Basal Cell Carcinoma Of The Nose
BCC of the nose tip is common . Larger tumours will infiltrate and eventually destroy the neighbouring areas. Infiltration of the delicate muscles of the distal nasal part and later on the cartilaginous structures is characteristic for locally advanced tumours. BCCs of the lateral part of lateral sidewall do not necessarily respect the nasofacial groove. They may infiltrate the muscles including the orbicularis oculi in advanced stages. BCCs of the nasal root are less common than those of the bridge .c]. Since inner canthus is in close proximity this may cause a particular challenge for defect closure.
Clinical presentation of basal cell carcinoma of the nose. Small solid but ulcerated BCC of the nose tip. Large adenoid-cystic BCC of the nasal root. Patients with 3 lesions suspicious for BCC: Morpheic BCC, larger and smaller solid BCC Ill-defined morphoeic BCC with partial destruction of nostril
The ala nasi is a common place for BCC. Larger tumours will involve the nostrils and/or alarfacial and nasofacial grooves . Tumours of the nasal bridge often extend to the lateral sidewall.
Even small tumours of the columella and tend to invade cartilagenous structures, mucous membranes, and subcutaneous tissue. Some patients present with multiple nasal BCC .
What Are Basal Cells
Human skin is made up of two main layers: the epidermis, which forms the top layer of skin, and the dermis, which forms the bottom layer.
The epidermis functions as the protective outer shell, while the dermis contains blood vessels, hair follicles, melanocytes, and other specialized biological structures.
Within the two layers of skin, several different types of cells can be found. Each type of cell serves a different role in the normal functioning of the skin.
Basal cells can be found in the deepest layer of the epidermis. While their specific purpose isnt completely clear, scientist believe basal cells serve as a type of stem cellbasal cells start out as relatively undifferentiated, but rapidly reproduce and aid in the process of creating new skin cells.
Recommended Reading: What Is Squamous Cell Carcinoma
What Causes A Basal Cell Cancer
The sun is responsible for over 90 percent of all skin cancers, including BCCs, which occur most frequently on the sun-exposed areas of the body: face, ears, neck, scalp, shoulders and back. Risk factors include light complexion, age greater than 60 years of age, male gender, blistering sunburns and indoor tanning exposure.
You May Like: Does Skin Cancer Itch And Burn
What Are The Clinical Features Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC is a locally invasive skin tumour. The main characteristics are:
- Slowly growing plaque or nodule
- Skin coloured, pink or pigmented
- Varies in size from a few millimetres to several centimetres in diameter
- Spontaneous bleeding or ulceration
BCC is very rarely a threat to life. A tiny proportion of BCCs grow rapidly, invade deeply, and/or metastasise to local lymph nodes.
Read Also: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
What Are The Advantages Of Mohs Surgery
The technique offers the highest possible cure rate for the treatment of skin cancer, compared to other therapeutic modalities. Mohs surgery also allows the physician to remove as little normal tissue as possible around the tumor, and thus in many cases can provide a superior cosmetic result. Our doctors also offer a variety of laser treatments to improve the appearance of scars after Mohs surgery. Another advantage is that with many large skin cancers, hospitalization can be avoided by performing Mohs surgery on an out-patient basis.
Read Also: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
The Clinical Course Of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Although most patients who develop SCCs have localized disease that can be cured, tumor recurrence, tumor spread to other parts of the body, and death occasionally occurs.
Larger tumors may cause disfigurement as they may penetrate into the underlying tissues causing nerve or muscle damage. SCCs that have spread into the underlying tissue have been resistant to previous therapy or have reoccurred are considered advanced SCCs.
What Causes Skin Cancer
Most cases of skin cancer are caused by repeated and unprotected skin exposure to ultraviolet light from sunlight and tanning beds.
