Can I Get Skin Cancer From Indoor Tanning
Many people believe indoor tanning is safe, but it’s actually very risky. You can get basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma from tanning beds, as well as photodamaged skin and premature aging. Regular use of a tanning bed, defined as at least five times in one year, before the age of 35 increases your risk of melanoma by 75%.
Second Cancers After Breast Cancer
Breast cancer survivors can be affected by a number of health problems, but often a major concern is facing cancer again. Cancer that comes back after treatment is called a recurrence. But some cancer survivors develop a new, unrelated cancer later. This is called a second cancer.
Women whove had breast cancer can still get other cancers. Although most breast cancer survivors dont get cancer again, they are at higher risk for getting some types of cancer, including:
- A second breast cancer
- Salivary gland cancer
- Melanoma of the skin
- Acute myeloid leukemia
The most common second cancer in breast cancer survivors is another breast cancer. The new cancer can occur in the opposite breast, or in the same breast for women who were treated with breast-conserving surgery .
Treatment Options For Skin Cancer
The goal of any skin cancer treatment is to remove the cancer before it has a chance to spread. If the skin cancer has spread to nearby tissues or organs, treating the cancer becomes more difficult. If it hasnt spread, though, treating skin cancer is often very successful.
Treatment options include:
- Surgery. Surgically removing the cancerous spot is a common option. In some cases, the spot can be removed easily in a doctors office. More advanced cases may require in-depth surgery.
- Cryosurgery. This type of surgery freezes the affected skin, killing the cancerous cells. Over time, the dead skin cells fall off.
