What Is A Five
Five-year survival rate refers to the average number of people with a particular disease or condition who are alive five years after being diagnosed.
Cancer experts based five-year survival rates for melanoma on information from a database called SEER, which stands for the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program.
Survival statistics from the SEER database are not based on AJCC melanoma staging. Instead, they’re based on if and how far the melanoma has spread:
| Type |
|---|
The five-year survival rate for all three SEER stages combined is 93%.
The five-year survival rate for all three SEER stages combined is 93%.
Number Of Metastatic Lymph Nodes Involved
If the melanoma has spread to the lymph nodes the risk of spread to other parts of the body is higher. The greater the number of lymph nodes containing melanoma, the less favourable the prognosis.
A sentinel node biopsy is a technique used to determine whether melanoma cells have spread to lymph nodes at the time of diagnosis of the skin primary lesion. The procedure involves the injection of a radioactive tracer by a radiologist , to show where the site and lymph node where the lymph fluid from the skin at the primary melanoma will flow. Afterwards, at the same time as the extra surgery for the primary melanoma a blue dye is injected around the site of the primary lesion. Using the guide from the radiologist a surgeon looks for the first lymph node to take up the dye. The lymph node is removed and sent to be examined by a histopathologist to determine if the node tests positive for melanoma. The procedure is considered when the Breslow thickness of the melanoma is more than 0.8mm.
Patients may develop lumps in the lymph node regions such as the neck, armpit and groin. This is lymph node metastasis.
Taking Care Of Yourself
Hearing that your cancer has spread is scary, but a lot of research is underway to find new treatments. And there are treatments available to try to stop the disease from spreading, so you can live longer.
Its important to have support and to talk about your fears and feelings, too. Your doctor can help you find a cancer support group.
These tips may help you feel better during melanoma treatment:
- If you lose your appetite, eat small amounts of food every 2 to 3 hours instead of bigger meals. A dietitian can give you other tips on nutrition and eating during your cancer treatment. Ask your doctor for a referral.
- Exercise can help you feel better overall and fight fatigue. But listen to your body, and balance rest and activity.
- Get the kind of emotional support thats right for you. It could be from family, friends, your cancer support group, or a religious group.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma On Face Prognosis
Stage 3 Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Peritoneal mesothelioma is the second-most common form of the disease. Instead of a formal staging system to measure progression, physicians typically use the existing Peritoneal Cancer Index to grade tumors in the abdomen. In addition, the PCI helps doctors determine the stage in many other abdominal cancers.
The PCI ranges from 0 to 39, measuring the spread of tumors across 13 different abdominal sectors. A score between 21 and 30 indicates stage 3 peritoneal mesothelioma. The characteristics of this stage are tumors localized within the abdomen, with some spread to nearby lymph nodes.
If a doctor refers to peritoneal mesothelioma as stage 3, it usually means tumors have spread throughout the abdominal lining and to nearby lymph nodes.Dr. Daniel A. LandauOncologist and hematologist
Also Check: What Are The Early Stages Of Melanoma
Putting The Results Of These Clinical Trials Into Context
The clinical studies described above have shown that both immunotherapies and targeted therapies are adjuvant treatment options following surgery, which are intended to delay or prevent the recurrence of melanoma in patients with high-risk stage III disease. Although both types of therapy provide good options for individuals with late-stage melanoma, patients should be aware of the clear differences in the side effect profiles of immunotherapies and targeted therapies.39
About 1 in 4 patients who received the checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab and about 1 in 3 patients who received the checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab in the clinical trials described above have reported experiencing severe side effects.31,36 Immune-related severe side effects that were observed in the clinical trials, such as the onset of type 1 diabetes or disorders of the thyroid and pituitary gland, have been confirmed in the treatment of real-world patients .
Because they work differently, targeted therapies do not carry the risk of triggering immune-related adverse effects. Nevertheless, about 2 of every 5 patients who received dabrafenib plus trametinib in the COMBI-AD study reported experiencing severe side effects.33 The proportion of patients treated with dabrafenib plus trametinib who withdrew from the study early because of side effects was 26%.33
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
How Often Should You Follow Up With Your Doctor
After your treatment, your doctor will recommend a regular follow-up schedule to monitor your cancer. Theyll be checking to make sure the cancer hasnt come back or new cancerous lesions havent appeared. The types of follow-up include:
A yearly skin check: Skin checks are an important aspect of detecting melanoma in its earliest, most treatable stages. You should also conduct a skin check on yourself once per month. Look everywhere from the bottoms of your feet to behind your neck.
Imaging tests every three months to a year: Imaging studies, such as an X-ray, CT scan, or brain MRI, look for cancer recurrence.
Physical exam as needed: A physical exam to assess your overall health is important when you have had melanoma. For the first two years, youll want to get an exam every three to six months. Then for the next three years, the appointments can be every three months to a year. After the fifth year, the exams can be as needed. Do a monthly self-examination of your lymph nodes to check your progress.
Your doctor may recommend a different schedule based on your overall health.
Survival For All Stages Of Melanoma
Generally for people with melanoma in England:
- almost all people will survive their melanoma for 1 year or more after they are diagnosed
- around 90 out of every 100 people will survive their melanoma for 5 years or more after diagnosis
- more than 85 out of every 100 people will survive their melanoma for 10 years or more after they are diagnosed
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These figures are for people diagnosed in England between 2013 and 2017.
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account that some people would have died from other causes if they had not had cancer.
Recommended Reading: Stage 5 Cancer Symptoms
Treating Stage Iv Melanoma
Stage IV melanomas have already spread to distant lymph nodes or other areas of the body. Skin tumors or enlarged lymph nodes causing symptoms can often be removed by surgery or treated with radiation therapy.
Metastases in internal organs are sometimes removed, depending on how many there are, where they are, and how likely they are to cause symptoms. Metastases that cause symptoms but cannot be removed may be treated with radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy.
The treatment of widespread melanomas has changed in recent years as newer forms of immunotherapy and targeted drugs have been shown to be more effective than chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy drugs called checkpoint inhibitors such as pembrolizumab or nivolumab are typically the first drugs tried, especially in people whose cancer cells do not have BRAF gene changes. These drugs can shrink tumors for long periods of time in some people. Ipilimumab , a different type of checkpoint inhibitor, is not typically used by itself as the first treatment, although it might be combined with nivolumab or pembrolizumab. This slightly increase the chances that the tumor will shrink, although itâs also more likely to result in serious side effects, which needs to be considered carefully. People who get any of these drugs need to be watched closely for serious side effects..
Itâs important to carefully consider the possible benefits and side effects of any recommended treatment before starting it.
Braf & Mek Kinase Inhibitors
The BRAF and MEK genes are known to play a role in cell growth, and mutations of these genes are common in several types of cancer. Approximately half of all melanomas carry a specific BRAF mutation known as V600E. This mutation produces an abnormal version of the BRAF kinase that stimulates cancer growth. Some melanomas carry another mutation known as V600K. BRAF and MEK inhibitors block the activity of the V600E and V600K mutations respectively.
Recommended Reading: What Does Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mean
Stages Iiia Iiib And Iiic
In order to better describe these variable factors, stage III melanoma is further divided into the following three categories:
- Stage III A: This stage includes microscopic levels of melanoma present in lymph nodes.
- Stage III B: This stage includes an ulcerated primary tumor, microscopic levels of melanoma in the skin near the primary tumor, microscopic levels of melanoma in lymph nodes, and melanoma in the draining nodes.
- Stage III C: This stage includes an ulcerated primary tumor and melanoma big enough to be felt in the draining nodes.
Treatment Of Stage Iii Melanoma
Medically reviewed by Dr. C.H. Weaver M.D. updated 8/2021
Stage III melanoma includes cancers of any thickness that have spread to the regional lymph nodes. Optimal treatment of stage III melanoma consists of surgical removal of the cancer followed by systemic adjuvant treatment to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence and prolong survival.
Also Check: Non Invasive Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Causes Ocular Melanoma
The exact cause of most eye cancer is unknown.
Risk factors for developing ocular melanoma include:
- Race/ethnicity
- The risk is higher in whites than it is in African Americans, Hispanics or Asian Americans
Surgical Treatment Of Stage Iii Disease
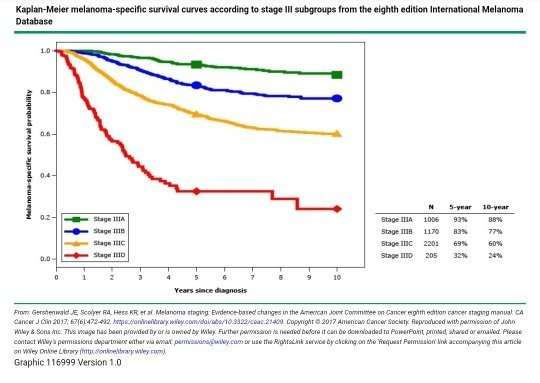
Outcomes of patients with stage III melanoma relates primarily to the extent of lymph node metastasis. Standard surgical treatment for patients with stage III melanoma is removal of the primary cancer with up to 2-centimeter margins of the adjacent skin, depending on the thickness of the primary tumor, and removal of all of the regional lymph nodes. Regional lymph node dissection may be performed in the neck, armpit or groin, depending on the site of the primary tumor and presence of palpable nodes. Chronic side effects of removing lymph nodes vary, depending on the extent of disease, body habits of the patient, and inclusion of postoperative radiation to site, but may include numbness, and swelling of the associated extremity, which is called lymphedema.
One of the challenges facing oncologists is assessing the risks for individual patients on the basis of data from previously published studies. Five-year overall survival rates for patients with stage III melanoma have been reported as ranging from 70% for stage IIIA to 27% for stage IIIC disease. In this group of patients, assembled largely during the pre-sentinel lymph node era, patients with stage I and II disease were reported to have 5-year recurrence-free survival rates of 90% and 70%, respectively. The 10% to 30% recurrence rates likely reflect unidentified microscopic disease, which can be detected with present-day techniques.