Risk factors for developing skin cancer include:
- Ultraviolet exposure from the sun or tanning beds
- Having certain types of moles
- Having fair skin that freckles or burns easily, light hair, and blue or green eyes
- Family history of skin cancer
- Personal history of skin cancers
- Having a compromised immune system, such as people who have HIV/AIDS, are organ transplant recipients, or are receiving certain medical treatments such as chemotherapy
- Older age: the risk increases as people age
- Being male
Recommended Reading: Can Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastasis
What Are The Symptoms Of Basal Cell Cancer Of The Head And Neck
Basal cell cancers usually present as an abnormal growth on the skin. The growth may have the appearance of a wart, crusty spot, reddish patch, mole, nodule or bump, or a sore that does not heal. It may or may not bleed and can sometimes be painful. These are usually slow-growing tumors that begin as small spots on sun-exposed areas of the face. Because they can have such a range of appearances, any new persistent skin lesion should be evaluated.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery Specialists
Our head and neck surgeons and speech language pathologists take a proactive approach to cancer treatment. Meet the Johns Hopkins specialists who will work closely with you during your journey.
How Can You Tell The Difference Between Squamous Cell Carcinoma And Basal Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinomacancerdifference between basal cellsquamous cell cancerssquamous cell cancer
. Likewise, what is the difference between basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma accounts for more than 90 percent of all skin cancers in the United States and is the most common of all cancers. Typically, it is a slow-growing cancer that seldom spreads to other parts of the body. Squamous cell carcinoma also rarely spreads, but does so more often than basal cell carcinoma.
Additionally, what does squamous cell carcinoma look like? Squamous cell carcinomas may appear as flat reddish or brownish patches in the skin, often with a rough, scaly, or crusted surface. They tend to grow slowly and usually occur on sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face, ears, neck, lips, and backs of the hands. Normal moles also develop from these skin cells.
Furthermore, which is more serious basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma?
Though not as common as basal cell ,squamous cell is more serious because it is likely to spread . Treated early, the cure rate is over 90%, but metastases occur in 1%â5% of cases.
Can basal cell carcinoma turn into squamous cell carcinoma?
Dr. Goldberg: The simple answer is no. People lump basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas together as ânonmelanoma skin cancers,â but that’s doing them a disservice. They’re not the same.
Recommended Reading: How To Identify Basal Cell Carcinoma
What Is The Treatment
Mohs micrographic surgery is a specialized technique for the removal of certain types of skin cancer. The skin cancer is removed one layer at a time and analyzed microscopically while you are in the office. Once the skin layer is removed, it is stained and carefully diagrammed. It is then processed immediately in the office by a specially trained technician who converts the tissue into micrographic slides. These slides are then reviewed by the physician to determine if all of the malignant cells have been removed. If there is residual tumor, it is possible to determine precisely where it is located since the tissue was previously diagrammed. The exact area where the tissue persists is then removed by taking another layer of tissue, and the process is repeated. The surgery itself takes only several minutes however, the tissue processing takes anywhere from twenty minutes to one hour, and then upon examination of the slides, a decision is made as to whether or not further surgery is indicated. Each procedure where tissue is removed is referred to as a stage.
Risk Of Further Melanomas
Most people treated for early melanoma do not have further trouble with the disease. However, when there is a chance that the melanoma may have spread to other parts of your body, you will need regular check-ups. Your doctor will decide how often you will need check-ups everyone is different. They will become less frequent if you have no further problems. After treatment for melanoma it is important to limit exposure to the sun’s UV radiation. As biological family members usually share similar traits, your family members may also have an increased risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. They can reduce their risk by spending less time in the sun and using a combination of sun protection measures during sun protection times. It is important to monitor your skin regularly and if you notice any changes in your skin, or enlarged lymph glands near to where you had the cancer, see your specialist as soon as possible.
Recommended Reading: Metastatic Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
How Is Basal Cell Cancer Of The Head And Neck Diagnosed
Diagnosis is made by clinical exam and a biopsy. Basal cell cancers are staged by size and extent of growth. These cancers rarely metastasize to lymph nodes or other organs, but they can grow quite large and invade small nerves and local structures.