- Immunotherapy. Immunotherapy uses a persons immune system to target and destroy cancer. In the case of skin cancer, a medicated cream is applied to the cancerous area. The immune system then works to destroy the cancer.
- Chemotherapy. If skin cancer has progressed beyond the skin, chemotherapy can help target and kill any cancer cells surgery cant remove. Chemotherapy comes in several forms, including oral medication, injected shots, and IV infusions. It can even be applied to the skin.
- Radiation therapy. Radiation seeks out and destroys cancer cells. Radiation is used to treat a larger area, or an area thats too difficult to treat with surgery.
- In this type of therapy, a chemical is applied to the skin cancer. After staying on the skin for many hours, the skin is exposed to a special light, destroying the cancer cells.
Read Also: Invasive Lobular Breast Cancer Survival Rate
What Are The Different Types Of Skin Cancer
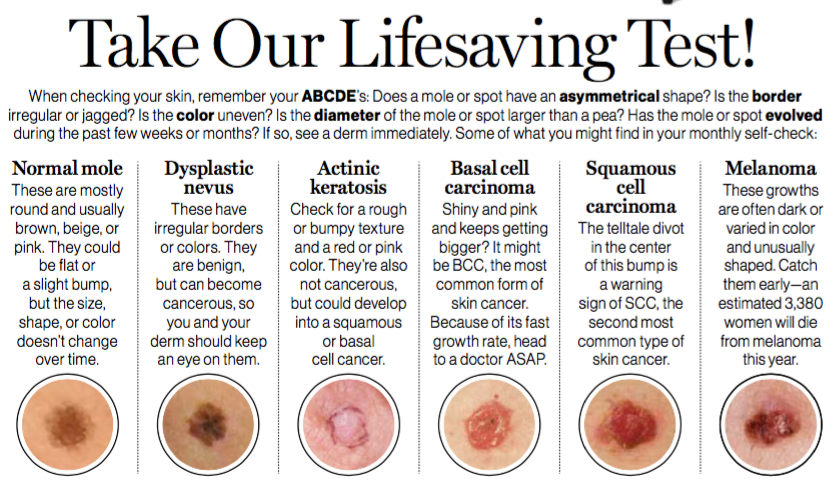
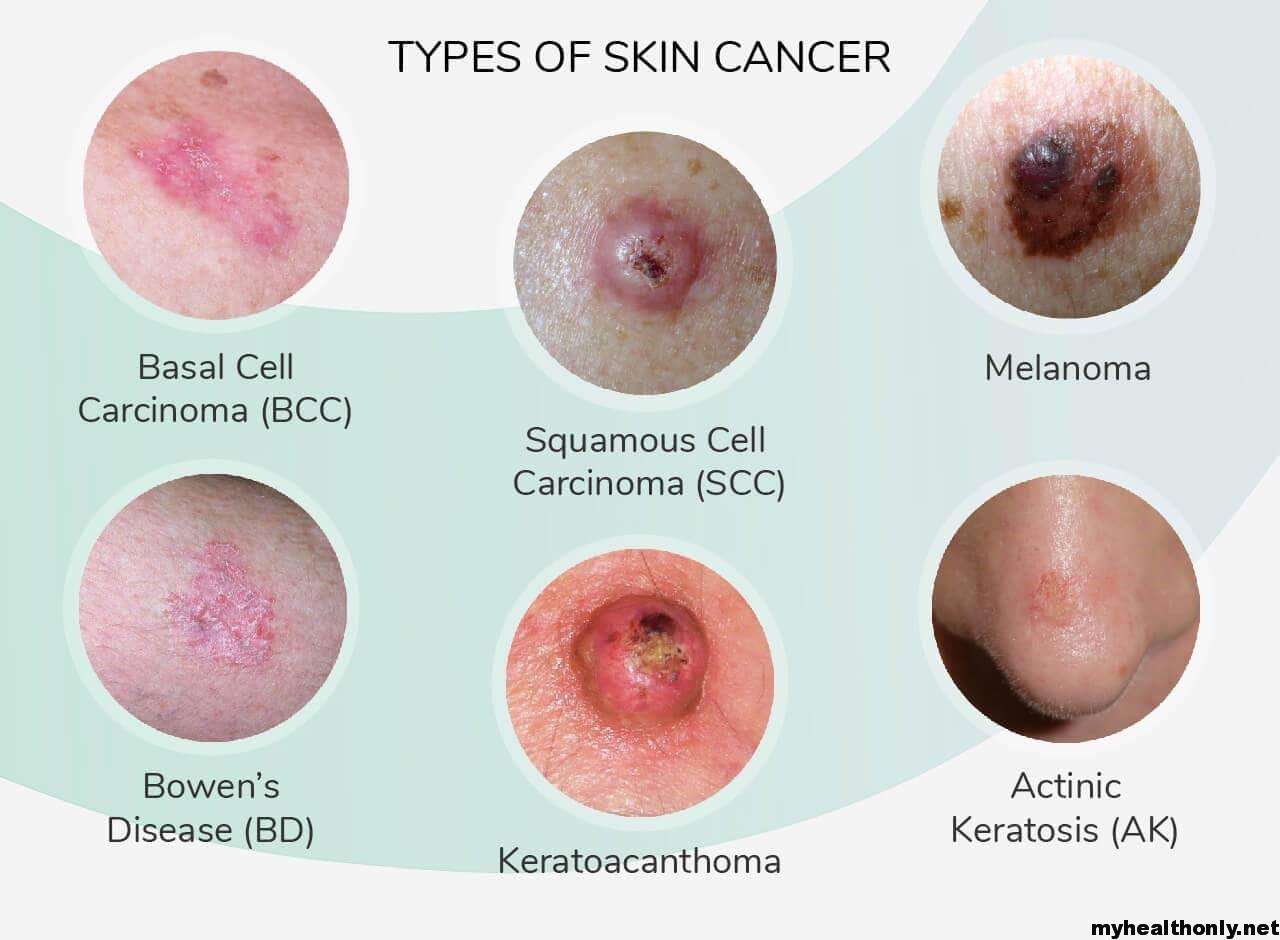
There are four main types of skin cancer. The three most common are malignant melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. The fourth type, Merkel cell carcinoma, is highly aggressive, but its also extremely rare.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer and is primarily caused by sun exposure. It often occurs on the head and neck, although it can develop on any part of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma is primarily caused by sun exposure or other types of damage to the skin, such as X-rays or chemicals. Melanoma is an aggressive form of skin cancer that is caused by a combination of environmental factors and genetics. It can spread to other parts of the body, including internal organs, if its not caught and treated early.
