Also known as BCC, this skin cancer tends to grow slowly and can be mistaken for a harmless pimple, scar, or sore.
Common signs and symptoms of basal cell carcinoma
This skin cancer often develops on the head or neck and looks like a shiny, raised, and round growth.
To help you spot BCC before it grows deep into your skin, dermatologists share these 7 warning signs that could be easily missed.
If you find any of the following signs on your skin, see a board-certified dermatologist.
Recommended Reading: What Stage Is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
What Causes Skin Cancer
Ultraviolet light exposure, most commonly from sunlight, is overwhelmingly the most frequent cause of skin cancer.
Other important causes of skin cancer include the following:
- Use of tanning booths
- Immunosuppression – This means impairment of the immune system. The immune system protects the body from foreign entities, such as germs or substances that cause an allergic reaction. This suppression may occur as a consequence of some diseases or can be due to medications prescribed to combat conditions such as autoimmune diseases or prevent organ transplant rejection.
- Exposure to unusually high levels of X-rays
- Contact with certain chemicals-arsenic , hydrocarbons in tar, oils, and soot
The following people are at the greatest risk:
- People with fair skin, especially types that freckle, sunburn easily, or become painful in the sun
- People with light hair and blue or green eyes
- Those with certain genetic disorders that deplete skin pigment such as albinism, xeroderma pigmentosum
- People who have already been treated for skin cancer
- People with numerous moles, unusual moles, or large moles that were present at birth
- People with close family members who have developed skin cancer
- People who had at least one severe sunburn early in life
A basal cell carcinoma usually looks like a raised, smooth, pearly bump on the sun-exposed skin of the head, neck, or shoulders.
A squamous cell carcinoma is commonly a well-defined, red, scaling, thickened patch on sun-exposed skin.
Curettage Electrodesiccation And Cryotherapy
Some dermatologists perform curettage, electrodesiccation, and cryotherapy to treat skin cancer. These are considered to be destructive techniques that are best suited for small, superficial carcinomas with definite borders. During the procedure, layers of skin cells are scraped away using a curette. Any remaining cancer cells are destroyed with the use of an electric needle.
In some cases, liquid nitrogen or cryotherapy is used to freeze the margins of the treatment area. Extremely low temperatures kill the malignant skin cells and create a wound, which will heal in a few weeks. The treatment may leave scars that are flat and round, similar to the size of the skin cancer lesion.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Survival Rate
I Feel Too Embarrassed To Touch Myself
The most serious and potentially deadly skin cancer. Consult a dermatologist if a mole changes in size, shape or color, has irregular edges, is more than one color, is asymmetrical or itches, oozes or bleeds.
Can look like a waxy or white bump, a scaly patch or an unhealed sore.
Could appear as a red nodule or rough bump, a scaly growth that bleeds or develops a crust, or a sore that doesnt heal. It most often appears on the nose, forehead, ears, lower lip, hands, and other sun-exposed areas of the body.
When In Doubt Get It Checked Out
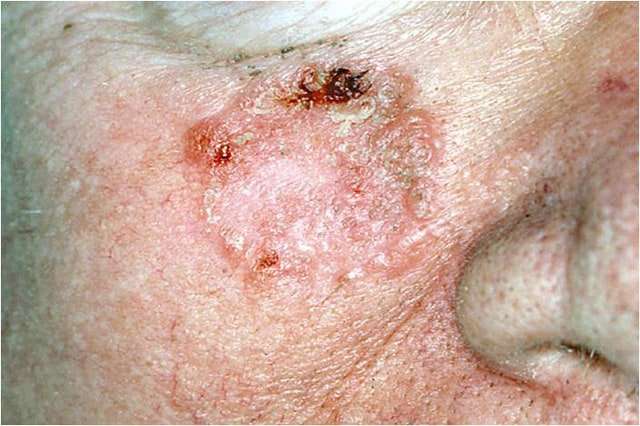
If you have any spots that sound like the above descriptions, or any spots that have changed and look different from how they looked a few months or years ago, then schedule an appointment for a full-body skin check to get those spots and all of your other spots evaluated to see if they need a biopsy.
Skin cancers can recur even after they have been removed properly. It is important to follow up with your dermatology specialist every 6 to 12 months to make sure the site is still healed and also to check for new spots. It is also important to take proper sun avoidance precautions to protect yourself from further sun damage that could cause more skin cancers.
Call and book your dermatology appointment in Ashburn, VA now 703-574-2588
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Early Stages
The second most common form of cancer in the skin is squamous cell carcinoma. At first, cancer cells appear as flat patches in the skin, often with a rough, scaly, reddish, or brown surface. These abnormal cells slowly grow in sun-exposed areas. Without proper treatment, squamous cell carcinoma can become life-threatening once it has spread and damaged healthy tissue and organs.
The Ugly Duckling Method
The ugly duckling method works on the premise that a personâs moles tend to resemble one another. If one mole stands out in any way, it may indicate skin cancer.
Of course, not all moles and growths are cancerous. However, if a person notices any of the above characteristics, they should speak with a doctor.
Recommended Reading: Etiology Of Skin Cancer
How To Diagnose Skin Cancer
First, a doctor will examine a personâs skin and take their medical history. They will usually ask the person when the mark first appeared, if its appearance has changed, if it is ever painful or itchy, and if it bleeds.
The doctor will also ask about the personâs family history and any other risk factors, such as lifetime sun exposure.
They may also check the rest of the body for other atypical moles and spots. Finally, they may feel the lymph nodes to determine whether or not they are enlarged.
The doctor may then refer a person to a skin doctor, or dermatologist. They may examine the mark with a dermatoscope, which is a handheld magnifying device, and take a small sample of skin, or a biopsy, and send it to a laboratory to check for signs of cancer.
The Signs Of Skin Cancer
Youve likely been told to look out for moles that change colour or size, but many more common types of skin cancer dont look like moles at all.
Skin cancer can come in the form of red sores, wart-like bumps, or even scaly patches. We tell people to look for anything new, or anything that doesnt heal after a while, explains Cheryl Rosen, a dermatologist at Toronto Western Hospital.
Read on to learn about the various types of skin cancers, what they look like, and how theyre treated.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Pictures
Squamous cell carcinoma also appears in areas most exposed to the sun and, as indicated in the pictures below, often presents itself as a scab or sore that doesnt heal, a volcano-like growth with a rim and crater in the middle or simply as a crusty patch of skin that is a bit inflamed and red and doesnt go away over time.
Any lesion that bleeds or itches and doesnt heal within a few weeks may be a concern even if it doesnt look like these Squamous cell carcinoma images.
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Infiltrative basal cell carcinoma occurs when a tumor makes its way into the dermis via thin strands between collagen fibers. This aggressive type of skin cancer is harder to diagnose and treat because of its location. Typically, infiltrative basal cell carcinoma appears as scar tissue or thickening of the skin and requires a biopsy to properly diagnose.
To remove this type of basal cell carcinoma, a specific form of surgery, called Mohs, is used. During a Mohs surgery, also called Mohs micrographic surgery, thin layers of skin are removed until there is no cancer tissue left.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
DermNet NZ
Superficial basal cell carcinoma, also known as in situ basal-cell carcinoma, tends to occur on the shoulders or the upper part of the torso, but it can also be found on the legs and arms. This type of cancer isnt generally invasive because it has a slow rate of growth and is fairly easy to spot and diagnose. It appears reddish or pinkish in color and may crust over or ooze. Superficial basal cell carcinoma accounts for roughly 15%-26% of all basal cell carcinoma cases.
You May Like: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
Determining If The Cancer Has Spread
As part of your diagnosis, your doctor will also determine what stage the cancer is in. The different stages refer to whether and how far the cancer has spread in your body, on a Roman numeral scale of I to IV. A stage I cancer is small and contained to the body part where it originated, whereas a stage IV cancer has spread aggressively to other parts of the body.
Depending on the type of skin cancer that a person has, it may be more or less likely that it has spread through the body. For instance, basal cell skin cancer rarely spreads beyond the skin where it starts. However, melanomas and large squamous cell carcinomas are more likely to spread into other regions of the body. Cases of melanoma, in particular, may call for further tests to determine the specific stage theyre in.
