How Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated
Although squamous cell carcinomas usually grow slowly, it is important to see a dermatologist quickly. “The sooner you see your doctor and the cancer is diagnosed and treated, the less complicated the surgery to remove it will be, and the faster you will make a complete recovery, Dr. Leffell explains. The treatment for squamous cell cancer varies according to the size and location of the lesion. The surgical options are the same as those for basal cell cancer:
- Surgical excision: Removing a squamous cell lesion is a simple procedure that typically takes place in the dermatologist’s office. After numbing the cancer and the area around it with a local anesthetic, the doctor uses a scalpel to remove the tumor and some of the surrounding skin to make sure all cancer is eliminated. Estimating how much to take requires skill and expertise, Dr. Leffell notes. The risk of taking too little tissue is that some cancer remains taking too much leaves a larger scar than is necessary. Shaped like a football, the wound is stitched together, using plastic surgery techniques. If dissolvable stitches are used, they will disappear on their own as the area heals. Though the procedure leaves some redness and a small scar, it tends to become less noticeable over time. “The cure rate for this type of excision is typically about 90 to 93 percent,” says Dr. Leffell. But, of course, this is dependent on the skill and experience of the doctor.”
What Are The Different Types Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
People assume there is just a single type of squamous cell carcinoma, but there are actually several different types. Some are more likely to spread than others, but in general, most types share similar characteristics. The primary difference between the following types is related to the unique characteristics of the cancerous cells.
The primary types of squamous cell carcinoma are:
- Adenoid/pseudoglandular squamous cell carcinoma
- Small cell keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma
- Spindle cell squamous cell carcinoma
- Verrucous squamous cell carcinoma
Where Do Skin Cancers Start
Most skin cancers start in the top layer of skin, called the epidermis. There are 3 main types of cells in this layer:
- Squamous cells: These are flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis, which are constantly shed as new ones form. When these cells grow out of control, they can develop into squamous cell skin cancer .
- Basal cells: These cells are in the lower part of the epidermis, called the basal cell layer. These cells constantly divide to form new cells to replace the squamous cells that wear off the skins surface. As these cells move up in the epidermis, they get flatter, eventually becoming squamous cells. Skin cancers that start in the basal cell layer are called basal cell skin cancers or basal cell carcinomas.
- Melanocytes: These cells make the brown pigment called melanin, which gives the skin its tan or brown color. Melanin acts as the bodys natural sunscreen, protecting the deeper layers of the skin from some of the harmful effects of the sun. Melanoma skin cancer starts in these cells.
The epidermis is separated from the deeper layers of skin by the basement membrane. When a skin cancer becomes more advanced, it generally grows through this barrier and into the deeper layers.
Also Check: Prognosis For Skin Cancer
Skin Cancer Types: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Overview
All content solely developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology gratefully acknowledges the support from Sanofi Genzyme and Regeneron.
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
What is squamous cell carcinoma of the skin?A common type of skin cancer, squamous cell skin cancer can develop from a pre-cancerous skin growth called an actinic keratosis .
Is it contagious? No
How Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Vagina Be Prevented
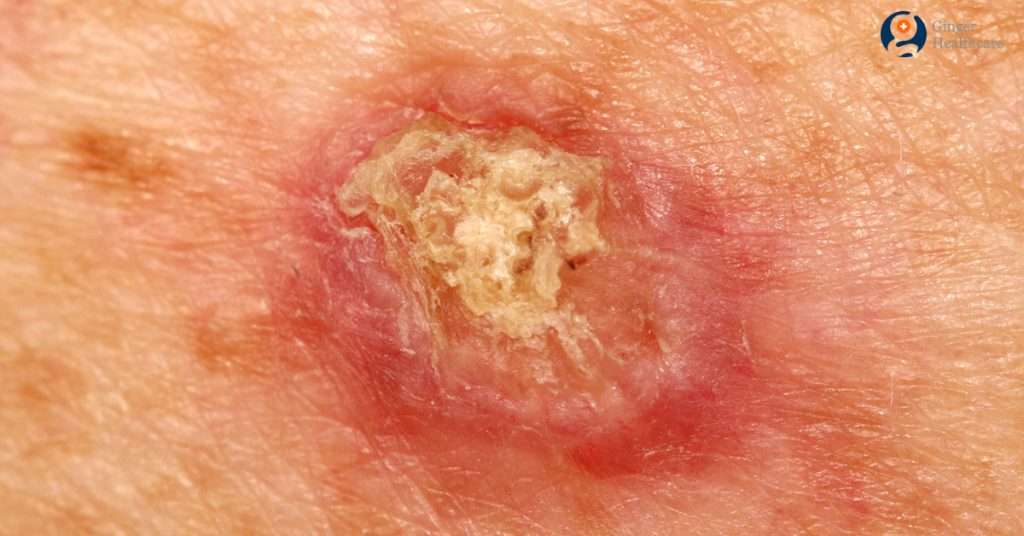
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Vagina may be prevented through the timely and adequate treatment of in situ Vaginal SCC. Some steps for the prevention of SCC of Vagina may include:
- Use of measures to prevent sexually-transmitted infections, such as usage of condoms, avoiding multiple sexual partners, and circumcision in men
- Avoidance of smoking
- Regular screening to detect pre-cancers:
- The American Cancer Society recommends screening of women from age 21 years
- A Pap smear is recommended every 3 years, from ages 21-29 years
- From age 30-65 years, a Pap smear and HPV testing is recommended, once every 5 years
- More frequent screenings are advised for women having a high-risk for cervical cancer
Note: Per se, Pap smears can only help in detecting cervical cancers. They are not helpful in screening for vaginal cancers. However, since cervical cancers are much more frequently noted, early screening to detect precancers is important.
- Vaccination against human papilloma virus :
- Two vaccines have been studied and approved for use in the United States – Gardasil and Cervarix
- Cervarix has been approved for use in females aged 10-25 years, while Gardasil may be used in the 9-26 years age group
- The American Cancer Society recommends routine vaccination of girls at 11-12 years of age
- HPV vaccines are not successful against women who are already infected though
Don’t Miss: Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rates
What Are The Risk Factors For Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Tongue
The risk factors for Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue include:
- Smoking and chewing of tobacco are strong risk factors for this type of Tongue Cancer
- Radiation therapy in the region of the tongue
- Arsenic exposure
- Coal tar exposure
- Individuals with weak immune system, which could be due to cancer treatment, AIDS, or those on immunosuppressant drugs after receiving an organ transplant
- Caucasians are more vulnerable compared to other dark-skinned individuals
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
How Do People Find Bcc On Their Skin
Many people find it when they notice a spot, lump, or scaly patch on their skin that is growing or feels different from the rest of their skin. If you notice any spot on your skin that is growing, bleeding, or changing in any way, see a board-certified dermatologist. These doctors have the most training and experience in diagnosing skin cancer.
To find skin cancer early, dermatologists recommend that everyone check their own skin with a skin self-exam. This is especially important for people who have a higher risk of developing BCC. Youll find out what can increase your risk of getting this skin cancer at, Basal cell carcinoma: Who gets and causes.
Images used with permission of:
-
The American Academy of Dermatology National Library of Dermatologic Teaching Slides.
-
J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 80:303-17.
Dont Miss: What Are The 4 Types Of Melanoma
Read Also: Does Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Vagina
The signs and symptoms of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Vagina may include:
- 7 in 10 cases are associated with abnormal vaginal bleeding, but in the absence of pain
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- There may be pain and discomfort during sex
- The presence of a poorly-defined lesion on the vagina the vaginal mass may be felt
- The presence of skin ulceration is often noted, which can lead to the bleeding
- Most squamous cell carcinomas are seen in the upper vagina the lower vaginal tract may be affected by non-HPV related SCCs
- An outward tumor growth is seen in most cases sometimes, an inward tumor growth that can constrict the vagina is known to occur
- Anemia
- Loss of weight, loss of appetite
- Usually, there are no symptoms, during the pre-cancer and early cancer stages
During the advanced stages of SCC of Vagina, the following signs and symptoms may be observed:
- Chronic pelvic pain lower back pain
- Frequent urination
- Urinary bladder pain and blood in urine
- Involvement of the pelvic muscles by tumor cells can cause pain radiating along the leg
- If the urinary bladder is involved, then it may obstruct the bladder and lead to retention of urine
- Urinary retention can cause the abnormal formation of a fistula in the urogenital area
- Rectal tenesmus or the urge to keep emptying the bowel, even after it is emptied
How Dangerous Is Scc
While the majority of SCCs can be easily and successfully treated, if allowed to grow, these lesions can become disfiguring, dangerous and even deadly. Untreated SCCs can become invasive, grow into deeper layers of skin and spread to other parts of the body.
Did you know?
Americans die each year from squamous cell carcinoma
You May Like: Late Stage Basal Cell Carcinoma
Signs And Symptoms Of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Clinically, cSCC presents as a shallow ulcer with elevated margins, often covered by a plaque and usually located in a sun-exposed area. Typical surface changes may include scaling, deep ulceration, crusting, and cutaneous horn.
A less common presentation of cSCC includes a pink cutaneous nodule without overlying surface changes. Regional metastasis of head and neck cSCC may result in enlarged and palpable submandibular or cervical lymph nodes.
If cSCC invades the adjacent peripheral nerve, it causes numbness, pain, and muscle weakness. These may be some of the clinical signs of invasion other than palpable lymph nodes.
What Is The Long
While the prevalence of head and neck cancer derived from HPV is steadily increasing, data suggest that it is easily treated. Patients with HPV-induced oropharyngeal cancer have a disease-free survival rate of 85-90 percent over five years. This is in contrast to the traditional patient population of excessive smokers and drinkers with advanced disease who have a five- year survival rate of approximately 25- 40 percent.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma On Face Prognosis
What Happens If Actinic Keratosis Is Left Untreated
Actinic keratosis causes rough, scaly skin patches. Left untreated, AK can lead to a skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma. The best way to prevent AK is to protect yourself from sun damage. If you notice new red or rough bumps on your skin, call your healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
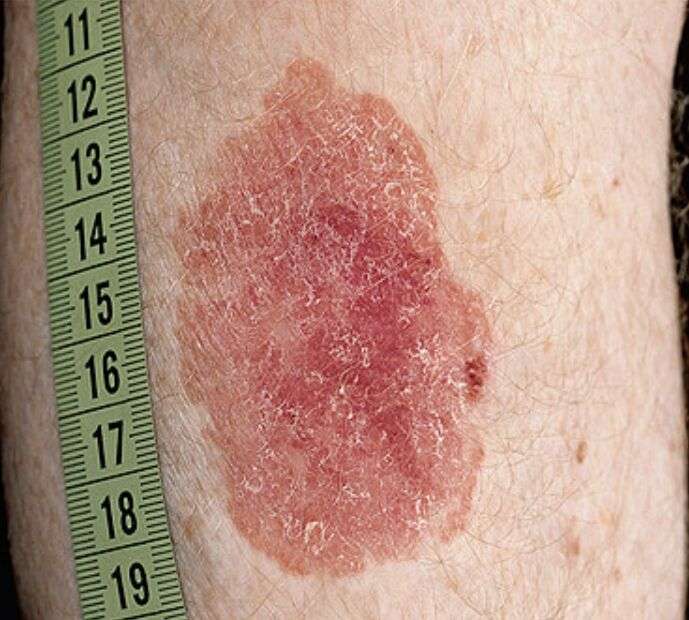
-
Usually locally destructive techniques
Treatment of squamous cell carcinoma is similar to that for basal cell carcinoma Treatment Basal cell carcinoma is a superficial, slowly growing papule or nodule that derives from certain epidermal cells. Basal cell carcinomas arise from keratinocytes near the basal layer, which are… read more and includes curettage and electrodesiccation, surgical excision, cryosurgery, topical chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy, or, occasionally, radiation therapy. Treatment and follow-up must be monitored closely because of the greater risk of metastasis compared with a basal cell carcinoma.
Squamous cell carcinoma on the lip or other mucocutaneous junction should be excised at times, cure is difficult.
Recurrences and large tumors should be treated aggressively with Mohs microscopically controlled surgery, in which tissue borders are progressively excised until specimens are tumor-free , or by a team approach with surgery and radiation therapy. Because tumors with perineural invasion are aggressive, radiation therapy should be considered after surgery.
Metastatic disease is responsive to radiation therapy if metastases can be identified and are isolated. Widespread metastases do not respond well to chemotherapeutic regimens. For inoperable advanced disease or metastatic disease, programmed death receptor 1 inhibitors are now an option.
Recommended Reading: How Fast Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Spread
What Causes Squamous Cell Cancer
Skin cancer is caused by mutations that occur in skin cell DNA. These changes cause abnormal cells to multiply out of control. When this occurs in the squamous cells, the condition is known as SCC.
UV radiation is the most common cause of the DNA mutations that lead to skin cancer. UV radiation is found in sunlight as well as in tanning lamps and beds.
While frequent exposure to UV radiation greatly increases your risk of skin cancer, the condition can also develop in people who dont spend much time in the sun or in tanning beds.
These people may be genetically predisposed to skin cancer, or they may have weakened immune systems that increase their likelihood of getting skin cancer.
Those who have received radiation treatment may also be at greater risk of skin cancer.
Risk factors for SCC include:
- having fair skin
- having light-colored hair and blue, green, or gray eyes
- having long-term exposure to UV radiation
- living in sunny regions or at a high altitude
- having a history of multiple severe sunburns, especially if they occurred early in life
- having a history of being exposed to chemicals, such as arsenic
Where Does Squamous Cell Carcinoma Start
About 2 out of 10 skin cancers are squamous cell carcinomas . These cancers start in the flat cells in the upper part of the epidermis. These cancers commonly appear on sun-exposed areas of the body such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and backs of the hands.
Untreated squamous cell carcinoma of the skin can destroy nearby healthy tissue, spread to the lymph nodes or other organs, and may be fatal, although this is uncommon.
Moreover, How often does squamous cell carcinoma spread?
BCCs hardly ever metastasize. Ive seen two cases in my entire career. But when SCCs that havent been treated early get big, then the chance of metastasis becomes real. Its uncommon, but its much more common than in BCC.
Secondly, Where does squamous cell carcinoma metastasize?
Cancer can begin in squamous cells anywhere in the body and metastasize through the blood or lymph system to other parts of the body. When squamous cell cancer spreads to lymph nodes in the neck or around the collarbone, it is called metastatic squamous neck cancer.
Simply so, Does squamous cell carcinoma appear suddenly?
A common type of squamous cell cancer is the keratoacanthoma. It is a rapidly growing tumor which tends to appear suddenly and may reach a considerable size. This tumor is often dome-shaped with a central area resembling a crater which is filled with a keratin plug.
What are the chances of squamous cell carcinoma spreading?
Recommended Reading: Melanoma Stage 3 Life Expectancy
What Is The Treatment For Advanced Or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Locally advanced primary, recurrent or metastatic SCC requires multidisciplinary consultation. Often a combination of treatments is used.
- Experimental targeted therapy using epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors
Many thousands of New Zealanders are treated for cutaneous SCC each year, and more than 100 die from their disease.
Classification Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma By Risk
Cutaneous SCC is classified as low-risk or high-risk, depending on the chance of tumour recurrence and metastasis. Characteristics of high-risk SCC include:
High-risk cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma has the following characteristics:
- Diameter greater than or equal to 2 cm
- Location on the ear, vermilion of the lip, central face, hands, feet, genitalia
- Arising in elderly or immune suppressed patient
- Histological thickness greater than 2 mm, poorly differentiated histology, or with the invasion of the subcutaneous tissue, nerves and blood vessels
Metastatic SCC is found in regional lymph nodes , lungs, liver, brain, bones and skin.
High-risk cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Read Also: Metastatic Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy
What Is The Prognosis Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Of Tongue
- In general, Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Tongue is an aggressive form of cancer. If metastasis is observed, then the prognosis is guarded or unpredictable
- Tumors in their early stage with complete excisional treatment typically have good prognosis
- In cases of metastasis, its prognosis depends upon a set of several factors that include:
- Stage of tumor: With lower-stage tumors, when the tumor is confined to site of origin, the prognosis is usually excellent with appropriate therapy. In higher-stage tumors, such as tumors with metastasis, the prognosis is poor
- The surgical respectability of the tumor
- Overall health of the individual: Individuals with overall excellent health have better prognosis compared to those with poor health
- Age of the individual: Older individuals generally have poorer prognosis than younger individuals
- Whether the tumor is occurring for the first time, or is a recurrent tumor. Recurring tumors have a poorer prognosis compared to tumors that do not recur
- Response to treatment: Tumors that respond to treatment have better prognosis compared to tumors that do not respond so well to treatment
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis And Survival Rate
If caught early, squamous cell carcinoma is highly treatable. While skin cancer is the most common cancer type among U.S. adults, cases are not required to be reported to cancer registries, so exact incidence breakdowns of types like squamous cell carcinoma are not known. However, according to numbers tracked by the Canadian Cancer Society, the five-year relative survival rate is 95 percent.
Expert cancer care
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Melanoma Cancer Life Expectancy
Unprotected Exposure To Uv Radiation
Cumulative, unprotected exposure to UV radiation is the main cause of SCC as well as a risk factor for most skin cancers. The more time you spend in the sun over your lifetime from long days at the beach to short periods of unprotected exposure the greater your likelihood of developing SCC. If you work outdoors or spend extensive leisure or recreation time in the sun, your risk is especially increased.
Its a fact: About 90 percent of nonmelanoma skin cancers are associated with exposure to UV radiation from the sun.
Your exposure to UV rays is also a risk that you can control. Find out more here.
Its a fact
of nonmelanoma skin cancers are associated with exposure to UV radiation from the sun.
How Does The Doctor Know I Have Skin Cancer
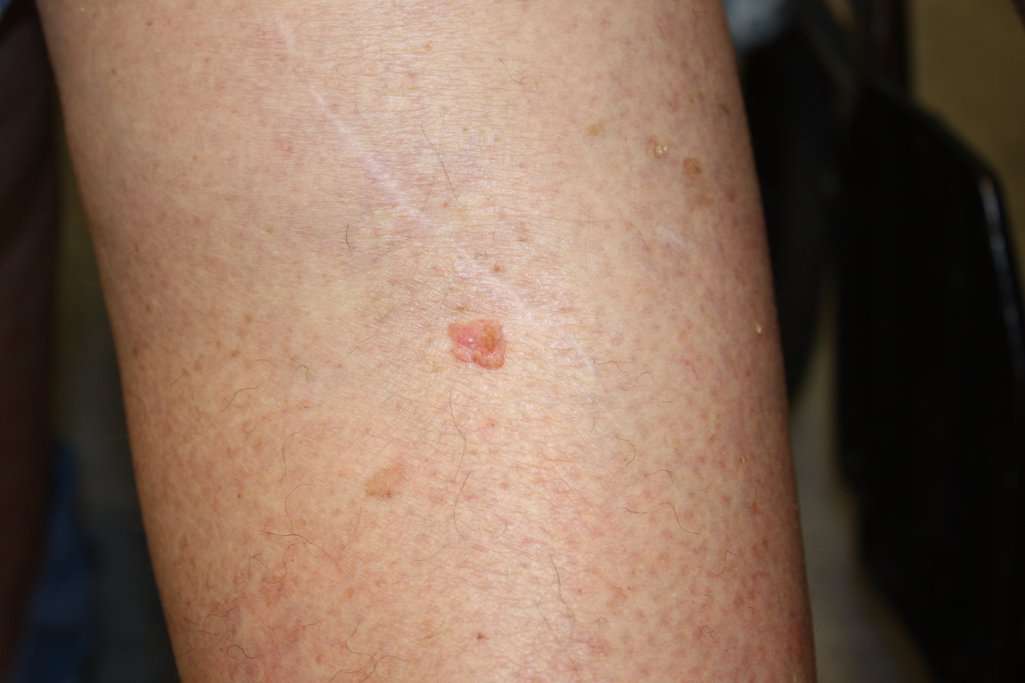
Basal and squamous skin cancer may look like:
- Flat, firm, pale or yellow areas that look a lot like a scar
- Raised reddish patches that might itch
- Rough or scaly red patches, which might crust or bleed
- Small, pink or red, shiny, pearly bumps, which might have blue, brown, or black areas
- Pink growths or lumps with raised edges and a lower center
- Open sores that dont heal, or that heal and then come back
- Wart-like growths
Read Also: Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer Survival Rate