Also Check: What Is Soft Tissue Carcinoma
Articles On Skin Cancer
Skin cancer — abnormal cell changes in the outer layer of skin — is by far the most common cancer in the world. It can usually be cured, but the disease is a major health concern because it affects so many people. About half of fair-skinned people who live to age 65 will have at least one skin cancer. Most can be prevented by protecting your skin from the sun and ultraviolet rays.
Every malignant skin tumor will, over time, show up on the skin‘s surface. That makes this the only type of cancer that is almost always found in its early, curable stages.
Also Check: Web Md Skin Cancers
Q: While All Types Of Skin Cancer Are Less Common In People Of Color Their Outcomes Are Dramatically Worse What Accounts For This Gap
Skin cancers are less prevalent in nonwhite racial ethnic groups, but when they occur, they tend to be diagnosed at a later stage and, as a result, have a worse prognosis. One study, for example, found an average five-year melanoma survival rate of only 67 percent in Black people versus 92 percent in white people. Another showed that late-stage melanoma diagnoses are more common in Hispanic and Black patients than in non-Hispanic white patients.
First, theres a lower public awareness overall of the risk of skin cancer among individuals of color. Second, from the perspective of health-care providers, theres often a lower index of suspicion for skin cancer in patients of color, because the chances of it actually are smaller. So these patients may be less likely to get regular, full-body skin exams. And third, the places on the body where skin cancers tend to occur in people of color are often in less sun-exposed, more out-of-the-way areas, which makes detection more difficult. For example, the most common location for melanoma in patients of color is the lower extremities the soles of the feet in particular.
Read Also: What Is Stage 2 Melanoma Skin Cancer
Major Types Of Skin Cancers And Their Distribution In People Of Color
Skin cancer is mainly divided into two main categories as Non melanoma Skin Cancer and Melanoma Skin Cancer . Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer includes basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma . Each of these most common cancers viz. Basal cell carcinoma , squamous cell carcinoma , and melanoma is named after the type of skin cell from which it arises and has been linked to the varying degree of sun exposure .
NMSC greatly outnumber melanomas in incidence but fortunately most are much easier to treat and have much better long-term prognosis . They are less deadly than melanoma mainly due to their tendency to remain confined to their primary site of disease which makes their management much more straightforward. The devastating majority of keratinocyte malignancies progress in the areas of skin most exposed to UV such as on the face and arms . The BCC and the SCCs often carry a UV-signature mutation indicating that these cancers are caused by UV-B radiation via the direct DNA damage . Although Asians display relative protection from basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, incidence rates of these non melanoma skin cancers have been increasing over 3 to 8 percent annually in the past three decades . Features of different types of skin cancers are listed in .
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 2 Survival Rate
What Causes Skin Cancer
The main cause of skin cancer is overexposure to sunlight, especially when it results in sunburn and blistering. Ultraviolet rays from the sun can damage the skin and, over time, lead to skin cancer. The UV light damages DNA in the skin and causes it to grow abnormally. Exposure to certain chemicals such as tar and coal can cause skin cancer for those with jobs that require them to frequently be in contact with these chemicals. Those with a weakened immune system also have an increased risk for skin cancer.
Do We Need Sunscreen Even If Its A Cloudy Day
The short answer is yes. Chronic sun exposure increases your risk of skin cancer by causing damage to your skin cells, which can lead to cancer, even if your skin isn’t obviously burned or red.
Pay attention to the UV index a high UV index may indicate that unprotected skin will burn faster and take the proper precautions if you’re going to be spending time in the sun. UVA can even penetrate through window glass, so it’s a good idea to protect your skin anytime it will be exposed to the sun.
Remember, there is no healthy tan. Even a light-pink burn is evidence of skin injury, and a suntan can result in premature aging and skin cancer.
Also Check: Melanoma Bone Cancer Life Expectancy
What Is The Outlook For People With Skin Cancer
Nearly all skin cancers can be cured if they are treated before they have a chance to spread. The earlier skin cancer is found and removed, the better your chance for a full recovery. Ninety percent of those with basal cell skin cancer are cured. It is important to continue following up with a dermatologist to make sure cancer does not return. If something seems wrong, call your doctor right away.
Most skin cancer deaths are from melanoma. If you are diagnosed with melanoma:
- The five-year survival rate if its detected before it spreads to the lymph nodes is 99%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to nearby lymph nodes is 66%.
- The five-year survival rate if it has spread to distant lymph nodes and other organs is 27%.
What Is The Probability Of Getting Cancer
Cancer is, unfortunately, all too common. In fact, over 1.8 million people were diagnosed with cancer in 2020, and over 600,000 died from the disease. These grim statistics might make you wonder, what are my chances of getting cancer?
The odds of getting cancer cause concern, with The American Cancer Society estimating 9.5 million people worldwide died from cancer-related diseases in 2018.Is cancer rare? According to Medical News Today, 1 in 2 women and 1 in 3 men in the US will develop cancer within their lifetime. These figures highlight that cancer is, indeed, not rare and something a large part of the population faces at some point in their life.
In this post, well explain the likelihood of developing cancer, the lifetime risk of developing or dying from cancer, how this risk is determined, and the steps to take in assessing your chances of having cancer.
Don’t Miss: Melanoma 3c
Why It Often Goes Undetected In People With Darker Skin
Despite the sun protection that additional melanin offers, Dr. Kyei says African Americans tend to suffer more melanoma deaths than any other ethnic group. But its not because skin cancer is harder to detect in people with dark skin.
The problem is that moles in dark-skinned people dont get checked as often because of the misconception that dark-skinned people dont get skin cancer, she says.
People with darker skin also tend to get skin cancer in different locations than people with fair skin. For example, in African Americans and Asians, we see it more often on their nails, hands and feet, Dr. Kyei says. Caucasians tend to get it more in sun-exposed areas.
Treatment For Skin Cancer
For the most part, skin cancer is treated the same way indark-skinned people as it is in those with lighter skin.
It begins with surgery to remove the cancer. However, takingadditional precautions can reduce scarring in people with darker skin, as theytend to suffer from thick scars, known as keloids.
If a patient comes to me with basal cell carcinoma, whichis the most common type of skin cancer, I ask about any previous experiencewith scars, Dr. Kyei explains. The reason I ask that question is that I dontwant someone to end up with a thick scar somewhere noticeable like their face.If youre someone who tends to get thick keloids and your cancer is verysuperficial and not high-risk, we might start with a chemotherapy cream as aninitial treatment method instead of surgery.
Despite the potential for scarring, surgery is the onlytreatment method for melanoma. Melanoma is deadly, Dr. Kyei says. It has tobe cut out no matter what.
Injected steroids can sometimes help minimize scarring.
You May Like: Stage 1 Cancer Symptoms
What Causes Of Skin Cancer Types Treatment And Prevention
- No Comments
We included links to products we believe would be of benefit to our readers. If you make a purchase after clicking on one of the links on this page, we may get a small commission. Heres how we do it.
- 0share
What causes of skin cancer? How do I know I have skin cancer?
Skin cancer is the abnormal growth of skin cells. It mostly occurs due to exposure to the sun. Although, it can spread to other areas of the skin.
The most frequent kind of cancer in the United States is skin cancer. However, it is one of the most treatable cancers if detected early.
Minimizing your exposure to ultraviolet radiation may help lower your chance of developing skin cancer.
Will One Bad Sunburn Give You Skin Cancer
by Garth Sundem | Jul 27, 2015 | Latest News, Patient Care
Recently at the Colorado Melanoma Foundation booth at the Colorado Dragon Boat Festival, a girl learns theres no such thing as too much sunscreen.
It seems like everybodys got a story about that one bad burn the time you fell asleep next to the pool and tattooed a white handprint on your lobster-red chest, or forgot to pack the sunscreen while hiking a Colorado 14er. As you know, sunburn increases your chance of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. But what about just one bad burn? And what can you do about it now?
Were still waiting for a definitive one-sunburn study to show us exactly how much melanoma risk increases with one blistering burn, but to the best of our knowledge, it seems like the answer is about 50 percent. One bad burn as a child makes you half-again more likely to develop melanoma as an adult, says Neil Box, PhD, investigator at the University of Colorado Cancer Center and assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at the CU School of Medicine. Dr. Box is also president of the Colorado Melanoma Foundation.
This year, about 250,000 people will be diagnosed with melanoma and 60,000 people will die from this most dangerous form of skin cancer. While the increased risk accompanying one bad burn is still imprecise, studies show that the overall lifetime risk of developing melanoma climbs 80 percent with 5 blistering burns in childhood.
Colorado Cancer Blogs
You May Like: Ductal Carcinoma Survival Rate
Where Does Skin Cancer Develop
Skin cancer is most commonly seen in sun-exposed areas of your skin your face , ears, neck, arms, chest, upper back, hands and legs. However, it can also develop in less sun-exposed and more hidden areas of skin, including between your toes, under your fingernails, on the palms of your hands, soles of your feet and in your genital area.
Who Is Most At Risk For Skin Cancer
Although anyone can develop skin cancer, youre at increased risk if you:
- Spend a considerable amount of time working or playing in the sun.
- Get easily sunburned have a history of sunburns.
- Live in a sunny or high-altitude climate.
- Tan or use tanning beds.
- Have light-colored eyes, blond or red hair and fair or freckled skin.
- Have many moles or irregular-shaped moles.
- Have actinic keratosis .
- Have a family history of skin cancer.
- Have had an organ transplant.
- Take medications that suppress or weaken your immune system.
- Have been exposed to ultraviolet light therapy for treating skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis.
Read Also: Immunotherapy For Malignant Melanoma
Getting Regular Checkups Vital
The main key to combating a melanoma recurrence is early detection.
After your treatment, its vital to continue to see your dermatologist or physician regularly. Your doctor will base the need for follow-up on your specific case. As time goes by without a relapse, the frequency of visits will gradually decline.
For patients who had melanoma before, we generally recommend seeing your physician every three to six months, Dr. Tarhini says. The higher the stage of melanoma you had, the higher your risk is for relapse.
He recommends seeing your physician every three months for a year. Then, every four to six months for the next year. After that, every six months up to five years.
If there is no evidence of another melanoma or disease relapse at that point, continue your follow-up once a year, he says.
Differences In Diagnosis And Outcomes
Although minority groups may be at a lower risk of developing skin cancer, they are disproportionately affected by worse outcomes and diagnoses. Overall:
- Black and Latino people are more likely to die than White people for all skin cancers.
- When it comes to melanoma specifically, Black people are more likely to be diagnosed at later stages or with distant metastasis when compared to White people.
- One study found that 91 percent of White people are diagnosed with earlier stage melanoma, compared to 74 percent and 48 percent of Latino and Black people, respectively.1,2
Read Also: Basaloid Tumor
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider
Make an appointment to see your healthcare provider or dermatologist as soon as you notice:
- Any changes to your skin or changes in the size, shape or color of existing moles or other skin lesions.
- The appearance of a new growth on your skin.
- A sore that doesnt heal.
- Spots on your skin that are different from others.
- Any spots that change, itch or bleed.
Your provider will check your skin, take a biopsy , make a diagnosis and discuss treatment. Also, see your dermatologist annually for a full skin review.