Biopsy can help determine if the basal cell cancer is a low-risk tumor or a high-risk tumor that requires more aggressive treatment. Low-risk tumors are often nodular and do not have nerve involvement. High-risk tumors in the head and neck are those that involve the central face, nose and eye area, as well as those tumors that are greater than or equal to 10 millimeters on the cheeks, scalp and neck tumors that are recurrent or arising from previously radiated tissue and tumors arising in patients who are immunosuppressed. An aggressive growth pattern on the pathology evaluation and perineural invasion are also features of high-risk basal cell cancers.
Are Actinic Keratoses Treatable

There are a number of effective therapies for treating actinic keratoses. Dr. Garcia-Zuazaga and his team will determine the best therapy for you based on the nature of the lesion and your overall health. Treatments include topical creams, liquid nitrogen, a variety of surgical options and photodynamic therapy .
Read Also: Soderstrom Skin Cancer Screening
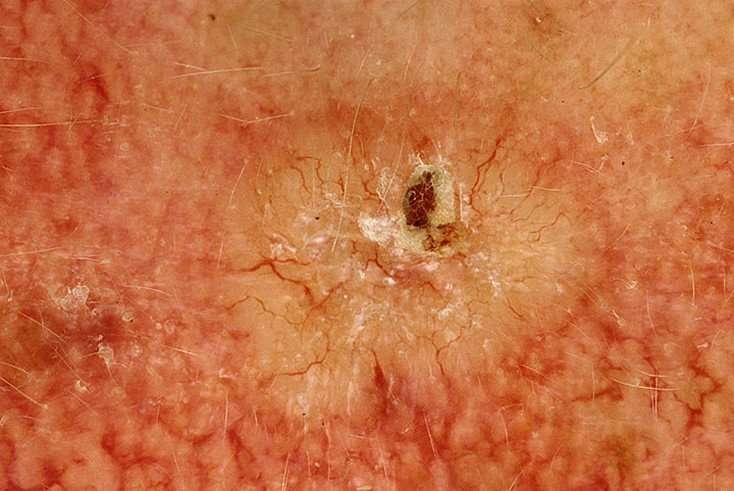
Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
2. Basal cell carcinoma. This is the most typical but least dangerous kind of skin cancer. It grows slowly, generally on the head, neck and upper torso. It may look like a lump or dry, scaly area. It can be red, pale or pearly in color. As it grows, it may ulcerate or resemble a sore that does not recover correctly March 3, 2018. Answer: How quickly does a basalcellcarcinoma grow. Basalcellcarcinomas typically grow slowly, but they can be invasive and destructive over time. The location also matters. 2mm of growth in the middle of the back would not make much difference. 2mm of growth on the nose or eyelid would have a greater impact A basal cell carcinoma anterior to the medial canthus: Note the pearly margins and the central crater. The most common type of eyelid cancer is basal cell carcinoma. Most basal cell carcinomas can be removed with surgery. However, many older patients will try to ignore these slow growing tumors Finally I found it was basal cell carcinoma. Thankfully, this is the least-dangerous type of skin cancer, and it’s one of the easiest forms of skin cancer to treat. And you do have to treat. Infiltrative Basal Cell. New Skin cancer forum requires membership for participation – click to join. I had to have 1cm. of my lower eyelid removed for a nodular bcc just before Christmas and I felt anything but brave, the days before the op. were the worst. I have just been diagnosed with an infiltrative basal cell carcinoma on my.
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
You May Like: Does Skin Cancer Make You Lose Hair
What Is A Basal Cell
One of three main types of cells in the top layer of the skin, basal cells shed as new ones form. BCC most often occurs when DNA damage from exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun or indoor tanning triggers changes in basal cells in the outermost layer of skin , resulting in uncontrolled growth.
What Are The Symptoms
One common symptom of a basal cell carcinoma is a wound or sore that will not heal. Typically, the wound or sore may bleed or ooze and remain unhealed for an abnormal length of time before eventually healing. It will then reopen and start to ooze or bleed. This process can repeat itself several times.Basal cell carcinomas present themselves as reddish areas of skin on the parts of the body that are exposed to the sun, including the face, neck, arms and legs. Itching is an occasional side effect.Basal cell carcinomas can also appear as a scar, pink growths, or as shiny bumps that appear red, pink or white. These shiny bumps are often mistaken for moles.
Also Check: What Is The Most Aggressive Skin Cancer
Prognosis Of Basal Cell Carcinoma
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma is nearly always successful, and the cancer is rarely fatal. However, almost 25% of people with a history of basal cell carcinoma develop a new basal cell cancer within 5 years of the first one. Thus, anyone with one basal cell carcinoma should have a yearly skin examination.
Articles On Skin Cancer
Skin cancer — abnormal cell changes in the outer layer of skin — is by far the most common cancer in the world. It can usually be cured, but the disease is a major health concern because it affects so many people. About half of fair-skinned people who live to age 65 will have at least one skin cancer. Most can be prevented by protecting your skin from the sun and ultraviolet rays.
Every malignant skin tumor will, over time, show up on the skin‘s surface. That makes this the only type of cancer that is almost always found in its early, curable stages.
Don’t Miss: Does Amelanotic Melanoma Blanch When Pressed
Eyelid Basal Cell Carcinoma
Eyelid basal cell carcinoma is the most common cancer of the skin around the eye. It most frequently originates in the lower eyelid and is more common in fair-skinned adults between 50 and 80 years of age. The lesion appears as a nodule or it can appear as a simply thickened eyelid with eyelash loss. Sometime it hides under a skin abrasion or ulcer. This can be invasive and grow deep into the soft tissues around the eye and into the brain where it becomes life-threatening
The goal of management of eyelid basal cell carcinoma is complete tumor control. This means that the tumor should be surgically removed completely. This is accomplished in the operating room and with pathologic proof of tumor-free frozen section margins. The eyelid then needs to be reconstructed so that it functions normally and covers the eye. This requires great skill and the need to borrow tissue from the opposite eyelid, neck, ear, or sometimes the mouth. Occasionally the eyelids must be sewn shut for two months so that the eye is protected as the eyelids heal. Sometimes eyelid basal cell carcinoma is treated with a cream that is used for several months or it can be treated with an injection of chemotherapy.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Know If Squamous Cell Carcinoma Has Spread
Is Stage 4 Basal Cell Carcinoma Serious
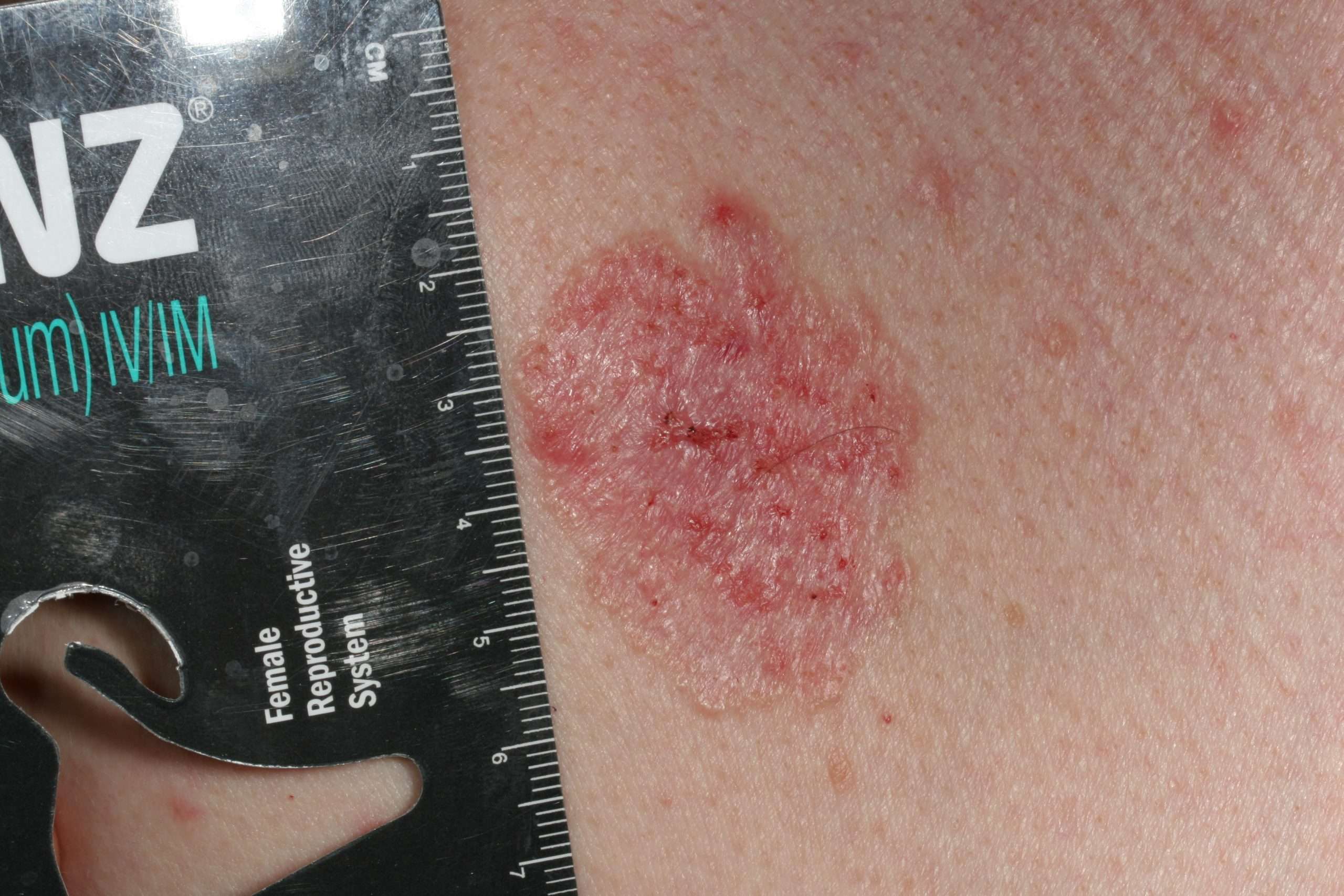
Stage 4 basal cell carcinoma is the fifth and final phase of development of the cancer, so its the most serious stage. Basal cell carcinoma isnt often life-threatening, but by the time it reaches stage 4, its already begun to spread to bones, lymph nodes, and other organs. This means treatment is more difficult by the time the cancer has reached this stage. Because of this, its important to see a doctor if you notice symptoms of stage 4 basal cell carcinoma.
Recommended Reading: Stage 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma Survival Rate
When Should I See My Doctor
If you have had one BCC, you have a 50% chance of developing another one, so it is important to check your skin regularly.
Most people find BCCs by checking their own skin and looking for changes. See a doctor if you find:
- a spot that is different from other spots on your skin
- a spot that has changed size, shape, colour or texture
- a sore that doesnt heal
- a sore that is itchy or bleeds
Can Basal Cell Carcinoma Cause Complications
The most common complication of basal cell carcinoma is recurrence. BCCs commonly recur, even after successful treatment. In some cases, BCC may reappear in the same place. It can also be disfiguring, especially if not treated promptly.
A diagnosis of BCC increases the chance of developing other types of skin cancer. This includes melanoma, which can metastasize and is the most life-threatening form of skin cancer.
Rare, aggressive forms of BCC can invade the body beyond the skin. It can destroy bone, nerves, and muscles. In rare cases it can metastasize to other parts of the body, including key organs, and become life-threatening.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Skin Cancer
What Happens When Skin Cancer Goes Untreated
If you notice an abnormality on your skin you may be tempted to ignore it. However, if it is skin cancer you could be putting your health at risk by waiting to get a skin and mole check. There are three main types of skin cancer in Australia with melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, and they each have their own set of unique characteristics. The most important thing to remember is that if you delay treatment of skin cancer it could have life threatening consequences: