When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Make an appointment to see your healthcare provider or dermatologist as soon as you notice:
- Any changes to your skin or changes in the size, shape or color of existing moles or other skin lesions.
- The appearance of a new growth on your skin.
- A sore that doesnt heal.
- Spots on your skin that are different from others.
- Any spots that change, itch or bleed.
Your provider will check your skin, take a biopsy , make a diagnosis and discuss treatment. Also, see your dermatologist annually for a full skin review.
Who Is At Risk For Developing Melanoma
Everyone is at some risk for melanoma, but increased risk depends on several factors. These are sun exposure, number of moles on the skin, skin type and family history .
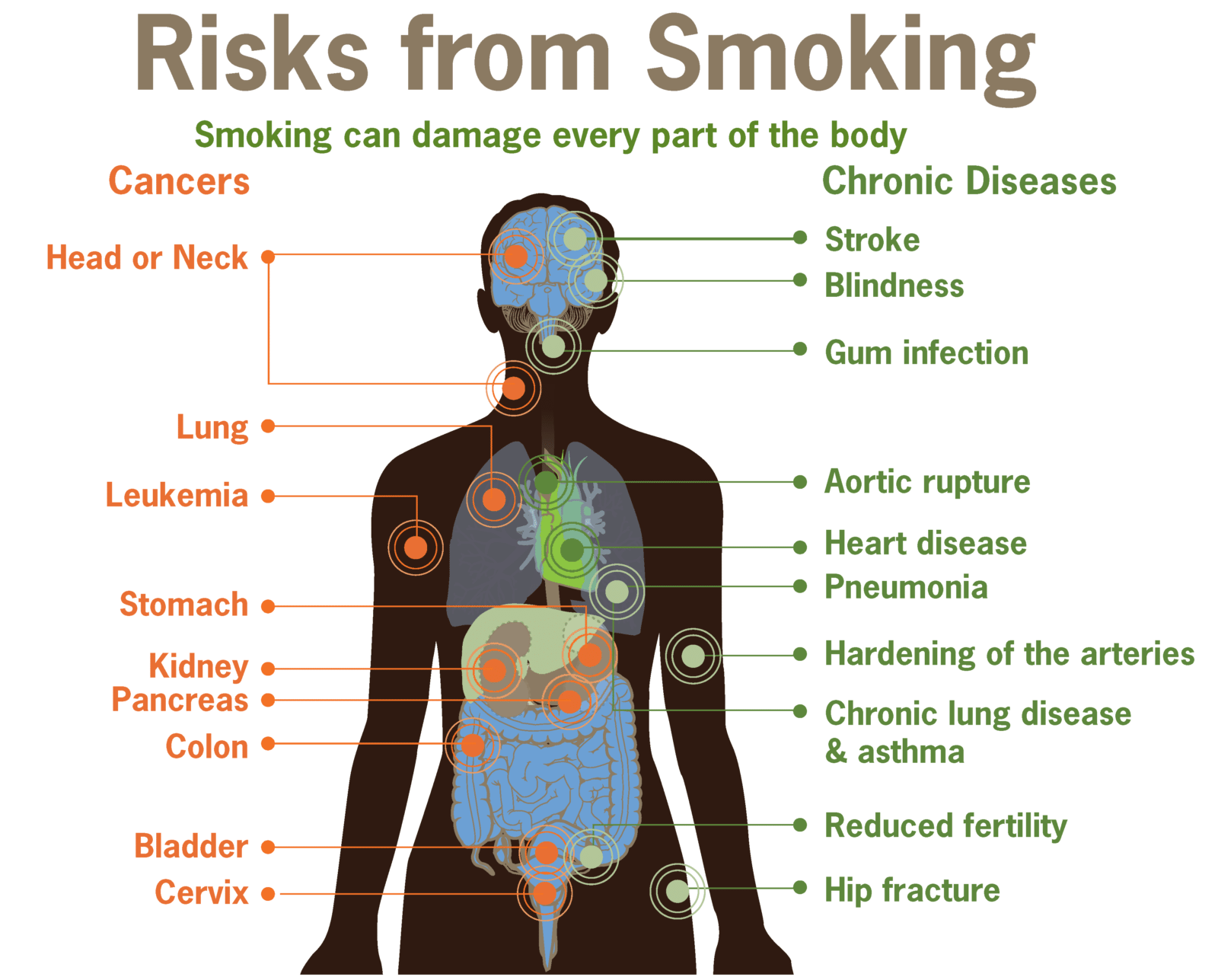
What Skin Cancer Looks Like
Skin cancer appears on the body in many different ways. It can look like a:
-
Changing mole or mole that looks different from your others
-
Dome-shaped growth
-
Non-healing sore or sore that heals and returns
-
Brown or black streak under a nail
It can also show up in other ways.
To find skin cancer on your body, you dont have to remember a long list. Dermatologists sum it up this way. Its time to see a dermatologist if you notice a spot on your skin that:
-
Differs from the others
-
Itches
-
Bleeds
To make it easy for you to check your skin, the AAD created the Body Mole Map. Youll find everything you need to know on a single page. Illustrations show you how to examine your skin and what to look for. Theres even place to record what your spots look like. Youll find this page, which you can print, at Body Mole Map.
Also Check: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rates
How Common Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in the U.S.
Other skin cancer facts:
- Around 20% of Americans develop skin cancer sometime in their life.
- Approximately 9,500 Americans are diagnosed with skin cancer every day.
- Having five or more sunburns in your life doubles your chance of developing melanoma. The good news is that the five-year survival rate is 99% if caught and treated early.
- Non-Hispanic white persons have almost a 30 times higher rate of skin cancer than non-Hispanic Black or Asian/Pacific Islander persons.
- Skin cancer in people with skin of color is often diagnosed in later stages when its more difficult to treat. Some 25% of melanoma cases in African Americans are diagnosed when cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Targeted Drugs And Hormone Therapy
Some types of targeted cancer drugs and hormone therapy cause skin rashes.
Targeted cancer drugs called EGFR inhibitors are most likely to cause skin reactions such as a rash and itching. These include erlotinib and cetuximab.
If you have a severe rash, you may need treatment with steroid creams or tablets, or antibiotic creams or tablets.
Also Check: What Does Melanoma In Situ Look Like
Preparing For Your Appointment
If you have any concerns about the health of your skin, it is important to share them with your doctor. After making an appointment, there are steps you can take to prepare yourself and make the most of your time with your doctor.
Here are some things to consider and be prepared to discuss before visiting the clinic or hospital:
-
What symptoms are you experiencing ?
-
When did you first notice your symptoms?
-
Have there been any major changes or stressors in your life recently?
-
What medications and/or vitamins are you taking?
-
What questions do you have for your doctor?
Who Is At Risk For Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer
A risk factor is anything that may increase your chance of having a disease. The exact cause of someones cancer may not be known. But risk factors can make it more likely for a person to have cancer. Some risk factors may not be in your control. But others may be things you can change.
The most common risk factors for nonmelanoma skin cancer include:
- Greater amount of time spent in the sun
- The use of tanning booths and sunlamps
- Certain features, such as fair skin, light hair , and green, blue, or gray eyes
- Lots of freckles
- HPV infection
- Certain rare inherited conditions, such as xeroderma pigmentosum
Talk with your healthcare provider about your risk factors for nonmelanoma skin cancer and what you can do about them.
You May Like: What Is Large Cell Carcinoma
Metoh Mitochondrial Energy Tonic
Do NOT use MetOH in more than a half a bottle a month dosage if you need to avoid swelling of tumors. In higher doses, the OH water in MetOH gets pulled into an acidic tumor and gets trapped there for a while, causing the tumor to swell.
The base of MetOH is a patented super OH water concentrate that is 300% stronger than 8.0 alkaline water or mineral solutions that alkalize water such as baking soda and water or coral calcium. As a concentrate it is about 12.5 pH. Mixed in distilled water to drink, the pH is 11, which is 300% more alkaline than 8.0 pH.
It also does a much better job of removing acids from your body.
Unlike alkaline water from machines, or any other alkaline water, MetOH actually seeks out and removes hydrogen containing acids from the body. Removing these acids is the key to health. The water in MetOH has one hydrogen atom removed – in a patented process, thereby turning H2O into OH water.
This OH water is a stable water that badly wants to get its missing Hydrogen ions back. So when you drink it, it is greatly attracted to molecules with excess hydrogen ions, and binds with them. The molecules with excess hydrogen are acids. Acids like lactic acid and uric acid, or toxins — which are also acidic.
Just as too many toxins and acids will cause an acidic, low oxygen environment ripe for the development of cancer, reversing this process and reducing acidity while increasing oxygenation will create an environment where cancer can’t grow.
How Cancer Affects A Person’s Life
1. )Cancer is an illness thats been around for decades. Cancer starts in the cells, and cancer types is classified by the area in which these cancer cells develop in . There are treatments that get rid of cancer . or slow it down but its a process with many side effects. People who suffer from cancer are not just the patient but also the people around them. Cancer has claimed many lives, but there have also been survivors
You May Like: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
What To Look For
Any new spots that appear on the skin could potentially be skin cancer, considering that one in five people will develop at least one skin cancer in their lifetime. Definitively distinguishing the different types of skin cancer requires a biopsy and microscopic evaluation, but the general appearance of these tumors also differs to some degree.
- Basal cell carcinomas are often shiny and have been described as “pearlescent.” They may be flat, raised, or dome-shaped, and are often pink, pale, or flesh-colored. On careful inspection, tiny blood vessels may be visible when compared with the surrounding skin. Basal cell cancer characteristically is very often ulcerated and has been called a rodent ulcer because it looks like a mouse has gnawed it.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
- Squamous cell carcinomas are often raised and feel crusty to touch. They can appear scaly and may be ulceratedthat is, have a central depression that is lighter and flatter than the surrounding area. These cancers sometimes bleed, ooze, or form scabs.
This photo contains content that some people may find graphic or disturbing.
Talking With Your Health Care Team About Side Effects
Before starting treatment, talk with your doctor about possible side effects. Ask:
- Which side effects are most likely?
- When are they likely to happen?
- What can we do to prevent or relieve them?
Be sure to tell your health care team about any side effects that happen during treatment and afterward, too. Tell them even if you do not think the side effects are serious. This discussion should include physical, emotional, social, and financial effects of cancer.
Also, ask how much care you may need at home and with daily tasks during and after treatment. This can help you make a caregiving plan. Create a caregiving plan with this 1-page fact sheet that includes an action plan to help make caregiving a team effort. This free fact sheet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
Also Check: Basal Cell Carcinoma Etiology
What Is The Outlook For People With Skin Cancer
Nearly all skin cancers can be cured if they are treated before they have a chance to spread. The earlier skin cancer is found and removed, the better your chance for a full recovery. Ninety percent of those with basal cell skin cancer are cured. It is important to continue following up with a dermatologist to make sure cancer does not return. If something seems wrong, call your doctor right away.
Most skin cancer deaths are from melanoma. If you are diagnosed with melanoma:
- The five-year survival rate if its detected before it spreads to the lymph nodes is 99%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 66%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to distant lymph nodes and other organs is 27%.
How Is Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer Diagnosed
Diagnosing skin cancer starts with checking out a bump, spot, or other mark on your skin. If your healthcare provider thinks you may have nonmelanoma skin cancer, you will need certain exams and tests. Your healthcare provider will ask you about your health history, your symptoms, risk factors, and family history of disease. They will also give you a physical exam. You will likely have a biopsy.
A biopsy is the only way to confirm cancer. Small pieces of tissue are taken out and checked in a lab for cancer cells. Your results will come back in about 1 week.
If your healthcare provider is concerned that your skin cancer is more aggressive, you may have other tests. These help your healthcare providers learn more about the cancer. They can help determine the stage of the cancer. The stage is how much and how far the cancer has spread in your body. It is one of the most important things to know when deciding how to treat the cancer.
Once your cancer is staged, your healthcare provider will talk with you about what the stage means for your treatment. Ask your healthcare provider to explain the stage of your cancer to you in a way you can understand.
Recommended Reading: Melanoma 3c
How Dangerous Is Melanoma
Melanoma is usually curable when detected and treated early. Once melanoma has spread deeper into the skin or other parts of the body, it becomes more difficult to treat and can be deadly.
- The estimated five-year survival rate for U.S. patients whose melanoma is detected early is about 99 percent.
- An estimated 7,180 people will die of melanoma in the U.S. in 2021.
How The Government Of Canada Protects You
The Public Health Agency of Canada monitors cancer in Canada. PHAC identifies trends and risk factors for cancer, develops programs to reduce cancer risks, and researches to evaluate risks from the environment and human behaviours. Health Canada also promotes public awareness about sun safety and the harmful effects of UV rays.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Lobular Carcinoma
Informative Speech On Sun Protection
General purpose: To inform the public on the importance of using sun protectionSpecific purpose: To educate the public on the importance of protecting skin from the sun, and to encourage the use sun protection, such as sunscreen and hats, on a daily basis to prevent exposure from the sun that causes unwanted and harmful diseases that could have been preventive.Thesis statement: Many people do not use sun protection on a daily basis and are unaware of the dangers that can be easily preventive
Who Is Most At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can develop skin cancer, youre at increased risk if you:
- Spend a considerable amount of time working or playing in the sun.
- Get easily sunburned have a history of sunburns.
- Live in a sunny or high-altitude climate.
- Tan or use tanning beds.
- Have light-colored eyes, blond or red hair and fair or freckled skin.
- Have many moles or irregular-shaped moles.
- Have actinic keratosis .
- Have a family history of skin cancer.
- Have had an organ transplant.
- Take medications that suppress or weaken your immune system.
- Have been exposed to ultraviolet light therapy for treating skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
You May Like: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
If Youre Getting Radiation Therapy To The Brain
People with brain tumors often get stereotactic radiosurgery if the cancer is in only one or a few sites in the brain. Side effects depend on where the radiation is aimed. Some side effects might show up quickly, but others might not show up until 1 to 2 years after treatment. Talk with your radiation oncologist about what to watch for and when to call your doctor.
If the cancer is in many areas, sometimes the whole brain is treated with radiation. The side effects of whole brain radiation therapy may not be noticeable until a few weeks after treatment begins.
Radiation to the brain can cause these short-term side effects:
- Headaches
- Trouble with memory and speech
- Seizures
Some of these side effects can happen because radiation has caused the brain to swell. Medicines are usually given to prevent brain swelling, but its important to let your cancer care team know about headaches or any other symptoms. Treatment can affect each person differently, and you may not have these particular side effects.
Radiation to the brain can also have side effects that show up later usually from 6 months to many years after treatment ends. These delayed effects can include serious problems such as memory loss, stroke-like symptoms, and poor brain function. You may also have an increased risk of having another tumor in the area, although this is not common.
Talk with your cancer care team about what to expect from your specific treatment plan.
How Fertility Might Be Affected
For women: Talk to your cancer care team about how radiation might affect your fertility . Its best to do this before starting treatment so you are aware of possible risks to your fertility.
Depending on the radiation dose, women getting radiation therapy in the pelvic area sometimes stop having menstrual periods and have other symptoms of menopause. Report these symptoms to your cancer care and ask them how to relieve these side effects.Sometimes menstrual periods will return when radiation therapy is over, but sometimes they do not.
See Fertility and Women With Cancer to learn more.
For men: Radiation therapy to an area that includes the testicles can reduce both the number of sperm and their ability to function. If you want to father a child in the future and are concerned about reduced fertility, talk to your cancer care team before starting treatment. One option may be to bank your sperm ahead of time.
See Fertility and Men With Cancer to learn more.
Don’t Miss: Treatment For Stage 4 Melanoma
Symptoms Of Skin Cancer
Skin cancers arent all identical, and they may not cause many symptoms. Still, unusual changes to your skin can be a warning sign for the different types of cancer. Being alert for changes to your skin may help you get a diagnosis earlier.
Watch out for symptoms, including:
- skin lesions: A new mole, unusual growth, bump, sore, scaly patch, or dark spot develops and doesnt go away.
- asymmetry: The two halves of the lesion or mole arent even or identical.
- border: The lesions have ragged, uneven edges.
- color: The spot has an unusual color, such as white, pink, black, blue, or red.
- diameter: The spot is larger than one-quarter inch, or about the size of a pencil eraser.
- evolving: You can detect that the mole is changing size, color, or shape.
Basal Cell And Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are the most common types of cancer, but also the least likely to spread. In particular, BCCs rarely spread beyond the initial tumor site. However, left untreated, BCCs can grow deeper into the skin and damage surrounding skin, tissue, and bone. Occasionally, a BCC can become aggressive, spreading to other parts of the body and even becoming life threatening. Also, the longer you wait to have your BCC treated, the more likely it is to return after treatment. Like BCCs, SCCs are highly curable when caught and treated early. However, if left to develop without treatment, an SCC can become invasive to skin and tissue beyond the original skin cancer site, causing disfigurement and even death. Over 15,000 Americans die each year from SCCs. And even if untreated carcinomas dont result in death, they can lead to large, open lesions on the skin that can cause discomfort, embarrassment, and infection.
Also Check: Braf Melanoma Treatment