How Can I Help My Child Live With Skin Cancer
If your child has skin cancer, you can help him or her during treatment in these ways:
-
Your child may have trouble eating. A dietitian or nutritionist may be able to help.
-
Your child may be very tired. He or she will need to learn to balance rest and activity.
-
Get emotional support for your child. Counselors and support groups can help.
-
Keep all follow-up appointments.
-
Keep your child out of the sun.
After treatment, check your child’s skin every month or as often as advised.
Getting Skin Cancer Where The Sun Dont Shine
For years, dermatologists have preached about the virtues of sun screens, for good reason. They work.
However, its also true that skin cancer can appear in areas of the body that have no skin exposed to the sun. Were talking about some mighty private areas as well as seemingly underexposed areas like the palms of the hand and soles of the feet.
Are There Different Types Of Radiation In Sunlight
Yes. The types of radiation include:
- visible light, which gives us the colours we see
- infrared radiation which gives us the warmth we feel
- ultraviolet radiation
Except in extreme situations, neither visible light nor infrared radiation from sunlight causes health problems. However, ultraviolet radiation can cause harmful effects to the skin.
There are three basic types of ultraviolet radiation:
- UVA
Table 1 summarizes the general features of each type.
| Table 1 Types of Ultraviolet Radiation and Their Features | |
|---|---|
| Ultraviolet Radiation Type | |
| Ultraviolet A radiation UVA, long-wave UV) | -not filtered out in the atmosphere -passes through glass -once considered harmless but now believed harmful over the long term -levels remain relatively constant throughout the day |
| Ultraviolet B radiation | -some filtered out in the atmosphere by the ozone layer -does not pass through glass -causes sunburn, tanning, wrinkling, aging of the skin and skin cancer -highest intensity at noontime |
| -filtered out in the atmosphere by the ozone layer before reaching earth -major artificial sources are germicidal lamps -burns the skin and causes skin cancer |
You May Like: What Is The Leading Cause Of Skin Cancer
Get Ready For Next Time
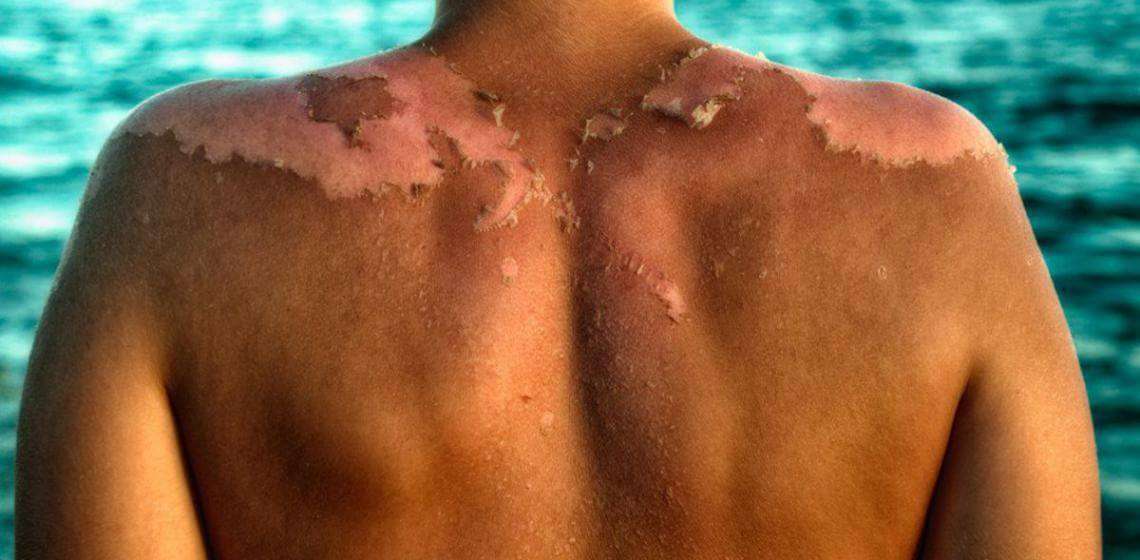
Once inflammation subsides, the lower layer of skin cells begins to grow quickly to replace the dead cells. Post-sunburn peeling is large sheets of dead cells being shed from the upper layer of the skin to make way for this new growth.
DNA damage also causes the cells in the upper layer of skin to signal the cells that produce melanin to get to work. This is what provides the tan that can come after the redness has faded.
The melanin settles over the skin cells to shield them from future UV exposure. But don’t rely on your tan to fully protect you next time, it’s only as protective as SPF 2 sunscreen.
Maxually/Flickr, CC BY
There’s nothing you can do for sunburn except giving the skin time to heal itself. In the meantime, you can relieve the discomfort by staying out of the sun, drinking plenty of water, applying a cool compress, and taking over-the-counter medications such as paracetamol.
If the pain can’t be managed by these measures, or there is extensive blistering, nausea, fever or dizziness, it’s time to see a doctor.
Once your sunburn has subsided and you’re thinking of venturing out again, you can best avoid another painful bout by using sun protection whenever the UV index reaches three or higher. This usually happens daily from September to April in the southern states and all year round further north. Use the SunSmart app to find out today’s UV index and sun protection times in your area.
This article was originally published on The Conversation.
Start At The Top Wear A Hat
Safeguard against wrinkles and skin cancer and look cool at the beach by wearing a great hat whenever youre outside. Hats are a perfect complement to UV-filtering sunglasses and broad-spectrum sunscreen to protect your face and eyes.
Heres what to look for in a sun-safe hat:
Wide Brim
The best hats for sun protection have a brim of at least three inches to shade the face, scalp, neck, shoulders and upper back, along with easily overlooked places like the tops of the ears and back of the neck.
Tight Knit
Look for a tightly woven hat rather than a loosely constructed straw hat that lets in the UV rays.
Recommended Reading: Squamous Cell Carcinoma Skin Metastasis
Looks Can Be Deceptive
Precancerous skin growths may look harmless. As you now know, their looks can be deceptive. Following your dermatologists recommendations can help protect your skin and your health.
Precancerous skin growths may look harmless
These arrows point to precancerous skin growths that are barely noticeable.
Related AAD resources
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed In A Child
The healthcare provider will examine your child’s skin. Tell the healthcare provider:
-
When you first noticed the skin problem
-
If it oozes fluid or bleeds, or gets crusty
-
If its changed in size, color, or shape
-
If your child has pain or itching
Tell the healthcare provider if your child has had skin cancer in the past, and if other your family members have had skin cancer.
Your child’s healthcare provider will likely take a small piece of tissue from a mole or other skin mark that may look like cancer. The tissue is sent to a lab. A doctor called a pathologist looks at the tissue under a microscope. He or she may do other tests to see if cancer cells are in the sample. The biopsy results will likely be ready in a few days or a week. Your child’s healthcare provider will tell you the results. He or she will talk with you about other tests that may be needed if cancer is found.
Recommended Reading: Can You Cure Stage 4 Melanoma
What Factors Besides Frequent Sun Exposure Contribute To Melanoma Development
This is correct, exposure to both natural ultraviolet radiation from the sun and UV radiation from artificial sources such as a tanning bed is the most notable known risk factors for most melanomas.
Sunburns seem to be particularly important. One study showed the risk of melanoma increased by 80% in those who had five or more blistering sunburns during the ages 15-20 years old.
Genetic factors also may play a role such as skin characteristics or genetic mutations which may be linked to melanoma or having a lowered immune system.
Having many moles, atypical or abnormal moles, or having a history of melanoma are also risk factors for melanoma.
What Is Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the US, and the number of cases continues to rise. It is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells. While healthy cells grow and divide in an orderly way, cancer cells grow and divide in a rapid, haphazard manner. This rapid growth results in tumors that are either benign or malignant .
There are three main types of skin cancer:
Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are less serious types and make up 95% of all skin cancers. Also referred to as non-melanoma skin cancers, they are highly curable when treated early.
Melanoma, made up of abnormal skin pigment cells called melanocytes, is the most serious form of skin cancer and causes 75% of all skin cancer deaths. Left untreated, it can spread to other organs and is difficult to control.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate For Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Will One Bad Sunburn Give You Skin Cancer
by Garth Sundem | Jul 27, 2015 | Latest News, Patient Care
Recently at the Colorado Melanoma Foundation booth at the Colorado Dragon Boat Festival, a girl learns theres no such thing as too much sunscreen.
It seems like everybodys got a story about that one bad burn the time you fell asleep next to the pool and tattooed a white handprint on your lobster-red chest, or forgot to pack the sunscreen while hiking a Colorado 14er. As you know, sunburn increases your chance of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. But what about just one bad burn? And what can you do about it now?
Were still waiting for a definitive one-sunburn study to show us exactly how much melanoma risk increases with one blistering burn, but to the best of our knowledge, it seems like the answer is about 50 percent. One bad burn as a child makes you half-again more likely to develop melanoma as an adult, says Neil Box, PhD, investigator at the University of Colorado Cancer Center and assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at the CU School of Medicine. Dr. Box is also president of the Colorado Melanoma Foundation.
This year, about 250,000 people will be diagnosed with melanoma and 60,000 people will die from this most dangerous form of skin cancer. While the increased risk accompanying one bad burn is still imprecise, studies show that the overall lifetime risk of developing melanoma climbs 80 percent with 5 blistering burns in childhood.
Colorado Cancer Blogs
Amount Of Exposure To Sunlight
The damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation accumulate over the years. In general, the risk of developing skin cancer increases with the amount of time spent under the sun and the intensity of radiation. The intensity of radiation varies according to the season of the year, time of day, geographic location , elevation above sea level, reflection from surfaces , stratospheric ozone, clouds, and air pollution.
Recent studies have focused on the effects of intermittent sun exposure in comparison to chronic exposure. It appears that the type of exposure may influence the type of cancer that develops. For example, intermittent solar exposure may be an important factor leading to the onset of basal cell carcinoma of the skin. Childhood sun exposure may also play an important part in the development of these cancers later in adult life. The pattern for cutaneous melanoma is similar to that for basal cell carcinoma.
In contrast, the relationship between squamous cell carcinoma and solar UVR appears to be quite different. For squamous cell tumours, high levels of chronic occupational sunlight exposure, especially in the 10 years prior to diagnosis, results in an elevated risk for this cancer in the highest exposure group.
Also Check: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
How Is Skin Cancer Diagnosed And Treated
Skin cancers are usually diagnosed by taking a biopsy from the suspected area. In the case of melanoma, the doctor might also check if there has been any spread to the lymph nodes.
Treatment for both non-melanoma and melanoma skin cancer mainly consists of surgery. Surgery is usually curative for non-melanoma skin cancer and can be successful in melanoma skin cancer if found early enough. In the case of advanced melanoma skin cancer, additional treatment might be given, including drugs that target specific genetic changes.
If you suspect you might have skin cancer or have found any changes to your skin, please contact your GP as soon as possible to get it checked out.
How Does Sunlight Affect The Skin
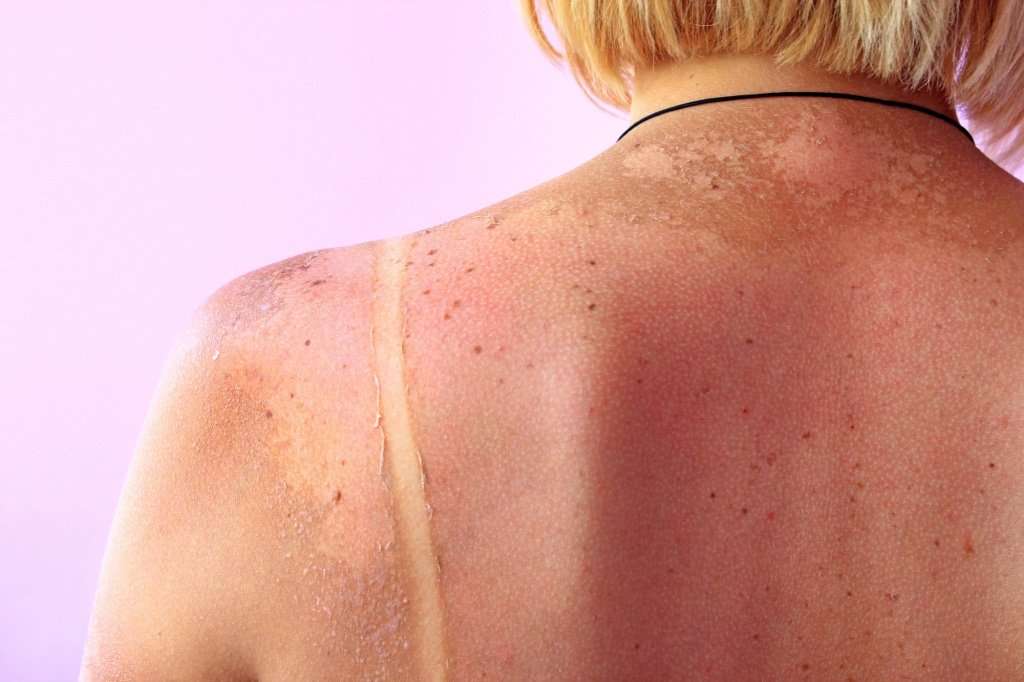
When ultraviolet radiation reaches the skin, some radiation is reflected away from the surface. The remaining radiation is scattered into the tissues just beneath the skin’s surface. A fraction of this radiation is absorbed by the skin’s living cells.
Ultraviolet radiation absorbed by living cells damages sensitive substances that influence the skin’s normal growth and appearance. Damage can result in:
- sunburn
- increased rate of aging of the skin
- skin cancer
Read Also: Can You Die From Basal Cell Skin Cancer
If You Have One Of The Two Types Of Non
- A sore that crusts, bleeds, or oozes without scabbing over and healing for a period of several weeks
- One patch of skin appears tight and shiny like a scar
- A red, raised patch with or without itching
- A dip in the skin with a raised border
- A shiny, pearl-like bump
The terms basal cell and squamous cell refer to the layer of the skin where a doctor diagnoses a carcinoma, which means the skin contains cancer cells. Basal cell skin cancer means that cancer is present in the skins epidermis. Squamous cell skin cancer resides in the skins subcutaneous layer.
Can Any Mole Become A Melanoma
Most nevi, also known as moles, do not cause any problems on our skin. At the same time, any mole on the body has the potential to change to an abnormal mole or even transform into the deadliest form of skin cancer called a melanoma.
Its important to know most melanomas form de novo, which means as a new lesion with no associated mole.
It is recommended to examine the skin regularly and not only identify any moles that might be changing in shape, color, texture or size, but also ones any lesions that are new. If anything is concerning on self-examination, notify your physician right away for further evaluation.
Recommended Reading: What Is Nodular And Infiltrating Basal Cell Carcinoma
Effect On Skin And Appearance
Menopause causes many changes to your skin. Your body stops making as much collagen. You lose some fat under your skin and your skin’s elasticity drops. That, combined with dryness caused by hormonal changes, can cause sagging — especially around the neck, jawline, and cheeks — and fine lines and wrinkles become more prevalent. The lines and wrinkles you get with menopause are often crow’s feet and lines above the upper lip. The reduction of oil causes dry, itchy, and easily irritable skin, its more prone to photodamage and hyperpigmentation and unwanted growth of facial hair.
A reduction of collagen makes the skin less elastic, the skin loses volume and tightness. Women lose 30% of the overall collagen content that is present in their skin within five years of menopause and then continues at around 2% every year.
Collagen loss is usually most noticeable around the eyes and lower face and unfairly, hormone fluctuations can also mean breakouts. These occur usually along the jawline, and sometimes even those who have never had breakouts will get them.
During menopause skin starts to become thinner and the natural rate of skin cell turnover slows right down. The skin can become more transparent due to a lack of essential fatty acids and lines can look deeper.
How People Of Color Can Reduce Their Skin Cancer Risk
Dermatologists in the United States tell their patients with skin of color to reduce their risk of getting skin cancer by doing the following:
Seek shade whenever possible. The sun causes many skin cancers.
Wear clothing that protects your skin from the sun. A wide-brimmed hat can shade your face and neck. You also want to wear shoes that cover the entire foot. African Americans often develop skin cancer on their feet.
Wear sunscreen. Yes, people of color should wear sunscreen. Dermatologists recommend that people of color use sunscreen that has:
Apply sunscreen to dry skin 15 to 30 minutes before going outdoors. You want to apply sunscreen to skin that will be bare. Be sure to apply sunscreen every day even on cloudy days.
When outdoors, reapply sunscreen. You want to reapply:
Never use tanning beds or sunlamps. These emit harmful UV rays, which can cause skin cancer.
Skin of color: How to prevent and detect skin cancer
Although people of color have a lower risk of developing skin cancer than Caucasians, when skin cancer develops in people of color, it is often diagnosed at a more advanced stage making it more difficult to treat.
Follow these tips from dermatologists to protect your skin from the sun and reduce your risk of skin cancer.
Read Also: Melanoma Bone Cancer Symptoms
What Causes Melanoma Skin Cancer
Many risk factors for melanoma have been found, but its not always clear exactly how they might cause cancer.
For example, while most moles never turn into a melanoma, some do. Researchers have found some gene changes inside mole cells that may cause them to become melanoma cells. But its still not known exactly why some moles become cancerous while most dont.
DNA is the chemical in each of our cells that makes up our genes, which control how our cells function. We usually look like our parents because they are the source of our DNA. But DNA affects more than just how we look.
Some genes control when our cells grow, divide into new cells, and die:
- Genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes.
- Genes that keep cell growth in check, repair mistakes in DNA, or cause cells to die at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
Cancers can be caused by DNA mutations that keep oncogenes turned on, or that turn off tumor suppressor genes. These types of gene changes can lead to cells growing out of control. Changes in several different genes are usually needed for a cell to become a cancer cell.
Myth : Tanning Beds Are Safer Than The Sun
Actually, the opposite is true: Devices like tanning beds and sun lamps can emit higher amounts of ultraviolet radiation than the sun, including both UVA and UVB radiation. UV radiation of any type increases your cancer risk, and the more you get, the higher your risk.
âTanning booths increase your risk of melanoma a ridiculous amount because they use really unnatural levels of UV light that youâre never exposed to in nature,â Lee said, referring to one of the most deadly types of skin cancer. Only 1 percent of people diagnosed each year with skin cancer have melanoma, according to the American Cancer Society, but itâs responsible for most skin cancer deaths.
A 2003 study of tanning facilities in North Carolina found that the average amount of UVA radiation emitted by the beds in the study was four times higher than whatâs emitted by the noontime sun, and the average UVB radiation level was nearly twice as high as the sun. The study also found that patrons were commonly in the beds for far longer than U.S. Food and Drug Administration-recommended limits for exposure to such dangerously high radiation .
Read Also: Stage 5 Cancer Symptoms