Also Check: Is A Sore That Doesn T Heal Always Cancer
What Are The Stages Of Melanoma
When a melanoma has been diagnosed, the pathology report provides information to determine the stage of the disease.
The prognosis of melanoma and the treatment options available depend on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed.
One of the most common areas of confusion is the difference between the levels of melanoma and the staging of melanoma. The level of melanoma relates to the depth of the melanoma in the skin and the staging of melanoma refers to how limited or advanced the melanoma is at the time of diagnosis.
The stages of melanoma are determined by reviewing different factors including:
Read Also: How To Treat Melanoma In Nails
Treating Stage 0 Melanoma
Stage 0 melanoma has not grown deeper than the top layer of the skin . It is usually treated by surgery to remove the melanoma and a small margin of normal skin around it. The removed sample is then sent to a lab to be looked at with a microscope. If cancer cells are seen at the edges of the sample, a second, wider excision of the area may be done.
Some doctors may consider the use of imiquimod cream or radiation therapy instead of surgery, although not all doctors agree with this.
For melanomas in sensitive areas on the face, some doctors may use Mohs surgery or even imiquimod cream if surgery might be disfiguring, although not all doctors agree with these uses.
Read Also: Is Cancer Painful Without Treatment
Surgical Treatment Of Stage Iii Melanoma
Standard surgical treatment for patients with stage III melanoma is removal of the primary cancer with up to 2-centimeter margins of the adjacent skin, depending on the thickness of the primary tumor, and removal of all of the regional lymph nodes. Outcomes of patients with stage III melanoma relate primarily to the extent of lymph node metastasis.
Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy are used to assess the presence of melanoma cells in the regional lymph nodes in order to help determine which patients may require regional lymph node dissections and systemic adjuvant therapy.
SLNB should be performed prior to wide excision of the primary melanoma to ensure accurate lymphatic mapping. If metastatic melanoma is detected, a complete lymph node dissection can be performed in a second procedure. Patients can be considered for a CLND if the sentinel node is microscopically or macroscopically positive.1-5
Systemic Adjuvant Treatment Of Stage Iii Melanoma
Systemic therapy is any treatment directed at destroying cancer cells throughout the body. Many patients with stage III melanoma are at high risk for disease recurrence because undetectable cancer cells referred to as micrometastases have already broken away from the primary cancer and traveled through the lymph and blood system to other locations in the body. The delivery of systemic cancer treatment following surgery is referred to as adjuvant therapy.
Adjuvant treatment of stage III melanoma with newer precision cancer medicines and immunotherapy drugs is the standard of care because they delay the time to cancer recurrence and prolong survival.
Also Check: Cancer Lesion Pictures
Survival Statistics For Melanoma Skin Cancer
Survival statistics for melanoma skin cancer are general estimates and must be interpreted very carefully. Because these statistics are based on the experience of groups of people, they cannot be used to predict a particular persons chances of survival.
There are many different ways to measure and report cancer survival statistics. Your doctor can explain the statistics for melanoma skin cancer and what they mean to you.
What Is Stage Iii Melanoma
Stage III melanomas are tumors that have spread to regional lymph nodes or have developed in-transit deposits of disease, but there is no evidence of distant metastasis. Stage III melanoma is regional melanoma, meaning it has spread beyond the primary tumor to the closest lymph nodes, but not to distant sites. There are four subgroups of Stage III melanoma: IIIA, IIIB, IIIC, IIID. Stage III is invasive melanoma.
- Subgroups are IIIA, IIIB, IIIC, IIID
- Stage III melanoma is defined by four primary characteristics
- Important distinction within Stage III: whether the spread to lymph nodes can be detected microscopically or macroscopically
- Microscopically, also called clinically occult = seen by pathologist during biopsy or dissection
- Macroscopically, also called clinically detected = seen by naked eye or felt by hand or seen on CT scans or ultrasound
- Risk: Intermediate to high for regional or distant spread
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
Clinical Staging And Pathologic Staging
To add to the complexity of staging, the cancer also may have a clinical stage and a pathologic stage.
Clinical staging takes place before surgery, based on blood tests, physical exams or imaging tests such as X-rays, a computed tomography scan, magnetic resonance imaging or positron emission tomography scans.
What doctors discover during surgery may provide more detailed information about the cancers size and spread. Often, some tissue from the surgery will be examined afterward to provide more clues. This process is known as pathologic staging, or surgical staging.
If surgery isnt possible, doctors will use the clinical stage when determining a treatment plan.
The Journey Through Stage Iii Melanoma: A Guide For Patients
Melanoma survivorSupported with funding by Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, with risk for the disease appearing to be on the rise. Historically, the outlook for patients diagnosed with stage III melanoma has been poor. In recent years, however, new therapies have changed the way in which patients with melanoma are treated. These treatments have already helped many patients to live longer lives with a reduced risk for a recurrence or return of their cancer. Because these treatments are so new, many patients may not know that they even exist, how they work, and what types of side effects they might cause. By providing information about the most recent advances in the treatment of melanoma, we hope to empower patients and their families as they navigate through their journey. It is our belief that this publication will help you to work with your healthcare team as you decide which therapies are best for you.
Recommended Reading: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate