Nanotechnology In Breast Cancer
The field of nanotechnology has rapidly evolved as evidenced by the fact that there are more than 150 ongoing clinical trials investigating the efficacy of nanotechnology based drug delivery carriers targeting cancer. Various liposomal doxorubicin formulations were developed in an effort to improve the therapeutic index of the conventional doxorubicin chemotherapy while maintaining its anti-tumor activity. For example, the efficacy of three liposomal doxorubicins are currently being used: liposomal daunorubicin , liposomal doxorubicin , and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin . Generally, these agents exhibit efficacies comparable to those of conventional doxorubicin, except with better safety profiles and less cardio toxicity. In addition to liposomal doxorubicin, albumin-bound paclitaxel is another example of an E PR based nanovector application for breast cancer chemotherapy. Paclitaxel is highly hydrophobic and dissolved in cremophor to prevent paclitaxel precipitation. However, cremophor-associated toxicities are severe and challenge the application of paclitaxel. Albumin-bound paclitaxel was developed to improve the solubility of paclitaxel
Treatment For Triple Negative Breast Cancer
Treatment for triple negative breast cancer usually involves surgery , radiotherapy if breast conserving surgery was performed, and chemotherapy. If you would like to read more about the main types of breast cancer surgery, visit the surgery section of this website.
As triple negative breast cancer is usually very responsive to chemotherapy, your medical oncologist will most likely develop a chemotherapy treatment plan for you. This will take into account your own individual needs and preferences.
Chemotherapy is usually given after breast cancer surgery. Sometimes it is given before surgery to shrink the tumour to allow for a smaller and easier operation. Some people may be offered chemotherapy before surgery this is called neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
Recommended Reading: How To Remove Skin Cancer On Face
Is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Fast Growing
invasive ductal carcinomainvasive ductal carcinomainvasive ductal carcinomagrow
. Similarly, how aggressive is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Over time, invasive ductal carcinoma can spread to the lymph nodes and possibly to other areas of the body. According to the American Cancer Society, more than 180,000 women in the United States find out they have invasive breast cancer each year. Most of them are diagnosed with invasive ductal carcinoma.
Furthermore, what stage is invasive ductal carcinoma? Specifically, the invasive ductal carcinoma stages are: Stage 1 A breast tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters in diameter and the cancer has not spread beyond the breast. Stage 2 A breast tumor measures 2 to 4 centimeters in diameter or cancerous cells have spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area.
Besides, what is the survival rate of invasive ductal carcinoma?
Certain breast cancer subtypes have a better statistical prognosis
| breast cancer sub-type |
|---|
| almost 100% |
| Infiltrating lobular carcinoma |
| 88% |
How curable is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Stage 0 breast cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ is a non-invasive cancer where abnormal cells have been found in the lining of the breast milk duct. Ductal Carcinoma In Situ is very early cancer that is highly treatable, but if it’s left untreated or undetected, it can spread into the surrounding breast tissue.
Also Check: What Is Clear Cell Carcinoma
Is Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Curable
4.3/5Ductal Carcinomacancertreatableread here
All together, invasive ductal carcinoma refers to cancer that has broken through the wall of the milk duct and begun to invade the tissues of the breast. Over time, invasive ductal carcinoma can spread to the lymph nodes and possibly to other areas of the body. Invasive ductal carcinoma also affects men.
Beside above, what stage is invasive ductal carcinoma? Specifically, the invasive ductal carcinoma stages are: Stage 1 A breast tumor is smaller than 2 centimeters in diameter and the cancer has not spread beyond the breast. Stage 2 A breast tumor measures 2 to 4 centimeters in diameter or cancerous cells have spread to the lymph nodes in the underarm area.
Secondly, what is the treatment for infiltrating ductal carcinoma?
Treatments for invasive ductal carcinoma include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, and targeted therapy. You and your doctor will decide what treatment or combination of treatments is right for you depending on the characteristics of the cancer and your personal preferences.
Is chemo necessary for invasive ductal carcinoma?
An entire course of chemotherapy usually takes approximately three to six months to complete, and can be repeated as necessary. Invasive ductal carcinoma chemotherapy can be effective for treating many types of breast cancer, including: Triple negative breast cancer. HER2/neu-positive breast cancer.
What Does It Mean To Have Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
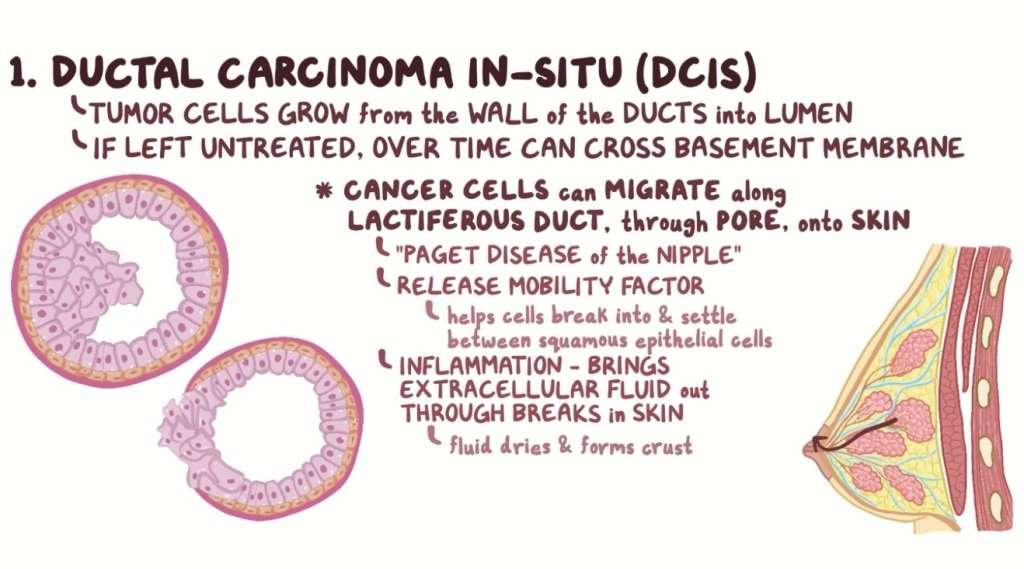
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma About 80% of all breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas. Invasive means that the cancer has invaded or spread to the surrounding breast tissues. Ductal means that the cancer began in the milk ducts, which are the pipes that carry milk from the milk-producing lobules to the nipple.
Read Also: Braf And Melanoma
What Can I Expect If I Have Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
If youve been diagnosed with invasive ductal carcinoma, your healthcare provider will discuss your treatment options with you in detail. For best results, youll want to begin treatment as soon as possible.
How curable is invasive ductal carcinoma?
Invasive ductal carcinoma is quite curable, especially when detected and treated early.
What is the survival rate for invasive ductal carcinoma?
The five-year survival rate for localized invasive ductal carcinoma is high nearly 100% when treated early on. If the cancer has spread to other tissues in the region, the five-year survival rate is 86%. If the cancer has metastasized to distant areas of your body, the five-year survival rate is 28%.
Keep in mind that survival rates cannot tell you how long you will live. These numbers are based on people who have undergone breast cancer treatment in the past. For more information about your specific case, talk to your healthcare provider.
Breast Cancer Survival By Age
Five-year survival for female breast cancer shows an unusual pattern with age: survival gradually increases from 85% in women aged 15-39 and peaks at 92% in 60-69 year olds survival falls thereafter, reaching its lowest point of 70% in 80-99 year-olds for patients diagnosed with breast cancer in England during 2009-2013.
Breast Cancer , Five-Year Net Survival by Age, Women, England, 2009-2013
Dont Miss: Can I Donate Blood If I Had Melanoma
Don’t Miss: Survival Rates For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What Is Stage 1 Breast Cancer
Stage 1 breast cancer is the earliest stage of invasive breast cancer. The breast cancer has spread from its original location to the surrounding tissue but it is still contained in a relatively small area.
If you are diagnosed with Stage 1 breast cancer, this means that the tumour is less than 2 centimetres in size. No cancer cells have been found in the lymph nodes or other parts of the body at this stage.
You May Like: What Do Skin Cancer Marks Look Like
How Is Dcis Detected And Diagnosed
Most DCIS is detected from a mammogram that shows abnormal calcifications in the breast. The doctor may need to conduct additional imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI. These are used to determine the full extent of the disease.
DCIS is diagnosed by a needle biopsy. Pathologists examine the abnormal cells to determine the grade of the DCIS and the hormone-receptor status. DCIS is classified as low, intermediate, or high grade, depending on how abnormal the cells look under a microscope. High-grade DCIS cells are the most abnormal and grow the fastest.
Hormone-receptor status refers to whether the cancer cells have receptors for estrogen, progesterone, or both. The presence of these receptors on the DCIS suggests that these hormones fuel the growth of the cells, which affects how well the DCIS responds to certain hormone-blocking drugs.
Recommended Reading: Stage 2 Cancer Symptoms
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma Survival Rates
Survival rates for cancer are typically calculated in terms of how many people live at least 5 years after their diagnosis. The average 5-year survival rate for breast cancer is 90 percent, and the 10-year survival rate is 83 percent. This is an average of all stages and grades.
The stage of the cancer is important when considering survival rates. For instance, if the cancer is only in the breast, the 5-year rate of survival is 99 percent. If it has spread to the lymph nodes, the rate decreases to 85 percent.
Because there are many variables based on the type and spread of cancer, its best to talk with your doctor about what to expect.
Treatment Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Surgical treatment of invasive breast cancer may consist of lumpectomy or total mastectomy. In breast cancer patients who have clinically negative nodes, surgery typically includes sentinel lymph node dissection for staging the axilla.
In the AMAROS trial, which involved patients with cT1-2N0 breast cancer up to 5 cm and clinically node-negative axillae who were undergoing either breast conservation or mastectomy with SLN mapping, axillary radiotherapy was found to be a better treatment option than ALN dissection in women with a positive SLN.
In this study, 744 of the patients with a positive SLN went on to receive ALND, and 681 received axillary radiotherapy. After 5 years of follow-up, the axillary recurrence rate was 0.54% in the ALND group and 1.03% in the radiotherapy group, and there were no significant differences between the groups with respect to either disease-free survival or overall survival . The rate of lymphedema in the ALND group after 5 years, however, was twice the rate seen in the radiotherapy group .
Recommended Reading: Ductal Carcinoma Breast Cancer Survival Rates
Invasive Ductal Carcinomas We Treat
Apart from IDC, New Hope Unlimited offers treatment for the less common types of invasive ductal carcinoma:
Medullary Ductal CarcinomaThis rare breast cancer does not always feel like a lump. Instead, it can feel like a spongy change of breast tissue.
Mucinous Ductal CarcinomaThis disease occurs when cancer cells within the breast secrete mucus, which also contains breast cancer cells. The cells and mucus combine to form a tumor.
Tubular Breast CancerThis breast cancers name comes from its appearance under the microscope like hundreds of tiny tubes. Tubular ductal carcinoma often has an excellent prognosis.
Papillary Breast CarcinomaMany papillary tumors are benign . This rare type of invasive ductal carcinoma accounts for fewer than 1 percent of all breast cancer diagnoses.
What Are The Possible Complications Of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast
The complications of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast may include:
- Emotional distress due to the presence of breast cancer
- Metastasis of the tumor to local and regional sites
- Side effects of chemotherapy, which may include nausea, vomiting, hair loss, decreased appetite, mouth sores, fatigue, low blood cell counts, and a higher chance of developing infections
- Side effects of radiation therapy that may include sunburn-like rashes, where radiation was targeted, red or dry skin, heaviness of the breasts, and general fatigue
- Lymphedema may occur after surgery or radiation therapy, due to restriction of flow of lymph fluid resulting in a build-up of lymph. It may form weeks to years after treatment that involves radiation therapy to the axillary lymph nodes
You May Like: Can I Donate Blood If I Had Melanoma
Don’t Miss: Stages Of Cancer Symptoms
What Increases The Risk Of Invasive Breast Cancer
Thereâs no way to know if youâll develop an invasive form of breast cancer, but there are things that increase your chances, many of which you canât change.
Older women are at higher risk. About 10% of women diagnosed with invasive breast cancer are under age 45. And 2 out of every 3 women with invasive breast cancer are age 55 or older when theyâre first diagnosed.
Your genetics and family history of breast cancer play roles. Itâs more common among white women than black, Asian, or Hispanic women.
Also, youâre at higher risk if youâre obese, your breasts are dense, you didnât have children, or you became pregnant after the age of 35.
Why Breast Cancer Survival Rates Are Going To Be Higher Than The Most Up
It is important to remember that the breast cancer survival rates that are listed on this page are, in reality, going to be higher.
This is because the breast cancer survival rates data is gathered from a large number of people with the disease over a 5 year period. Hence, even the most up-to-date statistics are still going to be a little out of date.
Thus, with the ongoing improvements and advancements in breast cancer screening, research, early detection and advanced tailored treatment, the outcomes at present will be even better than the statistics listed here.
Also Check: Tumor Calcification
Additional And Relevant Useful Information For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast :
- Japan is an exception of a developed nation with lowered incidences of breast cancer, unlike European nations and America.
- Current studies have shown that aromatase inhibitors, medications that block estrogen hormonal effects in the body, reduce the risk of recurrence of breast cancer. Recent studies have shown that treatment using aromatase inhibitors can be given up to 10 years without affecting the quality of life of women
- Tumors that are negative for estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2/neu have worse prognosis. Such tumors are called âtriple-negativeâ tumors
The following DoveMed website links are useful resources for additional information:
Certain Breast Cancer Subtypes Have A Better Statistical Prognosis
In general, tubular, mucinous and medullary breast carcinomas have a better prognosis than the other sub-types.
The table below gives a very general approximation of the survival rates that may be associated with the different breast cancer subtypes.
However, please bear in mind that these figures are a rough generalization only and survival will always be determined by the individual characteristics of each breast cancer and each patient.
Nonetheless, the relative aggressiveness of the different breast cancer subtypes can be interpreted from the table.
and is almost always near 100% curable.)
| breast cancer sub-type |
Read Also: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Does Dcis Always Require Surgery
DCIS is considered non-invasive or pre-invasive breast cancer. DCIS cant spread outside the breast, but it still needs to be treated because it can sometimes go on to become invasive breast cancer . In most cases, a woman with DCIS can choose between breast-conserving surgery and simple mastectomy.
What Does It Mean If My Report Mentions Paget Disease
Paget disease is when cells resembling the cells of ductal carcinoma in situ are found in the skin of the nipple and the nearby skin . Paget disease of the nipple is usually associated with DCIS or invasive carcinoma in the underlying breast tissue. If Paget disease is found on needle or punch biopsy, more tissue in that area usually needs to be removed with the goal of entirely removing the area of Paget disease. Talk to your doctor about the best treatment for you.
Read Also: Is A Sore That Doesn T Heal Always Cancer
Cancer Cure And All Clear
Many people who have cancer want to know if theyre cured. You may hear words like cure and all clear in the media.
Cured means theres no chance of the breast cancer coming back. However, its not possible to be sure that breast cancer will never come back. Treatment for breast cancer will be successful for most people, and the risk of recurrence gets less as time goes on. Recurrence, unfortunately, can happen even many years after treatment, so no one can say with certainty that youre definitely cured.
All clear, or in remission which is another term you may have heard used, means theres no obvious sign of cancer at the moment.
If your breast cancer has spread to other parts of your body this will affect your prognosis. Secondary breast cancer can be treated, sometimes for many years, but not cured. Find out more about secondary breast cancer.
In order to be as clear as possible, your treatment team is more likely to talk about your chances of survival over a period of time or the possibility of remaining free of breast cancer in the future.
Stages Of Breast Cancer
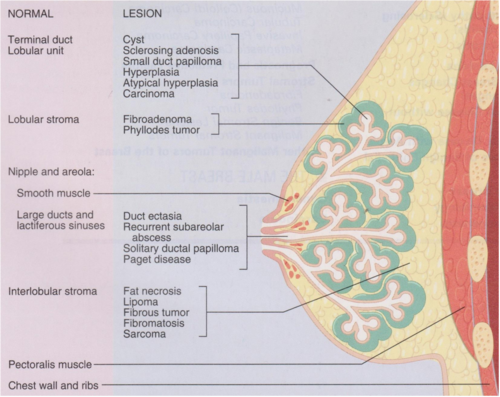
When cancer is diagnosed, a stage is assigned to it, based on how advanced it is. The stage helps doctors determine the most appropriate treatment and the prognosis. Stages of breast cancer may be described generally as in situ or invasive. Stages may be described in detail and designated by a number .
Read Also: Can You Get Cancer In The Back Of Your Neck
Who Gets Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast is a very common type of breast cancer. Almost 70-80% of breast cancers are Ductal Carcinoma NOS types
- Middle-aged and older women past the age of 40 years are affected, though women over 65 years have the highest risk
- Although both women and men are capable of developing the condition, it is much more common in women
- All racial and ethnic groups are affected and no specific predilection is seen
- Developed countries show higher prevalence rate for breast cancer than developing countries average of 80 cases per 100,000 populations, as against 18 cases per 100,000 populations seen in the developing countries. Thus, America, Europe, Australia have greater incidences than Asia and Africa
The Types Of Radiotherapy
The type of radiotherapy you have will depend on the type of breast cancer and the type of surgery you have. Some women may not need to have radiotherapy at all.
Types of radiotherapy include:
- breast radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery, radiation is applied to the whole of the remaining breast tissue
- chest-wall radiotherapy after a mastectomy, radiotherapy is applied to the chest wall
- breast boost some women may be offered a boost of high-dose radiotherapy in the area where the cancer was removed however, this may affect the appearance of your breast, particularly if you have large breasts, and can sometimes have other side effects, including hardening of breast tissue
- radiotherapy to the lymph nodes where radiotherapy is aimed at the armpit and the surrounding area to kill any cancer that may be in the lymph nodes
Don’t Miss: What Does Melanoma In Situ Look Like