Your doctor may evaluate multiple factors in order to stage the cancer. Using biopsies and imaging tests, your doctor may take a look at:
-
The size and thickness of the tumor, and whether it has grown into surrounding tissues
-
Nearby lymph nodes, to check for signs of cancer spread
Skin Cancer Pictures: What Does Skin Cancer Look Like
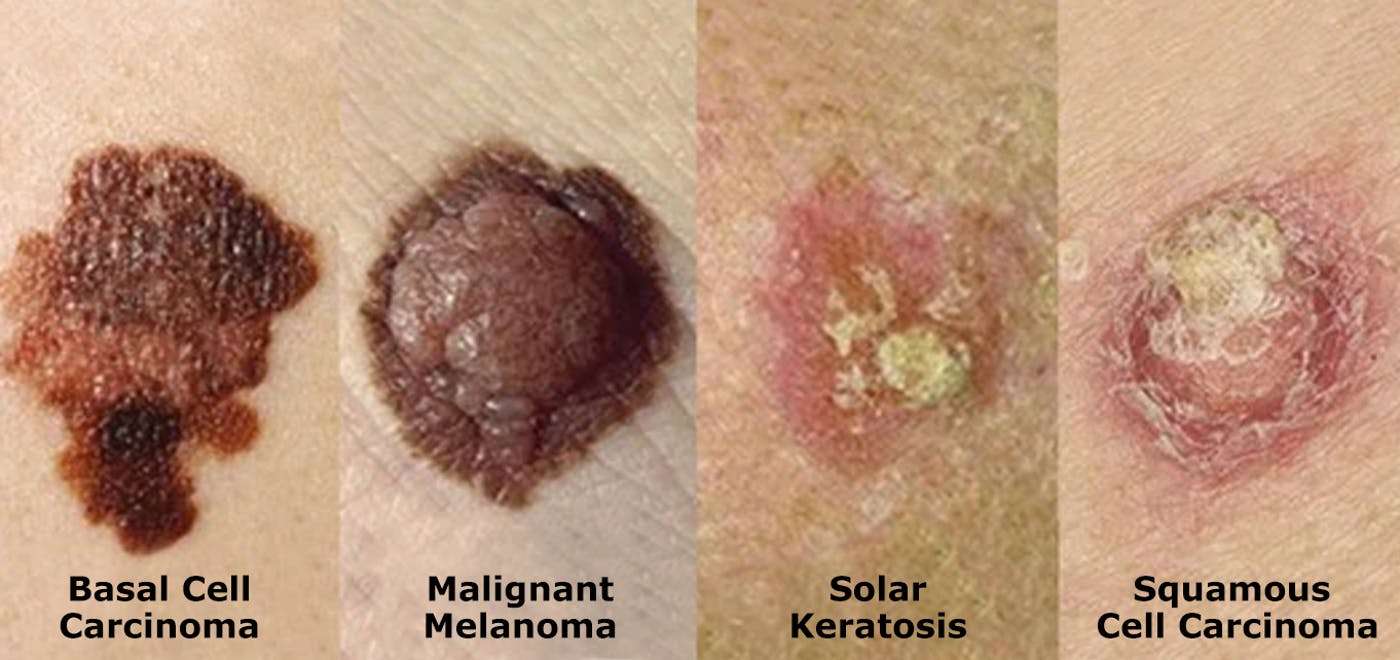
Skin cancer images by skin cancer type. Skin cancer can look different than the photos below.
Basal Cell Carcinoma | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Bowens Disease | Keratoacanthoma | Actinic Keratosis | Melanoma
Skin cancer often presents itself as a change in the skins appearance. This could be the appearance of a new mole or other mark on the skin or a change in an existing mole.
Please remember that you should always seek advice from your doctor if you have any concern about your skin. Skin cancers often look different from skin cancer images found online.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Actinic Keratosis Signs And Symptoms
Many people have actinic keratosis , also called solar keratosis, on their skin. It shows that youâve had enough sun to develop skin cancer, and it is considered a precursor of cancer, or a precancerous condition.
Usually AK shows up on the parts of your body that have received the most lifetime sun exposure, like the face, ears, scalp, neck, backs of the hands, forearms, shoulders and lips.
Some of the same treatments used for nonmelanoma skin cancers are used for AK to ensure it does not develop into a cancerous lesion.
Appearance
This abnormality develops slowly. The lesions are usually small, about an eighth of an inch to a quarter of an inch in size. You may see a few at a time. They can disappear and later return.
- AK is a scaly or crusty bump on the skinâs surface and is usually dry and rough. It can be flat. An actinic keratosis is often noticed more by touch than sight.
- It may be the same color as your skin, or it may be light, dark, tan, pink, red or a combination of colors.
- It can itch or produce a prickling or tender sensation.
- These skin abnormalities can become inflamed and be encircled with redness. Rarely, they bleed.