What Is The Significance Of The Reported Size Of The Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
If the entire tumor or area of DCIS is removed , the pathologist will say how big the DCIS is by measuring how long it is across , either by looking at it under the microscope or by gross examination of the tissue taken out at surgery. Another way to measure DCIS is to note the number of microscopic slides that contain DCIS. For example, the report may say that DCIS was found in 3 slides.
On needle biopsy, measurements of the area of DCIS are not often reported because this type of biopsy only samples a part of the tumor. Later, when the entire area of DCIS is removed , an accurate measurement can be done.
The larger the area of DCIS, the more likely it is to come back after surgery. Doctors use information about the size of the DCIS when recommending further treatments.
How Can Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Of Breast Be Prevented
The following measures may help in reducing the risk for Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast :
General lifestyle changes:
- Maintain a healthy weight and exercise regularly physical activity can reduce risk, especially in post-menopausal women
- Implement and follow a well-balanced diet a high intake of fiber via fresh fruits and vegetables can reduce the risk
- Drink alcohol in moderation limit to one or two drinks a day
- Limit combination hormone therapy used to treat symptoms of menopause. It is advised that individuals be aware of the potential benefits and risks of hormone therapy
- Cancer screenings can help detect any breast cancer, at its earliest stages
- Learn to do âbreast self-examsâ, in order to help identify any unusual lumps, signs in the breasts
In women with a high risk for developing Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast , the physician may suggest the following:
- Preventative medications: The medications tamoxifen and raloxifene are estrogen-blocking drugs that can help prevent the onset of breast cancer in women at high risk. Both drugs have potential side effects including being at a higher risk for blood clots
- Preventative mastectomy: Prophylactic mastectomy, a procedure to surgically remove healthy breasts, is another possible preventative option for women, at a high risk for breast cancer
Dcis Has The Same Risk Factors As Invasive Breast Cancers
“The same things that increase a woman’s risk for DCIS are really the same things that increase her risk of invasive breast cancer,” says Dr. Meyers. For example, having a strong family history can be a factorespecially if a woman tests positive for a high-risk BRCA gene mutation.
Women who have a longer period of estrogen stimulation, meaning they started menstruation early and/or entered menopause late, also have an increased risk of DCIS as well as invasive cancer. That also goes for women who don’t have children, or who have their first pregnancy after age 30.
Recommended Reading: Stage Iii Melanoma Treatment
Future Directions In Dcis
DCIS research is directed mainly at improving treatment and, above all, at preventing progression to invasive disease. As researchers continue to study the pathology of DCIS, they are finding that certain tumor characteristics help predict the treatment most likely to reduce the chance of recurrence. For example, some forms of breast cancer require estrogen in order to grow tumors that do are termed estrogen receptorpositive . Tamoxifen belongs to a class of drugs called selective estrogen-receptor modulators , which act by blocking estrogen receptors. Tamoxifen is more likely to prevent a recurrence in women with ER-positive DCIS than in women with ER-negative disease.
The use of aromatase inhibitors, which block estrogen production in the peripheral tissues and breast tissue, is being investigated in a trial of postmenopausal women with ER-positive DCIS. For women whose DCIS is ER-negative but who have the HER-2/neu gene, researchers are exploring the use of trastuzumab and lapatinib , which block the tumor growth factors produced by that gene.
A new way to administer radiation that is showing some promise in clinical trials is accelerated partial breast irradiation, in which the tumor site alone is treated for five days with a lighter dose of radiation. In another approach, intraoperative radiation therapy, a one-time dose of radiation is delivered to the involved area of the breast after the tumor has been removed but before the incision is closed.
Risk Of Developing Invasive Breast Cancer After Dcis
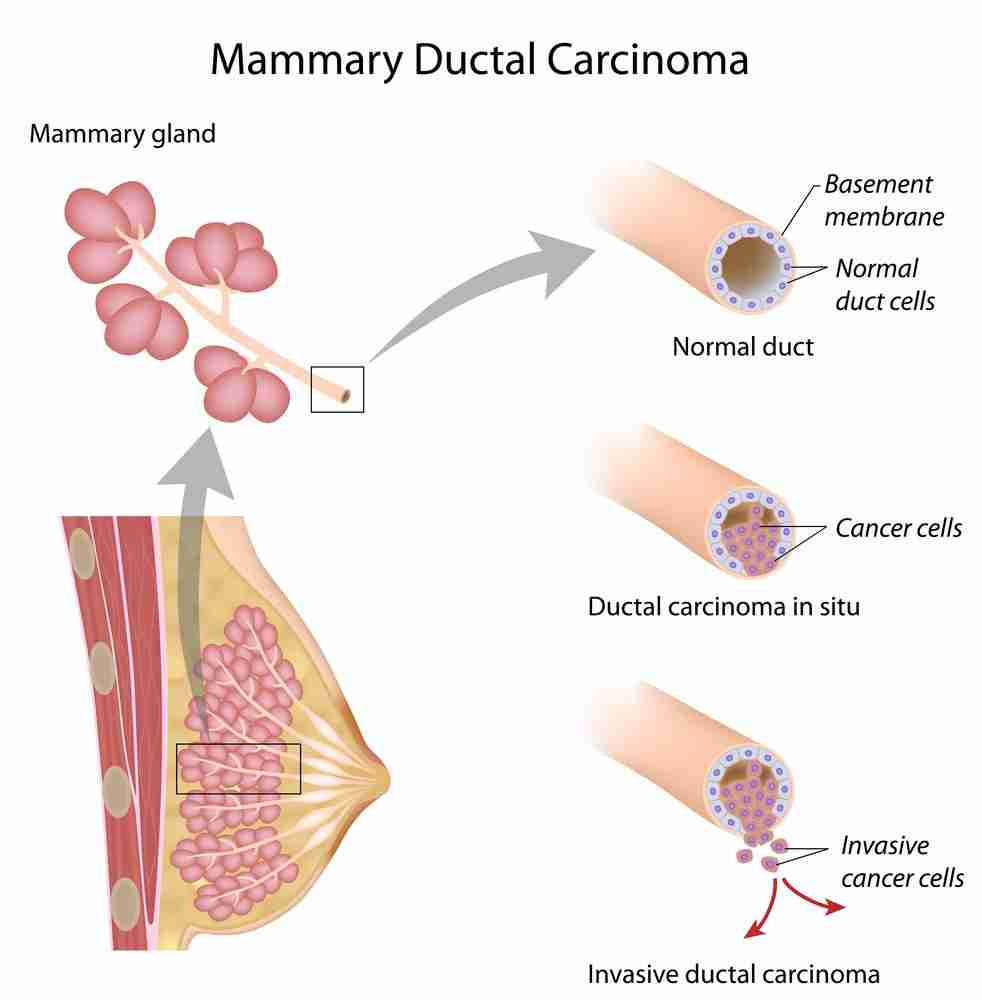
After treatment for DCIS, theres a small risk of:
- DCIS recurrence
- Invasive breast cancer
These risks are higher with lumpectomy plus radiation therapy than with mastectomy . However, overall survival is the same after either treatment .
Higher grade DCIS appears more likely than lower grade DCIS to progress to invasive cancer after treatment .
With close follow-up, invasive breast cancer is usually caught early and can be treated effectively.
Learn more about tumor grade.
If youve been diagnosed with DCIS, Susan G. Komen® has Questions to Ask Your Doctor resources that may be helpful. For example, we have a Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Breast Cancer Surgery resource and a Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Radiation Therapy and Side Effects resource.
You can download and print these resources and take them with you to your next doctor appointment. Theres plenty of space to write down the answers to these questions, which you can refer to later.
There are other Questions to Ask Your Doctor resources on many different breast cancer topics you may wish to download. They are a nice tool for people recently diagnosed with breast cancer, who may be too overwhelmed to know where to begin to gather information.
Also Check: Cell Cancer Symptoms
Comedo Dcis Usually Shows Small Groups Of Dead Cells
What typically happens in a breast comedo carcinoma is that some of the cells die off and form small groups. . It is a fast growing type of breast cancer with some risk of future invasive cancer status, but most of the time comedo breast carcinoma is considered to be intraductal, meaning, that it will be confined to the breast ducts. DCIS-comedo is generally diagnosed when at least one duct in the breast is filled and expanded by large, markedly atypical cells, and which also has abundant central luminal necrosis.
Why Is Dcis Treated
DCIS is non-invasive, but without treatment, the abnormal cells could progress to invasive cancer over time.
Health care providers cannot predict which cases of DCIS will progress to invasive breast cancer and which will not. Because DCIS might progress to invasive breast cancer, almost all cases of DCIS are treated.
Komen Perspectives
You May Like: Malignant Breast Cancer Survival Rate
Hormone Therapy After Breast Surgery
If the DCIS is hormone receptor-positive , treatment with tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor, such as exemestane or anastrozole, for 5 years after surgery can lower the risk of another DCIS or invasive cancer developing in either breast. If you have hormone receptor-positive DCIS, discuss the reasons for and against hormone therapy with your doctor.
Lumpectomy With Radiation Therapy
In this procedure, the surgeon will remove the tumor and some healthy breast tissue close by as a precaution.
Sometimes they may also remove the lymph nodes and request a biopsy to confirm that the cancer has not spread. Healthcare professionals call this a sentinel lymph node biopsy . They are more likely to do this if the tumor is large.
After surgery a person will receive radiation therapy to destroy any remaining cells.
Recommended Reading: What Does Well Differentiated Mean
What Are The Symptoms Of Dcis
DCIS usually has no symptoms. Most cases of DCIS are found during routine breast screening or if a mammogram is done for some other reason.
Occasionally DCIS is found when someone has a breast change such as a lump or discharge from the nipple. However, if someone with DCIS has a breast change its more likely they will also have an invasive breast cancer.
Some people with DCIS also have a type of rash involving the nipple known as Pagets disease of the nipple, although this is rare.
Difficult Decisions For Patients
Toro de Stefani is one of 60,000 U.S. women diagnosed with DCIS each year. Each must decide on a treatment option.
Current guidelines that recommend lumpectomy and radiation are causing concerns that the condition may be overtreated, since most cases never become invasive.
This gives medical professionals enormous uncertainty about how to advise women on an individual basis, says Thompson, professor of Surgery at MD Anderson. And therefore, historically the treatments have ranged from active surveillance on one end of the pectrum all the way to mastectomies on the other.
Thompson says DCIS diagnoses have increased as breast imaging has become more accurate and frequent. The National Institutes of Health estimates that by 2020, more than 1 million women in the U.S. will be living with a DCIS diagnosis, compared to 500,000 in 2005.
Before mammograms became common, many women had the condition for years without being aware of it, because it grows so slowly and causes no symptoms.
Perhaps, surprisingly, given that breast screening has been around for three or four decades, were only now really coming to grips with the fact that we often diagnose some conditions like DCIS as breast cancer even though theyre not conventional, invasive breast cancers, Thompson says.
Hes participating in three DCIS research studies that he hopes will make treatment decisions easier.
Read Also: Prognosis Of Skin Cancer
Stage Zero Breast Cancer: Whats The Optimal Treatment For Dcis
Before the advent of routine mammography, DCIS was rarely detected. But today, DCIS accounts for 20% of breast cancer diagnoses and would be the fifth most common cancer in women if classified independently.
Often called stage zero breast cancer, DCIS growths are confined to the inside of the breasts milk ducts, and many never develop into invasive cancers. Several treatment options are available, and opinions about the optimal treatment for DCIS vary widely among doctors.
A new study from researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons may help women and their physicians narrow down the treatment choices.
DCIS is considered a pre-invasive cancer, but the current standard of care is to treat it like an early-stage invasive breast cancer, says Apar Gupta, MD, assistant professor of radiation oncology at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and lead author of the study.
However, not all treatments for invasive breast cancer may be optimal for DCIS, Gupta says. His study suggests that in most cases of DCIS, the side effects of hormone therapy may outweigh its benefits.
The CUIMC Newsroom spoke with Gupta to learn how the studys findings can help providers and their patients navigate treatment for DCIS. Below are excerpts from the conversation:
Why is DCIS treatment controversial?
How does your study help women make a decision about treatment after lumpectomy?
Is there a role for hormone therapy?
How Does Dcis Affect Black Women
According to a 2019 article in the journal Cancer, compared to white women, Black women are more likely to:
- die of breast cancer after DCIS
- develop invasive breast cancer after DCIS
- develop ER-positive or PR-positive invasive breast cancer after DCIS
Additionally, basal-like tumors disproportionately affected Black women, and their chance of developing triple-negative breast cancer doubled after DCIS.
The researchers note that the higher mortality rates may be, in part, due to the higher chance of developing more aggressive breast cancer types, such as triple-negative breast cancer. However, it is also the result of health inequities, including a lack of access to competent oncology care and delays in treatment.
Learn more about how breast cancer affects Black women here.
Recommended Reading: Merkel Cell Carcinoma Immunotherapy
Stage 1b Breast Cancer Means One Of The Following Descriptions Applies:
Lymph nodes have cancer evidence with small clusters of cells between the approximate size of a pinprick to the approximate width of a grain of rice .
AND EITHER No actual tumor is found in the breast.
OR The tumor is smaller than the approximate size of a peanut .
Similar to stage 0, breast cancer at this stage is very treatable and survivable. When breast cancer is detected early, and is in the localized stage , the 5-year relative survival rate is 100%.
What Type Of Follow
Each patient is different, and the doctor will work with each individual on a follow-up plan after surgery and radiation therapy. Typically, a patient can expect to see the doctor for a physical exam every six to 12 months for five years after treatment, then annually after that. An annual mammogram will also be recommended.
Recommended Reading: What Is Stage 2 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Can Dcis Develop Into Invasive Breast Cancer
If DCIS is not treated, the cancer cells may develop the ability to spread outside the ducts, into the surrounding breast tissue. This is known as invasive breast cancer. Invasive cancer has the potential to also spread to other parts of the body.
In some cases, DCIS will never develop further or grows so slowly that it would never cause harm during a persons lifetime. Although the size and grade of the DCIS can help predict if it will become invasive, there is currently no way of knowing if this will happen. is more likely to become an invasive breast cancer and to do so over a shorter time than low-grade DCIS.
How Quickly Does Dcis Progress
Grade 1 DCIS is almost always ER and PR positive and is a very slow growing form of cancer. It can take years, even decades, to see progression of the disease. In some cases, it may take such a long time to spread beyond the breast duct that it is not an event that will happen during a persons lifetime.
You May Like: Melanoma Forearm
Does Dacera Suffer From Ra
Milk duct cancer syndrome is a condition in which there are abnormal cells confined to milk ducts. They have not yet reached the surrounding normal breast tissue but they cannot spread outside of the cell. More of a precancerous or invasive feature. In summary, DCIS is not life-threatening, but it is more likely to progress to invasive cancer cells.
Lifestyle Also Plays A Role
Some risk factors for DCIS are modifiable. Eating lots of fruits and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, and limiting alcohol intake have all been linked to lower breast cancer rates, says Dr. Meyers, and they are smart habits to develop no matter what type of breast cancer you’re trying to avoid.
For women who have already had DCIS, cutting back on drinking may reduce their risk of a recurrence, according to a 2014 study in the journal Cancer, Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention. “It is possible that alcohol consumption may increase risk of second breast cancer incidence,” the authors wrote in their paper, “but may not substantially increase the likelihood of aggressive second diagnoses that result in death, particularly among DCIS survivors.”
Don’t Miss: Infiltrating Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Stage Of Cancer Carcinoma In Situ And Additional Terms
A common question is, “What stage of cancer is carcinoma in situ?” Carcinoma in situ is referred to as stage 0 cancer. At this stage, cancer is considered non-invasive. Stage 1 cancers and beyond are considered invasive, meaning that even if low, there is a potential they could spread. Other terms that may be used in defining the same thing as carcinoma in situ or stage 0 cancer include:
- Non-infiltrating
- Intra-epithelial
Coping With A Diagnosis Of Dcis
Being told you have DCIS can be a difficult and worrying time. Everyone reacts differently to their diagnosis and have their own way of coping.
Although DCIS is an early form of breast cancer with a very good prognosis, people understandably may feel very anxious and frightened by the diagnosis. People can often struggle to come to terms with being offered treatments such as a mastectomy, at the same time as being told their DCIS may never do them any harm.
Some people are reluctant to say theyre anxious about a diagnosis of DCIS because they worry others will see it as less important than other types of breast cancer. Because of this they might feel less able to ask for support. But there are people who can support you so dont be afraid to ask for help if you need it. By letting other people know how you feel, particularly your family and friends, they can be more supportive.
Some people find it helpful to discuss their feelings and concerns with their breast care nurse or specialist. If youd like to talk through your feelings and concerns in more depth over a period of time, a counsellor or psychologist may be more appropriate. Your breast care nurse, specialist or GP can arrange this.
Find out more about coping emotionally with breast cancer.
If you want to talk you can also call our Helpline on 0808 800 6000.
You May Like: Immunotherapy For Malignant Melanoma
A Vaccine May Be Helpful
Patients diagnosed with DCIS may one day get a vaccine to help reduce their risk of developing an invasive breast cancer in the future, according to a 2016 study published in Clinical Cancer Research.
More clinical trials are underway, but researchers hope that a vaccine may be able to stimulate the immune system and keep early DCIS from progressing beyond the milk duct. If trials are successful, experts say it could eventually be an alternative to surgery and radiation for some patients.
To get our top stories delivered to your inbox, sign up for the Healthy Living newsletter
How Common Is Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
The American Cancer Society expects that 63,960 new cases of DCIS will be found in 2018. Today more and more women are aware of the importance of early detection and are getting mammograms each year. Because of this, the number of cases of DCIS has increased. In addition, mammography technology has greatly improved as well and is better able to detect problems at an earlier stage. An estimated 12.4% of women in the U.S. will develop invasive breast cancer at some time in their lives.
Read Also: Well Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma Prognosis